2020 LINCOLN CONTINENTAL inflation pressure
[x] Cancel search: inflation pressurePage 45 of 609

Note:
The rear inflatable seatbelts are
compatible with most infant and child safety
car seats and belt positioning booster seats
when properly installed. This is because they
are designed to fill with a cooled gas at a
lower pressure and at a slower rate than
traditional airbags. After inflation, the
shoulder portion of the seatbelt remains cool
to the touch.
The rear inflatable seatbelt consists of the
following:
• An inflatable bag in the shoulder seatbelt
webbing.
• Lap seatbelt webbing with automatic
locking mode.
• The same warning light, electronic
control and diagnostic unit as used for
the front seatbelts.
• Impact sensors in various parts of the
vehicle. How does the rear inflatable seatbelt
system work? WARNING: If a supplementary
restraint system component has deployed,
it will not function again. Have the system
and associated components inspected as
soon as possible. Failure to follow this
instruction could result in personal injury
or death.
The rear inflatable seatbelts function like
standard restraints in everyday usage. During a crash of sufficient force, the
inflatable belt inflates from inside the
webbing.
The fully inflated belt's increased diameter
more effectively holds the occupant in the
appropriate seating position, and spreads
crash forces over more area of the body than
regular seatbelts. This helps reduce pressure
on the chest and helps control head and
neck motion for passengers.
42
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing SeatbeltsE146364 E146365
Page 195 of 609

9. Fully close the fuel filler door.
Note:
The message may not immediately
reset. If the message continues to appear
and a warning lamp illuminates, have your
vehicle checked as soon as possible.
FUEL CONSUMPTION
Advertised Capacity
The advertised capacity is the maximum
amount of fuel that you can add to the fuel
tank after running out of fuel. Included in the
advertised capacity is an empty reserve. The
empty reserve is an unspecified amount of
fuel that remains in the fuel tank when the
fuel gauge indicates empty.
Note: The amount of fuel in the empty
reserve varies and should not be relied upon
to increase driving range.
Fuel Economy
Your vehicle calculates fuel economy figures
through the trip computer average fuel
function. See General Information (page
117). The first 1,000 mi (1,500 km) of driving is the
break-in period of the engine. A more
accurate measurement is obtained after
2,000 mi (3,000 km)
.
Impacting Fuel Economy
• Incorrect tire inflation pressures.
• Fully loading your vehicle.
• Carrying unnecessary weight.
• Adding certain accessories to your
vehicle such as bug deflectors, rollbars
or light bars, running boards and ski
racks.
• Using fuel blended with alcohol.
See
Fuel Quality (page 187).
• Fuel economy may decrease with lower
temperatures.
• Fuel economy may decrease when
driving short distances.
• You may get better fuel economy when
driving on flat terrain than when driving
on hilly terrain.
192
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Fuel and Refueling
Page 259 of 609

Why is the feature not available (line markings are gray) when I can s\
ee the lane markings on the road?
Transitioning between no lane markings to lane markings or vice versa.
There is standing water on the road.
Faint lane markings, for example partial yellow lane markings on concret\
e roads.
Lane width is too narrow or too wide.
The camera has not been calibrated after a windshield replacement.
Driving on tight roads or on uneven roads. Why does the vehicle not come back toward the middle of the lane, as expected, in the Aid or Aid + Alert mode?
High cross winds are present.
There is a large road crown.
Rough roads, grooves or shoulder drop-offs.
Heavy uneven loading of the vehicle or improper tire inflation pressure.
The tires have been changed, or the suspension has been modified.
256
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Driving Aids
Page 353 of 609
Fuel system
•
Fill the fuel tank with high-quality fuel
until the first automatic shutoff of the fuel
pump nozzle.
Cooling system
• Protect against freezing temperatures.
• When removing your vehicle from
storage, check coolant fluid level.
Confirm that there are no cooling system
leaks and that fluid is at the
recommended level.
Disconnecting Your 12 Volt Battery
• Check and recharge as necessary. Keep
connections clean.
• If storing your vehicle for more than 30
days without recharging the battery, we
recommend that you disconnect the
battery cables to maintain battery charge
for quick starting.
Note: It is necessary to reset memory
features if you disconnect the battery cables. Brakes
•
Make sure the brakes and parking brake
release fully.
Tires
• Maintain recommended air pressure.
Miscellaneous
• Make sure all linkages, cables, levers and
pins under your vehicle are covered with
grease to prevent rust.
• Move vehicles at least 25 ft (7.5 m) every
15 days to lubricate working parts and
prevent corrosion.
Removing Vehicle From Storage
When your vehicle is ready to come out of
storage, do the following:
• Wash your vehicle to remove any dirt or
grease film build-up on window surfaces.
• Check windshield wipers for any
deterioration. •
Check under the hood for any foreign
material that may have collected during
storage such as mice or squirrel nests.
• Check the exhaust for any foreign
material that may have collected during
storage.
• Check tire pressures and set tire inflation
per the Tire Label.
• Check brake pedal operation. Drive your
vehicle 15 ft (4.5 m) back and forth to
remove rust build-up.
• Check fluid levels (including coolant, oil
and gas) to make sure there are no leaks,
and fluids are at recommended levels.
• If you remove the battery, clean the
battery cable ends and check for
damage.
Contact an authorized dealer if you have any
concerns or issues.
350
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Vehicle Care
Page 355 of 609

GENERAL INFORMATION
The recommended tire inflation pressures
are on the tire information label on the driver
side B-pillar.
Check and set the tire pressure at the
ambient temperature in which you are
intending to drive your vehicle and when the
tires are cold. See Technical Specifications
(page 379).
Note: Check your tire pressures regularly to
optimize fuel economy.
Only use approved wheel and tire sizes.
Using other sizes could damage your vehicle
and could make the National Type Approval
invalid.
Installation of any tires that are not the
original equipment tire size can cause the
speedometer to display incorrect vehicle
speed. TIRE CARE
Important Information About Low-
Profile Tires
If your vehicle is equipped with
245/40R20 tires, they are low-profile
tires. These tires and wheels are
designed to give your vehicle a sport
appearance. With low-profile tires, you
may notice an increase in road noise
and faster tire wear, depending on road
conditions and driving styles. Due to
their design, low-profile tires and wheels
are more prone to road damage from
potholes, rough or unpaved roads, car
wash rails and curb contact than
standard tires and wheels.
Note:
Your vehicle's warranty does not
cover these types of damages. Extra
caution should be taken when operating
on rough roads to avoid impacts that
could cause wheel and tire damage. Information About Uniform Tire Quality
Grading
Tire Quality Grades apply to new
pneumatic passenger car tires. The
Quality grades can be found where
applicable on the tire sidewall between
tread shoulder and maximum section
width. For example:
Treadwear 200
Traction AA Temperature A.
These Tire Quality Grades are
determined by standards that the United
States Department of Transportation has
set.
352
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Wheels and TiresE142542
Page 357 of 609

passenger car tires must meet under the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 139. Grades B and A represent
higher levels of performance on the
laboratory test wheel than the minimum
required by law.
Glossary of Tire Terminology
•
Tire label: A label showing the
original equipment tire sizes,
recommended inflation pressure and
the maximum weight the vehicle can
carry.
• Tire Identification Number:
A
number on the sidewall of each tire
providing information about the tire
brand and manufacturing plant, tire
size and date of manufacture. Also
referred to as DOT code.
• Inflation pressure: A measure of the
amount of air in a tire. •
Standard load:
A class of P-metric or
Metric tires designed to carry a
maximum load at set pressure. For
example: For P-metric tires
35 psi
(2.4 bar) and for Metric tires 36 psi
(2.5 bar). Increasing the inflation
pressure beyond this pressure will
not increase the tire ’s load carrying
capability.
• Extra load:
A class of P-metric or
Metric tires designed to carry a
heavier maximum load at
42 psi
(2.9 bar). Increasing the inflation
pressure beyond this pressure will
not increase the tire ’s load carrying
capability.
• kPa:
Kilopascal, a metric unit of air
pressure.
• PSI:
Pounds per square inch, a
standard unit of air pressure.
• Cold tire pressure:
The tire pressure
when the vehicle has been stationary
and out of direct sunlight for an hour
or more and prior to the vehicle
being driven for 1 mile (1.6 km). •
Recommended inflation pressure:
The cold inflation pressure found on
the Safety Compliance Certification
Label (affixed to either the door
hinge pillar, door-latch post, or the
door edge that meets the door-latch
post, next to the driver's seating
position), or Tire Label located on the
B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’ s
door.
• B-pillar:
The structural member at
the side of the vehicle behind the
front door
• Bead area of the tire: Area of the tire
next to the rim.
• Sidewall of the tire:
Area between
the bead area and the tread.
• Tread area of the tire:
Area of the
perimeter of the tire that contacts the
road when mounted on the vehicle.
• Rim:
The metal support (wheel) for a
tire or a tire and tube assembly upon
which the tire beads are seated.
354
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Wheels and Tires
Page 359 of 609
F. 95: Indicates the tire's load index. It
is an index that relates to how much
weight a tire can carry. You may find this
information in your owner’ s manual. If
not, contact a local tire dealer.
Note: You may not find this information
on all tires because it is not required by
federal law.
G.
H: Indicates the tire's speed rating.
The speed rating denotes the speed at
which a tire is designed to be driven for
extended periods of time under a
standard condition of load and inflation
pressure. The tires on your vehicle may
operate at different conditions for load
and inflation pressure. These speed
ratings may need to be adjusted for the
difference in conditions. The ratings
range from 81 mph (130 km/h) to 186
mph (299 km/h). These ratings are listed
in the following chart.
Note: You may not find this information
on all tires because it is not required by
federal law. mph ( km/h)
Letter rating
81 mph (130 km/h)
M
87 mph (140 km/h)
N
99 mph (159 km/h)
Q
106 mph (171 km/h)
R
112 mph (180 km/h)
S
118 mph (190 km/h)
T
124 mph (200 km/h)
U
130 mph (210 km/h)
H
149 mph (240 km/h)
V mph ( km/h)
Letter rating
168 mph (270 km/h)
W
186 mph (299 km/h)
Y
Note: For tires with a maximum speed
capability over 149 mph (240 km/h), tire
manufacturers sometimes use the letters
ZR. For those with a maximum speed
capability over 186 mph (299 km/h), tire
manufacturers always use the letters
ZR.
H. U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number:
This begins with the letters DOT and
indicates that the tire meets all federal
standards. The next two numbers or
letters are the plant code designating
where it was manufactured, the next two
are the tire size code and the last four
numbers represent the week and year
the tire was built. For example, the
numbers 317 mean the 31st week of
1997. After 2000 the numbers go to four
356
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Wheels and Tires
Page 361 of 609
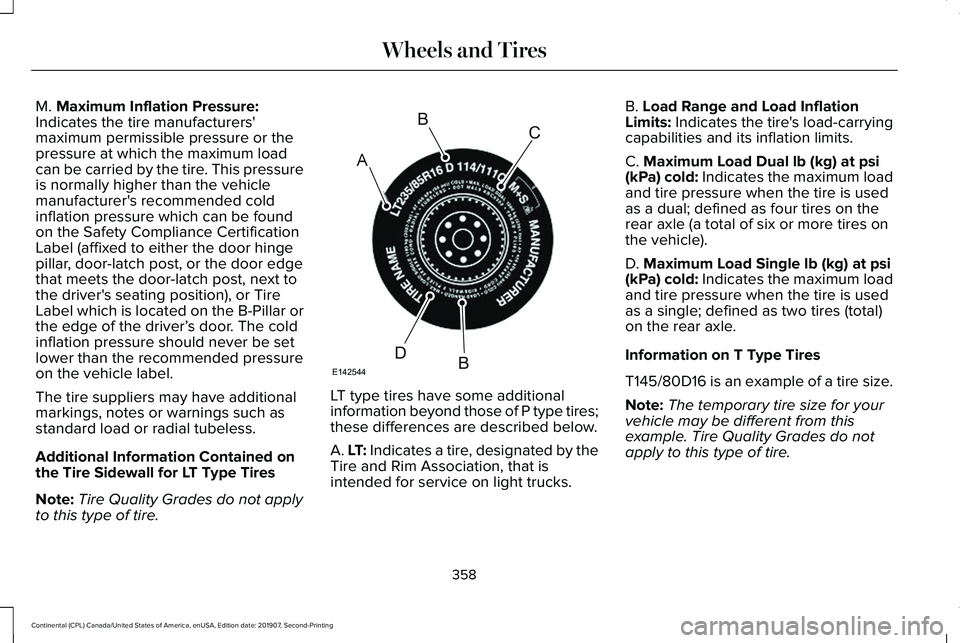
M. Maximum Inflation Pressure:
Indicates the tire manufacturers'
maximum permissible pressure or the
pressure at which the maximum load
can be carried by the tire. This pressure
is normally higher than the vehicle
manufacturer's recommended cold
inflation pressure which can be found
on the Safety Compliance Certification
Label (affixed to either the door hinge
pillar, door-latch post, or the door edge
that meets the door-latch post, next to
the driver's seating position), or Tire
Label which is located on the B-Pillar or
the edge of the driver’ s door. The cold
inflation pressure should never be set
lower than the recommended pressure
on the vehicle label.
The tire suppliers may have additional
markings, notes or warnings such as
standard load or radial tubeless.
Additional Information Contained on
the Tire Sidewall for LT Type Tires
Note: Tire Quality Grades do not apply
to this type of tire. LT type tires have some additional
information beyond those of P type tires;
these differences are described below.
A. LT: Indicates a tire, designated by the
Tire and Rim Association, that is
intended for service on light trucks.B. Load Range and Load Inflation
Limits: Indicates the tire's load-carrying
capabilities and its inflation limits.
C.
Maximum Load Dual lb (kg) at psi
(kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load
and tire pressure when the tire is used
as a dual; defined as four tires on the
rear axle (a total of six or more tires on
the vehicle).
D.
Maximum Load Single lb (kg) at psi
(kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load
and tire pressure when the tire is used
as a single; defined as two tires (total)
on the rear axle.
Information on T Type Tires
T145/80D16 is an example of a tire size.
Note: The temporary tire size for your
vehicle may be different from this
example. Tire Quality Grades do not
apply to this type of tire.
358
Continental (CPL) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, Edition date: 201907, Second-Printing Wheels and TiresA
BC
BDE142544