2023 JEEP CHEROKEE height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 30 of 276
28GETTING TO KNOW YOUR VEHICLE
SEATS
Seats are a part of the Occupant Restraint system of the
vehicle.
MANUAL ADJUSTMENT
(FRONT SEATS) — IF EQUIPPED
Some models may be equipped with a front passenger
manual adjustment seat. The forward/rearward
adjustment bar is located at the front of the seat, near the
floor. Height and recline levers are located on the
outboard side of the seat.
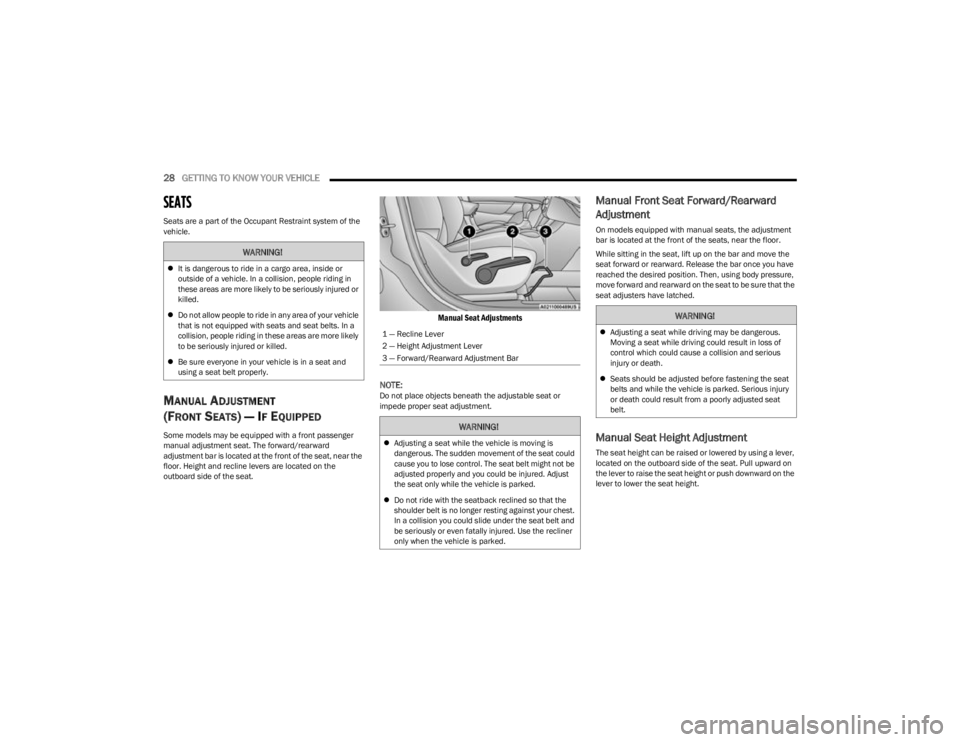
Manual Seat Adjustments
NOTE:
Do not place objects beneath the adjustable seat or
impede proper seat adjustment.
Manual Front Seat Forward/Rearward
Adjustment
On models equipped with manual seats, the adjustment
bar is located at the front of the seats, near the floor.
While sitting in the seat, lift up on the bar and move the
seat forward or rearward. Release the bar once you have
reached the desired position. Then, using body pressure,
move forward and rearward on the seat to be sure that the
seat adjusters have latched.
Manual Seat Height Adjustment
The seat height can be raised or lowered by using a lever,
located on the outboard side of the seat. Pull upward on
the lever to raise the seat height or push downward on the
lever to lower the seat height.
WARNING!
It is dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or
outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in
these areas are more likely to be seriously injured or
killed.
Do not allow people to ride in any area of your vehicle
that is not equipped with seats and seat belts. In a
collision, people riding in these areas are more likely
to be seriously injured or killed.
Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and
using a seat belt properly.
1 — Recline Lever
2 — Height Adjustment Lever
3 — Forward/Rearward Adjustment Bar
WARNING!
Adjusting a seat while the vehicle is moving is
dangerous. The sudden movement of the seat could
cause you to lose control. The seat belt might not be
adjusted properly and you could be injured. Adjust
the seat only while the vehicle is parked.
Do not ride with the seatback reclined so that the
shoulder belt is no longer resting against your chest.
In a collision you could slide under the seat belt and
be seriously or even fatally injured. Use the recliner
only when the vehicle is parked.
WARNING!
Adjusting a seat while driving may be dangerous.
Moving a seat while driving could result in loss of
control which could cause a collision and serious
injury or death.
Seats should be adjusted before fastening the seat
belts and while the vehicle is parked. Serious injury
or death could result from a poorly adjusted seat
belt.
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 28
Page 32 of 276

30GETTING TO KNOW YOUR VEHICLE
2. Fold the rear seatback completely forward.
NOTE:You may experience deformation in the seat cushion from
the seat belt buckles if the seats are left folded for an
extended period of time. This is normal and by simply
unfolding the seats, over time the seat cushion will return
to its normal shape.
TO RAISE THE REAR SEAT
NOTE:If interference from the cargo area prevents the seatback
from fully locking, you will have difficulty returning the seat
to its proper position.
Raise the seatback and lock it into place.
POWER ADJUSTMENT (FRONT SEATS) —
I
F EQUIPPED
Some models may be equipped with a power driver's seat
and/or power passenger seat. The power seat switches
are located on the outboard side of the seat near the floor,
and control the movement of the seat cushion and
seatback.
Power Seat Switches
NOTE:
Do not place objects beneath the adjustable seat or
impede proper seat adjustment.
Adjusting The Seat Forward Or Rearward
The seat can be adjusted both forward and rearward by
pushing the seat switch in the desired direction. Release
the switch when the desired position has been reached.
Adjusting The Seat Up Or Down
The height of the seats can be adjusted up or down. Pull
upward or push downward on the seat switch, the seat will
move in the direction of the switch. Release the switch
when the desired position is reached.
Tilting The Seat Up Or Down
The angle of the seat cushion can be adjusted in two
directions. Pull upward or push downward on the front of
the seat switch, the front of the seat cushion will move in
the direction of the switch. Release the switch when the
desired position has been reached.
Reclining The Seatback Forward Or
Rearward
The seatback can be reclined both forward and rearward
by using the seatback recline switch. The seatback will
move in the direction of the switch. Release the switch
when the desired position has been reached.
Power Lumbar — If Equipped
Vehicles equipped with power driver or passenger seats
may be equipped with power lumbar. The power lumbar
switch is located on the outboard side of the power seat.
WARNING!
Be certain that the seatback is securely locked into
position. If the seatback is not securely locked into
position the seat will not provide the proper stability for
child seats and/or passengers. An improperly latched
seat could cause serious injury.
1 — Seat Switch
2 — Seatback Switch
WARNING!
Do not ride with the seatback reclined so that the
shoulder belt is no longer resting against your chest. In
a collision you could slide under the seat belt, which
could result in serious injury or death.
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 30
Page 34 of 276

32GETTING TO KNOW YOUR VEHICLE
VENTILATED SEATS — IF EQUIPPED
Located in the seat cushion and seatback are fans that
draw the air from the passenger compartment and move
air through fine perforations in the seat cover to help keep
the occupant cooler in higher ambient temperatures.
Front Ventilated Seats — If Equipped
The front ventilated seat controls are located
within the climate and control screen in the
Uconnect system. The fans operate at two
speeds: HI and LO.
Press the ventilated seat button once to choose HI.
Press the ventilated seat button a second time to
choose LO.
Press the ventilated seat button a third time to turn the
ventilated seat off.
NOTE:The engine must be running for the ventilated seats to
operate.
For information on use with the Remote Start system, see
Úpage 19.
HEAD RESTRAINTS
Head restraints are designed to reduce the risk of injury by
restricting head movement in the event of a rear impact.
Head restraints should be adjusted so that the top of the
head restraint is located above the top of your ear.
NOTE:Do not reverse the head restraints (making the rear of the
head restraint face forward) in an attempt to gain addi -
tional clearance to the back of your head.
Reactive Head Restraints — Front Seats
The front driver and passenger seats are equipped with
Reactive Head Restraints (RHR). In the event of a rear
impact, the RHRs will automatically extend forward
minimizing the gap between the back of the occupant’s
head and the RHR.
The RHRs will automatically return to their normal position
following a rear impact. If the RHRs do not return to their
normal position, see an authorized dealer immediately. To raise the head restraint, pull upward on the head
restraint. To lower the head restraint, push the adjustment
button, located at the base of the head restraint, and push
downward on the head restraint.
NOTE:To remove the head restraint, raise it as far as it can go.
Then, push the release button and the adjustment button
at the base of each post while pulling the head restraint
up. Seatback angle may need to be adjusted to fully
remove the head restraint. To reinstall the head restraint,
put the head restraint posts into the holes and push
downward. Then adjust the head restraint to the appro
-
priate height.
Front Head Restraint
WARNING!
All occupants, including the driver, should not
operate a vehicle or sit in a vehicle’s seat until the
head restraints are placed in their proper positions in
order to minimize the risk of neck injury in the event
of a crash.
Head restraints should never be adjusted while the
vehicle is in motion. Driving a vehicle with the head
restraints improperly adjusted or removed could
cause serious injury or death in the event of a colli -
sion.
1 — Release Button
2 — Adjustment Button
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 32
Page 35 of 276

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR VEHICLE33
Rear Head Restraints
The rear outboard head restraints have two positions: up
and down. The center head restraint has three positions:
up, mid, and down. When the center seat is being
occupied the head restraint should be adjusted to the
occupant. When there is no occupant in the center seat,
the head restraint can be lowered for maximum visibility
for the driver.
To raise the head restraint, pull upward on the head
restraint. To lower the head restraint, push the adjustment
button, located at the base of the head restraint, and push
downward on the head restraint.
NOTE:
To remove the head restraint, raise it as far as it can go.
Then, push the release button and the adjustment
button at the base of each post while pulling the head
restraint up. To reinstall the head restraint, put the
head restraint posts into the holes and push down -
ward. Then, adjust the head restraint to the appro -
priate height.
The seatback may need to be reclined in order to fully
remove the outboard head restraints.
Outboard Head Restraint Center Head Restraint
WARNING!
A loose head restraint thrown forward in a collision or
hard stop could cause serious injury or death to occu -
pants of the vehicle. Always securely stow removed
head restraints in a location outside the occupant
compartment.
ALL the head restraints MUST be reinstalled in the
vehicle to properly protect the occupants. Follow the
reinstallation instructions prior to operating the
vehicle or occupying a seat.
Do not place items over the top of the Reactive Head
Restraint, such as coats, seat covers or portable DVD
players. These items may interfere with the operation
of the Reactive Head Restraint in the event of a colli -
sion and could result in serious injury or death.
1 — Release Button
2 — Adjustment Button
1 — Adjustment Button
2 — Release Button
WARNING!
ALL the head restraints MUST be reinstalled in the
vehicle to properly protect the occupants. Follow the
reinstallation instructions prior to operating the vehicle
or occupying a seat.
2
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 33
Page 117 of 276

STARTING AND OPERATING115
Gross Trailer Weight (GTW)
The GTW is the weight of the trailer plus the weight of all
cargo, consumables, and equipment (permanent or
temporary) loaded in or on the trailer in its “loaded and
ready for operation” condition.
The recommended way to measure GTW is to put your fully
loaded trailer on a vehicle scale. The entire weight of the
trailer must be supported by the scale.
Gross Combination Weight Rating (GCWR)
The GCWR is the total allowable weight of your vehicle and
trailer when weighed in combination.
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR)
The GAWR is the maximum capacity of the front and rear
axles. Distribute the load over the front and rear axles
evenly. Make sure that you do not exceed either front or
rear GAWR. Refer to “Vehicle Loading”
Úpage 113 for
further information.
Tongue Weight (TW)
The TW is the downward force exerted on the hitch ball by
the trailer. You must consider this as part of the load on
your vehicle.
Trailer Frontal Area
The frontal area is the maximum height multiplied by the
maximum width of the front of a trailer.
Trailer Sway Control (TSC)
The TSC can be a mechanical telescoping link that can be
installed between the hitch receiver and the trailer tongue
that typically provides adjustable friction associated with
the telescoping motion to dampen any unwanted trailer
swaying motions while traveling.
The electronic TSC (if equipped) recognizes a swaying
trailer and automatically applies individual wheel brakes
and/or reduces engine power to attempt to eliminate the
trailer sway.
Weight-Carrying Hitch
A weight-carrying hitch supports the trailer tongue weight,
just as if it were luggage located at a hitch ball or some
other connecting point of the vehicle. These kinds of
hitches are commonly used to tow small and medium
sized trailers.
Weight-Distributing Hitch
A weight-distributing hitch system works by applying
leverage through spring (load) bars. They are typically
used for heavier loads to distribute trailer tongue weight to
the tow vehicle's front axle and the trailer axle(s). When
used in accordance with the manufacturer's directions, it
provides for a more level ride, offering more consistent
steering and brake control thereby enhancing towing
safety. The addition of a friction/hydraulic sway control
also dampens sway caused by traffic and crosswinds and
contributes positively to tow vehicle and trailer stability.
Trailer sway control and a weight-distributing (load
equalizing) hitch are recommended for heavier Tongue
Weights (TW) and may be required depending on vehicle
and trailer configuration/loading to comply with Gross Axle
Weight Rating (GAWR) requirements.
WARNING!
If the Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) is 3,500 lb (1,587 kg)
or more, it is mandatory to use a weight-distributing
hitch to ensure stable handling of your vehicle. If you
use a standard weight-carrying hitch, you could lose
control of your vehicle and cause a collision.
WARNING!
It is important that you do not exceed the maximum
front or rear GAWR. A dangerous driving condition can
result if either rating is exceeded. You could lose control
of the vehicle and have a collision.
WARNING!
An improperly adjusted weight-distributing hitch
system may reduce handling, stability, braking
performance, and could result in a collision.
Weight-distributing hitch systems may not be
compatible with surge brake couplers. Consult with
your hitch and trailer manufacturer or a reputable
Recreational Vehicle dealer for additional informa -
tion.
4
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 115
Page 165 of 276

SAFETY163
Second Row Center Seat Belt Operating
Instructions — Fixed Rear Seat
(If Equipped)
The second row center seat belt may feature a seat belt
with a mini-latch plate and buckle, which allows the seat
belt to detach from the lower anchor when the seat is
folded. The mini-latch plate and regular latch plate can
then be stored out of the way in the left side trim panel for
added convenience to open up utilization of the storage
areas behind the front seats when the seat is not
occupied.
1. Remove the mini-latch plate and regular latch plate
from its stowed position in the left rear side trim
panel.
Mini-Latch Stowage
2. Grab the mini-latch plate and pull the seat belt over the seat.
Shoulder Belt Routed Through The Seat Belt Guide Loop
3. Route the shoulder belt through the seat belt guide loop on the top of the seatback near the inboard side
of the left head restraint.
Inserting Mini-Latch Plate Into Mini-Buckle
4. When the seat belt is long enough to fit, insert the mini-latch plate into the mini-buckle until you hear a
“click.”
Mini-Latch Plate Buckled
5. Sit back in seat. Slide the regular latch plate up the webbing as far as necessary to allow the seat belt to
go around your lap.
Position the shoulder belt across the shoulder and
chest with minimal, if any slack so that it is comfort -
able and not resting on your neck. The retractor will
withdraw any slack in the shoulder belt.
Misadjustment of the seat belt could reduce the
effectiveness of the safety belt in a crash.
Always make all seat belt height adjustments when
the vehicle is stationary.
WARNING!
6
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 163
Page 179 of 276

SAFETY177
Summary Of Recommendations For Restraining Children In Vehicles
Infant And Child Restraints
Safety experts recommend that children ride rear-facing in
the vehicle until they are two years old or until they reach
either the height or weight limit of their rear-facing child
restraint. Two types of child restraints can be used
rear-facing: infant carriers and convertible child seats.
The infant carrier is only used rear-facing in the vehicle. It
is recommended for children from birth until they reach
the weight or height limit of the infant carrier. Convertible
child seats can be used either rear-facing or
forward-facing in the vehicle. Convertible child seats often
have a higher weight limit in the rear-facing direction than
infant carriers do, so they can be used rear-facing by
children who have outgrown their infant carrier but are still
less than at least two years old. Children should remain
rear-facing until they reach the highest weight or height
allowed by their convertible child seat.
Older Children And Child Restraints
Children who are two years old or who have outgrown their
rear-facing convertible child seat can ride forward-facing in the vehicle. Forward-facing child seats and convertible
child seats used in the forward-facing direction are for
children who are over two years old or who have outgrown
the rear-facing weight or height limit of their rear-facing
convertible child seat. Children should remain in a
forward-facing child seat with a harness for as long as
possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by the
child seat.
All children whose weight or height is above the
forward-facing limit for the child seat should use a
belt-positioning booster seat until the vehicle’s seat belts
fit properly. If the child cannot sit with knees bent over the
vehicle’s seat cushion while the child’s back is against the
seatback, they should use a belt-positioning booster seat.
The child and belt-positioning booster seat are held in the
vehicle by the seat belt.
Child Size, Height, Weight Or Age
Recommended Type Of Child Restraint
Infants and ToddlersChildren who are two years old or younger and who have
not reached the height or weight limits of their child
restraint Either an Infant Carrier or a Convertible Child Restraint,
facing rearward in a rear seat of the vehicle
Small Children Children who are at least two years old or who have
outgrown the height or weight limit of their rear-facing child
restraint Forward-Facing Child Restraint with a five-point Harness,
facing forward in a rear seat of the vehicle
Larger Children Children who have outgrown their forward-facing child
restraint, but are too small to properly fit the vehicle’s seat
belt Belt Positioning Booster Seat and the vehicle seat belt,
seated in a rear seat of the vehicle
Children Too Large for Child Restraints Children 12 years old or younger, who have outgrown the
height or weight limit of their booster seat Vehicle Seat Belt, seated in a rear seat of the vehicle
WARNING!
Never place a rear-facing child restraint in front of an
air bag. A deploying passenger front air bag can
cause death or serious injury to a child 12 years or
younger, including a child in a rear-facing child
restraint.
Never install a rear-facing child restraint in the front
seat of a vehicle. Only use a rear-facing child
restraint in the rear seat. If the vehicle does not have
a rear seat, do not transport a rear-facing child
restraint in that vehicle.
6
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 177
Page 238 of 276

236SERVICING AND MAINTENANCE
TIRE SIZING CHART
EXAMPLE:
Example Size Designation: P215/65R15XL 95H, 215/65R15 96H, LT235/85R16C, T145/80D18 103M, 31x10.5 R15 LT
P = Passenger car tire size based on US design standards, or
"....blank...." = Passenger car tire based on European design standards, or
LT = Light truck tire based on US design standards, or
T or S = Temporary spare tire or
31 = Overall diameter in inches (in)
215, 235, 145 = Section width in millimeters (mm)
65, 85, 80 = Aspect ratio in percent (%)
Ratio of section height to section width of tire, or
10.5 = Section width in inches (in)
R = Construction code
"R" means radial construction, or
"D" means diagonal or bias construction
15, 16, 18 = Rim diameter in inches (in)
Service Description:
95 = Load Index
A numerical code associated with the maximum load a tire can carry
H = Speed Symbol
A symbol indicating the range of speeds at which a tire can carry a load corresponding to its load index under certain operating conditions
The maximum speed corresponding to the speed symbol should only be achieved under specified operating conditions (i.e., tire pressure, vehicle loading, road conditions, and
posted speed limits)
23_KL_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 236