2019 Ram ProMaster City child restraint
[x] Cancel search: child restraintPage 119 of 348
Side Impacts
The Side Air Bags are designed to activate in certain side
impacts. The Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC) deter-
mines whether the deployment of the Side Air Bags in a
particular impact event is appropriate, based on the sever-
ity and type of collision. The side impact sensors aid the
ORC in determining the appropriate response to impact
events. The system is calibrated to deploy the Side Air Bags
on the impact side of the vehicle during impacts that
require Side Air Bag occupant protection. In side impacts,
the Side Air Bags deploy independently; a left side impact
deploys the left Side Air Bags only and a right-side impact
deploys the right Side Air Bags only. Vehicle damage by
itself is not a good indicator of whether or not Side Air
Bags should have deployed.
The Side Air Bags will not deploy in all side collisions,
including some collisions at certain angles, or some side
collisions that do not impact the area of the passenger
compartment. The Side Air Bags may deploy during
angled or offset frontal collisions where the front air bags
deploy.Side Air Bags are a supplement to the seat belt restraint
system. Side Air Bags deploy in less time than it takes to
blink your eyes.
WARNING!
•
Occupants, including children, who are up against or
very close to Side Air Bags can be seriously injured
or killed. Occupants, including children, should
never lean on or sleep against the door, side win-
dows, or area where the side air bags inflate, even if
they are in an infant or child restraint.
• Seat belts (and child restraints where appropriate)
are necessary for your protection in all collisions.
They also help keep you in position, away from an
inflating Side Air Bag. To get the best protection
from the Side Air Bags, occupants must wear their
seat belts properly and sit upright with their backs
against the seats. Children must be properly re-
strained in a child restraint or booster seat that is
appropriate for the size of the child.
5
SAFETY 117
Page 124 of 348

in understanding how a vehicle’s systems performed. The
EDR is designed to record data related to vehicle dynamics
and safety systems for a short period of time, typically 30
seconds or less. The EDR in this vehicle is designed to
record such data as:
•How various systems in your vehicle were operating;
• Whether or not the driver and passenger safety belts
were buckled/fastened;
• How far (if at all) the driver was depressing the accel-
erator and/or brake pedal; and,
• How fast the vehicle was traveling.
These data can help provide a better understanding of the
circumstances in which crashes and injuries occur.
NOTE:
EDR data are recorded by your vehicle only if a
non-trivial crash situation occurs; no data are recorded by the
EDR under normal driving conditions and no personal data
(e.g., name, gender, age, and crash location) are recorded.
However, other parties, such as law enforcement, could
combine the EDR data with the type of personally identify-
ing data routinely acquired during a crash investigation.
To read data recorded by an EDR, special equipment is
required, and access to the vehicle or the EDR is needed. In addition to the vehicle manufacturer, other parties, such as
law enforcement, that have the special equipment, can read
the information if they have access to the vehicle or the
EDR.
Child Restraints
Everyone in your vehicle needs to be buckled up at all
times, including babies and children. Every state in the
United States, and every Canadian province, requires that
small children ride in proper restraint systems. This is the
law, and you can be prosecuted for ignoring it.
Children 12 years or younger should ride properly buckled
up in a rear seat, if available. According to crash statistics,
children are safer when properly restrained in the rear
seats rather than in the front.
WARNING!
In a collision, an unrestrained child can become a
projectile inside the vehicle. The force required to hold
even an infant on your lap could become so great that
you could not hold the child, no matter how strong you
are. The child and others could be badly injured or
killed. Any child riding in your vehicle should be in a
proper restraint for the child’s size.
122 SAFETY
Page 125 of 348

There are different sizes and types of restraints for children
from newborn size to the child almost large enough for an
adult safety belt. Always check the child seat Owner ’s
Manual to make sure you have the correct seat for your
child. Carefully read and follow all the instructions and
warnings in the child restraint Owner ’s Manual and on all
the labels attached to the child restraint.
Before buying any restraint system, make sure that it has a
label certifying that it meets all applicable Safety Stan-
dards. You should also make sure that you can install it in
the vehicle where you will use it.NOTE:
•
For additional information, refer tohttp://www.nhtsa.gov/
parents-and-caregivers
or call: 1–888–327–4236
•Canadian residents should refer to Transport Canada’s web-
site for additional information: http://www.tc.gc.ca/eng/
motorvehiclesafety/safedrivers-childsafety-index-53.htm
Summary Of Recommendations For Restraining Children In Vehicles
Child Size, Height, Weight Or Age Recommended Type Of Child
Restraint
Infants and Toddlers Children who are two years old or
younger and who have not reached the height or weight limits of their child restraint Either an Infant Carrier or a Convert-
ible Child Restraint, facing rearward in a rear seat of the vehicle
Small Children Children who are at least two years
old or who have outgrown the
height or weight limit of their rear- facing child restraint Forward-Facing Child Restraint with
a five-point Harness, facing forward in a rear seat of the vehicle
5
SAFETY 123
Page 126 of 348

Child Size, Height, Weight Or AgeRecommended Type Of Child
Restraint
Larger Children Children who have outgrown their
forward-facing child restraint, but
are too small to properly fit the vehi- cle’s seat belt Belt Positioning Booster Seat and the
vehicle seat belt, seated in a rear seat of the vehicle
Children Too Large for Child Restraints Children 12 years old or younger,
who have outgrown the height or weight limit of their booster seat Vehicle Seat Belt, seated in a rear seat
of the vehicle
Infant And Child Restraints
Safety experts recommend that children ride rear-facing in
the vehicle until they are two years old or until they reach
either the height or weight limit of their rear-facing child
restraint. Two types of child restraints can be used rear-
facing: infant carriers and convertible child seats.
The infant carrier is only used rear-facing in the vehicle. It
is recommended for children from birth until they reach
the weight or height limit of the infant carrier. Convertible
child seats can be used either rear-facing or forward-facing
in the vehicle. Convertible child seats often have a higher
weight limit in the rear-facing direction than infant carriers
do, so they can be used rear-facing by children who have
outgrown their infant carrier but are still less than at least
two years old. Children should remain rear-facing until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by their
convertible child seat.
WARNING!
•
Never place a rear-facing child restraint in front of an
air bag. A deploying passenger front air bag can
cause death or serious injury to a child 12 years or
younger, including a child in a rear-facing child
restraint.
• Never install a rear-facing child restraint in the front
seat of a vehicle. Only use a rear-facing child re-
straint in the rear seat. If the vehicle does not have a
rear seat, do not transport a rear-facing child restraint
in that vehicle.
124 SAFETY
Page 127 of 348

Older Children And Child Restraints
Children who are two years old or who have outgrown
their rear-facing convertible child seat can ride forward-
facing in the vehicle. Forward-facing child seats and con-
vertible child seats used in the forward-facing direction are
for children who are over two years old or who have
outgrown the rear-facing weight or height limit of their
rear-facing convertible child seat. Children should remain
in a forward-facing child seat with a harness for as long as
possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by the
child seat.
All children whose weight or height is above the forward-
facing limit for the child seat should use a belt-positioning
booster seat until the vehicle’s seat belts fit properly. If the
child cannot sit with knees bent over the vehicle’s seat
cushion while the child’s back is against the seatback, they
should use a belt-positioning booster seat. The child and
belt-positioning booster seat are held in the vehicle by the
seat belt.
WARNING!
•Improper installation can lead to failure of an infant
or child restraint. It could come loose in a collision.
The child could be badly injured or killed. Follow
the child restraint manufacturer ’s directions exactly
when installing an infant or child restraint.
• After a child restraint is installed in the vehicle, do
not move the vehicle seat forward or rearward be-
cause it can loosen the child restraint attachments.
Remove the child restraint before adjusting the ve-
hicle seat position. When the vehicle seat has been
adjusted, reinstall the child restraint.
• When your child restraint is not in use, secure it in
the vehicle with the seat belt or LATCH anchorages,
or remove it from the vehicle. Do not leave it loose in
the vehicle. In a sudden stop or accident, it could
strike the occupants or seatbacks and cause serious
personal injury.
5
SAFETY 125
Page 129 of 348
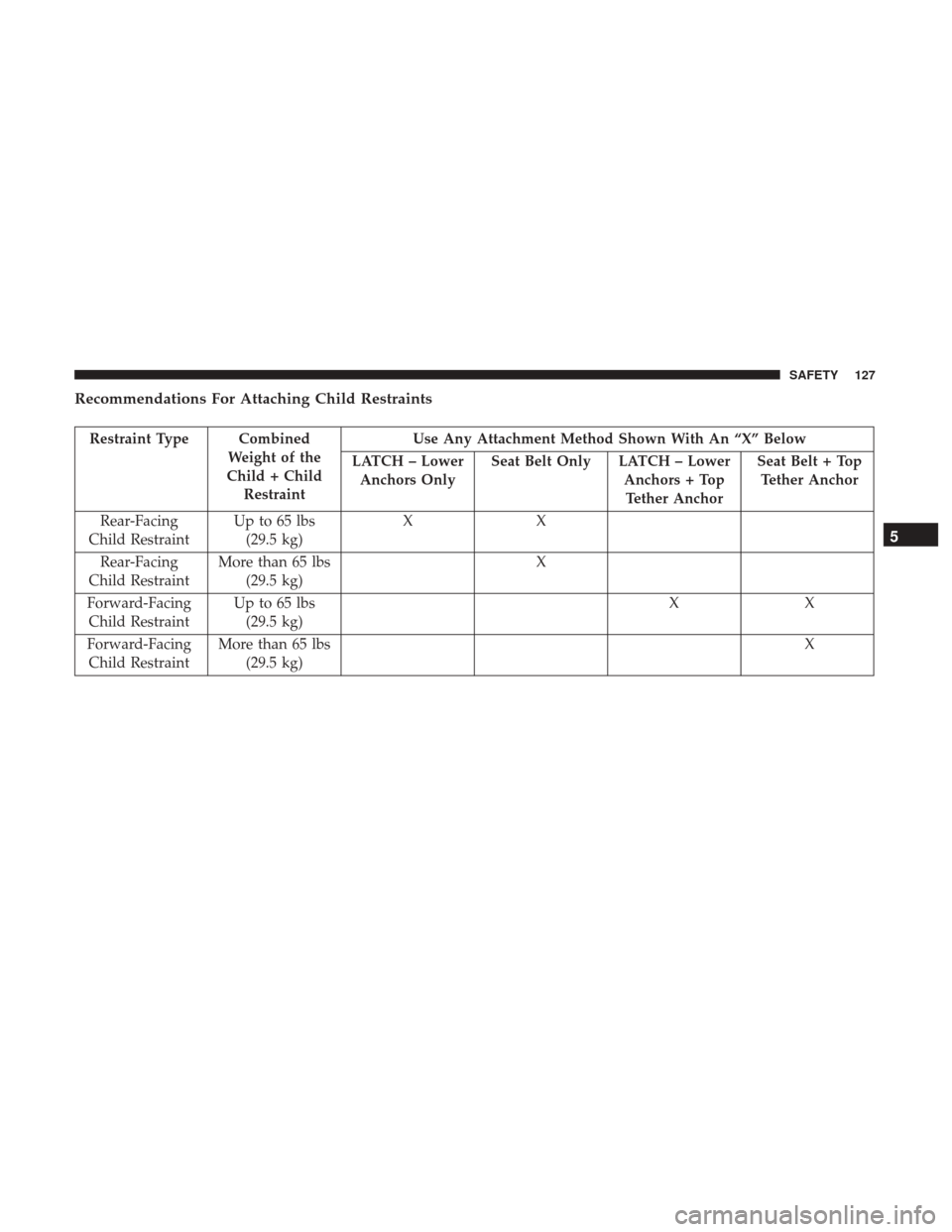
Recommendations For Attaching Child Restraints
Restraint Type CombinedWeight of the
Child + Child Restraint Use Any Attachment Method Shown With An “X” Below
LATCH – Lower Anchors Only Seat Belt Only LATCH – Lower
Anchors + TopTether Anchor Seat Belt + Top
Tether Anchor
Rear-Facing
Child Restraint Up to 65 lbs
(29.5 kg) XX
Rear-Facing
Child Restraint More than 65 lbs
(29.5 kg) X
Forward-Facing Child Restraint Up to 65 lbs
(29.5 kg) XX
Forward-Facing Child Restraint More than 65 lbs
(29.5 kg) X
5
SAFETY 127
Page 130 of 348

Lower Anchors And Tethers For CHildren (LATCH)
Restraint System
Your vehicle is equipped with the child restraint anchorage
system called LATCH, which stands for Lower Anchors
and Tethers for CHildren. The LATCH system has three
vehicle anchor points for installing LATCH-equipped child
seats. There are two lower anchorages located at the back
of the seat cushion where it meets the seatback and one top
tether anchorage located behind the seating position. These
anchorages are used to install LATCH-equipped child seats
without using the vehicle’s seat belts. Some seating posi-
tions may have a top tether anchorage but no lower
anchorages. In these seating positions, the seat belt must beused with the top tether anchorage to install the child
restraint. Please see the following table for more
information.
LATCH Positions For Installing Child Restraints In
This Vehicle — Vehicles Equipped With Rear
Seating
LATCH Label
Lower Anchor / Top Tether Locations — Vehicle With Rear
Seat
Lower Anchorage Symbol (2 Anchorages Per Seating Position)Top Tether Anchorage Symbol
128 SAFETY
Page 131 of 348

Frequently Asked Questions About Installing Child Restraints With LATCH
What is the weight limit (child’s weight + weight of the child re-
straint) for using the LATCH anchor- age system to attach the child re- straint? 65 lbs (29.5 kg)
Use the LATCH anchorage system
until the combined weight of the
child and the child restraint is 65 lbs
(29.5 kg). Use the seat belt and tether anchor instead of the LATCH system once the combined weight is more than 65 lbs (29.5 kg).
Can the LATCH anchorages and the
seat belt be used together to attach a rear-facing or forward-facing child restraint? No
Do not use the seat belt when you
use the LATCH anchorage system to
attach a rear-facing or forward-facing child restraint.
Booster seats may be attached to the
LATCH anchorages if allowed by the booster seat manufacturer. See your booster seat owner ’s manual for more information.
Can a child seat be installed in the center position using the innerLATCH lower anchorages? No
Use the seat belt and tether anchor to
install a child seat in the center seat- ing position.
5
SAFETY 129