2022 HYUNDAI KONA EV torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 11 of 548

Foreword / Electric Vehicle System Overview
1-6
Electric Vehicle (EVs)
An electric vehicle is driven using a
battery and an electric motor. While
general vehicles use an internal
combustion engine and gasoline as fuel,
electric vehicles use electrical energy
that is charged inside the high voltage
battery. As a result, electric vehicles are
eco-friendly in that they do not require
fuel and do not emit exhaust gases.
Characteristics of Electric
Vehicles (EVs)
1. EVs are using the electrical energy that is charged inside the high voltage
battery. In terms of air pollution and
greenhouse gas emissions, EVs are
cleaner than conventional vehicles.
2. A 150 kW electric drive motor mated to a reduction gearbox comprises
the vehicle drivetrain. This electric-
only powertrain significantly reduces
engine room noise and vibration while driving.
3. When decelerating or driving downhill, regenerative braking is
utilized to charge the high voltage
battery. This helps to minimize energy
loss and increases vehicle range.
4. When the state of charge (SOC) of the
battery is low, the EV battery can be
recharged through several different
charging methods. Refer to “Charging
Information” later in this section.
Information
What does regenerative braking do?
It uses an electric motor when decelerating and braking and transforms kinetic
energy to electrical energy in order to
charge the high voltage battery. (Torque
is applied in the opposite direction when
decelerating to generate braking force and
electric energy.)
Battery Information
• The vehicle is composed of a high
voltage battery that drives the motor
and air-conditioner, and an auxiliary
battery (12 V) that drives the lamps,
wipers, and audio system.
• The auxiliary battery is automatically
charged when the vehicle is in the
ready (
) mode or the high voltage
battery is being charged.
eleCTriC VeHiCle
Page 12 of 548

01
1 -7
main ComponenTs oF eleCTriC VeHiCle
Main Components of Electric
Vehicle
• On-Board Charger (OBC) : A device
that charges the high voltage battery
by converting AC power from a
charging station to DC power. Inverter
: A device that transforms direct
current (DC) from the high voltage
battery into alternating current (AC)
to supply power to the electric motor
and transforms AC back into DC when
available to charge the high voltage
battery.
• LDC : An LDC is a Low Voltage DC-to-
DC converter that transforms power
from the high voltage battery to the
low voltage battery (12V) in order
to supply electrical power to the
vehicle to operate the lights, wipers,
multimedia, etc.
• Electric Motor : A device that
converts electrical energy from the
high voltage battery into mechanical
energy which is then transferred as
rotational torque to the wheels in
order to drive the vehicle.
• Reduction gear : Delivers rotational
force of the motor to the tires at
appropriate speeds and torque.
• EV Battery (Lithium-ion) : On board
high voltage storage device with a
capacity up to 64 kWh
à OBC : On-Board Charger
à LDC : Low Voltage DC-DC Converter
WARNING
• Do not intentionally remove
or disassemble high voltage
components and high voltage
battery connectors and wires. Also,
be careful not to damage high
voltage components and the high
voltage battery. It may cause serious
injury and significantly impact the
performance and durability of the
vehicle.
• When inspection and maintenance
is required for high voltage
components and the high voltage
battery, we recommend that you
contact an authorized HYUNDAI
dealer.
High Voltage Battery
(lithium-ion polymer)
• The charge amount of the high
voltage battery may gradually
decrease when the vehicle is not
being driven.
• The battery capacity of the high
voltage battery may decrease when
the vehicle is stored in high/low
temperatures.
• Electric range may vary depending
on the driving conditions, even if the
charge amount is the same. The high
voltage battery may expend more
energy when driving at high speed or
uphill. These actions may reduce the
vehicle electric range.
• The high voltage battery is used when
using the air-conditioner / heater. This
may reduce the vehicle range. Make
sure to set moderate temperatures
when using the air-conditioner/heater.
• Natural degradation may occur with
the high voltage battery depending
on the number of years the vehicle
is used. This may reduce the vehicle
range.
Page 72 of 548

02
2-7
DiMensions
Itemsmm (in)
Overall length 4205 (165.6)
Overall width 1800 (70.9)
Overall height 1555 (61.2) / 1570 (61.8) * 1
Front tread 1564 (61.6)
Rear tread 1575 (62.0)
Wheelbase 2600 (102.4)
*1 : with roof rack
eLectric VeHicLe speciFications
Items Specifications
Motor Max. output 150 kW
Max. torque 395 Nm
Battery
(Lithium-ion Polymer) Capacity 64 kWh
Power output 170 kW
Voltage 356 V
Charger (OBC) Max. Output 7.2 kW
OBC : On-Board Battery Chargers
Page 74 of 548
02
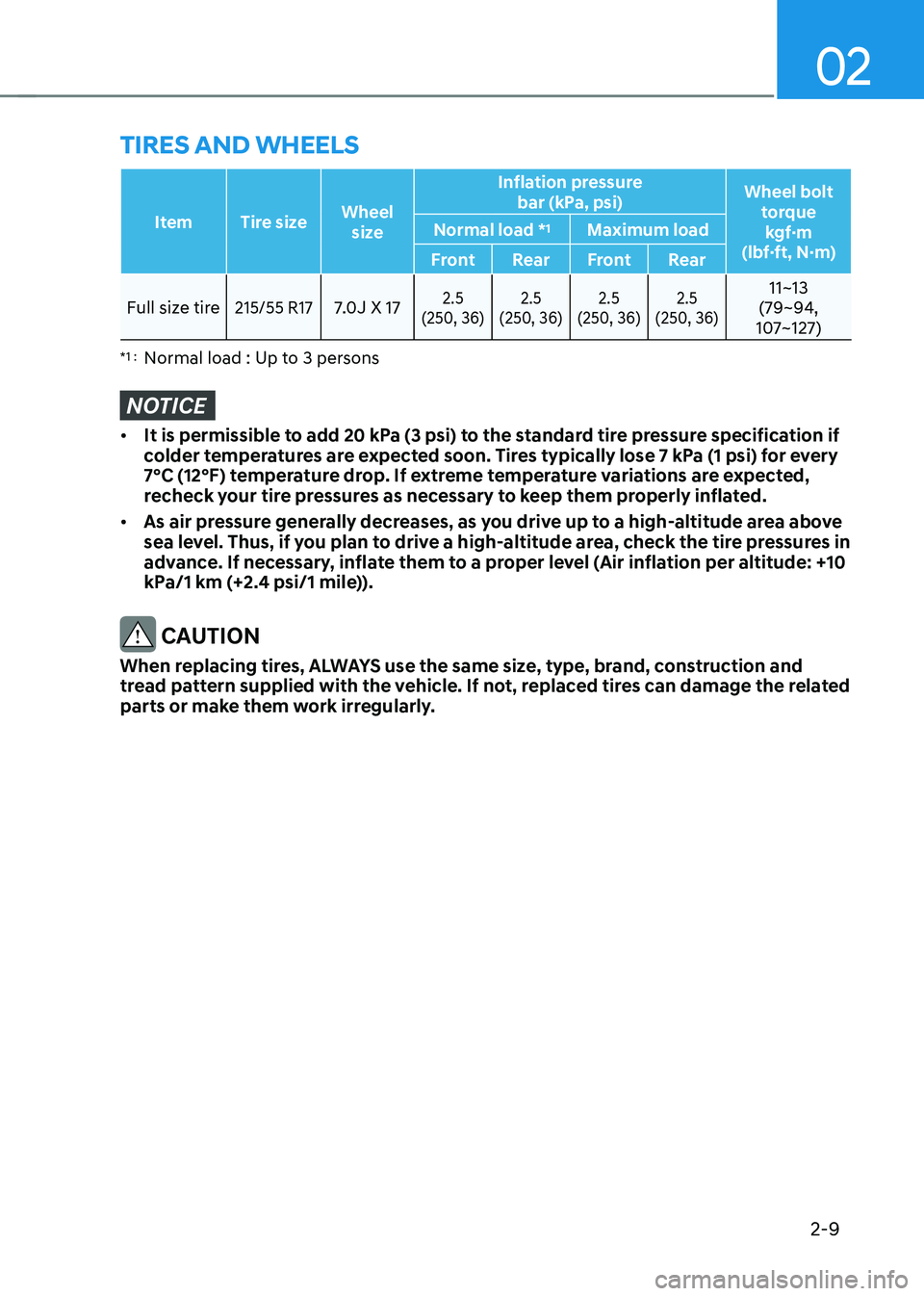
2-9
Item Tire sizeWheel
size Inflation pressure
bar (kPa, psi) Wheel bolt
torquekgf·m
(lbf·ft, N·m)
Normal load *
1
Maximum load
Front RearFront Rear
Full size tire215/55 R177.0J X 172.5
(250, 36) 2.5
(250, 36) 2.5
(250, 36) 2.5
(250, 36)11~13
(79~94,
107~127)
*1 : Normal load : Up to 3 persons
NOTICE
• It is permissible to add 20 kPa (3 psi) to the standard tire pressure specification if
colder temperatures are expected soon. Tires typically lose 7 kPa (1 psi) for every
7°C (12°F) temperature drop. If extreme temperature variations are expected,
recheck your tire pressures as necessary to keep them properly inflated.
• As air pressure generally decreases, as you drive up to a high-altitude area above
sea level. Thus, if you plan to drive a high-altitude area, check the tire pressures in
advance. If necessary, inflate them to a proper level (Air inflation per altitude: +10
kPa/1 km (+2.4 psi/1 mile)).
CAUTION
When replacing tires, ALWAYS use the same size, type, brand, construction and
tread pattern supplied with the vehicle. If not, replaced tires can damage the related
parts or make them work irregularly.
tires anD wHeeLs
Page 315 of 548

06
6-35
NOTICE
Driving with wheels and tires with
different sizes may cause ESC to
malfunction. Before replacing tires,
make sure all four tires and wheels are
the same size. Never drive the vehicle
with different sized wheels and tires
installed. ESC OFF usage
When Driving
The ESC OFF mode should only be used
briefly to help free the vehicle if stuck in
snow or mud, by temporarily stopping
operation of ESC, to maintain wheel
torque.
To turn ESC off while driving, press the
ESC OFF button while driving on a flat
road surface.
NOTICE
• Do not allow wheel(s) of one axle to
spin excessively while the ESC, ABS,
and parking brake warning lights
are displayed. The repairs would not
be covered by the vehicle warranty.
Reduce vehicle power and do not
spin the wheel(s) excessively while
these lights are displayed.
• When operating the vehicle
on a dynamometer, make sure
ESC is turned off (ESC OFF light
illuminated).
Information
Turning ESC off does not affect ABS or standard brake system operation.
Vehicle Stability Management
(VSM)
Vehicle Stability Management (VSM)
is a function of the Electronic Stability
Control (ESC). It helps ensure the
vehicle stays stable when accelerating
or braking suddenly on wet, slippery
and rough roads where traction over the
four tires can suddenly become uneven.
WARNING
Take the following precautions when
using Vehicle Stability Management
(VSM): • ALWAYS check the speed and the
distance to the vehicle ahead. VSM
is not a substitute for safe driving
practices.
• Never drive too fast for the road
conditions. VSM will not prevent
accidents. Excessive speed in bad
weather, on slippery and uneven
roads can result in severe accidents.
VSM operation
VSM ON condition
VSM operates when: • Electronic Stability Control (ESC) is on.
• Vehicle speed is approximately under
150 km/h (93 mph) when the vehicle is
braking on rough roads.
When operating
When you apply your brakes under
conditions which may activate ESC, you
may hear sounds from the brakes, or feel
a corresponding sensation in the brake
pedal. This is normal and it means your
VSM is active.
Page 485 of 548

09
9-9
EXPLANATION OF SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE ITEMS
Cooling system
Check the cooling system parts, such
as radiator, coolant reservoir, hoses and
connections for leakage and damage.
Replace any damaged parts.
Coolant
The coolant should be changed at the
intervals specified in the maintenance schedule.
Reduction gear fluid
The reduction gear fluid should be
inspected according to the intervals
specified in the maintenance schedule.
Brake hoses and lines
Visually check for proper installation,
chafing, cracks, deterioration and any
leakage. Replace any deteriorated or
damaged parts immediately.
Brake fluid
Check the brake fluid level in the brake
fluid reservoir. The level should be
between “MIN” and “MAX” marks on the
side of the reservoir. Use only hydraulic
brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 or DOT 4
specification.
Brake pads, calipers and rotors
Check the pads for excessive wear, discs
for run out and wear, and calipers for
fluid leakage.
For more information on checking the
pads or lining wear limit, refer to the
HYUNDAI web site.
(http://service.hyundai-motor.com)
Suspension mounting bolts
Check the suspension connections for
looseness or damage. Retighten to the
specified torque.
Steering gear box, linkage &
boots/lower arm ball joint
With the vehicle stopped, check for
excessive free-play in the steering wheel.
Check the linkage for bends or damage.
Check the dust boots and ball joints
for deterioration, cracks, or damage.
Replace any damaged parts.
Drive shafts and boots
Check the drive shafts, boots and clamps
for cracks, deterioration, or damage.
Replace any damaged parts and, if
necessary, repack the grease.
Air conditioning refrigerant/
compressor
Check the air conditioning lines and
connections for leakage and damage.
Page 498 of 548
Maintenance
9-22
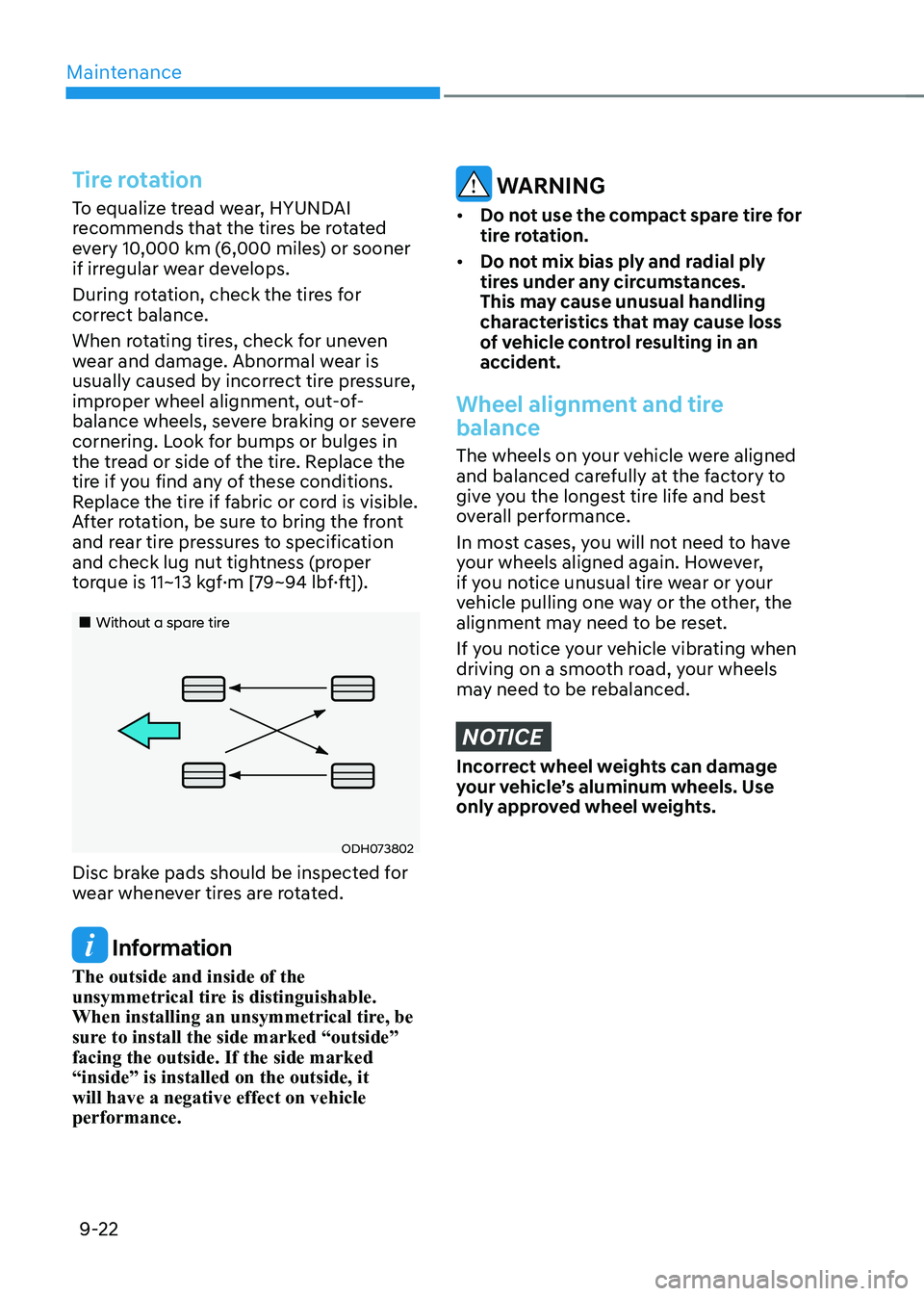
Tire rotation
To equalize tread wear, HYUNDAI
recommends that the tires be rotated
every 10,000 km (6,000 miles) or sooner
if irregular wear develops.
During rotation, check the tires for
correct balance.
When rotating tires, check for uneven
wear and damage. Abnormal wear is
usually caused by incorrect tire pressure,
improper wheel alignment, out-of-
balance wheels, severe braking or severe
cornering. Look for bumps or bulges in
the tread or side of the tire. Replace the
tire if you find any of these conditions.
Replace the tire if fabric or cord is visible.
After rotation, be sure to bring the front
and rear tire pressures to specification
and check lug nut tightness (proper
torque is 11~13 kgf·m [79~94 lbf·ft]).
„„Without a spare tire
ODH073802
Disc brake pads should be inspected for
wear whenever tires are rotated.
Information
The outside and inside of the
unsymmetrical tire is distinguishable.
When installing an unsymmetrical tire, be
sure to install the side marked “outside” facing the outside. If the side marked “inside” is installed on the outside, it will have a negative effect on vehicle performance.
WARNING
• Do not use the compact spare tire for
tire rotation.
• Do not mix bias ply and radial ply
tires under any circumstances.
This may cause unusual handling
characteristics that may cause loss
of vehicle control resulting in an
accident.
Wheel alignment and tire
balance
The wheels on your vehicle were aligned
and balanced carefully at the factory to
give you the longest tire life and best
overall performance.
In most cases, you will not need to have
your wheels aligned again. However,
if you notice unusual tire wear or your
vehicle pulling one way or the other, the
alignment may need to be reset.
If you notice your vehicle vibrating when
driving on a smooth road, your wheels
may need to be rebalanced.
NOTICE
Incorrect wheel weights can damage
your vehicle’s aluminum wheels. Use
only approved wheel weights.