1953 JEEP DJ service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 69 of 376

'Jeep9
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
h.
Check
ignition (distributor) timing; reset if
necessary.
i.
Check
carburetor
adjustments; reset if necessary,
j.
With
engine
fully warmed up, tighten cylinder
head and manifold
bolts
and nuts to specified
torque.
Check
cylinder head gaskets and
bolts
for
air
or coolant leaks.
Note:
Tightness of cylinder head
bolts
should be
checked and corrected after 500 to 600 miles [800
a
960 km.] of normal operation.
k.
Check
fan belt tension; adjust if necessary.
I.
Check
for and correct any oil leak, fuel leak or
coolant leak.
D-107.
VALVE
ADJUSTMENT
Proper
valve adjustment is important to prevent
burning
of valves and poor
engine
performance.
This
adjustment consists of obtaining a specified
lash
in the valve mechanism. The exhaust valve
tappets and the intake valve rocker arms should be adjusted to the proper clearance with the
engine
cold (at room temperature). Valve clearance can
be properly adjusted only when the tappet is on the
heel or low portion of the cam.
INTAKE
OPENS
9°
BTC?
FIG.
D-43-
10270
-VALVE
TIMING
D-108. Valve Adjustment Procedure
The
exhaust valve tappets are adjusted by turning
the adjusting screw in or out of the tappet as neces
sary
to obtain the proper clearance. Where special
wrenches can be obtained, they should be used to facilitate the adjustment. The proper clearance is .016" [0,406 mm.]
between
the end of the adjusting
screw and the
bottom
of the exhaust valve.
Crank
the
engine
over to
close
a valve and check
the clearance with a feeler
gauge.
To adjust, hold
the tappet with one wrench and
turn
the adjusting
screw,
with the other.
Check
and adjust each of
the tappets in proper sequence.
Adjust
each intake valve by adjusting the rocker
arm
screw at the push rod to obtain .018" [0,457 mm.] clearance
between
the rocker arm and the
valve stem with tappet on the heel of the cam.
D-109.
Check
Valve
Timing
To
check the valve timing, carefully set the intake
valve rocker arm adjustment for No. 1 cylinder to .026"
[0,6604
mm.]
between
the rocker arm and the
valve stem. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until
the piston in No. 1 cylinder is ready for the intake stroke. The intake valve
opens
9° before top center
(BTC).
Note
the distance
between
the
"TC"
and
"5°"
marks on the indicator on the timing gear
cover and estimate the 9° before top center position.
See
Fig.
D-43.
With
the crankshaft in this position, timing is correct if the rocker arm is just tight
against the intake valve stem. Do not overlook resetting the rocker arm adjustment to the correct
running
clearance.
D-110. Positive
Crankcase
Ventilation
Be
sure there are no air leaks at the tube connec
tions
between
the air cleaner and the oil filler tube,
and
that the oil filler tube cap gasket is in
good
condition. Always keep the cap locked securely in
place. When tuning the
engine
or grinding valves, remove the control valve and clean it thoroughly.
If
the valve is blocked with carbon, the ventilating
system
will
not operate and, should the valve
fail
to seat, it
will
be impossible to make the
engine
idle satisfactorily. Refer to Par. C-6 for servicing.
D-111. Oil
Filter
The
engine
is equipped with a throw-away type
oil
filter.
This
oil filter must be serviced periodi
cally
as outlined in the
Lubrication
Section. 69
Page 70 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
D-112.
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
Poor
Fuel
Economy Ignition Timing Slow or Spark Advance Stuck
Carburetor
Float High
Accelerator Pump Not Properly Adjusted
High
Fuel
Pump Pressure
Fuel
Leakage
Leaky
Fuel
Pump Diaphragm
Loose Engine Mounting Causing High
Fuel
Level
in
Carburetor
Low
Compression Valves Sticking
Spark
Plugs Bad
Spark
Plug Cables Bad Weak
Coil
or Condenser Improper Valve Tappet Clearance
Carburetor
Air Cleaner Dirty
High Oil Level in Air Cleaner Dragging Brakes
Front
Wheels Out of Alignment
Tires
Improperly Inflated Inaccurate Odometer
Faulty
Fuel
Tank
Cap
Clogged
Muffler or Bent Exhaust Pipe
Lack
of Power
Low
Compression Ignition System (Timing Late)
Improper Functioning Carburetor or
Fuel
Pump
Fuel
Lines
Clogged
Air
Cleaner Restricted
Engine Temperature High Improper Tappet Clearance
Sticking Valves Valve Timing Late
Leaky
Gaskets
Muffler
Clogged
Bent Exhaust Pipe
Defective
Spark Plugs—Clean or Replace
Defective
Breaker Points—Replace
Points
Incorrect Breaker Point Gap—Reset
Points
Defective
Condenser or Coil—Replace
Loose Electrical Connections—Locate and Tighten
Broken Valve Spring—Replace Spring Broken Piston or Rings—Replace
Defective
Head Gasket—Replace Gasket
Cracked
Distributor Cap—Replace Cap
Low
Compression
Leaky
Valves
Poor Piston Ring Seal Sticking Valves
Valve Spring Weak or Broken
Cylinder
Scored or Worn
Tappet Clearance Incorrect
Piston Clearance too Large
Leaky
Cylinder Head Gasket
Burned Valves and
Seats
Sticking Valves or too Loose in Guides Improper Timing
Excessive Carbon Around Valve Head and Seat Overheating
Valve Spring Weak or Broken Burned Valves and Seats—Continued
Valve Tappet Sticking
Valve Tappet Clearance Incorrect
Clogged
Exhaust System
Valves Sticking Warped Valve Improper Tappet Clearance
Carbonized or Scored Valve
Stems
Insufficient Clearance Valve Stem to Guide
Weak or Broken Valve Spring Valve Spring Cocked Contaminated Oil
Overheating Inoperative Cooling System
Thermostat Inoperative Improper Ignition Timing
Improper Valve Timing
Excessive Carbon Accumulation
Fan
Belt too Loose
Clogged
Muffler or Bent Exhaust Pipe
Oil
System Failure
Scored or Leaky Piston Rings
Popping-Spitting-Detonation
Improper Ignition
Improper Carburetion
Excessive Carbon
Deposit
in Combustion
Cham
bers
Poor Valve Seating Sticking Valves
Broken Valve Spring Tappets Adjusted too Close
Spark
Plug Electrodes Burned
Water or Dirt in
Fuel
Clogged
Lines Improper Valve Timing
Excessive Oil Comsumption Piston Rings Stuck in Grooves, Worn or Broken Piston Rings Improperly Fitted or Weak Piston Ring Oil Return
Holes
Clogged
Excessive Clearance, Main and Connecting Rod
Bearings
Oil
Leaks at Gaskets or Oil Seals
Excessive Clearance, Valve Stem to Valve Guide (Intake)
Cylinder
Bores Scored, Out-of-Round or Tapered Too Much Clearance, Piston to Cylinder Bore
Misaligned Connecting Rods
High Road
Speeds
or Temperature
Crankcase
Ventilator Not Operating
Bearing Failure
Crankshaft
Bearing Journal Out-of-Round
Crankshaft
Bearing Journal Rough
Lack
of Oil
Oil
Leakage
Dirty
Oil
Low
Oil Pressure or Oil Pump Failure
Drilled
Passages
in Crankcase or Crankshaft
Clogged
Oil
Screen Dirty Connecting Rod Bent 70
Page 71 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
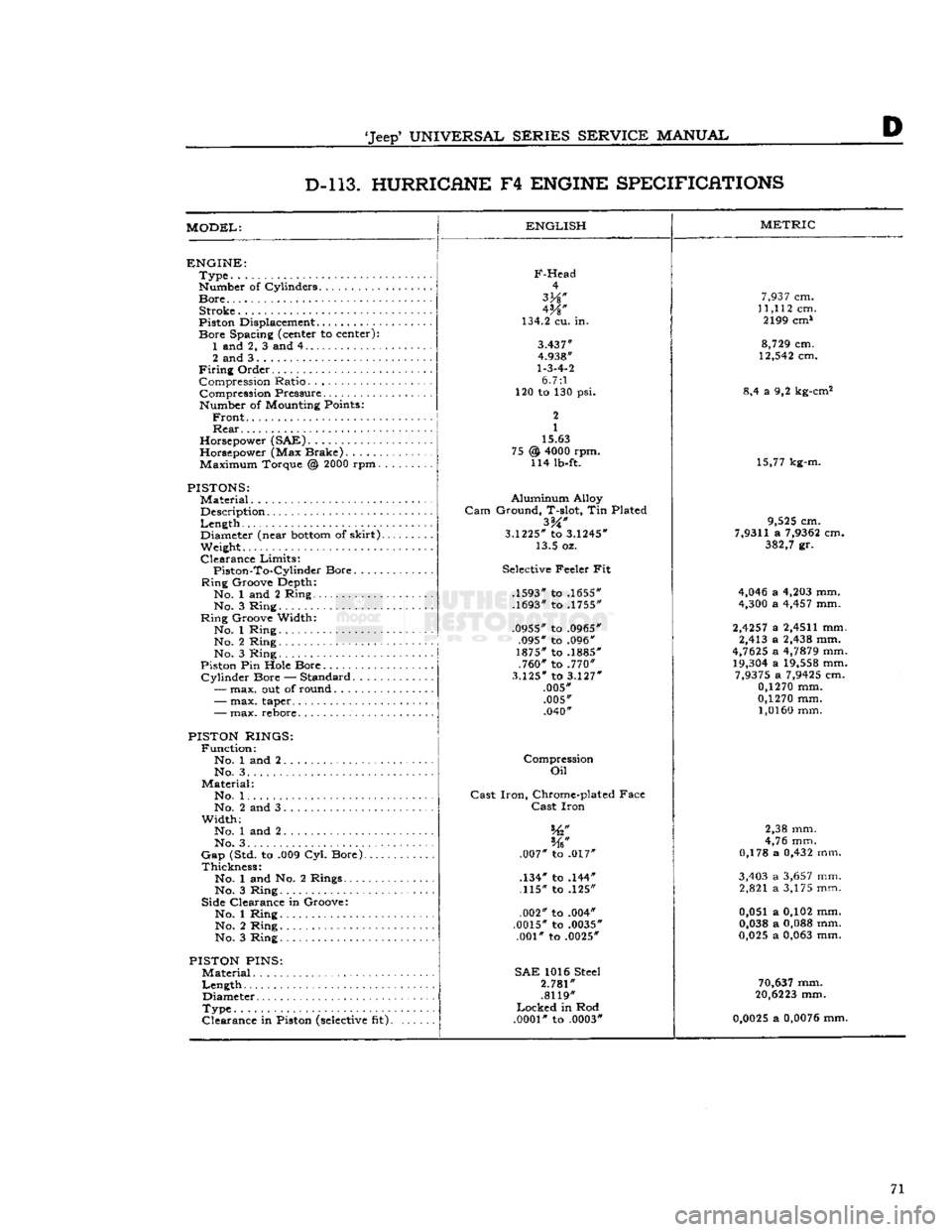
D D-l 13. HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL:
ENGLISH
ENGINE:
Type
Number of Cylinders
Bore
Stroke
Piston Displacement...........
Bore
Spacing (center to center): 1 and 2, 3 and 4
2 and 3
Firing
Order Compression Ratio Compression Pressure... .
Number of Mounting Points:
Front
Rear
Horsepower (SAE)
Horsepower (Max Brake) Maximum Torque @
2000
rpm.
PISTONS:
Material
Description
Length
,.
Diameter (near
bottom
of
skirt).
Weight.
Clearance
Limits:
Piston-To-Cylindcr
Bore
Ring
Groove Depth:
No. 1 and 2 Ring No. 3 Ring
Ring
Groove Width:
No. 1 Ring No. 2 Ring
No. 3 Ring
Piston Pin Hole Bore
Cylinder
Bore — Standard.....
—
max. out of round
F-Head
4
W
134.2 cu. in.
3.437"
4.938"
1-3-4-2
6.7:1
120 to 130 psi.
2
1
15.63
@
4000
rpm. 114 lb-ft. 75
-
max. taper..
-
max. rebore.
PISTON RINGS:
Function:
No. 1 and 2 No. 3. .
Material:
No. 1. .
No. 2 and 3
Width;
No. 1 and 2
No. 3. . . .
Gap
(Std. to .009 Cyl. Bore).
Thickness:
No. 1 and No. 2 Rings....
No. 3 Ring
Side Clearance in Groove:
No. 1 Ring No. 2 Ring
No. 3 Ring
PISTON
PINS:
Material
Length
Diameter
Type
Clearance
in Piston
(selective
fit).
Aluminum
Alloy
Gam
Ground, T-slot, Tin Plated
3.1225*
to
3.1245*
13.5 oz.
Selective Feeler Fit
.1593" to .1655"
.1693" to .1755"
.0955" to .0965" .095" to .096"
1875" to .1885" .760" to .770"
3.125"
to
3.127"
.005" .005" .040"
Compression
Oil
Cast
Iron,
Chrome-plated Face
Cast
Iron
.007" to .017"
.134" to .144" .115" to .125"
.002" to .004"
.0015" to .0035" .001" to .0025"
SAE
1016 Steel
2.781"
.8119"
Locked
in Rod
.0001"
to .0003"
METRIC
7,937
cm.
11,112
cm. 2199 cm*
8,729
cm.
12,542
cm.
8,4 a 9,2 kg-cm2
15,77 kg-m.
9,525
cm.
7,9311
a
7,9362
cm.
382,7
gr.
4,046
a
4,203
mm.
4,300
a
4,457
mm.
2,4257
a
2,4511
mm. 2,413 a
2,438
mm.
4,7625
a
4,7879
mm.
19,304
a
19,558
mm.
7,9375
a
7,9425
cm.
0,1270
mm.
0,1270
mm.
1,0160
mm.
2,38 mm.
4,76 mm.
0,178 a
0,432
mm.
3,403
a
3,657
mm. 2,821 a 3,175 mm.
0,051 a 0,102 mm.
0,038
a
0,088
mm.
0,025
a
0,063
mm.
70,637
mm.
20,6223
mm.
0,0025
a
0,0076
mm. 71
Page 73 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
D-l 13. HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
(Continued)
MODEL:
VALVE
SYSTEM:
(Continued) Timing: Intake:
Opens Closes
Duration
Exhaust: Opens
Closes Duration
Valve Opening Overlap
Valves: Intake: Material
Length Over All. Head Diameter.
.........
Angle
of Seat.
Stem
Diameter
Stem-to-Guide
Clearance..
Lift
Exhaust: Material
Length Over All Head Diameter
Angle
of
Seat Seat
Insert Material
Stem
Diameter
Stem-to-Guide
Clearance..
Lift
Springs: Intake:
Free
Length Standard: Pressure % Length: Valve Closed........
Valve Open
Service Minimum: Pressure @ Length: Valve Closed Valve Open
Exhaust:
Free
Length Pressure @ Length: Standard: Valve Closed
Valve Open
Service Minimum: Valve Closed. Valve Open
LUBRICATION SYSTEM:
Type of Lubrication:
Main
Bearings Connecting Rods
Piston Pins Camshaft Bearings
Tappets
Timing Gears.'.
Cylinder
Walls
Oil
Pump: Type Drive
Minimum
Safe
Oil Pressure:
At
Idle
At
2000
rpm. (35 mph.)..
Relief Valve Opens Normal Oil Pressure
Oil
Pressure
Sending
Unit
Oil
Intake
Oil
Filter
System
ENGLISH
9°
BTC
50°
ABC
239°
47°
BBC 12* ATC
239°
21°
SAE
5150
4.781"
2*
46°
.3733"
to
.3738"
.0007"
to
.0022'
.260"
Uniloy 21-12
5.909"
1.47"
46°
Eatonite EMS 58 .371" to .372"
.0025"
to
.0045'
.351"
1.97"
73 lb. @ 1.66"
153 lb. @ 1.40* 66 lb.
140 lb. 1.66*
)
1.40" 53 lb. (
120 lb.
2.109"
\
1.750*
47 lb. @2W
110 lb. @ l%*
Pressure
Pressure Splash
Pressure
Splash
Nozzle
Nozzle
Internal
Rotor
Camshaft
Gear
6 psi.
20 psi.
40 psi.
35 psi. @
2000
rpm.
Electric
Floating
Partial
Flow
METRIC
12,14 cm. 5,08 cm.
9,481 a
9,494
mm.
0,0178
a
0,0559
mm.
6,604
mm.
15,008
cm.
3,733
cm.
9,423
a
9,449
mm.
0,0635
a
0,1143
mm. 8,915 mm.
5,003
cm.
33,1 kg.
(i(<
4,216 cm.
69,4 kg. (a.
3,556
cm.
29,9 kg. (d 4,216 cm.
63,5 kg. ((i
3,556
cm.
6,350
cm.
24 kg. (a
5,356
cm.
54,3 kg. (a
4,445
cm.
21,3 kg. (n 5,
356cm.
49,9 kg. («
4,445
cm.
0,4 kg-cm2 1,4 kg-cm2
2,8 kg-cm2
2,4 kg-cm2 @
2000
rpm. 73
Page 75 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
SUBJEC
GENERAL
.... . . Dl-1 Oil Pump Cl(
ENGINE DESCRIPTION
D1-2
Engine
Mounts Dl-3
ENGINE REMOVAL
Dl-4
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Dl-5
Alternator
and Fan Belt Dl-11
Camshaft
.... Dl-26
Cooling Fan and Water Pump.
......
.Dl-12
Crankshaft
Front Oil Seal .Dl-21
Crankshaft
Pulley D1-17
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper Dl-18
Cylinder
Head Assembly Dl-24
Distributor
Dl-9
Exhaust
Manifold .Dl-8
Flywheel
Dl-28
Flywheel
Housing and
Clutch
Dl-27
Fuel
Pump. ... . .Dl-10
Intake
Manifold and
Carburetor
Assembly.
.............
.Dl-7
Main
Bearing and Crankshaft. Dl-32 Mounting Engine on Engine Stand. . . . .Dl-6
Oil
Dipstick. Dl-16
Oil
Filter
Dl-13
Oil
Pan.. ...
.......
.Dl-29
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit Dl-15
Oil
Pump Dl-19
Oil
Pump Intake Pipe and Screen Dl-30
Piston and Rod Assembly. Dl-31
Push
Rod and Valve
Lifter.
.Dl-25
Rocker
Arm Cover Dl-23
Starter
Motor Dl-14
Timing
Chain
and Sprocket Dl-22
Timing
Chain
Cover Dl-20
ENGINE CLEANING, INSPECTION AND REPAIR
. . ... .Dl-33
Camshaft
Cleaning and Inspection Dl-55
Connecting Rod Bearing Inspection
and
Fitting .Dl-49
Crankshaft
Cleaning Dl-38
Crankshaft
Inspection and Repair Dl-39
Crankshaft
Main Bearing Cleaning
and
Inspection Dl-41
Crankshaft
Main Bearings. Dl-40
Crankshaft
Pulley Inspection. Dl-70
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper Inspection. D1-69
Cylinder
Block .Dl-34
Cylinder
Block Cleaning Dl-35
Cylinder
Block Inspection Dl-36
Cylinder
Block Repair. .Dl-37
Cylinder
Head and Valve Repair .Dl-63
Cylinder
Head and Valve Cleaning
and
Inspection.. . .Dl-62
Flywheel
Cleaning and Inspection Dl-52
Flywheel
Housing Cleaning
and
Inspection Dl-54
Hydraulic
Valve
Lifter
Leakdown Test. .Dl-57
Main
Bearing Fitting or
Shim
Stock Dl-42, Dl-43
Oil
Pan Cleaning and Inspection .Dl-51
PAR.
and
Inspection. .... .Dl-68
Oil
Pump Intake and Screen Cleaning. . .Dl-50
Piston and Rod Assembly.
...........
.Dl-48
Piston and Rod Cleaning and Inspection.D1-45
Piston and Rod Disassembly Dl-44
Piston Fitting Dl-46
Piston Ring Fitting. .Dl-47
Ring
Gear
Replacement. .Dl-53
Rocker
Arm Assembly. Dl-60
Rocker
Arm Cleaning and Inspection. . .Dl-59
Rocker
Arm Cover Cleaning
and
Inspection D1-65
Rocker
Arm Disassembly .Dl-58
Timing
Chain
and Sprocket Inspection. . .Dl-66
Timing
Chain
Cover Cleaning
and
Inspection.. . Dl-67
Valve
Installation D1-64
Valve
Lifter
and Push Rod
Cleaning
and Inspection. . Dl-56
Valve
Removal Dl-61
ENGINE REASSEMBLY
Dl-71
Alternator
and Fan Belt Dl-96
Camshaft
Dl-80
Clutch
and Flywheel Housing Dl-79
Cooling Fan.. . .Dl-95
Crankshaft
End Play Check. . Dl-74
Crankshaft
Front Oil Seal Dl-85
Crankshaft
Pulley Dl-89
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper Dl-88
Cylinder
Block and Crankshaft
Rear
Oil Seals Dl-72
Cylinder
Head Assembly .Dl-82
Distributor
Dl-99
Exhaust
Manifold Dl-98
Flywheel
.Dl-78
Fuel
Pump.. .. . Dl-97
Intake
Manifold and Carburetor Assembly Dl-101
Main
Bearing and
Crankshaft
Installation
.
Dl-73
Oil
Filter
Dl-93
Oil
Level
Dipstick Dl-90
Oil
Pan Dl-77
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit Dl-91
Oil
Pump.. .Dl-87
Oil
Pump Intake and Screen Assembly. .Dl-76
Piston and Rod Installation Dl-75
Rocker
Arm Cover. Dl-83
Spark
Plugs.. Dl-100
Starter
Motor Dl-92
Timing
Chain
and Sprocket.
..........
.Dl-84
Timing
Chain
Cover Dl-86
Valve
Lifter
and Push Rod Dl-81
Water
Pump. Dl-94
ENGINE INSTALLATION
Dl-102
FINAL
IN-VEHICLE
ADJUSTMENTS.
D1-103
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
Dl-104
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
. .Dl-105 75
Page 76 of 376
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
DM.
GENERAL
This
section describes service and repair of the
Dauntless V-6 engine. The
engine
code
number shown in
Fig.
A-4 is provided to identify the Daunt
less
V6-225 engine. The meaning of the coded letters and numbers that are stamped on the right front face of the crankcase, just below the rocker
arm
cover,
between
exhaust manifold ports, is given
below.
Letter
to
Designate
Market
M
—
Military
E
—
Export
D
— Domestic
Letter
to
Designate
Year
Built
N
— 1967
P
— 1968
R
— 1969
S
— 1970
T
— 1971
Letter
to Designate
Engine
and Compression
Ratio
H—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
Y—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
Marine
(Low
Profile)
(2
Bbl.Carb.)
Z—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
Marine
(High
Profile)
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
K—V6-225
7.6 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
L—V6-225
7.4 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
Market
Domestic
—
Year
"1967"
Engine
J
Day
Plus Chg. If
Any-
Service Engine "S"
Short
Block
"R" -Oversize Bores "B"
Undersize Crank
&
"A"
Rod
Bearings
The
identifying letter or letters follow the
engine
letters are decoded as follows:
A—.010"
Undersize
Main
and Connecting Rod
Bearings
B—.010"
Oversize Pistons
AB—Combination
of A and B
S—Service
Engine
R—Short
Block
All
disassembly and assembly procedures are pre sented in logical order, assuming a complete
engine
overhaul
with
engine
removed from the vehicle.
However,
many of
these
procedures can also be
performed as on-vehicle services if vehicle or
engine
components are removed to gain access to parts
involved.
Note:
Some
engines
are equipped with an exhaust
emission control system. Service information on
the components of this system is given in sec tion F2.
Dl-2.
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The
Dauntless V-6
engine
has a displacement of
225 cubic inches. It has a compression ratio of
9.0 to 1, which permits use of regular-grade
gaso
line.
See
Figs.
Dl-1 and Dl-2.
The
cylinder block is made of cast
iron.
Two banks
of cylinders (three cylinders per bank) are cast at a
90-degree
angle. The lower part of the cylinder-
block
extends
below the centerline of the
crank
shaft, forming a continuous flat surface with the
rear
crankshaft main bearing cap and the timing
chain
cover.
This
design allows installation of an
oil
pan with a
one-piece
gasket. The cylinders in
the left bank (as viewed from the driver's seat) are
numbered
1-3-5,
from front to
rear.
The cylinders
in
the right bank are numbered
2-4-6,
from front
to
rear.
The
crankshaft is supported in the cylinder block
by four steel-backed full-precision bearings, all of
which
have an identical diameter.
Crankshaft
main bearings are numbered 1 to 4, front to
rear.
The
thrust
bearing is flanged to maintain crankshaft position and to compensate against crankshaft end
thrust
The No. 2 bearing is the thrust bearing.
The
crankshaft is counterbalanced by weights,
which
are cast integral with the
crank
cheeks. The
weights
are shaped to a contour which
gives
mini
mum
clearance with cylinder barrels and piston
skirts
to conserve space.
Connecting
rods have I-beam sections with
bosses
on each side. Metal is removed, as required, to secure correct weight and balance. The lower end
of each connecting rod has a steel-backed preci
sion bearing. The piston pin is a press fit into the upper end. The outer ends of the piston pin
are
a slide fit in the piston
bosses.
The
full-skirted, aluminum alloy pistons are cam ground and tin plated. Two compression rings and
one oil control ring are installed above the piston
pin.
The cast iron compression rings in the two
upper
grooves
of the piston have a
groove
or bevel cut around the inner
edge
on one side. The
top compression ring is installed with this
groove
or
bevel up. The lower compression ring is installed
with
bevel down. The oil
ring,
in the lower groove,
consists of two thin steel
rails
separated by a
spacer.
It is backed by a hump-type spring-steel
expander.
V-6
engine
cylinder heads are made of cast
iron.
Their
valve
guides
are cast integrally. Right and left cylinder heads are identical and interchange
able. In service, however, it is
good
practice to
install
the cylinder heads on the side from which
they were removed.
The
valves are in line in each head, at an angle
10°
above the centerline of the cylinder bores.
Each
valve has a spring strong enough to ensure
positive valve seating throughout the operating speed range of the engine. The valve rocker arm
mechanism is protected by a
sheet
metal cover.
This
cover is seated on a raised surface of the
cylinder
head. It is gasketed to prevent oil leaks.
The
rocker arms for each bank of cylinders are mounted on a tubular steel shaft, supported on
the cylinder head by brackets. The rocker arms
are
made of aluminum. They have inserts at the
push
rod socket and the valve stem contact face.
The
camshaft is located above the crankshaft be
tween the two cylinder banks; it is supported in
four steel-backed babbitt-metal bearings. The cam shaft is driven at one-half crankshaft speed by
sprockets and a single outside-guide type chain.
Hydraulic
valve lifters and
one-piece
push rods operate overhead rocker arms and valves of both
banks
of cylinders from a single camshaft.
This
system requires no lash adjustment during assem
bly
or in service.
In
addition to its normal function of a cam follower,
each hydraulic valve lifter also serves as an auto- 76
Page 77 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
©©©©©©©©©
12697
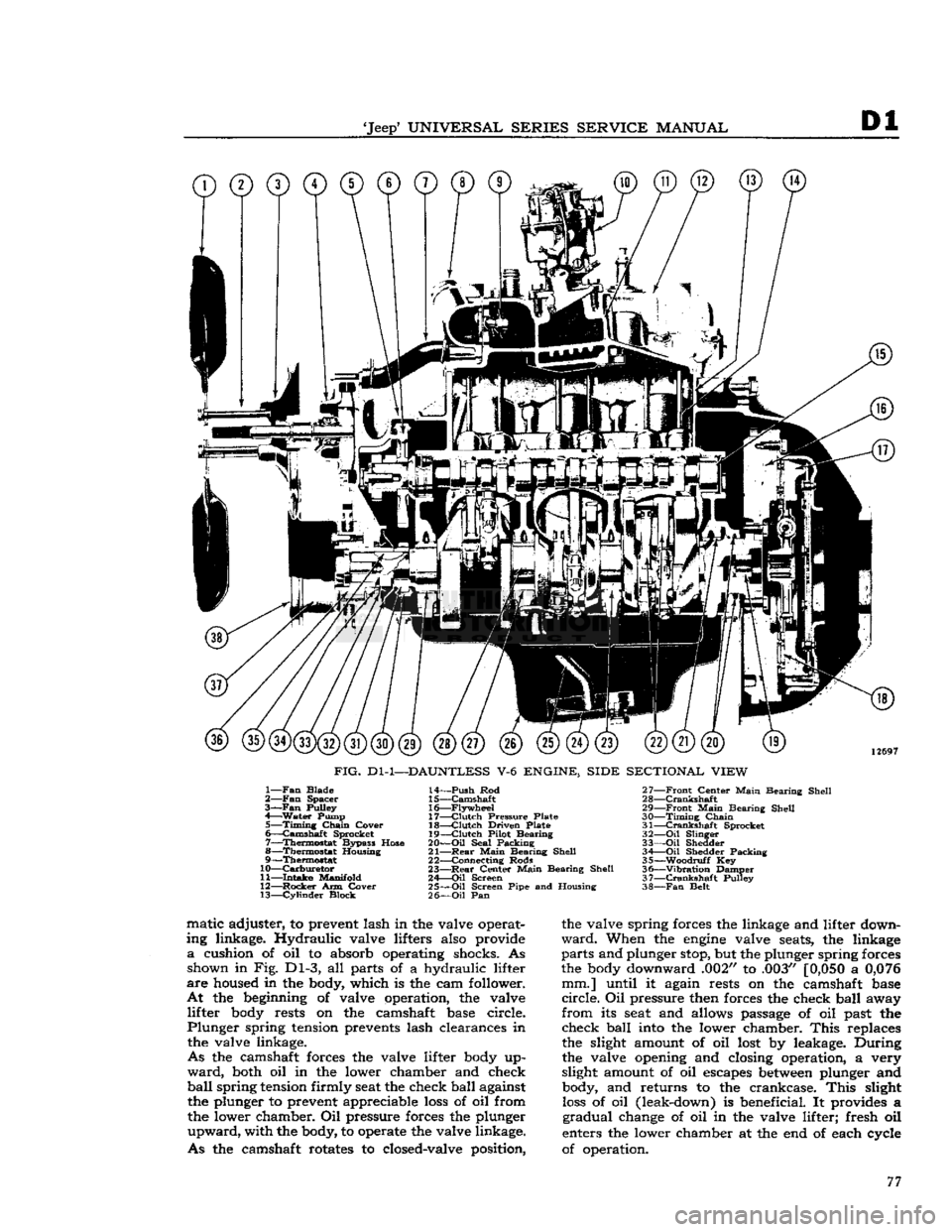
FIG.
Dl-1—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE, SIDE SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Fan
Blade
2—
Fan
Spacer
3—Fan
Pulley
4—
Water
Pump 5—
Timing
Chain
Cover
6—
Camshaft
Sprocket
7—
Thermostat
Bypass Hose
8—
Thermostat
Housing
9—
Thermostat
10—
Carburetor
11—
Intake
Manifold
12—
Rocker
Arm Cover 13—
Cylinder
Block 14—
Push
Rod
15—
Camshaft
16—
Flywheel
17—
Clutch
Pressure Plate
18—
Clutch
Driven Plate
19—
Clutch
Pilot Bearing
20—
Oil
Seal Packing
21—
Rear
Main
Bearing Shell
22— Connecting Rods
23—
Rear
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
24—
Oil
Screen
25—
Oil
Screen Pipe and Housing
26—
Oil
Pan 27—
Front
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
28—
Crankshaft
29—
Front
Main
Bearing Shell
30—
Timing
Chain
31—
Crankshaft
Sprocket
32—
Oil
Slinger
33—
Oil
Shedder 34 Oil Shedder Packing
35—
-Woodruff
Key
36—
"Vibration
Damper
37—
Crankshaft
Pulley
38—
Fan
Belt matic adjuster, to prevent lash in the valve operat
ing linkage. Hydraulic valve lifters also provide
a
cushion of oil to absorb operating shocks. As shown in Fig. Dl-3, all parts of a hydraulic lifter
are
housed in the body, which is the cam follower.
At
the beginning of valve operation, the valve lifter body rests on the camshaft base circle.
Plunger
spring tension prevents lash clearances in the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft forces the valve lifter body up
ward,
both oil in the lower chamber and check
ball
spring
tension firmly seat the check ball against the plunger to prevent appreciable
loss
of oil from
the lower chamber. Oil pressure forces the plunger
upward,
with the body, to operate the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft rotates to closed-valve position, the valve spring forces the linkage and lifter down
ward.
When the
engine
valve seats, the linkage
parts
and plunger stop, but the plunger spring forces
the body downward .002" to .003"
[0,050
a
0,076
mm.] until it again rests on the camshaft base
circle.
Oil pressure then forces the check ball away
from
its seat and allows passage of oil past the check ball into the lower chamber.
This
replaces
the slight amount of oil lost by leakage. During
the valve opening and closing operation, a very
slight amount of oil escapes
between
plunger and body, and returns to the crankcase.
This
slight
loss
of oil (leak-down) is beneficial. It provides a
gradual
change of oil in the valve lifter; fresh oil
enters the lower chamber at the end of each cycle
of operation. 77
Page 79 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12710
FIG.
D1
-3—HYDRAULIC VALVE
LIFTER
ASSEMBLY, CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Snap
Ring
6—Ball Retainer
2— Rod
Seat
7—Plunger Spring
3—
Oil
Inlets
8—Lifter
Body
4—
Plunger
9—Bronzed
Cap
5— Feed
Hole
sages
in the block and cylinder head.
The
water cooled system is pressurized to provide efficient
engine
cooling. It consists of a centrifugal-
type water pump, mounted on the timing chain cover, and is driven by the
engine
fan pulley. The
pump provides coolant flow equally to both
cylin
der banks under control of a thermostat. Coolant
flow is around the cylinders and through the
cylinder
head to dispel the heat of combustion in
the engine.
Dl-3.
Engine Mounts
The
engine-transmission unit is mounted to the chassis at three points by rubber pads. The two
front mounts are bolted to the
engine
cylinder
block and the frame members. These mounts sup port most of the
engine
weight, and absorb
vibra
tion which would otherwise be caused by changes
in
engine
output torque. The single
rear
mount is
placed
between
the transmission and the trans mission support. It supports part of the engine'
and
transmission weight, and locates the
rear
of
the
engine
with respect to the centerline of the
vehicle.
Dl-4. ENGINE REMOVAL
To
remove the
engine
from the vehicle follow the
procedurers listed below:
a.
Remove hood. b. Disconnect battery cables from battery and
engine. c. Remove air cleaner.
d.
Drain
coolant from radiator and engine.
e.
Drain
engine
oil.
f. Disconnect alternator wiring harness from con nector at regulator.
cj.
Disconnect the fuel evaporative purge line con nected to the
P.C.V.
valve.
h.
Disconnect upper and lower radiator
hoses
from
the engine.
i.
Remove right and left radiator support
bars,
j.
Remove radiator from the vehicle.
k.
Disconnect
engine
wiring harnesses from con
nectors located on
engine
firewall.
I.
On
engines
equipped with exhaust emission con
trol,
remove the air pump, air distribution manifold,
and
anti-backfire (gulp) valve. See Section F2 for
procedure.
m.
Disconnect battery cable and wiring from en
gine
starter assembly.
n.
Remove
engine
starter assembly from engine,
o.
Disconnect
engine
fuel
hoses
from fuel lines at
right
frame
rail,
p. Plug fuel lines.
q.
Disconnect choke cable from carburetor and cable support bracket mounted on engine,
r.
Disconnect exhaust pipes from right and left
engine
manifolds.
s. Place
jack
under transmission and support trans
mission weight.
f. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to front motor mounts.
u.
Attach suitable sling to
engine
lifting
eyes
and,
using hoist, support
engine
weight.
v. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to flywheel housing.
w. Raise
engine
slightly and slide
engine
forward
to remove transmission main shaft from clutch plate spline.
Note:
Engine and transmission must be raised
slightly to release the main shaft from the clutch
plate while sliding the
engine
forward.
x. When
engine
is free of transmission shaft raise
engine
and remove from vehicle,
y. Place
engine
on suitable blocking or
engine
stand and remove sling from engine.
Dl-5.
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Engine
disassembly is presented in the sequence to be followed when the
engine
is to be completely
overhauled after removal from the vehicle. Some of the operations of the procedure are also applicable separately with the
engine
in the vehicle,
provided that wherever necessary the part of the
engine
to be worked on is first made accessible by removal of
engine
accessories or other parts.
When
the disassembly operations are performed
with
the
engine
out of the vehicle, it is assumed,
in
this procedure, that all of the accessories have
been removed
prior
to starting the disassembly and
the oil has been drained.