1953 JEEP CJ service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 185 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
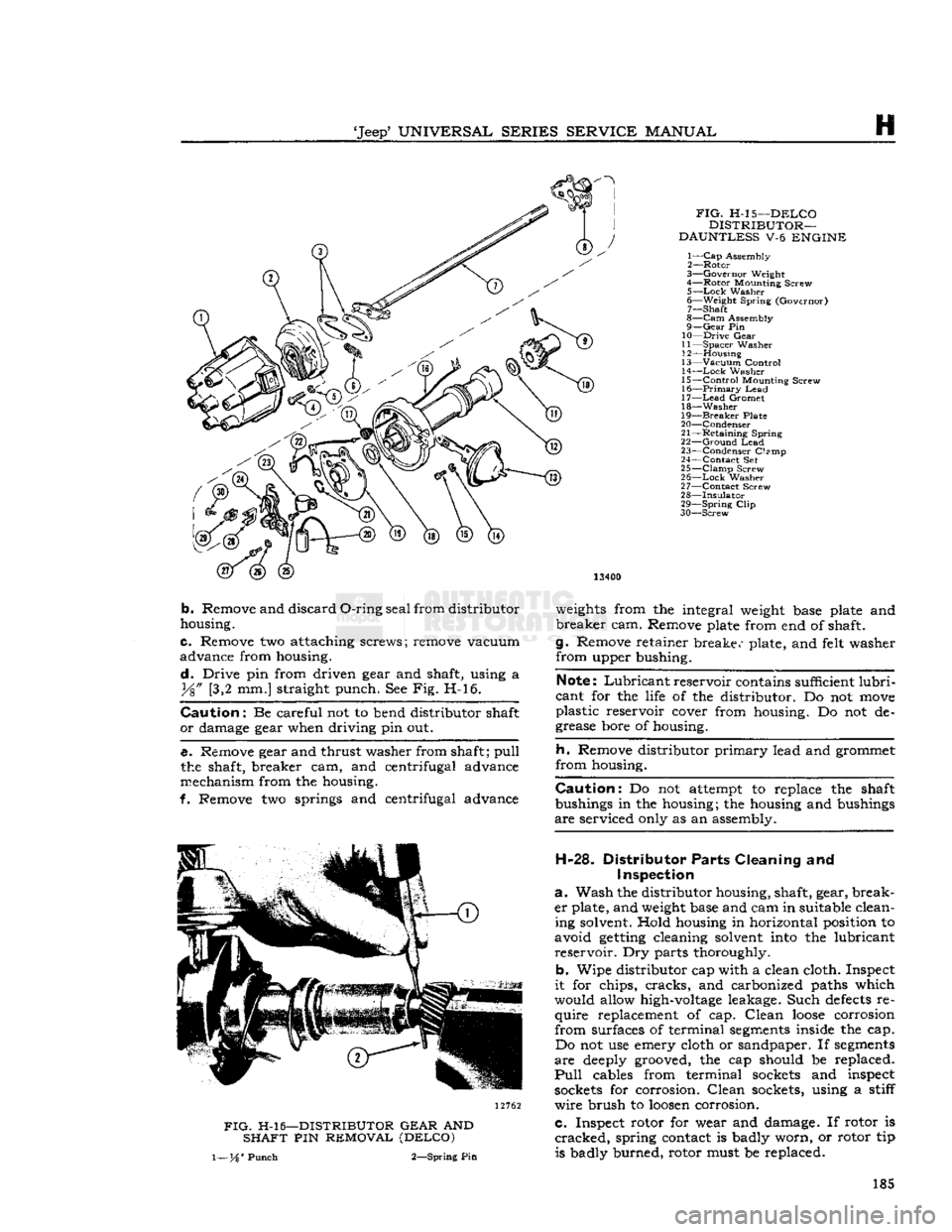
FIG.
H-l 5 -DELCO
DISTRIBUTOR—
DAUNTLESS V-6 ENGINE
1—
Cap Assembly
2— Rotor
3— Governor Weight
4— Rotor
Mounting
Screw 5—
Lock
Washer
6—
Weight
Spring (Governor) 7— Shaft
8— Cam Assembly
9—
Gear
Pin
10—
Drive
Gear
11—
Spacer
Washer
12—
Housing
13—
Vacuum
Control
14—
Lock
Washer
15—
Control
Mounting
Screw
16—
Primary
Lead
17— Lead Gromet
18— Washer
19—
Breaker
Plate
20—
Condenser
21—
Retaining
Spring
22—
Ground
Lead
23—
Condenser
Clsmp
24— Contact Set
25— Clamp Screw
26—
Lock
Washer
27— Contact Screw
28—
Insulator 29—
Spring
Clip
30—
Screw 13400
b.
Remove and discard
O-ring
seal from distributor
housing.
c. Remove two attaching screws; remove vacuum
advance from housing.
d.
Drive pin from driven gear and shaft, using a
y%"
[3,2 mm.] straight punch. See Fig. H-l6.
Caution:
Be careful not to bend distributor shaft
or damage gear when driving pin out.
e.
Remove gear and thrust washer from shaft; pull the shaft, breaker cam, and centrifugal advance
mechanism from the housing.
f. Remove two springs and centrifugal advance
weights
from the integral
weight
base plate and
breaker
cam. Remove plate from end of shaft.
g. Remove retainer breaker plate, and
felt
washer from upper bushing.
Note:
Lubricant
reservoir contains sufficient
lubri
cant for the life of the distributor. Do not
move
plastic reservoir cover from housing. Do not de-
grease bore of housing.
h. Remove distributor primary lead and grommet
from housing.
Caution:
Do not attempt to replace the shaft
bushings in the housing; the housing and bushings
are
serviced only as an assembly.
FIG.
H-l6—DISTRIBUTOR GEAR AND
SHAFT PIN REMOVAL (DELCO) 1— H' Punch
2—Spring
Pin
H-28.
Distributor Parts
Cleaning
and
Inspection
a.
Wash the distributor housing, shaft, gear, break
er
plate, and
weight
base and cam in suitable clean ing solvent. Hold housing in horizontal position to
avoid
getting
cleaning solvent
into
the lubricant
reservoir.
Dry parts thoroughly.
b.
Wipe distributor cap with a clean cloth. Inspect
it for chips,
cracks,
and carbonized paths which
would allow
high-voltage
leakage. Such
defects
re
quire
replacement of cap.
Clean
loose
corrosion
from surfaces of terminal
segments
inside the cap. Do not use emery cloth or sandpaper. If
segments
are
deeply
grooved, the cap should be replaced.
Pull
cables from terminal
sockets
and inspect
sockets
for corrosion.
Clean
sockets, using a stiff
wire
brush to
loosen
corrosion.
c.
Inspect rotor for wear and damage. If rotor is
cracked,
spring contact is badly worn, or rotor tip is badly burned, rotor must be replaced. 185
Page 187 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
12746
FIG.
H-l8—VACUUM
ADVANCE
MECHANISM
(DELCO)
A—Full
Advance
B—No
Advance
1—Vacuum
Pull
Rod
e.
To adjust breaker point cam dwell and set tim
ing of engine, refer to
Pars.
C-10 and
C-ll.
H-31. Coil
— V-6 Engine
The
sealed coil
does
not require any special service
other than keeping the terminals and wire connec
tions clean and tight.
The
positive (+) terminal of the coil is connected
to the ignition switch through the ballast resistor,
and
is also connected directly to the starter
sole
noid to by-pass the resistance during cranking of
engine.
The
negative (—) terminal is connected to the
distributor.
The secondary (high tension) terminal
is connected by a short cable to the center terminal
in
the distributor cap.
Always
make certain the coil wires are connected to the proper coil terminals to ensure correct
coil
polarity.
Note:
The ignition coil and ballast resistor must
be of the same manufacturer. Ballast resistors
and
ignition coils of one manufacturer are interchangeable with both units of the other. H-32.
Ballast
Resistor
•
V-6 Engine.
An
ignition ballast resistor is in series with the
primary
winding of the coil. The ballast resistor
helps regulate the flow of
primary
current through
out the speed range. At low
speeds
when the con
tacts remain closed longer, the ballast heats and
increases in resistance, thereby limiting the flow of
primary
current. At higher
speeds
when the con
tacts remain closed for shorter periods of time, the ballast
cools
and thereby decreases in resistance
to allow more
primary
current and reduce the
fall
off
in
available voltage.
During
starting, the resistor compensates for the lowered battery
voltage
re
sulting from the starter load and permits an in crease in
primary
current, resulting in a higher
secondary
voltage
for starting.
The
only
test
required of the ignition ballast re
sistor is a continuity check. Characteristics of the ballast produce wide variations in resistance with
changes in ballast temperature. Therefore, check ing
voltage
drop across the ballast would be mis
leading.
Caution:
Never make a connection that connects
the ballast across the battery as this
will
burn
the ballast resistor winding.
H-33.
Spark
Plugs
Clean
and gap
spark
plugs as described in
Par.
C-4.
Inspect them for excessive burning and erosion of
electrodes, blistering of porcelain at the firing tip,
black
deposits, or fouling. These conditions indicate
that the plugs have not been operating at the cor
rect
temperature.
Note:
Prolonged idling just before removing and
checking the plugs should be avoided as it may
produce false indications.
Spark
plug operating temperatures may have been
too hot, too cold, or normal as described.
a.
At too hot a temperature, the tip of the insulator
will
show
dark
spots
and blisters after fairly short service. As high-temperature operation is con
tinued, the whole insulator
nose
will
discolor, show
ing fused and blistered
deposits
near the electrode
as well as considerable erosion and burning of the
electrodes. After extreme service, the porcelain it self may be fused, cracked, and blistered at the tip.
The
electrodes
will
show extreme erosion and
burn
ing and possibly even surface cracking.
Note:
If such cracking appears on certain plugs
after fairly short service, it may be caused by water
leaks in the associated cylinders.
b. At too cold a temperature plug operation, in
the early
stages,
will
result in a
dull
black
sooting
of the plug.
This
condition frequently is found in new vehicles during the break-in period and is no
indication of trouble in this case. As the condition progresses, black
deposits
of oil and carbon build
up on the base of the shell and on the insulator
until,
in extreme cases, the space
between
insulator
and
shell may be almost completely filled. Excessive
electrode erosion
will
seldom be found in cases of cold plug operation. These indications can be pro
duced by the use of an excessively
rich
air-fuel mixture and the carburetor should be checked if
this condition is suspected. Fouling
will
also be
caused by leaking rings or intake valve
guides
that
permit excessive oil to reach the combustion
chambers.
The use of a hotter plug
will
help
burn
away
some
of this fouling but the mechanical con dition of the
engine
should be corrected.
c. In normal temperature operation the plug
will
accumulate grayish-tan to reddish-brown
deposits
with
fairly uniform discoloration of the insulator
nose
and slight, localized electrode erosion. If the
insulator shows any blotches, blisters,
irregular
dis
coloration, etc., look for hot-plug symptoms. Too
hot or too cold plug operation may be caused by
the use of plugs of other than the specified heat
rating
but if the plugs are as specified a hotter or 187
Page 188 of 376

H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
colder plug may be desirable. However, under- or
over-heating is usually caused by factors other than the type of
spark
plugs and the cause should be determined before changing plugs. The design of the
engine
calls for plugs equivalent to Champion
J-8
for F4
engines
and
A.C.
44S or
UJ12Y
Champ
ion for the V6 engines, (as installed in production)
though any factor that consistently affects
engine
operating temperature may cause this requirement
to change. Overheating may be caused by in sufficient tightening of the plug in the head, which interferes with the flow of heat away from the firing
tip.
If this is the case, the plug gasket
will
show very
little flattening. Over-tightening, in
turn,
will
pro duce too easy a heat flow path and result in cold
plug operation.
This
will
be evident by excessive
flattening
and
deformation of the gasket.
Prevailing
temperatures, condition of the cooling system, and
air-fuel
mixture can affect the
engine
operating temperature and should be taken into consideration.
H-34.
GENERATOR
— F4
ENGINE
The
generator is an air-cooled, two-brush unit
which
cannot be adjusted to increase or decrease output. For replacement,
voltage
regulator and generator must be matched for
voltage
and capa
city,
polarity, and common source of manufacture.
Otherwise,
either a
loss
of ampere capacity or a
burned
out generator
will
result. Generators for
these
vehicles are 12-volt. Par. H-l explains the 12-volt system. Refer to the specifications at the
end of this section for information on correct generator rating for a specific model series.
The
circuit
breaker,
voltage
regulator, and current-
limiting
regulator are built into one combination
unit.
Because the regulator and battery are part
of the generator
circuit,
the output of the generator
depends upon the
state
of charge and temperature
of the battery.
With
a discharged battery, the
output
will
be high, decreasing proportionally as the battery
becomes
charged. For service informa
tion covering current regulator see Par. H-41.
H-36.
Generator
Maintenance
A
periodic inspection should be made of the charg
ing
circuit,
Fig. H-l9. The interval
between
these
checks
will
vary
depending upon type of service.
Dust,
dirt
and high speed operation are factors 10541
FIG.
H-19—CHARGING
CIRCUIT
1—
Battery
4-—Starter Switch
2—
Voltage
Regulator 5-—Charge Indicator
3—
Generator
which
contribute to increased wear of bearings
and
brushes.
Under
normal conditions a check should be made
each 6000 miles
[9.600
km.].
A
visual inspection should be made of all wiring,
to be sure there are no broken or damaged wires.
Check
all connections to be sure they are tight and
clean.
Should
the commutator be rough or worn the
armature
should be removed and the commutator
turned
and undercut. See Par. H-37.
The
brushes should slide freely in their holders.
Should
they be oil soaked or if they are worn to
less
than one-half their original length they should
be replaced. When new brushes are installed they should be sanded to provide
full
contact with the
commutator. Generators should not be checked for
output until the brushes are seated.
Brush
spring tension is important. High tension causes
rapid
brush and commutator wear while
low tension causes arcing and reduced output.
Test
the tension with a spring scale.
Check
the
specifications section at end of this section for
correct
spring tension for generator in question.
H-36.
Generator Disassembly
•
Refer to Fig. H-20:
Before beginning disassembly of the generator to
correct
electrical system malfunctions proceed with
inspection and
test
procedures as detailed in Par.
H-46
thru
H-62. If it is definitely determined that trouble exists within the generator, which necessitates dismantling, proceed as follows. Remove the two frame screws in the commutator
end plate and remove the end plate assembly. Next
pull
the armature and drive head complete
from
the generator housing. Remove the generator pulley from the armature by removing the nut
and
washer. Do not
lose
the Woodruff key when
the pulley is removed. After this, remove the drive
end head assembly which includes the oil seal and
bearing.
To remove the bearing, remove the three
screws and lockwashers in the grease retainer and remove the retainer and felt washer, after which,
remove the bearing, oil guard and felt washer.
H-37.
Armature
If
the commutator is rough or worn,
turn
it down
in
a lathe. After turning, the mica insulation be tween the
segments
should be undercut to a depth of 34* [0,8 mm.].
To
test
the armature for a ground, connect one
prod
of a
test
lamp to the core or shaft (not on
bearing
surface) and touch each commutator
seg
ment with the other prod. If the lamp lights, the
armature
segment
is grounded and the armature must be replaced.
To
test
for short in armature coils, a growler,
Fig.
H-21, is necessary. Place the armature on the growler and lay a thin steel strip on the armature
core.
The armature is then rotated slowly by hand
and
if a coil is shorted, the steel strip
will
vibrate.
Should
a coil be shorted the armature must be
replaced.
If
precision
test
equipment is available, the cus
tomary
accurate
tests
can be made in accordance 188
Page 189 of 376
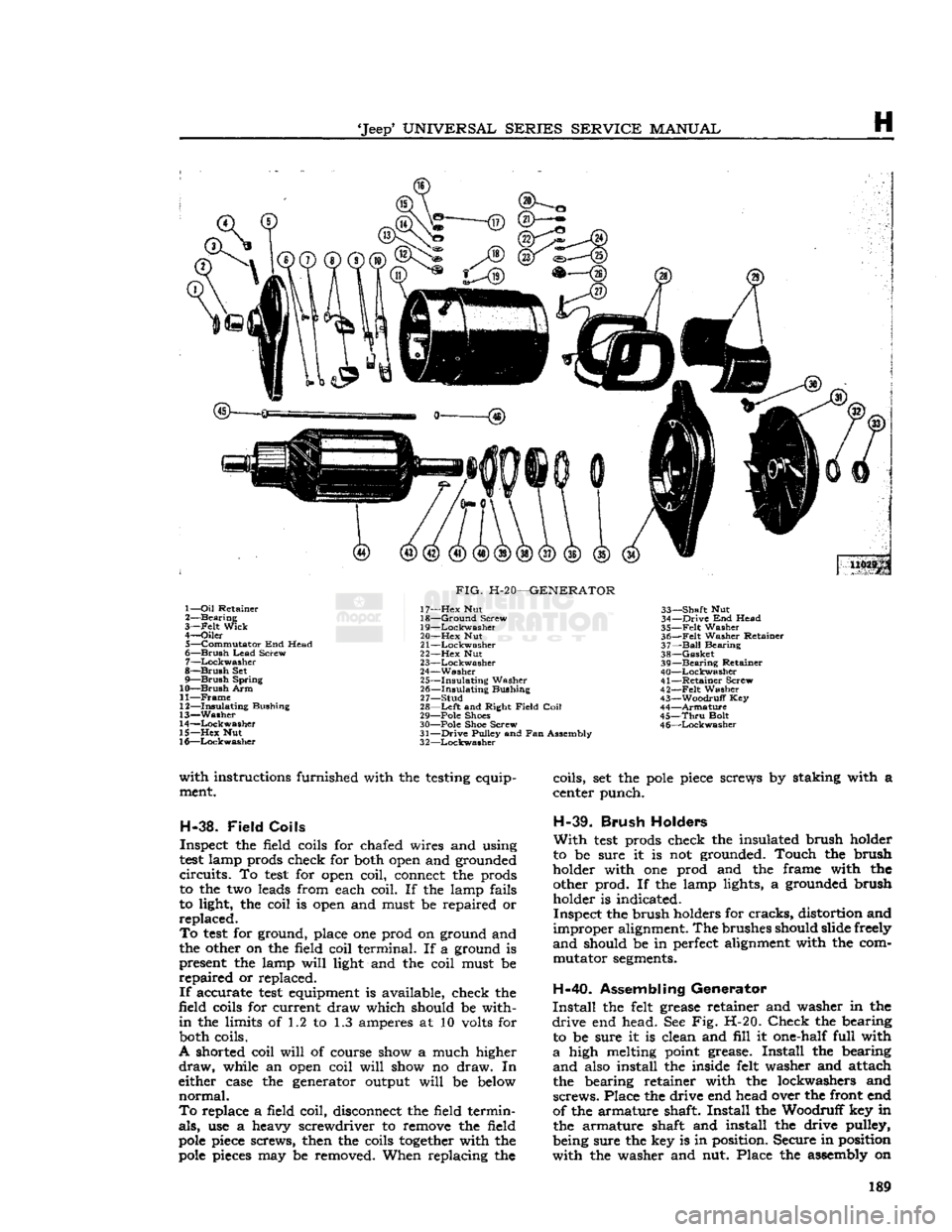
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
H
U029p 1—
Oil
Retainer
2—
Bearing
3—
-Felt
Wick
4—
Oiler
5—
Commutator
End Head
6—
Brush
Lead
Screw
7—
Lockwasher
8—
Brush
Set
9—
Brush
Spring
10—
Brush
Arm
11—
Frame
12—
Insulating
Bushing
13—
Washer
14—
Lockwasher
15—
Hex
Nut
16—
Lockwasher
FIG.
H-20—GENERATOR
17—
Hex
Nut
18—
Ground
Screw
19—
Lockwasher
20—
Hex
Nut
21
—Lockwasher
22—
Hex
Nut
23—
Lockwasher
24—
Washer
25—
Insulating
Washer
26—
Insulating
Bushing
27—
Stud
28—
Left
and Right
Field
Coil
29— Pole Shoes
30— Pole Shoe Screw
31—
Drive
Pulley and Fan Assembly
3
2—Lockwasher
33—
Shaft
Nut
34—
Drive
End Head
35—
Felt
Washer
36—
Felt
Washer Retainer
37—
Ball
Bearing
38—
Gasket
39—
Bearing
Retainer
40—
Lockwasher
41—
Retainer
Screw
42—
-Felt
Washer
43—
Woodruff
Key
44—
Armature
45—
Thru
Bolt
4
6—Lockwasher
with
instructions furnished with the testing equip ment.
H-38.
Field
Coils
Inspect the field coils for chafed wires and using
test
lamp prods check for both open and grounded
circuits.
To
test
for open coil, connect the prods
to the two leads from each coil. If the lamp fails
to light, the coil is open and must be repaired or
replaced.
To
test
for ground, place one prod on ground and
the other on the field coil terminal. If a ground is present the lamp
will
light and the coil must be
repaired
or replaced.
If
accurate
test
equipment is available, check the
field coils for current draw which should be with
in
the limits of 1.2 to 1.3 amperes at 10 volts for both coils.
A shorted coil
will
of course show a much higher
draw,
while an open coil
will
show no draw. In
either case the generator output
will
be below
normal.
To
replace a field coil, disconnect the field termin
als,
use a heavy screwdriver to remove the field
pole
piece screws, then the coils
together
with the
pole
pieces may be removed. When replacing the coils, set the
pole
piece screws by staking with a
center punch.
H-39.
Brush
Holders
With
test
prods check the insulated brush holder
to be sure it is not grounded. Touch the brush
holder with one prod and the frame with the other prod. If the lamp lights, a grounded brush holder is indicated.
Inspect the brush holders for
cracks,
distortion and
improper
alignment. The brushes should slide freely
and
should be in perfect alignment with the com mutator
segments.
H-40.
Assembling Generator
Install
the felt grease retainer and washer in the
drive
end head. See Fig. H-20.
Check
the bearing to be sure it is clean and
fill
it one-half full with
a
high melting point grease.
Install
the bearing
and
also install the inside felt washer and attach
the bearing retainer with the lockwashers and
screws.
Place the drive end head over the front end
of the armature shaft.
Install
the Woodruff key in the armature shaft and install the drive pulley,
being sure the key is in position. Secure in position
with
the washer and nut. Place the assembly on 189
Page 191 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
long as the circuit values allow the voltage to build
up to the operating voltage.
The
electromagnet of the voltage regulator unit has
a
winding of many turns of fine wire and is con
nected across the charging circuit so that the sys tem voltage controls the amount of magnetism.
The
contacts of the voltage regulator unit are con
nected in the generator field circuit so that the field
circuit
is completed through the contacts when they
are
closed and through a resistor when the contacts
are
opened.
When
the voltage rises to a predetermined value
there is sufficient magnetism created by the regu
lator
winding to
pull
the
armature
down.
This
opens
the contacts and inserts resistance in the field
cir
cuit
of the generator thus reducing the
field
current.
The
generated voltage immediately drops, which
reduces the
pull
on the
armature
to the point where
the spring closes the contacts. The output again
rises
and the cycle is repeated.
These
cycles occur at high enough frequencies to
hold the generated voltage at a constant value and
will
continue as long as the voltage of the circuit
is high enough to keep the voltage regulator unit
in
operation.
With
the addition of a current load great enough to lower the battery voltage below
the operating voltage of the unit, the contacts
will
remain
closed and the generator
will
maintain a
charging
rate as limited by its speed or the current
limiting
regulator.
Due
to the
effect
of heat on the operating
charac
teristics of regulator windings it is necessary to
compensate for the changes in coil resistance when
the regulator is operating under varying tempera
ture
conditions.
This
is accomplished through the
use of a nickel iron magnetic by-pass on the volt
age regulator unit.
This
shunt by-passes
some
of
the magnetic flux when the unit is cold and allows most of the flux to act on the armature when the
unit
is hot.
Thus
when the coil is hot and not as
efficient, the magnetic shunt reduces the amount of flux needed to vibrate the armature.
The
compensation is usually more than enough to
offset
the changes in regulator coil resistance due
to heat. The excess compensation allows the regu
lator
to operate at higher voltage under cold
operating conditions than under hot conditions.
This
is necessary as it requires a higher voltage to charge a battery with its internal resistance in
creased
by low temperatures.
H-45.
Current-Limiting
Regulator
The
function of the current-limiting regulator is to limit the output of the generator to its maxi
mum
safe output.
The
electromagnet of the current regulator unit
consists of
a
winding of heavy
wire
that is connected
in
series with the generator output. When the gen
erator
output reaches a predetermined value, the
current
in the winding produces enough magnetism
to overcome the spring tension and
pull
the
arma
ture
down.
This
opens
the contacts and inserts re
sistance in the field circuit of the generator.
With
the field current reduced by the resistance, the
generator output falls and there is no longer enough
magnetism to hold the contacts open. As soon as
the spring closes the contacts, the output rises and the cycle is repeated. These cycles occur at high
enough frequencies to limit the output to a mini
mum
fluctuation.
H-46.
Preliminary Inspection
a.
Wiring—Check
the wiring to see that it is prop
erly
connected to the generator.
b.
Generator
Performance—Make
sure the genera
tor operates correctly without the regulator in the
circuit.
Remove the armature and battery leads
from
the regulator and connect an ammeter be
tween them. Remove the field lead from the regu
lator
and while operating at idle speed touch the
field
lead
to the regulator base. Increase the speed slowly noting the charging rate.
CAUTION:
Do not increase the output above
the rated output of the generator.
If
the generator output
will
not build up inspect
the wiring harness for shorts and
opens
and remove the generator for an overhaul. To check the genera
tor circuit when a suitable ammeter is unavailable,
Fig.
H-19, disconnect the armature cable at the
regulator.
Connect one lead of
a
12v
test
lamp to the regulator terminal marked "armature" and with
the engine running, ground the other lead. Should
the
test
light
fail
to
burn
there is a fault either in the generator or regulator. To localize the fault, discon
nect both the
"Field"
and
"Armature"
cables at the generator. Connect a wire from the
"Field"
ter
minal
to ground and use a 60 watt, 110 volt
test
lamp
to ground the
"Armature"
terminal. If the
generator is charging satisfactorily the
test
lamp
will
glow
at approximately 1500 rpm. engine speed
and
the fault
will
be definitely localized in the
regulator.
c.
Incorrect Regulator—Make sui he regulator
is the correct type for use with the generator.
d.
Battery—Check
the specific gravity and termi
nal
voltage of the battery. If the \ ttery is not up
to specifications substitute temporarily
for
test
pur
poses
a fully charged battery of the same type and
capacity.
e. High Resistance Connections—Inspect the
wir
ing between the generator, regulator and battery for broken wires and high resistance connections.
Pay
special attention to the ground connections at
all
three units. Connect a reliable ammeter with 1-ampere graduations in series with the regulator
B-terminal
and the lead removed from this
terminal.
Run
the generator at a medium speed and
turn
on the lights or accessories until the ammeter shows a 10-ampere charging rate. At this charging rate
measure the voltage drop between the following
points using an accurate voltmeter graduated in
,1-volt divisions. The voltmeter should not show
a
reading above the maximum noted.
Generator
"A" terminal to regulator
"A"
terminal
—.1-volt maximum.
Generator
"F"
terminal to regulator
"F"
terminal
—.05-volt maximum.
Battery
terminal to regulator "B" terminal— .1-volt maximum.
Regulator
ground screw to generator frame— .03-volt maximum. 191
Page 193 of 376

'Jeep1
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
will
cause the battery to gas excessively and
will
shorten the life of the ignition contacts and, in
general,
will
have a detrimental
effect
on all con
nected load.
Connect
an ammeter in series with the regulator
"B"
terminal and the lead removed from the termi
nal.
Run the generator at a medium speed and per
form
the following operation. After each
test
is
completed reconnect whatever leads have been opened.
H-51.
Test One
Disconnect the field lead at the generator.
a.
Output drops to zero—shorted field circuit in regulator or in wiring harness. See
test
2.
b.
Output
does
not drop—shorted field circuit in
generator. Inspect generator.
H-52.
Test Two
Disconnect the field lead at the regulator.
a.
Output drops to zero—shorted field in regulator.
See
test
3.
b.
Output
does
not drop—shorted wiring harness.
Repair
or replace wiring harness.
H-53.
Test
Three
Remove the regulator cover and hold the
voltage
regulator contacts open.
a.
Output drops to zero—regulator contacts stick
ing,
regulator out of adjustment, or regulator in operative.
Check
operation
(test
5), check for high
resistance
(test
4), and clean contacts per instruc
tions in Par. H-56.
b.
Output
does
not drop—shorted field circuit in
the regulator.
Clean
the regulator contacts and in spect the regulator visually for incorrect wiring be
tween units and shorted leads.
H-54.
Test
Four
Operate
the units at 10 amperes output and meas
ure
the
voltage
drop from the regulator base to
the generator frame.
a.
Voltage reading below .03 volts—ground
cir
cuit
is satisfactory. See
test
5.
b.
Voltage reading above .03 volts—Inspect ground
circuit
for poor connections and eliminate the high
resistance. See
test
5.
H-56.
Test
Five
Connect
a headphone from the regulator field ter
minal
to the base and hold the current regulator
contacts closed.
a.
A steady beat is heard—voltage regulator oper
ating.
Reset regulator as in the operation
test,
Par.
H-47.
b.
An unsteady beat is heard—dirty or sticking
contacts.
Clean
contacts per instructions in Par.
H-56.
c.
No beat is heard—inoperative
voltage
regulator
unit.
Adjust regulator operation as in the operation
test.
If the regulator cannot be adjusted within
limits,
remove for overhaul.
H-56.
Cleaning of Contacts
Clean
the
voltage
regulator contacts with a #6
American
Swiss cut equalling file.
File
lengthwise
and
parallel to the armature and then clean the
contacts with clean linen tape.
First
draw a piece
of tape that has been wet with carbon tetrachlor
ide
between
the contacts then follow with dry tape. Reset the regulator operation as in the oper
ation
test,
Par. H-47.
H-57.
Low Battery and a Low or No Charging Rate
Check
all wiring for
loose
connections, frayed in
sulation and high resistance connections and cor
rect
any fault.
Make
sure the generator operates correctly with
out the regulator in the
circuit.
Remove the "A"
and
"B" leads from the regulator and connect an
ammeter
between
them. Remove the field lead from
the regulator and while operating at idle speed
touch the field lead to the regulator base. Increase
the speed slowly noting the charging rate. Do not
increase
the output above the rated output of the generator. If the generator output
will
not build
up,
inspect the wiring harness for shorts and
opens
and
remove the generator for an overhaul.
Connect
an ammeter
between
the battery lead and
the regulator
"B"
terminal. Connect the field lead to the regulator "F" terminal and connect the
armature
lead to the regulator
"A"
terminal.
Con
nect a voltmeter from the regulator
"A"
terminal to
the regulator base. Operate the generator at a medium speed and perform the following
tests:
H-58.
Test Six
Read
the voltmeter.
a.
Voltage builds up—open series
circuit.
See
test
7.
b.
Voltage
does
not build up—regulator out of ad
justment, field circuit open, grounded series
circuit.
See
test
8.
H-59.
Test Seven
Remove the regulator cover and with the generator
operating at a medium speed hold the circuit
breaker
contacts closed.
a.
Ammeter shows no charge—open
circuit
breaker
shunt winding, incorrect setting of circuit breaker,
or
dirty contacts.
Clean
contacts and reset circuit
breaker
as in
Par.
H-47d. If the circuit breaker
can
not be set, the shunt coil is open and the regulator
should be removed for overhaul.
b.
No generator output—clean the circuit breaker
contacts and try the
test
again. If there is
still
no
charge the series windings are open and the regu
lator
should be removed for overhaul.
H-60.
Test
Eight
Run
the generator at idle speed and momentarily
connect a jumper from the
F-terminal
to the regu
lator
base.
a.
Voltage builds up—open field circuit or regula
tor out of adjustment. See
test
9.
b.
Voltage
does
not build up—grounded series
cir
cuit.
Remove regulator for overhaul. 193
Page 195 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
no soldering or unsoldering of leads; two complete
rectifying
diode assemblies
which
eliminate the need
for removing and replacing individual diodes; a
corpplete isolation diode assembly; and a rotor
assembly complete with shaft,
pole
pieces, field
coil,
and slip rings.
The
transistorized
voltage
regulator is an electronic
switching device. It
senses
the
voltage
appearing
at the auxiliary terminal of the alternator and
supplies the necessary field current for maintaining
the system
voltage
at the output terminal. The
output current is determined by the battery electri
cal
load; such as headlights, heater, etc.
The
transistorized
voltage
regulator is a sealed
unit,
has no adjustments, and must be replaced
as a complete unit.
H-64. ALTERNATOR
PRECAUTIONS
The
following precautions must be observed to
prevent damage to the alternator and regulator.
a.
Never reverse battery connections. Always
check
the battery polarity with a voltmeter before
any
connections are made to be sure that all con
nections correspond to the battery ground polarity of the vehicle.
b.
Booster batteries for starting must be properly
connected. Make sure that the negative cable of
the booster battery is connected to the negative
terminal
of the battery in the vehicle. The positive
cable of the booster battery should be connected
to the positive terminal of the battery in the
vehicle.
c.
Disconnect the battery cables before using a fast charger.
d.
Never use a fast charger as a booster for
starting
the vehicle.
e.
Never disconnect the
voltage
regulator while
the
engine
is running.
f.
Do not ground the alternator output terminal.
g.
Do not operate the alternator on an open
circuit
with
the field energized.
h.
Do not attempt to polarize an alternator.
These
precautions are stated here as an aid to
service
personnel. They are also restated at appro
priate
places in the
text
of this section of the
manual.
H-65. ALTERNATOR
CHARGING
SYSTEM SERVICE
Important:
All alternator
tests
for the 35, 40 and
55 amp alternator are the same, however, there is a
difference
between
the location of the various ter
minals
and field current specifications. The field
current
of the 35 amp alternator should be 1.7 to 2.3 amps, 40 and 55 amp alternators should be 1.8
to 2.4 amps, with
full
battery
voltage
applied to
the filed coil. Disassembly and assembly procedures
are
the same for all three alternators.
Terminal
locations and wire harness color
codes
for the 35,
40 and 55 amp alternator are shown in Fig. H-38.
H-66.
Service Diagnosis
In
diagnosing a suspected malfunction of the
alternator
charging system, consideration must
be given to the complete electrical power plant of the vehicle; including the alternator, regulator,
ignition switch, charge indicator lamp, battery,
and
all associated wiring. If it is suspected that the
alternator
is not fully charging the battery and
fulfilling
the electrical requirements of the electrical
system, several checks should be made before
checking
the alternator itself:
Note:
Whenever service is required in connection
with
an alternator problem, the first
step
should be to verify that the wiring harness hook-up is correct
as indicated in Fig. H-38.
a.
Test the condition of the battery and
state
of
charge
(Par. H-2).
If the battery is not fully charged
and
in
good
condition, use a replacement battery
for making alternator system
tests.
Caution:
Make certain that the negative battery
post
is connected to ground when making the
battery installation. Serious damage to the alter
nator
can result if battery polarity is reversed.
b.
Check
fan belt for proper tension (Par.
C-27).
Caution:
To increase belt tension, apply pressure
to alternator front housing only as permanent damage can result if pressure is applied to
rear
housing.
H-67.
Alternator In Vehicle Tests
The
following
tests
are made with the alternator
in
the vehicle with output and regulator connec
tions maintained to the alternator except as noted
in
Fig. H-27 and H-28. The field plug and
voltage
regulator are disconnected for
these
tests.
The
tests
are given in proper order and detail in the
following paragraphs.
a.
Isolation Diode Test: To determine if the isola
tion diode is open or shorted, refer to Par. H-69.
b.
Alternator Output Test: To isolate the trouble
to the alternator or regulator, refer to Par. H-70.
c.
Alternator
Field
Circuit
Test: To determine the condition of the field
circuit
(brushes and rotor),
refer
to Par. H-73.
d.
Brush
Insulation
and Continuity
Test:
To deter
mine the condition of the
brush,
refer to
Par.
H-75.
e.
Rotor In-Vehicle Test: To determine whether
the rotor coil is open or shorted, refer to
Par.
H-73.
f. Any further
tests
must be conducted with the
alternator
removed and disassembled. When this
is done, the condition of the rotor, the rectifying
and
isolation diodes, and the stator can be further
tested.
A
commercial alternator tester Sun
Electric
Model
VAT-20
or equivalent can be used to make all
necessary
tests
on the alternator system. If a com
mercial
tester is used, follow the recommended
testing procedure outlined by the tester manu
facturer.
If
a commercial tester is not available, follow the
testing procedure as outlined in this manual.
H-68.
Test Equipment
a.
Volt Ampere Tester such as Sun
Electric
Model
VAT-20
or equivalent with meter ranges as shown
in
the following list can be used. 195
Page 197 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
H-72.
Removal
and
Installation
of
Voltage Regulator
The
transistorized
voltage
regulator is a sealed unit.
It
cannot be disassembled or adjusted. If found to
be defective in any way, it must be replaced as
a
unit.
The
transistorized
voltage
regulator is mounted on
the fender dust shield by three mounting screws.
Wiring
connections to the charging circuit are made through a three-prong connector.
To
remove the regulator, disconnect the three
-
prong connector and remove the three mounting
screws.
Installation of the regulator is the reverse
of the removal. (Refer to Fig. H-26.)
FIG.
H-26—VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
H-73.
Alternator Field Circuit Test
Voltage
Test — Refer to Fig. H-27.
a.
With the ignition key on and
engine
not
run
ning,
the correct
voltage
at the auxiliary terminal is
approximately 1.5 volts. If the
voltage
at auxiliary
terminal
is higher than 2 volts, field circuit is defective — check brushes.
GREEN
13404
FIG.
H-27—FIELD
CIRCUIT TEST—VOLTAGE If
voltage
reads zero volts at auxiliary terminal,
check charge indicator lamp and associated circuit.
If
this
voltage
is not correct, continue with the fol
lowing
test
described in paragraph b.
Amperage Test — Refer to Fig. H-28. b.
This
test
evaluates complete field circuit, inde
pendent of
voltage
regulator.
Circuit
is through
brushes, slip rings, rotor to ground. With ignition switch off, current should be 2 to 2.5 amps. If
less
than
this, check brushes and slip rings. It is de
sirable
to use a field rheostat in series with meter
for protection of the meter. If field is shorted, ex
cessive current
will
flow through meter and dam
age may result.
GREEN
FIELD
WIRE
DISCONNECTED
13405
FIG.
H-28—FIELD
CIRCUIT TEST- AMPERAGE
DRAW
H-74.
Brush Removal
and
Inspection
Refer
to Fig. H-29.
The
brushes can be removed and inspected while
the alternator is in the vehicle.
a.
Disconnect the plug to the field terminal. b. Remove the two screws and brush cover.
c. Remove brushes.
d.
Inspect brushes for excessive wear and proper
tension. The brushes can be installed by reversing
the above procedure.
H-75.
Brush Insulation
and
Continuity Test
Refer
to Fig. H-30.
a.
Connect leads of a 12-volt
test
lamp to field
FIG.
H-29—BRUSH
REMOVAL
1—
Screw
2—
Cover
3—
Brush
and
Holder
Assembly
4—
Alternator
197