Page 236 of 432
ENGINE REMOVAL
6-7
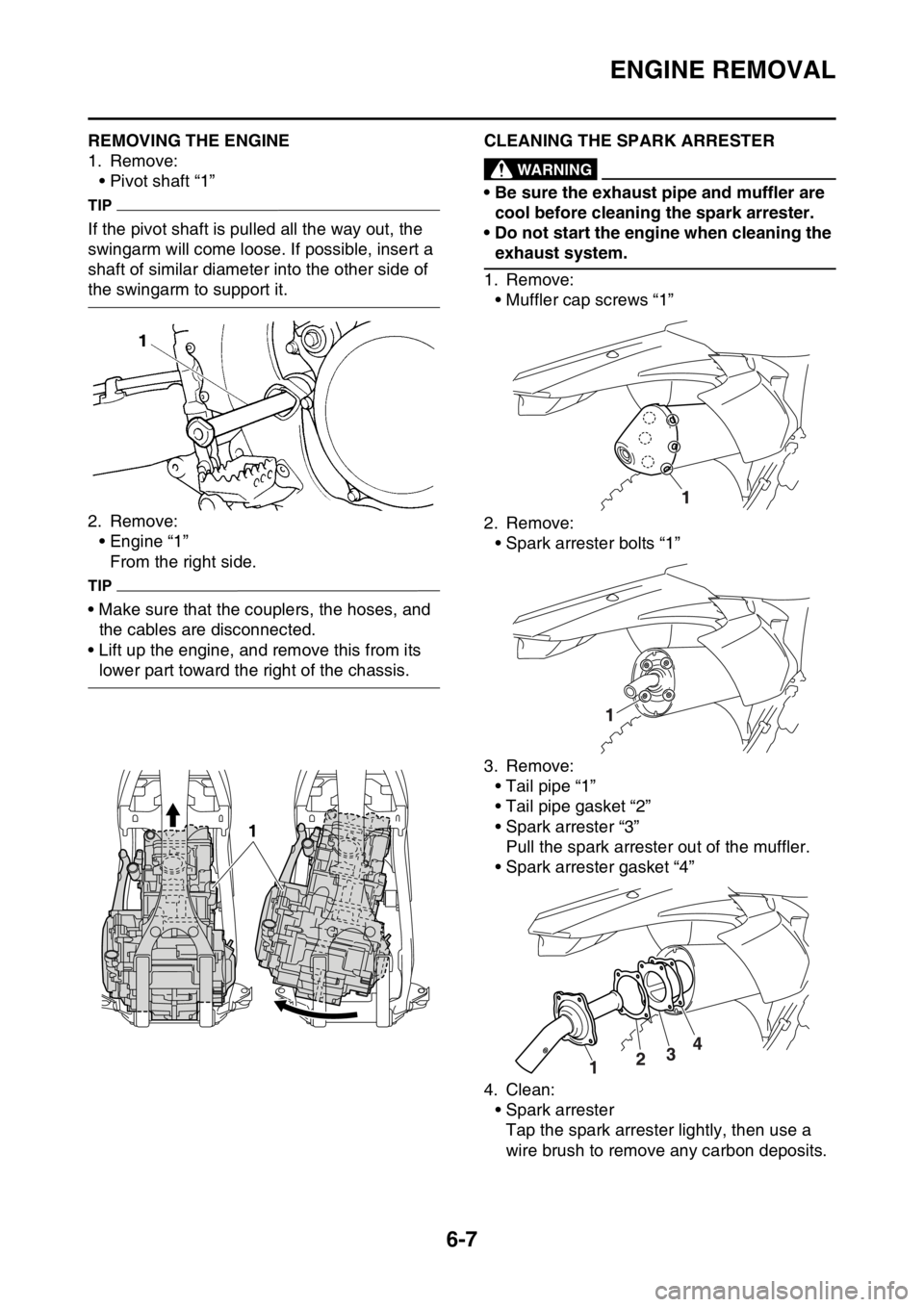
EAS2GBB230REMOVING THE ENGINE
1. Remove:
• Pivot shaft “1”
TIP
If the pivot shaft is pulled all the way out, the
swingarm will come loose. If possible, insert a
shaft of similar diameter into the other side of
the swingarm to support it.
2. Remove:
• Engine “1”
From the right side.
TIP
• Make sure that the couplers, the hoses, and
the cables are disconnected.
• Lift up the engine, and remove this from its
lower part toward the right of the chassis.
EAS2GBB231CLEANING THE SPARK ARRESTEREWA
WARNING
• Be sure the exhaust pipe and muffler are
cool before cleaning the spark arrester.
• Do not start the engine when cleaning the
exhaust system.
1. Remove:
• Muffler cap screws “1”
2. Remove:
• Spark arrester bolts “1”
3. Remove:
• Tail pipe “1”
• Tail pipe gasket “2”
• Spark arrester “3”
Pull the spark arrester out of the muffler.
• Spark arrester gasket “4”
4. Clean:
• Spark arrester
Tap the spark arrester lightly, then use a
wire brush to remove any carbon deposits.
1
Page 311 of 432
TRANSMISSION
6-82
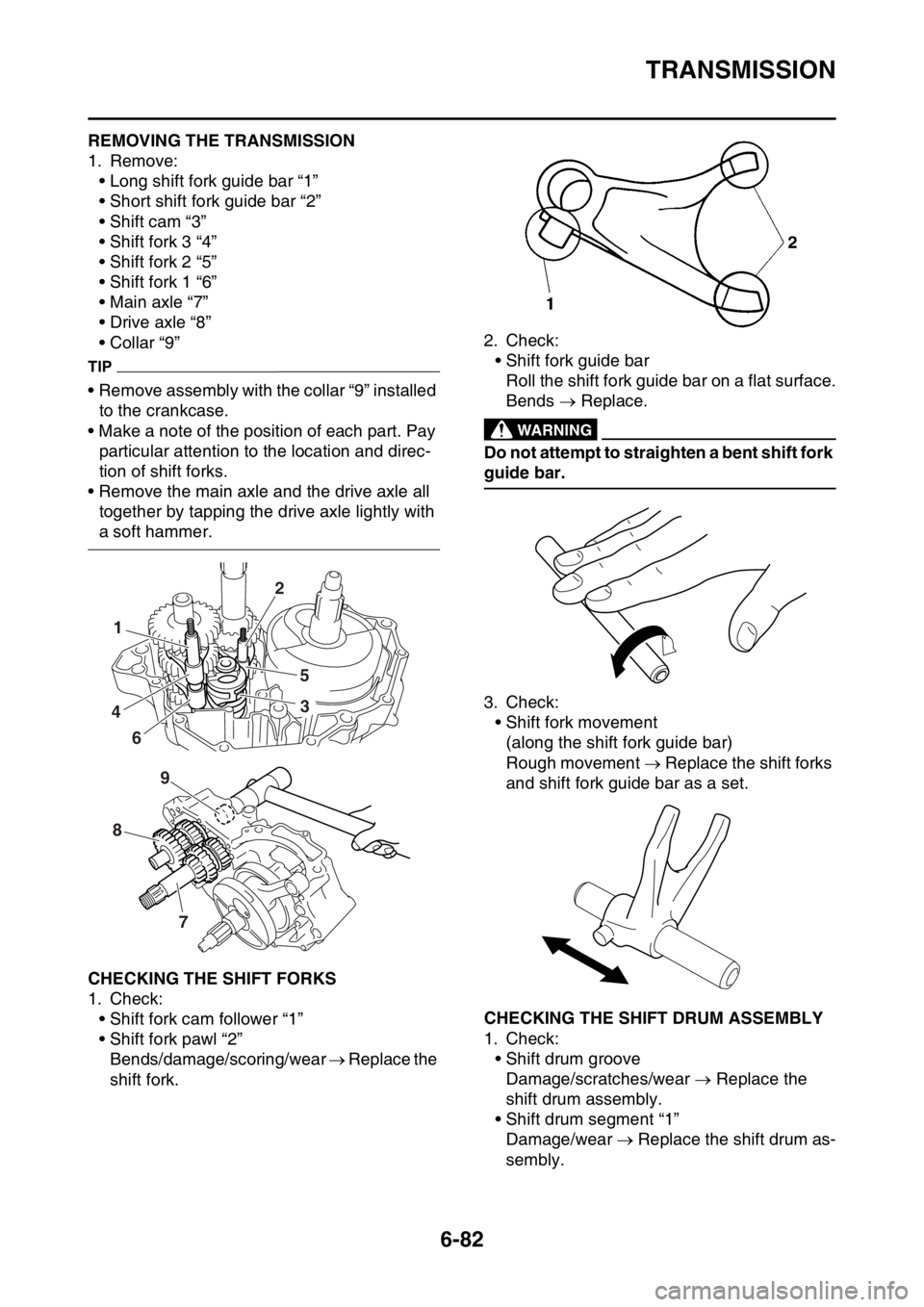
EAS2GBB323REMOVING THE TRANSMISSION
1. Remove:
• Long shift fork guide bar “1”
• Short shift fork guide bar “2”
• Shift cam “3”
• Shift fork 3 “4”
• Shift fork 2 “5”
• Shift fork 1 “6”
• Main axle “7”
• Drive axle “8”
• Collar “9”
TIP
• Remove assembly with the collar “9” installed
to the crankcase.
• Make a note of the position of each part. Pay
particular attention to the location and direc-
tion of shift forks.
• Remove the main axle and the drive axle all
together by tapping the drive axle lightly with
a soft hammer.
EAS2GBB324CHECKING THE SHIFT FORKS
1. Check:
• Shift fork cam follower “1”
• Shift fork pawl “2”
Bends/damage/scoring/wear Replace the
shift fork.2. Check:
• Shift fork guide bar
Roll the shift fork guide bar on a flat surface.
Bends Replace.
EWA
WARNING
Do not attempt to straighten a bent shift fork
guide bar.
3. Check:
• Shift fork movement
(along the shift fork guide bar)
Rough movement Replace the shift forks
and shift fork guide bar as a set.
EAS2GBB325CHECKING THE SHIFT DRUM ASSEMBLY
1. Check:
• Shift drum groove
Damage/scratches/wear Replace the
shift drum assembly.
• Shift drum segment “1”
Damage/wear Replace the shift drum as-
sembly.
1
4
62
5
3
8
7
9
Page 327 of 432
FUEL TANK
8-4
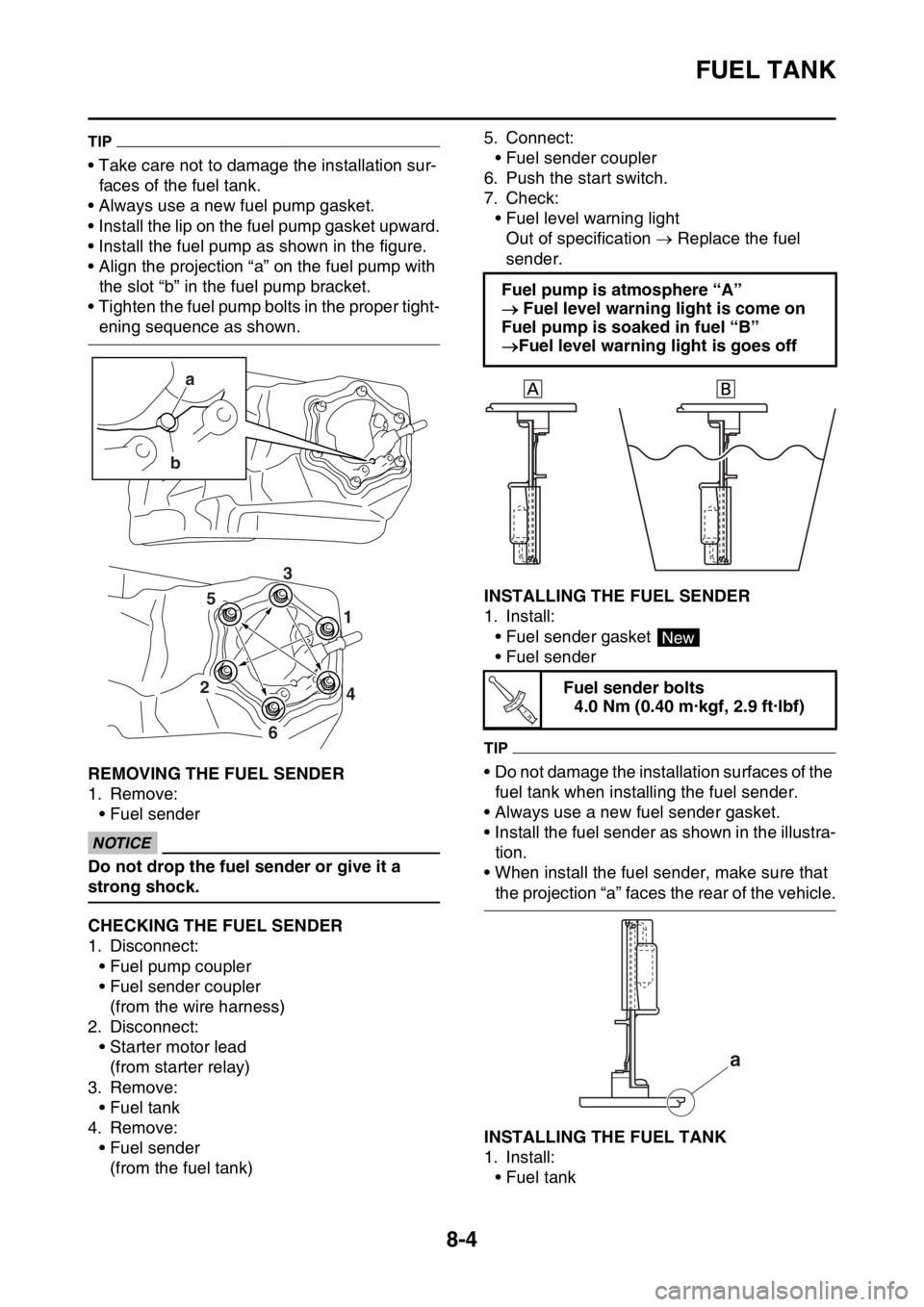
TIP
• Take care not to damage the installation sur-
faces of the fuel tank.
• Always use a new fuel pump gasket.
• Install the lip on the fuel pump gasket upward.
• Install the fuel pump as shown in the figure.
• Align the projection “a” on the fuel pump with
the slot “b” in the fuel pump bracket.
• Tighten the fuel pump bolts in the proper tight-
ening sequence as shown.
EAS2GBB344REMOVING THE FUEL SENDER
1. Remove:
• Fuel sender
ECA
NOTICE
Do not drop the fuel sender or give it a
strong shock.
EAS2GBB345CHECKING THE FUEL SENDER
1. Disconnect:
• Fuel pump coupler
• Fuel sender coupler
(from the wire harness)
2. Disconnect:
• Starter motor lead
(from starter relay)
3. Remove:
• Fuel tank
4. Remove:
• Fuel sender
(from the fuel tank)5. Connect:
• Fuel sender coupler
6. Push the start switch.
7. Check:
• Fuel level warning light
Out of specification Replace the fuel
sender.
EAS2GBB346INSTALLING THE FUEL SENDER
1. Install:
• Fuel sender gasket
• Fuel sender
TIP
• Do not damage the installation surfaces of the
fuel tank when installing the fuel sender.
• Always use a new fuel sender gasket.
• Install the fuel sender as shown in the illustra-
tion.
• When install the fuel sender, make sure that
the projection “a” faces the rear of the vehicle.
EAS2GBB347INSTALLING THE FUEL TANK
1. Install:
• Fuel tank
a
b
4 1
2
6
53
Fuel pump is atmosphere “A”
Fuel level warning light is come on
Fuel pump is soaked in fuel “B”
Fuel level warning light is goes off
Fuel sender bolts
4.0 Nm (0.40 m·kgf, 2.9 ft·lbf)
New
T R..
a
Page 357 of 432
SIGNALING SYSTEM
9-21
1. Joint connector
2. Joint connector
3. Joint connector
7. Main relay
9. Battery
10.Frame ground
11.Starter relay
12.Main fuse
15.Indicator light
17.Fuel level warning light
18.Resistor
19.Fuel sender
22.ECU (engine control unit)
30.Joint connector
42.Joint connector
46.Speed sensor
47.Multi-function display
48.Frame ground
Page 359 of 432
SIGNALING SYSTEM
9-23
The fuel level warning light fails to come on.
1. Check the fuel sender.
Refer to “CHECKING THE FUEL
SENDER” on page 9-77.NG
Replace the fuel sender assembly.
OK
2. Check the resistor.
Refer to “CHECKING THE RESIST-
ER” on page 9-78.NG
Replace the resistor.
OK
3. Check the entire signaling system’s
wiring.
Refer to “CIRCUIT DIAGRAM” on
page 9-20.NG
Properly connect or repair the signaling
system’s wiring.
OK
Replace the indicator light assembly.
Page 365 of 432
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
9-29
1. Joint connector
2. Joint connector
3. Joint connector
4. AC magneto
7. Main relay
9. Battery
10.Frame ground
11.Starter relay
12.Main fuse
15.Indicator light
16.Engine trouble warning light
22.ECU (engine control unit)
25.Injector
30.Joint connector
31.Intake air temperature sensor
32.Coolant temperature sensor
33.Throttle position sensor
34.Intake air pressure sensor
35.Lean angle sensor
36.Engine stop switch
37.Neutral switch
38.Diode
39.Starting circuit cut-off relay
40.Clutch switch
42.Joint connector
48.Frame ground
Page 366 of 432

FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
9-30
EAS2GBB374ECU SELF-DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION
The ECU is equipped with a self-diagnostic function in order to ensure that the fuel injection system
is operating normally. If this function detects a malfunction in the system, it immediately operates the
engine under substitute characteristics and illuminates the engine trouble warning light to alert the
rider that a malfunction has occurred in the system. Once a malfunction has been detected, a fault
code number is stored in the memory of the ECU.
• To inform the rider that the fuel injection system is not functioning, the engine trouble warning light
flashes while the start switch is being pushed to start the engine.
• If a malfunction is detected in the system by the self-diagnostic function, the ECU provides an ap-
propriate substitute characteristic operation, and alerts the rider of the detected malfunction by illu-
minating the engine trouble warning light.
Engine trouble warning light indication and fuel injection system operation
* The warning light flashes when any one of the following conditions is present and the start switch
is pushed:
Checking the engine trouble warning light
The engine trouble warning light comes on for around 2 seconds when pushing the start switch to
turn on the meter light and the engine trouble warning light comes on while the start switch is being
pushed.Warning light indica-
tionECU operationFuel injection opera-
tionVehicle operation
Flashing* Warning provided
when unable to start
engineOperation stopped Cannot be operated
Remains on Malfunction detected Operated with substi-
tute characteristics in
accordance with the
description of the mal-
functionCan or cannot be oper-
ated depending on the
fault code
12: Crankshaft position sensor 41: Lean angle sensor
(open or short circuit)
30: Lean angle sensor
(latch up detected)50: ECU internal malfunction
(faulty ECU memory)
33: Ignition coil
(Malfunction detected in the primary wire
of the ignition coil)
a. The meter light does not come on.
b. The meter light comes on.
c. Light OFF
d. Light ON for 2 seconds
ab
cdc
Page 367 of 432

FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
9-31
ECU detects an abnormal signal from a sensor
If the ECU detects an abnormal signal from a sensor while the vehicle is being driven, the ECU illu-
minates the engine trouble warning light and provides the engine with alternate operating instructions
that are appropriate for the type of malfunction.
When an abnormal signal is received from a sensor, the ECU processes the specified values that are
programmed for each sensor in order to provide the engine with alternate operating instructions that
enable the engine to continue operating or stop operating, depending on the conditions.
EAS2GBB375TROUBLESHOOTING METHOD
The engine operation is not normal and the engine trouble warning light comes on.
1. Check:
• Fault code number
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the Yamaha diagnostic tool. Refer to “YAMAHA DIAGNOSTIC TOOL” on page 9-32.
b. Check the fault code number displayed on the Yamaha diagnostic tool.
c. Identify the faulty system with the fault code number.
d. Identify the probable cause of the malfunction.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
2. Check and repair the probable cause of the malfunction.
3. Perform the reinstatement action for the fuel injection system. Refer to “Confirmation of service
completion” in the appropriate table in “TROUBLESHOOTING DETAILS” on page 9-35.
4. After pushing the engine stop switch, push the start switch to check whether the fault code number
is displayed.
TIP
If another fault code number is displayed, repeat steps (1) to (4) until no fault code number is dis-
played.
5. Erase the malfunction history in the diagnostic mode. Refer to “SENSOR OPERATION TABLE”
(Diagnostic code No.62).
TIP
Turning off the meter light will not erase the malfunction history.
The engine operation is not normal, but the engine trouble warning light does not come on.
1. Check the operation of the following sensors and actuators in the diagnostic mode. Refer to
“TROUBLESHOOTING DETAILS” on page 9-35.
If a malfunction is detected in the sensors or actuators, repair or replace all faulty parts.
If no malfunction is detected in the sensors and actuators, check and repair the inner parts of the
engine.Fault code No. No fault code No.
Check and repair. Refer to “TROUBLESHOOT-
ING DETAILS” on page 9-35.
Monitor the operation of the sensors and actua-
tors in the diagnostic mode. Refer to “TROU-
BLESHOOTING DETAILS” on page 9-35 and
“LIST OF SELF-DIAGNOSTIC AND FAIL-SAFE
ACTIONS” on page 10-5.Check and repair.
01: Throttle position sensor signal (throttle angle)
30: Ignition coil
36: Injector