Page 432 of 560
7-8
Maintenance
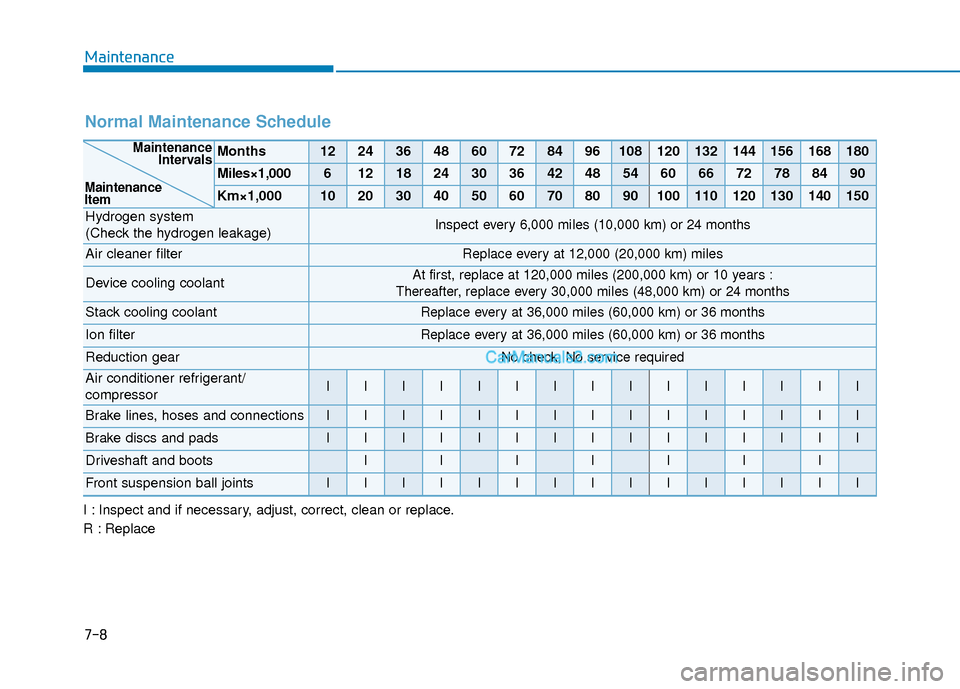
Normal Maintenance Schedule
Months1224364860728496108120132144156168180
Miles×1,00061218243036424854606672788490
Km×1,000102030405060708090100110120130140150
Hydrogen system
(Check the hydrogen leakage)Inspect every 6,000 miles (10,000 km) or 24 months
Air cleaner filterReplace every at 12,000 (20,000 km) miles
Device cooling coolantAt first, replace at 120,000 miles (200,000 km) or 10 years :
Thereafter, replace every 30,000 miles (48,000 km) or 24 months
Stack cooling coolantReplace every at 36,000 miles (60,000 km) or 36 months
Ion filterReplace every at 36,000 miles (60,000 km) or 36 months
Reduction gearNo check, No service required
Air conditioner refrigerant/
compressorIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
Brake lines, hoses and connectionsIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
Brake discs and padsIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
Driveshaft and bootsIIIIIII
Front suspension ball jointsIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
Maintenance Intervals
Maintenance
Item
I : Inspect and if necessary, adjust, correct, clean or replace.
R : Replace
Page 434 of 560
7-10
Maintenance
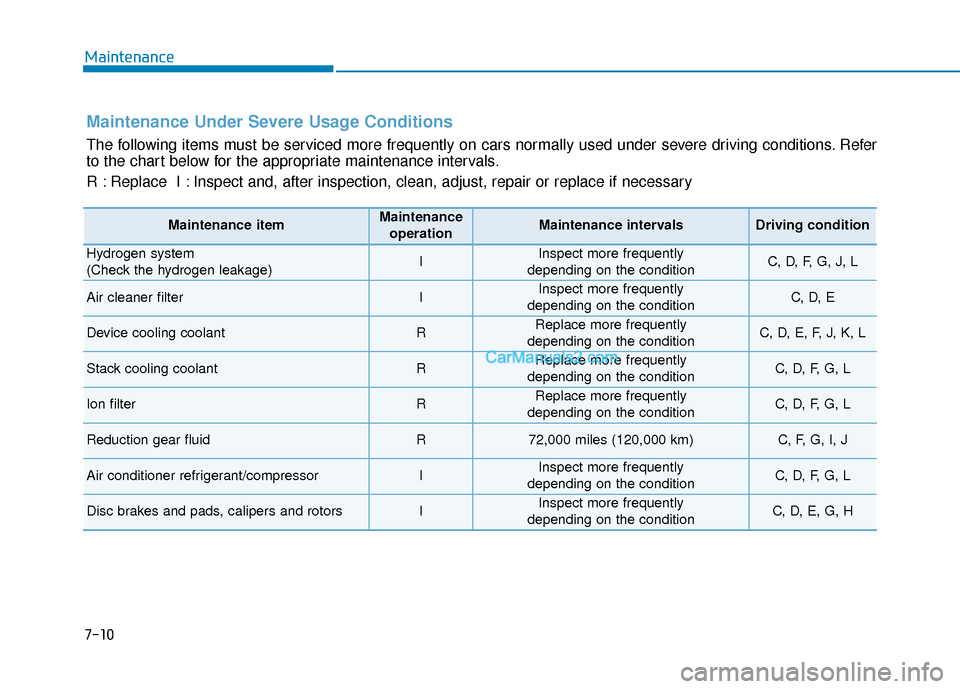
Maintenance Under Severe Usage Conditions
The following items must be serviced more frequently on cars normally used under severe driving conditions. Refer
to the chart below for the appropriate maintenance intervals.
R : Replace I : Inspect and, after inspection, clean, adjust, repair or replace if neces\
sary
Maintenance itemMaintenanceoperationMaintenance intervalsDriving condition
Hydrogen system
(Check the hydrogen leakage)IInspect more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, F, G, J, L
Air cleaner filterIInspect more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, E
Device cooling coolantRReplace more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, E, F, J, K, L
Stack cooling coolantRReplace more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, F, G, L
Ion filterRReplace more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, F, G, L
Reduction gear fluidR72,000 miles (120,000 km)C, F, G, I, J
Air conditioner refrigerant/compressorIInspect more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, F, G, L
Disc brakes and pads, calipers and rotorsIInspect more frequently
depending on the conditionC, D, E, G, H
Page 475 of 560
7-51
7
Maintenance
Fuse NameFuse RatingProtected Component
AMP25AAMP
MULTI MEDIA15AA/V & Navigation Head Unit, Center Fascia Switch Panel
MODULE510AFront Air Ventilation/Seat Heater Seat Control Module, AMP, A/V & Navigation Head Unit,
A/C Control Panel, PTC Heater, A/C Control Module, Electro Chromic Mirror, Rear Seat Heater
WIPER (RR)15AICM Relay Box (Rear Wiper Relay), Rear Wiper Motor
DOOR LOCK20ADoor Lock Relay, Door Unlock Relay, ICM Relay Box (Two Turn Door Unlock Relay)
IBU115AIBU
BRAKE
SWITCH10AIBU, Stop Lamp Switch
P/SEAT PASS25APassenger Seat Manual Switch
A/C7.5AA/C Control Module, Incar Temperature Sensor, A/C Control Panel,
Cluster Ionizer, A/C Compressor, PE Room Junction Block (Blower Relay)
AIR BAG210ASRS Control Module
WASHER15AMultifunction Switch
Instrument panel fuse panel
Page 499 of 560
8-5
88
Specifications, Consumer information and Reporting safety defectsV
VO
O L
LU
U M
M E
E
A
A N
N D
D
W
W E
EI
IG
G H
H T
T
A
A I
IR
R
C
C O
O N
ND
DI
IT
T I
IO
O N
NI
IN
N G
G
S
S Y
Y S
ST
T E
EM
M
Contact an authorized HYUNDAI dealer for more details.
Gross Vehicle Weight
lbs. (kg)Luggage Volume cu ft ( l)
Min.Max.
5,159 (2,340)16.28(461)51.77 (1,466)
ItemsWeight of VolumeClassification
Refrigerant
oz. (g) 20.28±0.88 (575±25)R-1234yf
Compressor lubricantoz. (cc) 4.59±0.35 (130±10)POE
Page 508 of 560
H4
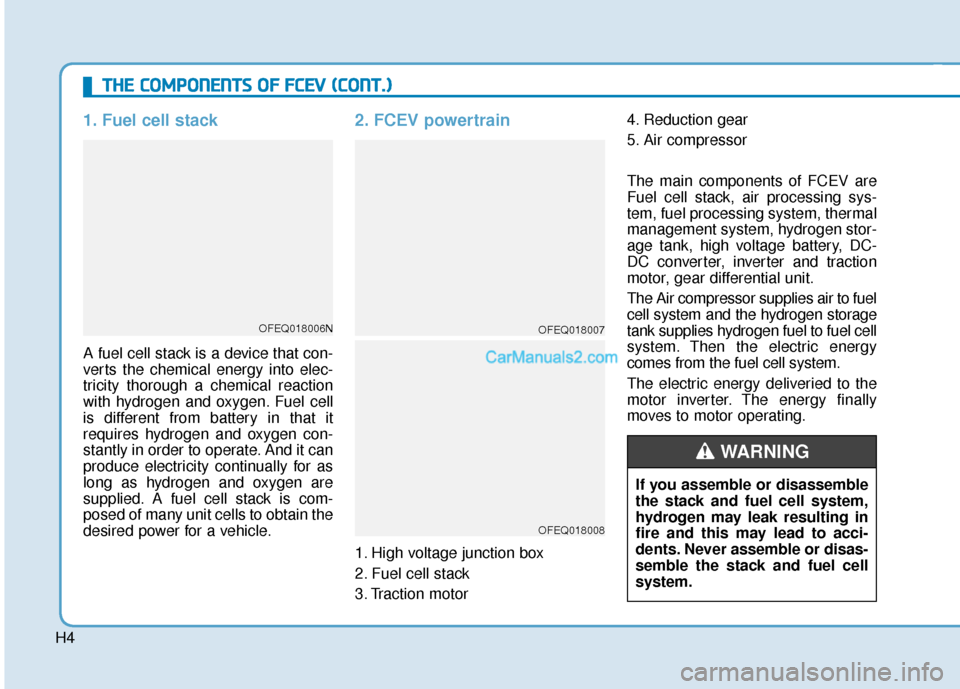
1. Fuel cell stack
A fuel cell stack is a device that con-
verts the chemical energy into elec-
tricity thorough a chemical reaction
with hydrogen and oxygen. Fuel cell
is different from battery in that it
requires hydrogen and oxygen con-
stantly in order to operate. And it can
produce electricity continually for as
long as hydrogen and oxygen are
supplied. A fuel cell stack is com-
posed of many unit cells to obtain the
desired power for a vehicle.
2. FCEV powertrain
1. High voltage junction box
2. Fuel cell stack
3. Traction motor4. Reduction gear
5. Air compressor
The main components of FCEV are
Fuel cell stack, air processing sys-
tem, fuel processing system, thermal
management system, hydrogen stor-
age tank, high voltage battery, DC-
DC converter, inverter and traction
motor, gear differential unit.
The Air compressor supplies air to fuel
cell system and the hydrogen storage
tank supplies hydrogen fuel to fuel cell
system. Then the electric energy
comes from the fuel cell system.
The electric energy deliveried to the
motor inverter. The energy finally
moves to motor operating.
T T
H
H E
E
C
C O
O M
M P
PO
O N
NE
EN
N T
TS
S
O
O F
F
F
F C
C E
E V
V
(
( C
C O
O N
NT
T.
.)
)
OFEQ018006NOFEQ018007
OFEQ018008
If you assemble or disassemble
the stack and fuel cell system,
hydrogen may leak resulting in
fire and this may lead to acci-
dents. Never assemble or disas-
semble the stack and fuel cell
system.
WARNING
Page 535 of 560
H31
CategoryQuestionsAnswers
Vehicle
overview
(10 items)
5. Why is there an engine noise at low speeds, even though there is no engine?The noise is generated from the air compressor and cooling pump
working to supply air to the fuel cell or it's from Virtual Engine
Sound System (VESS).
6. When turning on and off the vehicle incold weather, there's a loud noise. Is this
noise cause for concern?
When you turn on the vehicle or turn off the vehicle in cold weather,
the air compressor removes the generated water inside the fuel cell
system and the noise is generated during this process, which is nor-
mal. In this case, certain amount of water may drain through the
vehicle bottom and exhaust pipe.
7. Why does a noise emanate when thevehicle moves in reverse?
Normally, the noise is a result of the Virtual Engine Sound System
(VESS) working when the FCEV runs at low velocity (1~12 mph
(1~20 km/h)) after shifting to D or N. However, when shifting to R,
the VESS operates immediately, regardless of vehicle speed. In
addition, a separate warning chime will sound to have the pedestri-
an aware of the approaching vehicle.
8. The FCEV is equipped with a reductiongear but no transmission. What makes it
different from standard vehicles?
The transmission of standard vehicles delivers power as conditions
require via multiple transmission gears. However, the reduction gear
of the FCEV is designed to deliver power by reducing the motor's
RPM as operating conditions dictate, or to move backwards by
reversing the rotational direction of the shaft.