Page 13 of 90

13
1
2
3
4
5
6
2.4.2 Position markers
2.4.2.1 Selected map location (Cursor) and selected map object
You can mark a map location in the following ways:
•
Select the map during route guidance.
•
Select the map when asked so that the destination can be confirmed after the
search is completed.
•
Select the destination from the map. (page 54)
When a map location is selected, the Cursor appears at the selected point on the
map. A symbol
with a combined crosshair and red circle is displayed for easy
visibility of any map scale size.
The location of the Cursor can be used as the destination of the route.
You can search for a POI (point of interest), or you can save it as one of your
Favorites destinations.
You can also select some of the objects on the map. If you select the map at the icon
of a POI (point of interest) or a traffic event, the object will be selected. You can
then get information about this object or use it as a route point.
Some functions are not available depending on some countries and regions.
2.4.3 Objects
on the map
2.4.3.1 Streets and roads
The navigation system shows the roads in different widths and colors so that they
can be easily identified. A
highway/freeway will be thicker and a different color than
a small street.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 132015/02/20 15:09:07
Page 16 of 90

16
2.4.3.3 Lane
information and Signposts
When navigating on multilane roads, it is important to take the appropriate lane
in order to follow the recommended route. If lane information is available in
the map data, the navigation system displays the lanes and their directions using
small arrows at the bottom of the map. Highlighted arrows represent the lanes and
direction you need to take.
Lane guidance is provided constantly if there is map information. Signposts are
displayed at the top of the map. The color and style of the signposts are similar
to the real ones you see above road or by the roadside. They show the available
destinations and the number of the road the lane leads to.
When navigating a route, only the signpost that points to the lane(s) to be taken is
displayed in bright colors; all others are darker
. All signposts and lane guidance
arrows are displayed in vivid colors while driving (when there is no recommended
route).
If you want to hide the currently displayed signposts, touch anywhere and the
normal Map screen returns until new signpost information is received.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 162015/02/20 15:09:07
Page 19 of 90

19
1
2
3
4
5
6
2.4.3.6 Elements of the active route
The navigation system shows the route in the following way:
Symbol NameDescription
Current car position
markerIf there is a road close by, a blue-colored
arrow symbol moves to the road which is the
closest.
The red mark present around a blue-colored
arrow symbol indicates the correct GPS
information. It may be indicated away from
the road because there is no existing road
information.
Waypoint
(intermediate
destination) An intermediate destination of the route
before reaching the final destination.
Destination (end
point)
The final destination of the route.
Route color The route always stands out with its color on the map, both in daytime and in nighttime
mode.
Streets and roads
that are excluded
from the navigation You can choose whether you want to use or
avoid certain road types (page 80). However,
when the navigation system cannot avoid
such roads, the route will include them and
it will show them in a color that is different
from the route color.
Streets and roads
that are affected by
traffic events Road segments may be affected by traffic
events received. These streets and roads are
displayed in an alternate color, and small
symbols displayed along the route show the
type of traffic event.
Some functions are not available depending on some countries and regions.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 192015/02/20 15:09:07
Page 20 of 90
20
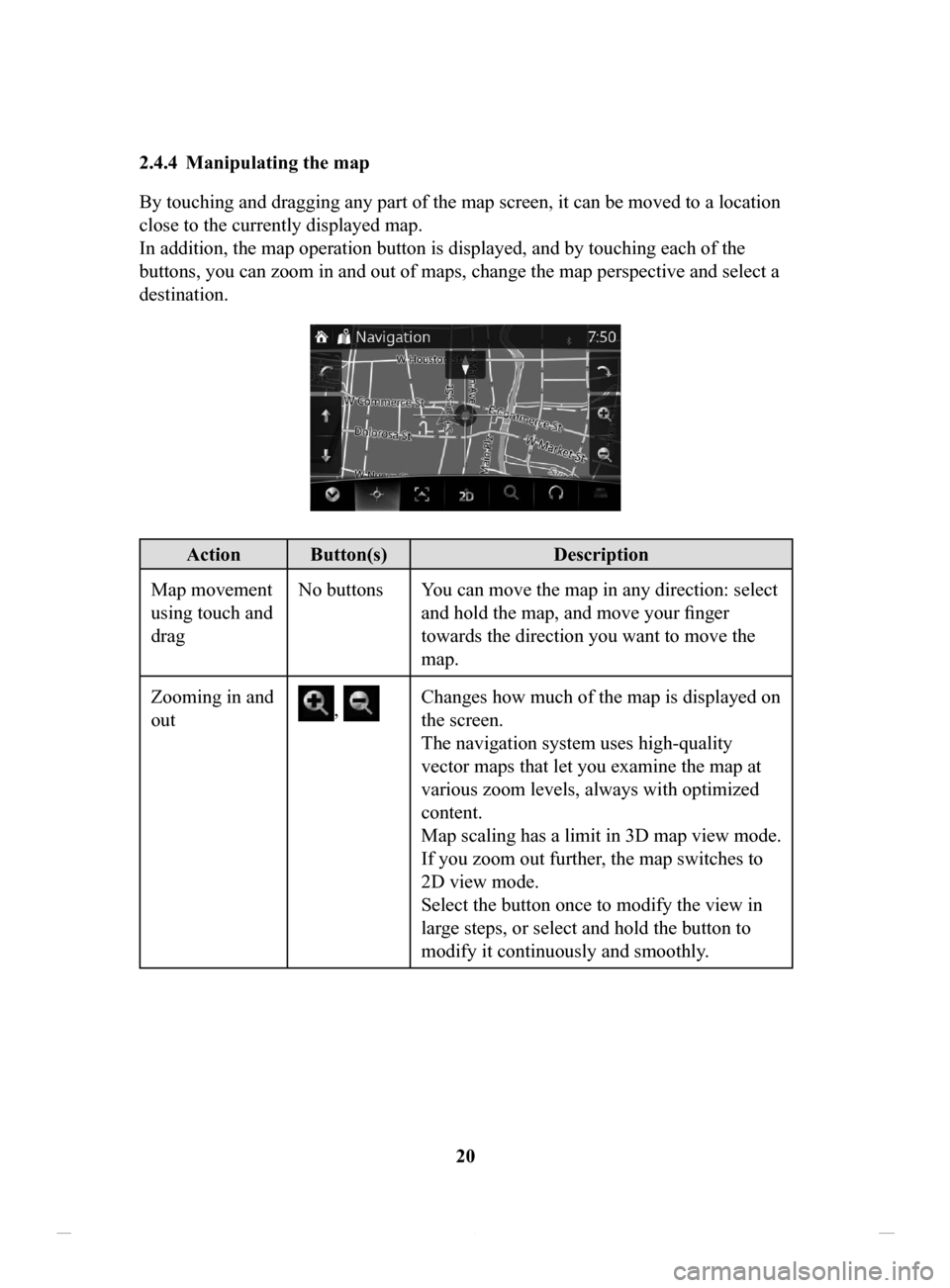
2.4.4 Manipulating
the map
By touching and dragging any part of the map screen, it can be moved to a location
close to the currently displayed map.
In addition, the map operation button is displayed, and by touching each of the
buttons, you can zoom in and out of maps, change the map perspective and select a
destination.
Action Button(s) Description
Map movement
using touch and
drag No buttons You can move the map in any direction: select
and hold the map, and move your finger
towards the direction you want to move the
map.
Zooming in and
out
, Changes how much of the map is displayed on
the screen.
The navigation system uses high-quality
vector maps that let you examine the map at
various zoom levels, always with optimized
content.
Map scaling has a limit in 3D map view mode.
If you zoom out further, the map switches to
2D view mode.
Select the button once to modify the view in
large steps, or select and hold the button to
modify it continuously and smoothly.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 202015/02/20 15:09:07
Page 21 of 90

21
1
2
3
4
5
6
Action Button(s)Description
Tilting up and
down
, Changes the vertical view angle of the map in
3D mode.
Select the button once to modify the view in
large steps, or select and hold the button to
modify it continuously and smoothly.
Rotating left
and right
, Changes the horizontal view angle of the map.
Select the button once to modify the view in
large steps, or select and hold the button to
modify it continuously and smoothly.
Compass
The direction of the compass shows North.
Select the button to switch to North-up view,
and then select again to rotate the map in the
previous direction.
Open/close
, The UMP (menu bar) is displayed on the
lower part of the screen.
Hides the displayed UMP if the UMP has been
displayed.
Select
destination
Select this button to select the Cursor as a
new destination. The route is automatically
calculated.
Return to
normal
navigation
Select this button to move the map back to
follow the current GPS position. Automatic
map rotation is also re-enabled.
The map manipulation buttons disappear and
navigation continues.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 212015/02/20 15:09:08
Page 24 of 90
24
3 On-road navigation
You can set up your route in different ways:
If you need a route for immediate navigation, you can select the destination and start
navigating to it right away (normal navigation).
You can plan routes with multiple destinations. Select the first destination. Then
select a second destination and add it to your route to create a multi-point route. You
can add as many destinations to your route as you like.
3.1 Selecting the destination of a route
The navigation system offers you several ways of choosing your destination:
•
Enter a full address or a part of an address (page 25).
•
Select a POI (point of interest) from a database as your destination (page 38).
•
Searches the destination from the map (page 54).
•
Use a previously saved Favorite destination (page 56).
•
Select a location from the History of previously used destinations (page 58).
•
Enter the coordinate of the destination (page 60).
There are other convenient functions.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 242015/02/20 15:09:08
Page 25 of 90
25
1
2
3
4
5
6
3 On-road navigation
You can set up your route in different ways:
If you need a route for immediate navigation, you can select the destination and start
navigating to it right away (normal navigation).
You can plan routes with multiple destinations. Select the first destination. Then
select a second destination and add it to your route to create a multi-point route. You
can add as many destinations to your route as you like.
3.1 Selecting the destination of a route
The navigation system offers you several ways of choosing your destination:
• Enter a full address or a part of an address (page 25).
• Select a POI (point of interest) from a database as your destination (page 38).
• Searches the destination from the map (page 54).
• Use a previously saved Favorite destination (page 56).
• Select a location from the History of previously used destinations (page 58).
• Enter the coordinate of the destination (page 60).
There are other convenient functions.
3.1.1 Entering an address or a part of the address
If you know at least a part of the address, it is the quickest way to select the
destination of the route.
Using the same screen, you can find an address by entering:
•
Destination address
•
The center of a city
•
An intersection
•
The midpoint of a street
If an address or part of a facility name is input, a search candidate list including
the input characters is displayed. The greater the number of characters input the
more the list is refined.
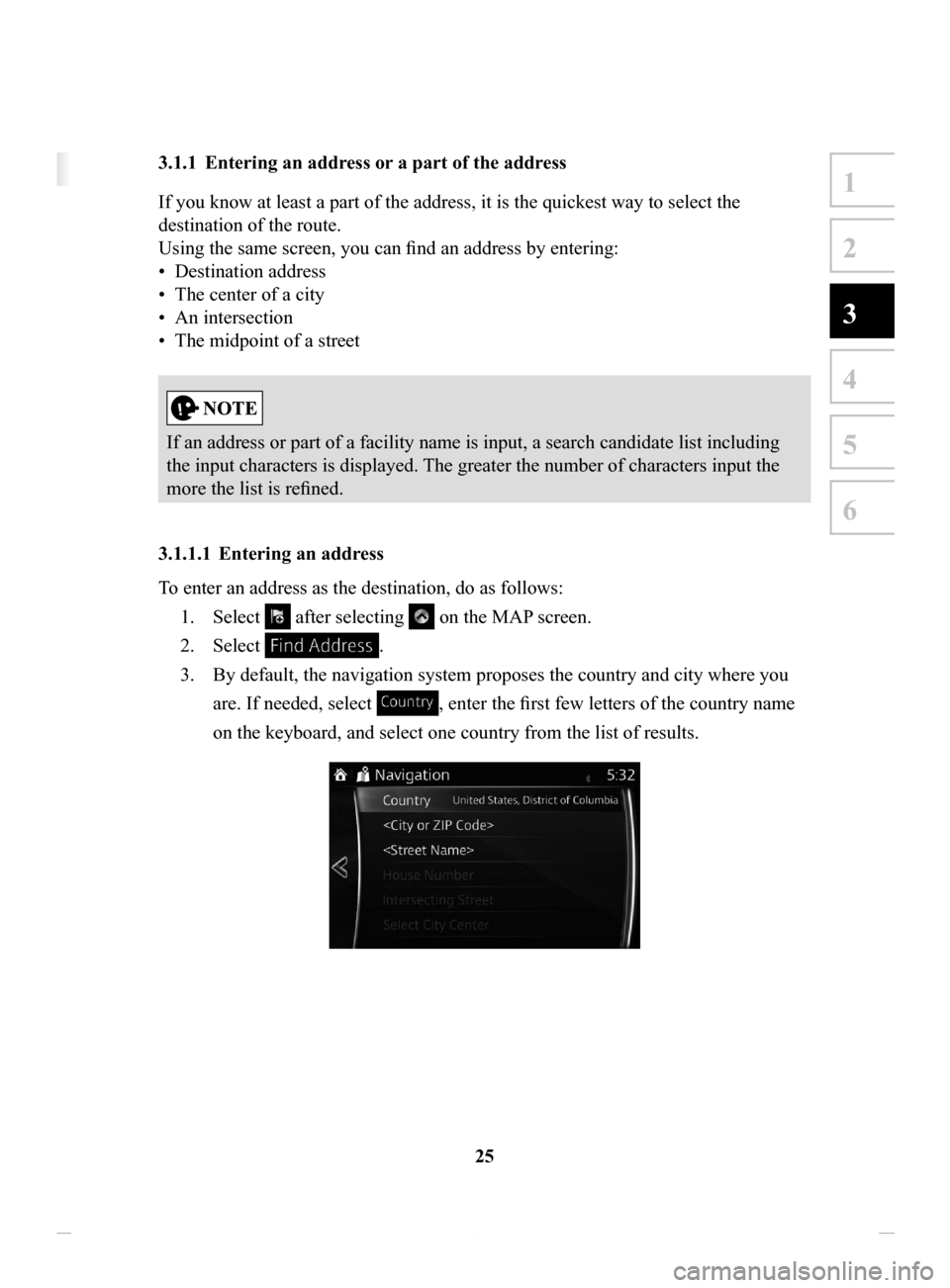
3.1.1.1 Entering
an address
To enter an address as the destination, do as follows: 1.
Select after selecting on the MAP screen.
2.
Select .
3.
By default, the navigation system proposes the country and city where you
are. If needed, select
, enter the first few letters of the country name
on the keyboard, and select one country from the list of results.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 252015/02/20 15:09:08
Page 29 of 90
29
1
2
3
4
5
6
8. Navigation starts if is selected, or after 10 seconds of no user
interaction.
By touching the location displayed on the screen, you can verify the route.
Additionally, the route can be revised by selecting other options.
NAV-12AVUAE.indb 292015/02/20 15:09:09