1953 JEEP DJ torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 49 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
D
FIG.
D-ll—CHECKING PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
ALIGNMENT 1—
Feeler
Gauge
2—
Fixture
the
opposite
side from the oil spray
hole
in the
bearing
end of the connecting rod. See Fig. D-10.
Install
the piston pin lock screw and torque 35 to
41 lb-ft. [4,8 a 5,7 kg-m.].
d.
Place piston and rod assembly in a connecting
rod
aligning fixture and check alignment of the
assembly as shown in
Fig. D-ll.
Follow instructions
furnished
with the fixture.
e. Using a feeler
gauge
and new piston rings, check the width of the two compression ring
grooves
and
the oil ring groove. Replace the piston if the widths of the
grooves
are not with the limits given in
the specifications.
Insert
feeler
gauge
between
ring and piston to back
of groove. Replace piston if ring
grooves
are not
within
allowable tolerances. If a feeler
gauge
larger
FIG.
D-l 2—CHECKING PISTON RING
SIDE
CLEARANCE
1—
Feeler
Gauge
2—
Piston
Ring
FIG.
D-13—PISTON
RING
GAP
than
.006" [0,152 mm.] can be inserted
J^6"
[1,6
mm.]
between
piston and upper compression
ring,
groove
is worn excessively bell-mouthed and
piston should be replaced.
f.
Check
piston ring end gap by placing compres sion ring in cylinder bore below ring travel using head of an inverted piston as a plunger to push
ring
in squarely. End gap must be as shown in
Par.
D-37 for all rings. If less, file ends to obtain
minimum
gap.
With
cylinders bored to an exact
ring
oversize of
+.020", +.030",
or
+.040"
[0,508-
0,762-1,016
mm.] the proper end clearance as given in Par. D-37
will
result. If end
gaps
are
not within the limits given in Par.
D-3
7, rings are
of the wrong size or were incorrectly filed for fitting.
g.
Install
a new ring set using either production replacement rings or service type oil control rings.
Production
type replacement piston rings are the
same as the original factory-installed rings while
service oil control ring
sets
have different com
ponents, notably the oil ring expander. Follow
instructions of
manufacturer
for proper installation.
Use
a piston ring expander to install rings on pistons. Do not expand rings more than necessary
to install, also be careful not to
burr
the piston
with
ends of rings.
Install
bottom
(oil) ring first, center ring second, and top ring last.
The
width of the compression rings is [2,38
mm.] and that of the oil control ring is f^" [4,78
mm.].
While the compression rings are of the same
size, they are different in construction and must
not be interchanged.
Install
these
rings as shown
in
Fig. D-14. The upper compression ring has an
inside beveled
edge
which must be installed toward
the piston top. The face of the lower compression
ring
is tapered approximately .001" [0,025 mm.].
The
letters T or TOP on the upper
edge
indicate
how the ring is to be installed. 49
Page 51 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
-Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E>
[5,928 a
5,926
cm.] for all main bearings. Allowable
taper or out-of-round of the journals is .001"
[0,0254
mm.].
D-42.
Checking Connecting Ro JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
-Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E>
[5,928 a
5,926
cm.] for all main bearings. Allowable
taper or out-of-round of the journals is .001"
[0,0254
mm.].
D-42.
Checking Connecting Ro](/manual-img/16/57041/w960_57041-50.png)
-Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E>
[5,928 a
5,926
cm.] for all main bearings. Allowable
taper or out-of-round of the journals is .001"
[0,0254
mm.].
D-42.
Checking Connecting Rod
Crankpins
Check
the crankpin diameters with a micrometer
to ensure that they are not out-of-round or tapered more than .001"
[0,0254
mm.] The standard
crank-
pin
diameter is
1.9383*
to
1.9375"
[4,9233
a
4,9213
cm.].
D-43.
Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
The
crankshaft rotates on three main bearings
with
a running clearance of .0003" to .0029"
[0,0076
a
0,0736
mm.].
These
bearings are positioned and prevented from
rotating in their supports in the cylinder block by
dowel pins. Dowel pins are used in both the center
and
the
rear
bearing caps. No dowel pins are used
in
the front bearing cap because the bearing has
a
flange. The front main bearing takes the end
thrust
of the crankshaft. The main bearings are of premium type which provides long bearing life.
They
are replaceable and when correctly installed, provide proper clearance without filing, boring,
scraping,
or shimming. Crankshaft bearings can
be removed from this
engine
only with the
engine
out of the vehicle. Crankshaft bearings must be replaced as a complete set of three bearings, each
bearing consisting of two halves.
Main
bearings
are
available in the standard size and the following
undersizes:
.001" [0,025mm.] .012" [0,305 mm.] .002" [0,051mm.] .020" [0,508 mm.] .010" [0,254mm.] .030" [0,762 mm.]
The
.001" and .002" undersize main bearings are
for use with standard size crankshafts having
slightly worn
journals.
The .010", .020", and .030" undersize bearings are for use with undersize
crankshafts
in
those
sizes. The .012" undersize
bearings are for use with .010" undersize
crank
shafts having slightly worn journals. Bearing sizes
are
rubber stamped on the reverse side of each
bearing half.
D-44. Crankshaft
Main
Bearing Inspection
The
crankshaft
journals
must be carefully inspected
as detailed previously in Par. D-41. Worn journals
will
require undersize bearings. Scored, flaked, or
worn
bearings must be replaced. Measure the main
bearing bores in the cylinder block using a
telescope
gauge
and micrometer. Measure the bores at right
angles to the split line and at 45° to the split line.
The
bores should not be over .001"
[0,0254
mm.]
out-of-round or .001" in taper from end to end.
Also,
the bores should not be more then .001"
oversize, considering the average diameter of the
bore.
D-45.
Fitting Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
Using
Plastigage
After
wiping and carefully inspecting the bearing bore, install the proper bearing. See that the oil
hole
in the bearing upper half registers properly
with
the oil
hole
in the block, and that the bearing
lock fits properly in the notch in the block.
Install
the crankshaft if replacing bearings with the
engine
out of the vehicle. The desired running fit (dif
ference
between
the diameter of the crankshaft
journal
and the inside diameter of the fitted bear ing) for a main bearing is .0003" to .0029"
[0,0076
a
0,0736
mm.]. With a dimension in
excess
of this
standard
running fit, a satisfactory bearing replacement cannot be made and it
will
be necessary to
regrind
the crankshaft.
Install
the bearing lower
half
and the bearing cap and draw the nuts down
equally and only slightly tight. Rotate the
crank
shaft by hand to be sure it turns freely without
drag.
Pull
the nuts tighter, first one then the other,
a
little at a time, intermittently rotating the
crank
shaft by hand until the recommended torque of
35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.] is reached. If the
bearings are of the correct size, and lubricated with
light oil before installation, the crankshaft should
turn
freely in the bearings. If the crankshaft cannot
be turned, a larger bearing is
required.
If there is no binding or tightness, it is still necessary to check
clearance to guard against too
loose
a fit. Never file
either the bearing cap or the bearing to compensate
for too much clearance. Do not use shims under a
bearing cap or behind a bearing shell. Do not run a
new bearing half with a worn bearing half. The use
of "Plastigage" of the proper size to measure .001" [0,025 mm.] clearance is recommended for check
ing crankshaft main bearing clearance. The method
of checking clearance is as follows:
a.
Remove the bearing cap and carefully wipe
all
oil from the bearing and the
journal.
b.
Lay a piece of "Plastigage" y%" [3 mm.]
shorter than the width of the bearing across the
journal
(lengthwise of the crankshaft).
c.
Install
the bearing and cap and tighten first
one nut, then the other, a little at a time to the specified torque. As the bearing
tightens
down
around
the
journal,
the "Plastigage" flattens to a
width that indicates the bearing clearance.
d.
Remove the cap and measure the width of
the flattened "Plastigage," using the scale printed
on the
edge
of the envelope. The proper size "Plasti
gage"
will
accurately measure clearance down to .001".
e. If the flattened "Plastigage" tapers toward the middle, or toward the end, or both ends, there
is a difference in clearance, indicating a taper, a
low
spot,
or other irregularity of the bearing or
journal.
D-46.
Fitting Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
Using
Shim Stock
Thin
feeler or shim stock may be used instead of "Plastigage" to check bearing clearances. The
method is simple, but care must be taken to protect
the bearing metal surface from
injury
by too much pressure against the feeler stock,
a.
Cut a piece of .001" [0,025 mm.] thick, by Yl [12,7 mm.] wide, feeler stock }4" [3 mm.]
shorter than the width of the bearing. Coat this 51
Page 52 of 376
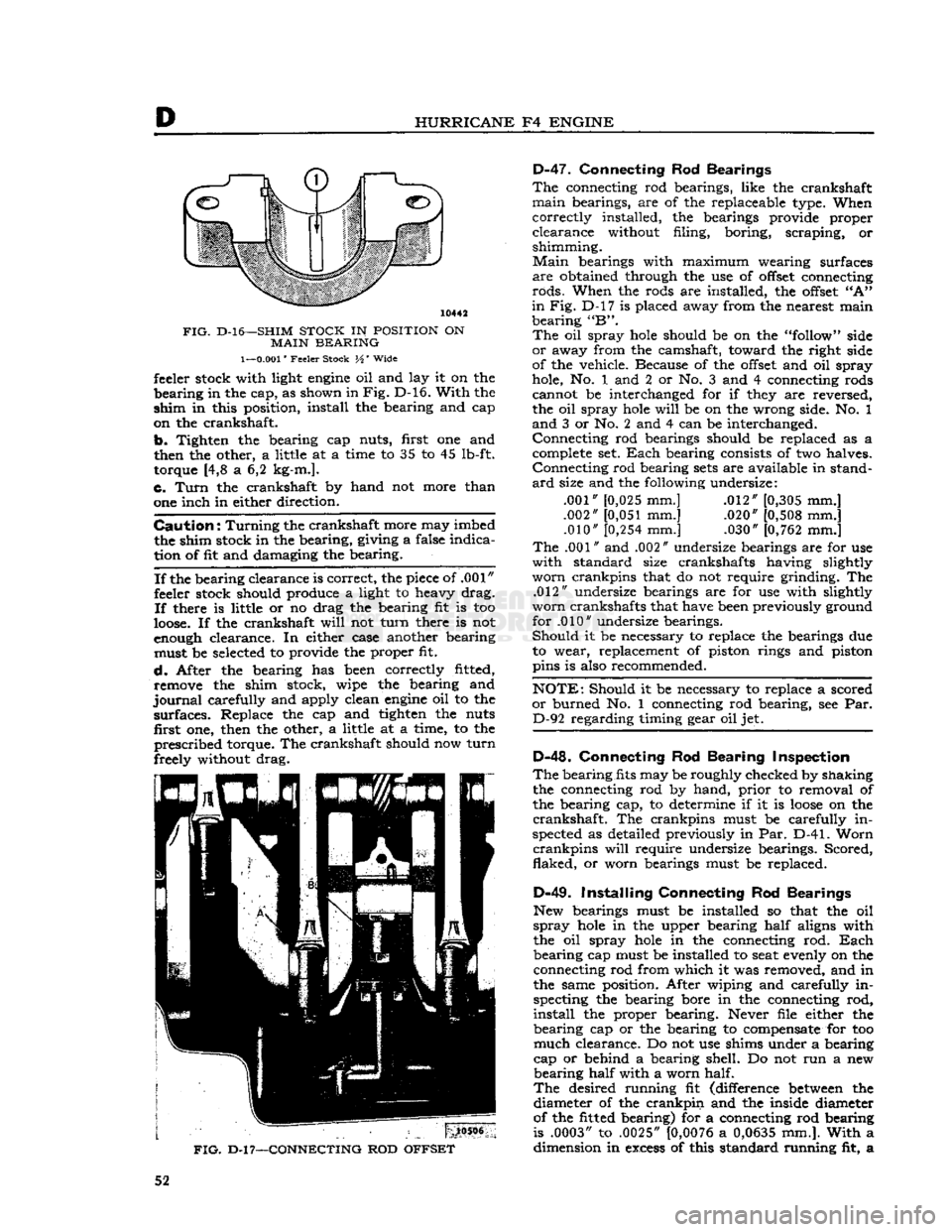
D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
10442
FIG.
D-l6—SHIM
STOCK
IN
POSITION
ON
MAIN
BEARING
1—0.001"
Feeler Stock H' Wide feeler stock with light
engine
oil and lay it on the
bearing
in the cap, as shown in
Fig.
D-16.
With
the
shim
in this position, install the bearing and cap
on the crankshaft.
b.
Tighten the bearing cap nuts, first one and
then the other, a little at a time to 35 to 45 lb-ft. torque [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.].
c.
Turn
the crankshaft by hand not more than
one inch in either direction.
Caution:
Turning
the crankshaft more may imbed the shim stock in the bearing, giving a false indica
tion of fit and damaging the bearing.
If
the bearing clearance is correct, the piece of .001"
feeler stock should produce a light to heavy drag.
If
there is little or no drag the bearing fit is too
loose.
If the crankshaft
will
not
turn
there is not
enough clearance. In either case another bearing must be selected to provide the proper fit.
d.
After the bearing has been correctly fitted, remove the shim stock, wipe the bearing and
journal
carefully and apply clean
engine
oil to the
surfaces.
Replace the cap and tighten the nuts first one, then the other, a little at a time, to the
prescribed
torque. The crankshaft should now
turn
freely without drag.
FIG.
D-l
7—CONNECTING
ROD
OFFSET
D-47.
Connecting Rod Bearings
The
connecting rod bearings, like the crankshaft
main
bearings, are of the replaceable type. When
correctly
installed, the bearings provide proper
clearance
without filing, boring, scraping, or
shimming.
Main
bearings with maximum wearing surfaces
are
obtained through the use of
offset
connecting
rods.
When the rods are installed, the
offset
"A"
in
Fig. D-l7 is placed away from the nearest main
bearing
"B".
The
oil spray
hole
should be on the "follow" side
or
away from the camshaft, toward the right side
of the vehicle. Because of the
offset
and oil spray
hole, No. 1 and 2 or No. 3 and 4 connecting rods cannot be interchanged for if they are reversed,
the oil spray
hole
will
be on the wrong side. No. 1
and
3 or No. 2 and 4 can be interchanged.
Connecting
rod bearings should be replaced as a complete set.
Each
bearing consists of two halves.
Connecting
rod bearing
sets
are available in stand
ard
size and the following undersize:
.001" [0,025 mm.] .012" [0,305 mm.]
.002"
[0,051
mm.] .020" [0,508 mm.] .010"
[0,254
mm.] .030" [0,762 mm.]
The
.001" and .002" undersize bearings are for use
with
standard size crankshafts having slightly
worn
crankpins that do not require grinding. The .012" undersize bearings are for use with slightly
worn
crankshafts that have been previously ground for .010" undersize bearings.
Should
it be necessary to replace the bearings due to wear, replacement of piston rings and piston
pins is also recommended.
NOTE:
Should it be necessary to replace a scored
or
burned No. 1 connecting rod bearing, see Par. D-92 regarding timing gear oil jet.
D-48.
Connecting Rod Bearing Inspection
The
bearing fits may be roughly checked by shaking the connecting rod by hand,
prior
to removal of
the bearing cap, to determine if it is
loose
on the
crankshaft.
The crankpins must be carefully in
spected as detailed previously in Par. D-41.
Worn
crankpins
will
require undersize bearings. Scored,
flaked,
or
worn bearings must be replaced.
D-49.
Installing Connecting Rod Bearings
New bearings must be installed so that the oil
spray
hole
in the upper bearing
half
aligns with
the oil spray
hole
in the connecting rod.
Each
bearing
cap must be installed to seat evenly on the connecting rod from which it was removed, and in
the same position. After wiping and carefully in specting the bearing bore in the connecting rod,
install
the proper bearing. Never file either the
bearing
cap or the bearing to compensate for too
much
clearance. Do not use shims under a bearing
cap or behind a bearing shell. Do not run a new
bearing
half
with a worn half.
The
desired running fit (difference
between
the diameter of the
crankpin
and the inside diameter
of the fitted bearing) for a connecting rod bearing
is .0003" to .0025"
[0,0076
a
0,0635
mm.].
With
a dimension in
excess
of this standard running fit, a 52
Page 53 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
D
satisfactory bearing replacement cannot be made
and
it
will
be necessary to regrind the crankshaft.
Install
the bearing lower
half
and the connecting
rod
cap and draw the cap bolt nuts down equally
and
only slightly tight. Move the connecting rod
endwise, one way or the other, on the crankshaft to be sure the bearing is not tight.
Pull
the nuts tighter, first one then the other, a little at a time,
and
keep trying the fit of the rod on the crankshaft by hand until the recommended torque of 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.] is reached. If the
bearings are of the correct size, and have been
properly
lubricated with light
engine
oil before in
stallation,
the connecting rod should be easy to
slide back and forth parallel to the
crankpin.
If
the connecting rod is tight on the crankshaft, a
larger
bearing is required. If there is no binding
or
tightness, it is
still
necessary to check clearance
to guard against too
loose
a fit. The use of "Plasti
gage"
or shim stock of the proper size to measure .001" [0,025 mm.] clearance is recommended for
checking
connecting rod bearing clearances.
This
is the same material recommended for checking
crankshaft
main bearings and the method of check
ing is
similar.
Refer to
Par.
D-45 or D-46. Connect
ing rod bearings are fitted to the same clearance as the main bearings but the torque specified for con
necting rod cap
bolts
is different.
D-50.
Connecting
Rod
Side Play
Check
the connecting rod side play with a feeler
gauge
as shown in Fig. D-l8. The side clearance is .004" to .010"
[0,101
a
0,254
mm.].
D-51.
Camshaft and Bearings
The
camshaft is supported at four points in the
cylinder
block. The front is supported in a re placeable, steel-shell, babbit-lined bearing. The
bearing
is pressed into place The other three bear-
FIG.
D-18—CONNECTING
ROD
SIDE
PLAY
ing surfaces are precision machined in the cylinder
block. The camshaft bearings are pressure
lubri
cated through drilled passages in the crankcase.
End
thrust of the camshaft is taken by a thrust plate bolted to the crankcase. The camshaft is
driven
by a silent helical-cut
tooth
timing gear at
the front of the engine. A worm gear, integral with
the camshaft, drives the oil pump and distributor.
The
fuel pump is actuated by an eccentric forged
onto
the camshaft.
Clean
the camshaft thoroughly in cleaning solvent.
Inspect
all camshaft bearing surfaces to determine
if
they are scored or rough. The cam faces must be
perfectly smooth throughout their contact face
and
must not be scored or worn.
D-52.
Camshaft
Front Bearing Replacement
Use
a suitable driver to remove the camshaft front
bearing
from the cylinder block. To install a new
bearing,
align the oil
hole
in the bearing with the
bored oil
hole
in the cylinder block and drive the
bearing
in until the front end of the bearing is
flush
with the front surface of the cylinder block.
Make
sure the oil
hole
is open and clear. It is not
necessary to line-ream the bearing after installation because bearings for replacement are precision
reamed
to the finished size. Do not stake the
bearing.
D-53-
Camshaft End Play
End
play of the camshaft is determined by running
clearance
between
the
rear
face of the camshaft gear and the thrust plate and is established by the
spacer
thickness. The standard clearance is .004"
to .007"
[0,101
a 0,178 mm.] and can be measured by a
dial
indicator. As a general rule this clearance
will
change but little through wear or when a new gear is installed. To predetermine the correct end
float with the gear, spacer, and thrust plate re
moved, measure the thickness of both the thrust
plate and spacer with a micrometer. The thickness
of the spacer should be approximately .006" [0,152 mm.] greater than that of the thrust plate.
When
this is correct and the parts are assembled
and
drawn tightly
together
by the gear retaining
screw,
the end play should
come
within standard
limits.
D-54.
Timing Gears
and
Cover
The
timing gears are mounted at the front of the
engine. Camshaft drive is through helical-cut
timing gears; a steel gear on the crankshaft and a
pressed fiber gear on the camshaft. The gears are keyed to their respective shafts. The camshaft
driven
gear is secured on the front end of the
camshaft by means of a capscrew and a plain
washer.
The crankshaft gear is secured on the
front end of the crankshaft by a nut threaded
onto
the front end of the crankshaft holding the
crank
shaft pulley, crankshaft oil slinger, and the
crank
shaft drive gear spacer. The timing gears are
lubricated
through a jet threaded into the
crank
case directly above the gear contact and oil supplied
through a drilled passage from the front main
bearing.
The timing gears are enclosed by the
sealed timing cover. The oil seal in the cover bears 53
Page 54 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
against the hub of the crankshaft pulley.
Timing
gears are accessible for inspection or replacement
with
the
engine
installed in the vehicle after re moving the radiator, belt drive pulley, and timing
cover.
Should
it be necessary to replace the timing gears, attention must be given to the end float of both
the camshaft and crankshaft and to the running
clearance
of both gears. It is also advisable to
check
both the oil jet and oil passage to the
crank
shaft front bearing to be sure that they are clear.
D-55.
Inspection and
Repair
Check
the general condition of both gears and
inspect for evidence of excessive wear. Replace
excessively worn or damaged gears. Inspect the
cover and replace if bent or damaged. It is recom mended that the crankshaft oil seal in the cover
be replaced when the cover is removed to ensure a
good
seal around the crankshaft. To replace this
seal
with the
engine
in the vehicle
requires
removing
the radiator and water pump.
D-56.
Valves, Springs, and Guides
The
exhaust valves seat on the top of the cylinder
block
with the
stems
extending down through
replaceable valve guides. The exhaust valves are actuated by the camshaft through exhaust valve
tappets. The exhaust valve springs are assembled
and
locked on the lower end of the exhaust valve
stems. The retaining locks are the split type, which
fit in a recess on the valve
stems
and into the taper
in
the valve spring retainers.
Adjustment
of exhaust valves is by means of the
adjusting
screw threaded into the upper end of the
exhaust valve tappets. An exhaust valve rotator used as a valve spring retainer is installed on the
lower end of the exhaust valve.
This
valve rotator,
known
as "Roto Cap", is a spring-loaded
ball
bearing
device. On each lift, or opening stroke of
a
valve, the rotator
gives
the valve a slight positive
clockwise rotation.
The
intake valves operate in valve
guides
in the
cylinder
head and are actuated by rocker arms.
The
rocker arms are actuated by valve push rods
and
the intake valve tappets. The intake valve
springs,
the intake valve spring retainers, and the
intake
valve spring retainer locks make up the
remainder
of the valve operating parts. An intake
valve spring retainer oil seal which encircles the
upper
end of the intake valve
between
the valve
locks and the upper end of the valve spring re
tainer,
controls the passage of oil along the valve
stem and guide.
Note:
When
engine
trouble indicates defective
valves as a possible source of trouble, also check
all
vacuum line connections for possible leaks.
D-57.
Inspection of Valves, Springs,
and
Guides
Clean
the valves on a wire wheel, making sure that
all
carbon is removed from the top and the under
side of the heads and that all gum and varnish
deposits
are removed from the stems.
Polish
the valve
stems
with steel wool or crocus
cloth.
Visually
inspect all valves for warpage,
cracks,
or excessive burning and discard if one of
these
conditions exists. Replace any worn, pitted,
or
corroded valves that cannot be cleaned with a
wire
brush.
Replace any valves when
seats
are pitted, burned, or corroded so badly that they
cannot be cleaned up with a light refacing on a valve refacing machine.
Replace
valves with marks of scoring or abrasion visible on the stem. Replace any valves with bent
stems
which
will
be apparent when the valve is
mounted in the valve refacing machine.
Note:
Use only hard-face exhaust valves for
replacement.
Examine
the
stems
of valves which employ the
ball
bearing rotators.
Wear
marks around the
cir
cumference of the
stems
indicates that the valve is
rotating satisfactorily.
Vertical
heavy pressure
areas
indicate that the valve is not rotating and the valve spring retainer (Roto
Cap)
should be replaced
if
at fault.
Check
the diameter of the valve stem at two or three places along the length of the stem
with
a micrometer. The intake valve stem diameter is .3733" to .3738" [9,482 a
9,495
mm.]. The
exhaust valve stem diameter is .371" to .372"
[9,423
a
9,449
mm.].
Note:
Exhaust
and intake valve springs are
similar
in appearance. They must not be inter
changed as they have different spring
charac
teristics.
Wash
the valve springs thoroughly in solvent.
Visually
examine the springs and replace any that
are
deformed or obviously damaged. Examine for
corrosion
from moisture or acid etching which might
FIG.
D-19—TESTING
VALVE
SPRING
1—
Torque
Wrench
2—
Spring
Testing
Fixture
3—
Valve
Spring
54
Page 55 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
develop
into surface cracks and cause failure.
Measure
the over all free length of the springs and
replace any that do not measure to standard: 1%" [35,7 mm.] for intake valve springs and 2j^"
[63,5 mm.] for exhaust valve springs. If possible,
check each valve spring in a valve spring testing
fixture C-647 or equivalent as shown in Fig. D-l9.
Test
each spring when compressed to the two
different spring lengths given (representing valve closed and valve open spring length). If any spring
fails to register spring tension equal to or greater
than
the minimum load limit in pounds specified for that spring length, replace the spring.
Length
Minimun
Load
Intake
valve spring. . .
1.660"
[4,216 cm.] 66 lb. [29,9 kg.]
1.400"
[3,556 cm.] 140 lb. [63,5 kg.]
Exhaust
valve spring. 2.109" [5,356 cm.] 47 lb. [21,3 kg.]
1.750"
[4,445 cm.] 110 lb. [49,9 kg.]
Note:
When using a spring checking fixture C-647
or
equivalent as shown in Fig. D-l9, it is necessary
to convert the torque wrench reading which is in pounds-feet to the static pound pressure specified above according to the instructions furnished with
the wrench. For example, should the torque wrench reading be 50 lb-ft. and the wrench is two
feet
long
the static pressure of the spring
will
be 50 x 2 or 100 lbs.
Clean
the valve
guides
with a standard valve guide
cleaner or a wire
brush.
Check
the valve
guides
in the cylinder block. Replace valve
guides
which are
broken
or worn enough to cause excessive valve
stem-to-guide
clearance. See Par. D-61.
Standard
intake valve clearance is .0007" to .0022"
[0,0178
a
0,0559
mm.] and the exhaust valve
clearance is .0025" to .0045" [0,0635 a
0,1143
mm.].
Excessive
clearance
between
the valve
stems
and
guides
will
cause improper seating and burned
valves. When there is a tendency to draw oil vapor
through the guide causing excessive oil consump tion, fouled
spark
plugs, and poor low-speed per
formance. To check the clearance of the valve stem
to the valve guide, take a new valve and place in
each valve guide.
Check
the clearance with a
suitably mounted
dial
indicator or feel the clearance by moving the valve stem back and forth. If this
check shows excessive clearance it
will
be necessary to replace the valve guide.
D-58.
Refacing Valves
Re
face the valves with a valve refacer. The valve
refacer
manufacturer's instructions should be fol
lowed carefully to ensure a valve face concentric
with
the valve stem. Reface both intake and ex
haust valves to an angle of 46°.
Take
off only the
minimum
of metal required to clean up the valve faces.
If
the thickness of the
edge
of the valve head is
reduced to
less
than
J^>"
[0>8 mm.] replace the valve.
Note:
Cocked or deformed valve springs or im
properly
installed or missing locks can be responsible
for valve problems.
D-59.
Valve Seat Inspection
and
Refacing
Inspect the valve
seats
for
cracks,
burns, pitting,
ridges, or improper angle.
During
any general
engine
overhaul it is advisable to reface the valve
seats
in both the cylinder block and head regardless
of their condition. If the valve
guides
are to be re placed, this must be
done
before refacing the valve
seats.
Note
that later
engines
have hardened
exhaust valve seat inserts.
Valve
seat inserts must be concentric with finish
ream
of valve stem
guides
(exhaust) within .002"
[0,051
mm.] total indicator reading.
When
necessary to reface the valve seats, use a
valve seat grinder in accordance with the grinder
manufacturer's
instructions. Any grinding of valve
seats
should be preceded by touching up the
grinding
stone
so that their angles are accurate and
the
stone
is not
clogged.
Grind
each valve seat to
a
true 45° angle. Never grind any more than is necessary to clean up pits, grooves, or to correct
the valve seat runout.
Check
the valve
seats
with
10465
FIG.
D-20—VALVE
WITH
ROTO
CAP
FIG.
D-21—GAUGING
VALVE
SEATS
55
Page 62 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE d.
Remove the intake valve adjusting screw lock-
nuts from each of the rocker arm valve lash ad
justing
screws. Remove the screws from the rocker
arms.
D-76.
Inspection and
Repair
Run
a round wire brush through the bore of the
rocker
arm shaft and clean out the drilled oil holes.
Clean
out the oil
holes
in the rocker arm shaft
brackets,
and the oil
holes
and
grooves
in the bores
of the rocker arm.
Inspect
the diameter of the shaft at the rocker arm
bearing
areas. Replace the shaft if there are scores
or
abrasion marks along the length of the shaft.
Check
the shaft for alignment by rolling it across
a
smooth level surface. If the shaft
will
not
roll
freely, or if it rolls with a bumping motion, the
shaft is out of alignment and must be replaced.
Inspect
the threads of the adjusting screw
hole
in
the rocker arms and if necessary clean with a
proper
size tap. Replace the adjusting screw lock-
nut or the adjusting screw if either part is damaged
or
deformed.
Inspect
the threads in the tapped
hole
in the top
of the rocker arm shaft brackets and if necessary
clean
with a proper size tap. Replace the bracket
if
either side is worn or scored.
D-77.
Reassembly
a.
Install
two rocker arm shaft plugs, one in each
end of the shaft. Slide two
rocker
arm
shaft brackets
onto
the center of the shaft. Align the tapped
holes
in
the brackets with the drilled
holes
in the top of
the shaft and install the rocker arm shaft lock
screws,
making sure the points of the screws enter
the drilled
holes
in the shaft.
b.
Screw the intake valve adjusting screws into
the rocker arms and install the locknuts.
c.
The rocker arms are paired; that is, two of the
arms
are angled to the right and two are angled to
the left. One of each type is used on each end of
the rocker arm shaft. Slide a rocker arm with the
adjusting
screw end of the rocker arm angling
away
from the bracket
onto
the shaft so that the
adjusting
screw is on the same side of the shaft
as the mounting
hole
in the bracket.
d.
Temporarily
secure the end bracket in place by
installing
a rocker arm cover stud in the tapped
opening in the top of the support.
e. Assemble the parts on the
opposite
end of the
rocker
arm shaft repeating
steps
c and d above.
D-78. ENGINE REASSEMBLY
The
engine
reassembly procedure in the following
paragraphs
is given in the sequence to be followed
when the
engine
is being completely overhauled.
Individual
inspection,
repair,
and fitting operations
previously covered in detail are made throughout
the reassembly procedure. The reassembly pro
cedure
does
not cover accessories. If a new cylinder
block
fitted with pistons is used, many of the
operations
will
not be required.
Mount
the cylinder block in an
engine
repair stand.
If
an
engine
stand is not available, perform the fol
lowing reassembly operation in a manner designed to protect personnel against an accident and the
engine
and its parts against damage.
Note:
During
engine
reassembly, use Perfect Seal
Aerosol
Spray
Sealer
Part
No.
994757
on all
engine
gaskets to ensure against vacuum, oil, gasoline and
water
leaks. Apply to head gaskets, valve covers,
water
pumps, oil pan gaskets, radiator and heater
hose
connections, felt gaskets, gasoline and oil line
connections, stud bolts,
spark
plug threads, and
grease retainer washers. Refer to manufacturer's in
structions on container for proper application pro
cedure.
D-79.
Install
Oil
Gallery
Plug
Coat
plug threads with a suitable sealing compound
and
install the plugs in the front and
rear
ends of
the oil gallery in the cylinder block and the
rear
end of the cylinder head. Torque the plugs 20 to 25 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
There
is also a pipe plug
(}/g,f
[3,2 mm.] slotted, headless) in the opening in the main oil gallery inside the cylinder block at No. 2 cylinder and another pipe plug
(}/g
"
square-head) in the opening
in
the oil passage directly below the oil pump intake
passage. If
these
two pipe plugs were removed,
make
certain they are reinstalled in the locations
described above or the counterweight of the
crankshaft
might strike the projecting head of the
square-head
plug.
D-80.
Install
Tappets
Turn
the block upside down. Beginning at the
rear
end of the cylinder block, install the intake
and
exhaust valve tappets in the tappet bores in the cylinder block in the following order: one
exhaust, two intake, two exhaust, two intake, and
finally
one exhaust valve tappet.
Check
the tappet to bore fit of each tappet as it
is installed in the block. If the stem-to-block
clearance
tolerance of .0005" to .002" [0,0127 a
0,051 mm.] is
exceeded
install a new tappet fitting
within
this tolerance or ream the bore to accomo date the next oversize tappet which is available
in
.004" oversize.
D-81.
Install
Camshaft and
Thrust
Plate
Lubricate
all camshaft bearings and cam surfaces generously with clean, light
engine
oil.
Carefully,
so not to damage or score the camshaft front bear
ing,
install the camshaft, locating it properly in the bearings. Do not allow the
rear
end of the camshaft to strike sharply against the expansion plug
installed
in the
rear
end of the bore.
Install
the camshaft thrust plate. Slide the thrust
plate spacer
onto
the end of the camshaft with the
beveled inner
edge
of the spacer facing the cam
shaft. If the same camshaft is being reinstalled,
install
any shims previously removed. These shims
are
placed
between
the camshaft shoulder and the
spacer.
Torque the thrust plate attaching
bolts
20
to 26 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,6 kg-m.].
End
play of the camshaft is determined by running
clearance
between
the
rear
face of the camshaft
gear and the thrust plate. The standard clearance 62
Page 63 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
is .004" to .007"
[0,102
a 0,178 mm.] as measured
by a dial indicator. Should a check
show
too little
end play, place a shim of suitable thickness
JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
is .004" to .007"
[0,102
a 0,178 mm.] as measured
by a dial indicator. Should a check
show
too little
end play, place a shim of suitable thickness](/manual-img/16/57041/w960_57041-62.png)
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
is .004" to .007"
[0,102
a 0,178 mm.] as measured
by a dial indicator. Should a check
show
too little
end play, place a shim of suitable thickness
between
the camshaft shoulder and the spacer. Too much
end play may be corrected by removing shims or
dressing off the spacer a slight amount. See Fig. D-33.
D-82. Install Crankshaft and Bearings
Fit
the three upper main bearings
into
their
respective
locations
in the cylinder block. Fit the
three lower main bearings
into
their respective
bearing caps.
NOTE:
It is
possible
to incorrectly install the front main bearing. The bearing is properly installed in
the cap with the narrower of the two radial oil
grooves
toward the front
edge
of the cap. If this
bearing is not properly installed, the oil
grooves
in
the two halves of the bearing will not match at the
parting line and premature failure of the bearing
will
result.
Lubricate
all bearing surfaces
generously
with
clean, light
engine
oil. Place the crankshaft in
position
in the cylinder block and install the main
bearing caps. Torque the
bolts
65 to 75 lb-ft.
[9,0 a 10,4 kg-m.] rotating the crankshaft after
each bearing cap is
tightened
D-83. Check Crankshaft End-Play
End
play of the crankshaft is set by the running
clearance
between
the crankshaft thrust washer
and the front
face
of the front main bearing. The
standard end play is .004" to .006"
[0,102
a 0,152
mm.] which is controlled by .002"
[0,051
mm.]
shims placed
between
the thrust washer and the
shoulder on the crankshaft. Check the end play
with a dial indicator as shown in
Fig.
D-34. If clear ance is incorrect, adjustment is made by adding or
removing shims.
Install
the thrust washer with the
beveled
inner
edge
toward the front bearing.
10668
FIG.
D-33—VALVES, CAMSHAFT,
AND
TIMING GEARS
1— Nut
2—
Left
Rocker Arm
3—
Rocker
Arm Shaft Spring
4—
Rocker
Shaft
Lock
Screw 5—
Rocker
Shaft
6— Nut 7—
Right
Rocker Arm
8—
Rocker
Arm Shaft Bracket
9—
Intake
Valve Tappet Adjusting Screw
10—
Intake
Valve Upper Retainer
Lock
11—
Oil
Seal
12—
Intake
Valve Spring Upper Retainer 13—
Intake
Valve Spring
14—
Intake
Valve Push Rod 15—
Intake
Valve
16—
Intake
Valve Tappet
17—
Camshaft
18—
Camshaft
Front Bearing
19—
Camshaft
Thrust Plate Spacer
20—
Camshaft
Thrust Plate
21— Bolt and Lockwasher
22— Bolt 13—Lockwasher
24—Camshaft
Gear
Washer 25—
Crankshaft
Gear
26—
Camshaft
Gear
27— Woodruff Key No. 9
28—
Exhaust
Valve Tappet
29— Tappet Adjusting Screw
30—
Spring
Retainer
Lock
31— Roto Cap Assembly
32—
Exhaust
Valve Spring
33—
Exhaust
Valve
34—
Rocker
Shaft Support Stud
35—
Washer
36—
Rocker
Arm Cover Stud 63