2019 NISSAN ARMADA suspension
[x] Cancel search: suspensionPage 398 of 536

5-138Starting and driving
The Vehicle Dynamic Control (VDC) sys-
tem uses various sensors to monitor
driver inputs and vehicle motion. Under
certain driving conditions, the VDC sys-
tem helps to perform the following func-
tions.
.Controls brake pressure to reduce
wheel slip on one slipping drive wheel
so power is transferred to a non
slipping drive wheel on the same axle.
. Controls brake pressure and engine
output to reduce drive wheel slip
based on vehicle speed (traction con-
trol function).
. Controls brake pressure at individual
wheels and engine output to help the
driver maintain control of the vehicle
in the following conditions:
— understeer (vehicle tends to not
follow the steered path despite
increased steering input)
— oversteer (vehicle tends to spin due to certain road or driving condi-
tions).
The VDC system can help the driver to
maintain control of the vehicle, but it
cannot prevent loss of vehicle control in
all driving situations.
When the VDC system operates, the VDC
warning light
in the instrument panel
flashes so note the following: .
The road may be slippery or the
system may determine some action
is required to help keep the vehicle on
the steered path.
. You may feel a pulsation in the brake
pedal and hear a noise or vibration
from under the hood. This is normal
and indicates that the VDC system is
working properly.
. Adjust your speed and driving to the
road conditions.
If a malfunction occurs in the system, the
VDC warning light
illuminates in the
instrument panel. The VDC system auto-
matically turns off.
The VDC OFF switch is used to turn off the
VDC system. The VDC off indicator
illuminates to indicate the VDC system is
off. When the VDC switch is used to turn
off the system, the VDC system still
operates to prevent one drive wheel from
slipping by transferring power to a non
slipping drive wheel. The VDC warning
light
flashes if this occurs. All other
VDC functions are off, and the VDC
warning light
will not flash. The VDC
system is automatically reset to on when
the ignition switch is placed in the OFF
position then back to the ON position.
When the 4L position is selected with the
4WD shift switch, the VDC system is
disabled and the VDC off indicator light illuminates (for 4WD models).
See “Vehicle Dynamic Control (VDC) warn-
ing light” (P.2-17) and “Vehicle Dynamic
Control (VDC) off indicator light” (P.2-20).
The computer has a built-in diagnostic
feature that tests the system each time
you start the engine and move the vehicle
forward or in reverse at a slow speed.
When the self-test occurs, you may hear a
“clunk” noise and/or feel a pulsation in the
brake pedal. This is normal and is not an
indication of a malfunction.
WARNING
.
The VDC system is designed to
help improve driving stability but
does not prevent accidents due
to abrupt steering operation at
high speeds or by careless or
dangerous driving techniques.
Reduce vehicle speed and be
especially careful when driving
and cornering on slippery sur-
faces and always drive carefully.
. Do not modify the vehicle’s sus-
pension. If suspension parts such
as shock absorbers, struts,
springs, stabilizer bars, bushings
and wheels are not NISSAN re-
commended for your vehicle or
VEHICLE DYNAMIC CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM
Page 411 of 536
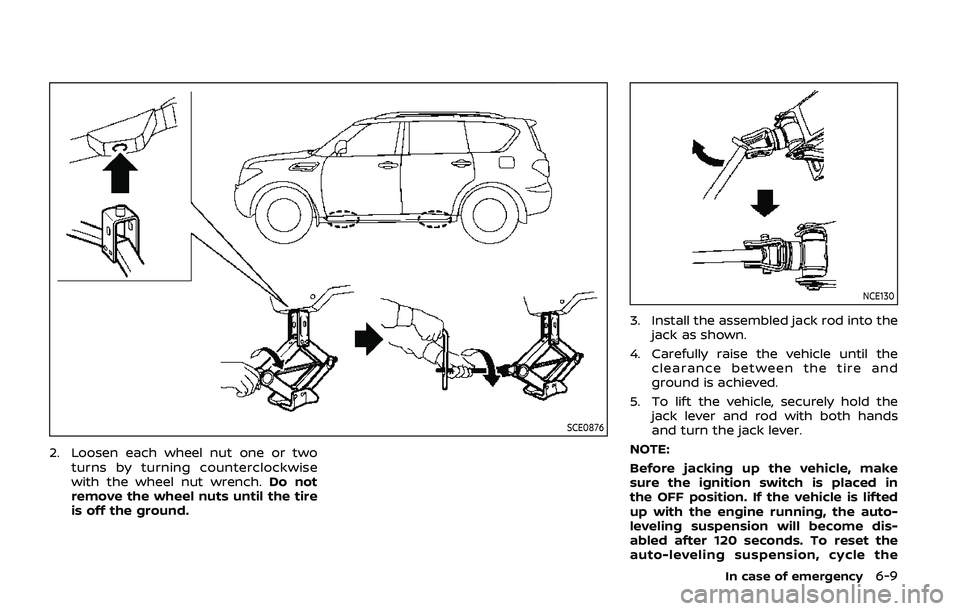
SCE0876
2. Loosen each wheel nut one or twoturns by turning counterclockwise
with the wheel nut wrench. Do not
remove the wheel nuts until the tire
is off the ground.
NCE130
3. Install the assembled jack rod into the
jack as shown.
4. Carefully raise the vehicle until the clearance between the tire and
ground is achieved.
5. To lift the vehicle, securely hold the jack lever and rod with both hands
and turn the jack lever.
NOTE:
Before jacking up the vehicle, make
sure the ignition switch is placed in
the OFF position. If the vehicle is lifted
up with the engine running, the auto-
leveling suspension will become dis-
abled after 120 seconds. To reset the
auto-leveling suspension, cycle the
In case of emergency6-9
Page 421 of 536
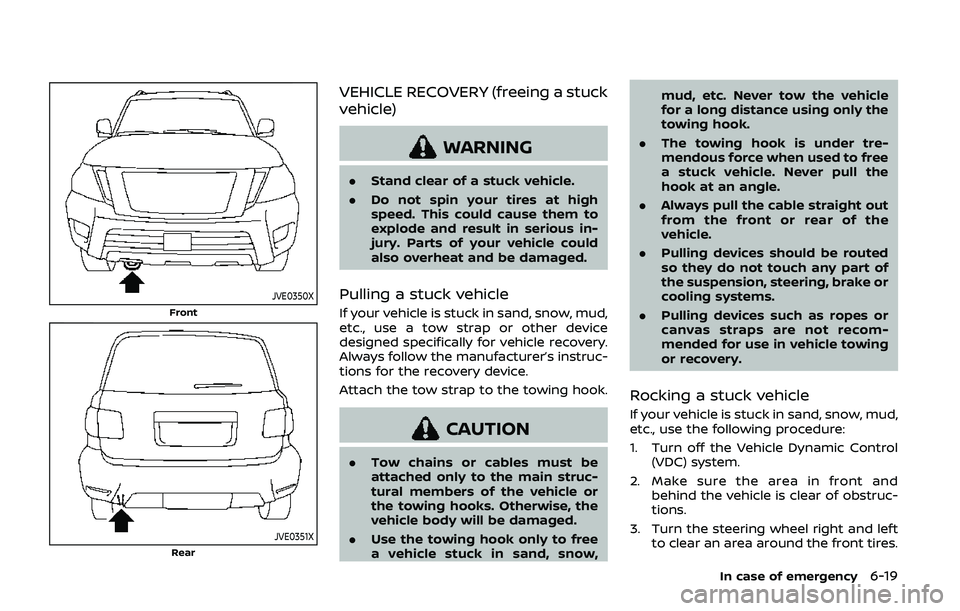
JVE0350X
Front
JVE0351XRear
VEHICLE RECOVERY (freeing a stuck
vehicle)
WARNING
.Stand clear of a stuck vehicle.
. Do not spin your tires at high
speed. This could cause them to
explode and result in serious in-
jury. Parts of your vehicle could
also overheat and be damaged.
Pulling a stuck vehicle
If your vehicle is stuck in sand, snow, mud,
etc., use a tow strap or other device
designed specifically for vehicle recovery.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instruc-
tions for the recovery device.
Attach the tow strap to the towing hook.
CAUTION
.Tow chains or cables must be
attached only to the main struc-
tural members of the vehicle or
the towing hooks. Otherwise, the
vehicle body will be damaged.
. Use the towing hook only to free
a vehicle stuck in sand, snow, mud, etc. Never tow the vehicle
for a long distance using only the
towing hook.
. The towing hook is under tre-
mendous force when used to free
a stuck vehicle. Never pull the
hook at an angle.
. Always pull the cable straight out
from the front or rear of the
vehicle.
. Pulling devices should be routed
so they do not touch any part of
the suspension, steering, brake or
cooling systems.
. Pulling devices such as ropes or
canvas straps are not recom-
mended for use in vehicle towing
or recovery.
Rocking a stuck vehicle
If your vehicle is stuck in sand, snow, mud,
etc., use the following procedure:
1. Turn off the Vehicle Dynamic Control
(VDC) system.
2. Make sure the area in front and behind the vehicle is clear of obstruc-
tions.
3. Turn the steering wheel right and left to clear an area around the front tires.
In case of emergency6-19
Page 471 of 536
tires. Skid and traction capabilities of
studded snow tires, on wet or dry sur-
faces, may be poorer than that of non-
studded snow tires.
TIRE CHAINS
Use of tire chains may be prohibited
according to location. Check the local
laws before installing tire chains. When
installing tire chains, make sure they are
the proper size for the tires on your
vehicle and are installed according to
the chain manufacturer’s suggestions.
Use only SAE Class S chains.Class “S”
chains are used on vehicles with re-
stricted tire to vehicle clearance. Vehicles
that can use Class “S” chains are designed
to meet the SAE standard minimum
clearances between the tire and the
closest vehicle suspension or body com-
ponent required to accommodate the
use of a winter traction device (tire chains
or cables). The minimum clearances are
determined using the factory equipped
tire size. Other types may damage your
vehicle. Use chain tensioners when re-
commended by the tire chain manufac-
turer to ensure a tight fit. Loose end links
of the tire chain must be secured or
removed to prevent the possibility of
whipping action damage to the fenders
or underbody. If possible, avoid fully load-
ing your vehicle when using tire chains. In addition, drive at a reduced speed. Other-
wise, your vehicle may be damaged and/
or vehicle handling and performance may
be adversely affected.
Tire chains must be installed only on
the rear wheels and not on the front
wheels.
Do not use tire chains on dry roads.
Driving with tire chains in such conditions
can cause damage to the various me-
chanisms of the vehicle due to some
overstress.
SDI1662
CHANGING WHEELS AND TIRES
Tire rotation
NISSAN recommends rotating the
tires every 5,000 miles (8,000 km).
(See “Flat tire” (P.6-3) for tire repla-
cing procedures.)
As soon as possible, tighten the
wheel nuts to the specified torque
with a torque wrench.
Wheel nut tightening torque:98 ft-lb (133 N·m)
The wheel nuts must be kept
tightened to the specification at
Do-it-yourself8-37
Page 480 of 536

9-6Maintenance and schedules
Exhaust system:
Visually inspect the exhaust pipes, muffler
and hangers for leaks, cracks, deteriora-
tion, and damage. Tighten connections or
replace parts as necessary.
Propeller shaft(s):
Check for damage, looseness, and grease
leakage.
In-cabin microfilter:
Replace at specified intervals. When driv-
ing for prolonged periods in dusty condi-
tions, replace the filter more frequently.
Steering gear and linkage, axle and
suspension parts:
Check for damage, looseness, and leak-
age of oil or grease. Under severe driving
conditions, inspect more frequently.
Tire rotation:
Tires should be rotated every 5,000 miles
(8,000km). When rotating tires, check for
damage and uneven wear. Replace if
necessary.
Transmission fluid/oil, differential oil:
Visually inspect for signs of leakage at
specified intervals.
Off-road maintenance:
Check the following items frequently
whenever you drive off-road through
deep sand, mud or water:.
Brake pads and rotors
. Brake linings and drums
. Brake lines and hoses
. Differential, transmission and transfer
case oil
. Steering linkage
. Propeller shaft(s) and front drive
shafts
. Engine air filter
. Clutch housing drain (AWD only) To help ensure smooth, safe and eco-
nomical driving, NISSAN provides two
maintenance schedules that may be
used, depending upon the conditions in
which you usually drive. These schedules
contain both distance and time intervals,
up to 120,000 miles (192,000 km)/144
months. For most people, the odometer
reading will indicate when service is
needed. However, if you drive very little,
your vehicle should be serviced at the
regular time intervals shown in the sche-
dule.
After 120,000 miles (192,000 km)/144
months, continue maintenance at the
same mileage/time intervals.
ADDITIONAL MAINTENANCE ITEMS
FOR SEVERE OPERATING CONDI-
TIONS
Additional maintenance items for se-
vere operating conditions;
should be
performed on vehicles that are driven
under especially demanding conditions.
Additional maintenance items should be
performed if you primarily operate your
vehicle under the following conditions:
. Repeated short trips of less than 5
miles (8 km).
. Repeated short trips of less than 10
miles (16 km) with outside tempera-
tures remaining below freezing.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
Page 485 of 536
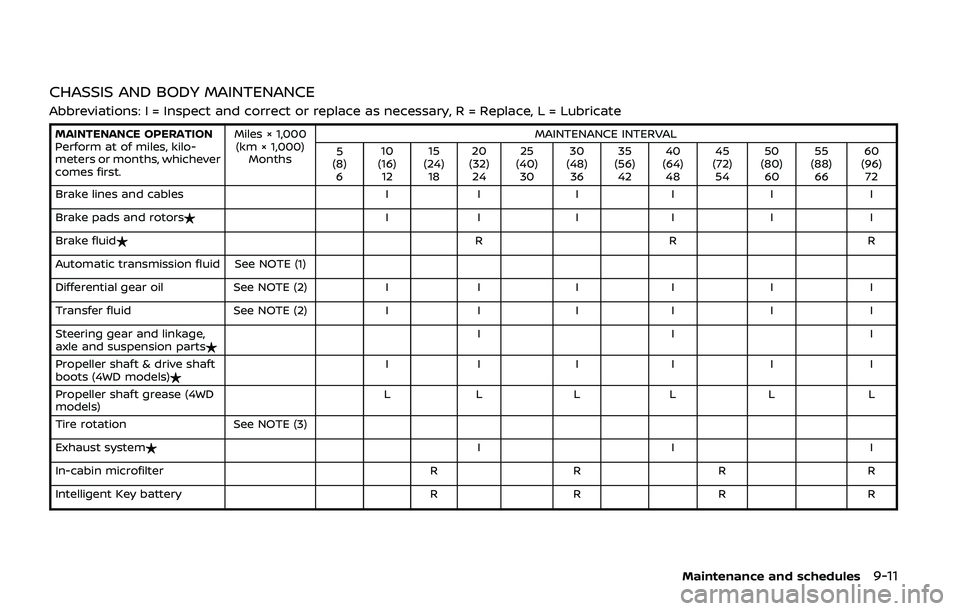
CHASSIS AND BODY MAINTENANCE
Abbreviations: I = Inspect and correct or replace as necessary, R = Replace, L = Lubricate
MAINTENANCE OPERATION
Perform at of miles, kilo-
meters or months, whichever
comes first.Miles × 1,000
(km × 1,000) Months MAINTENANCE INTERVAL
5
(8) 6 10
(16) 12 15
(24) 18 20
(32) 24 25
(40) 30 30
(48) 36 35
(56) 42 40
(64) 48 45
(72) 54 50
(80) 60 55
(88) 66 60
(96) 72
Brake lines and cables II II I I
Brake pads and rotors$ II I I I I
Brake fluid$ RR R
Automatic transmission fluid See NOTE (1)
Differential gear oil See NOTE (2)II II I I
Transfer fluid See NOTE (2)II II I I
Steering gear and linkage,
axle and suspension parts$ II I
Propeller shaft & drive shaft
boots (4WD models)$ II I I I I
Propeller shaft grease (4WD
models) LL L L L L
Tire rotation See NOTE (3)
Exhaust system$ II I
In-cabin microfilter RR R R
Intelligent Key battery RR R R
Maintenance and schedules9-11
Page 486 of 536
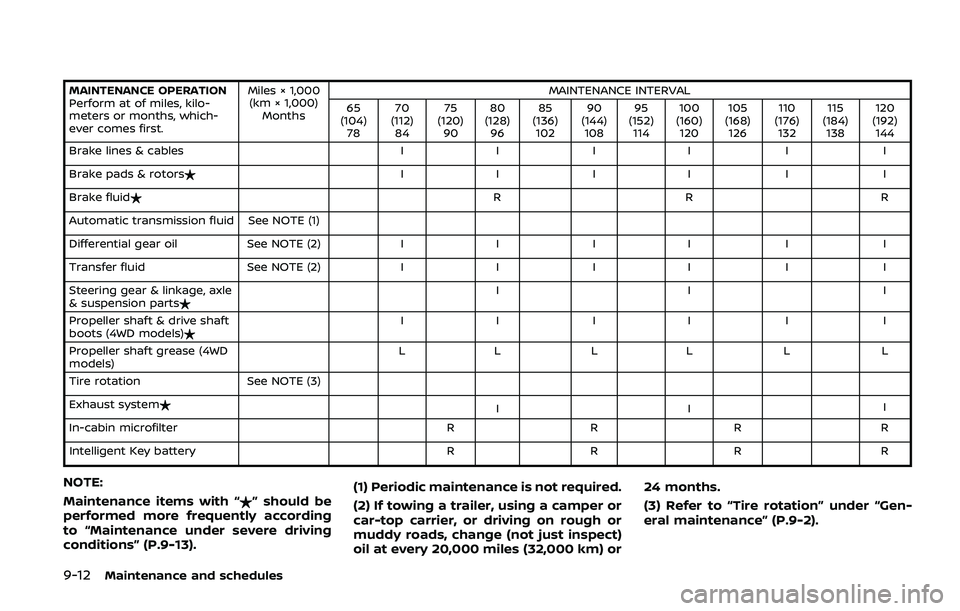
9-12Maintenance and schedules
MAINTENANCE OPERATION
Perform at of miles, kilo-
meters or months, which-
ever comes first.Miles × 1,000
(km × 1,000) Months MAINTENANCE INTERVAL
65
(104) 78 70
(112) 84 75
(120) 90 80
(128) 96 85
(136) 102 90
(144) 108 95
(152) 114 100
(160) 120 105
(168) 126 110
(176) 132 115
(184) 138 120
(192) 144
Brake lines & cables II II I I
Brake pads & rotors$ II II I I
Brake fluid$ RR R
Automatic transmission fluid See NOTE (1)
Differential gear oil See NOTE (2)II II I I
Transfer fluid See NOTE (2)II II I I
Steering gear & linkage, axle
& suspension parts$ II I
Propeller shaft & drive shaft
boots (4WD models)$ II II I I
Propeller shaft grease (4WD
models) LL LL L L
Tire rotation See NOTE (3)
Exhaust system$ III
In-cabin microfilter RRR R
Intelligent Key battery RRR R
NOTE:
Maintenance items with “$” should be
performed more frequently according
to “Maintenance under severe driving
conditions” (P.9-13). (1) Periodic maintenance is not required.
(2) If towing a trailer, using a camper or
car-top carrier, or driving on rough or
muddy roads, change (not just inspect)
oil at every 20,000 miles (32,000 km) or24 months.
(3) Refer to “Tire rotation” under “Gen-
eral maintenance” (P.9-2).
Page 487 of 536
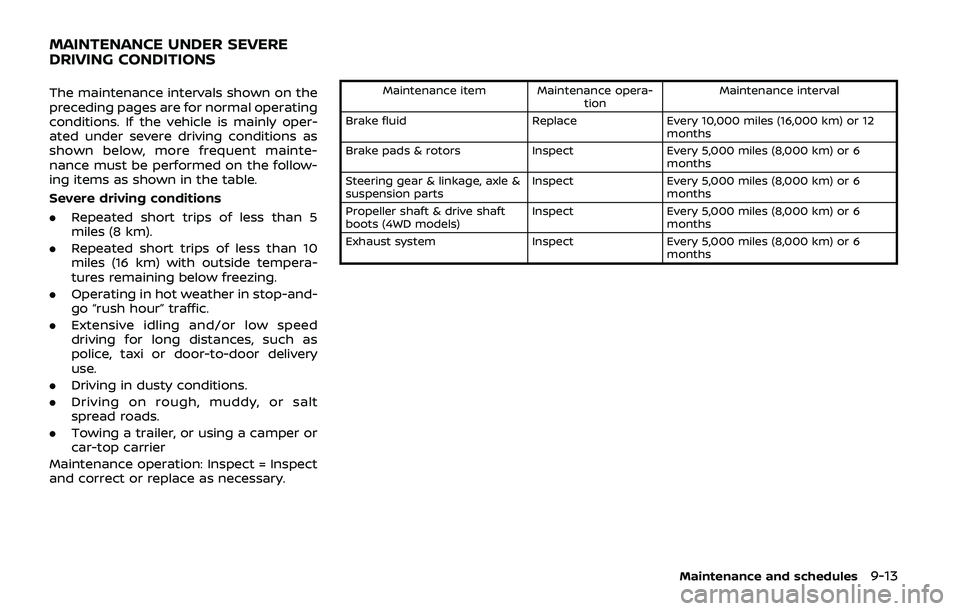
The maintenance intervals shown on the
preceding pages are for normal operating
conditions. If the vehicle is mainly oper-
ated under severe driving conditions as
shown below, more frequent mainte-
nance must be performed on the follow-
ing items as shown in the table.
Severe driving conditions
.Repeated short trips of less than 5
miles (8 km).
. Repeated short trips of less than 10
miles (16 km) with outside tempera-
tures remaining below freezing.
. Operating in hot weather in stop-and-
go “rush hour” traffic.
. Extensive idling and/or low speed
driving for long distances, such as
police, taxi or door-to-door delivery
use.
. Driving in dusty conditions.
. Driving on rough, muddy, or salt
spread roads.
. Towing a trailer, or using a camper or
car-top carrier
Maintenance operation: Inspect = Inspect
and correct or replace as necessary.Maintenance item Maintenance opera- tionMaintenance interval
Brake fluid ReplaceEvery 10,000 miles (16,000 km) or 12
months
Brake pads & rotors InspectEvery 5,000 miles (8,000 km) or 6
months
Steering gear & linkage, axle &
suspension parts Inspect
Every 5,000 miles (8,000 km) or 6
months
Propeller shaft & drive shaft
boots (4WD models) Inspect
Every 5,000 miles (8,000 km) or 6
months
Exhaust system InspectEvery 5,000 miles (8,000 km) or 6
months
Maintenance and schedules9-13
MAINTENANCE UNDER SEVERE
DRIVING CONDITIONS