2015 SKODA OCTAVIA ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 137 of 268

Assist systems
General information
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Radar sensor
135WARNINGThe following general information regarding the use of assistance systems
must be observed.■
The assistance systems only serve to support and do not relieve the driv-
er of the responsibility for driving the vehicle.
■
The increased safety provision, as well as the increased occupant protec-
tion provided by the assistance systems must not tempt you to take risks -
risk of accident!
■
Adjust the speed and driving style to the current visibility, weather, road
and traffic conditions.
■
The assistance systems have physical and system-related limitations. For
this reason, the driver may experience some undesired or delayed system
responses in certain situations. You should therefore always be alert and
ready to intervene!
■
Only activate, deactivate or set the assistance systems so that you have
the vehicle fully under control in every traffic situation - risk of accident!
Radar sensor
Fig. 154
Mounting location of the radar
sensor
Read and observe on page 135 first.
The radar sensor » Fig. 154 (From here on referred to as sensor) is used to as-
sess the traffic situation in front of the vehicle.
The sensor can distinguish objects by radiating and receiving electromagnetic waves.
The sensor is a component of the ACC » page 150 and Front Assist
» page 155 systems.
The sensor function may be impaired in the events of one of the following. ▶ The sensor is soiled by mud, snow and the like.
▶ The area in front and around the sensor is obscured by labels, auxiliary lights
and similar.
▶ When visibility is poor, (e.g. fog, heavy rain, thick snowfall).
If the sensor is covered or dirty, the corresponding message appears in the in-
strument cluster display for the ACC system » page 155 or Front Assist system
» page 157 .
WARNING■
If you suspect that the sensor is damaged, deactivate the ACC system
» page 150 and Front Assist system » page 155. Have the sensor checked
by a specialist garage.■
The sensor can become misaligned by collisions or by damage to the front
of the vehicle, the wheel arch or the underside of the vehicle. This can lead
to impaired function of the sensor - risk of accidents! Have the sensor
checked by a specialist garage.
■
The area in front and around the sensor should not be obscured by labels,
auxiliary lights and similar. This can lead to impaired function of the sensor
- risk of accidents!
CAUTION
Remove the snow with a brush and the ice with a solvent-free de-icer.
Braking and stabilisation systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Stability Control (ESC)
136
Anti-lock braking system (ABS)
136
135Assist systems
Page 139 of 268

During a TCS intervention, the indicator light flashes in the instrument clus-
ter.
Activating/deactivating TCS
The activation or deactivation of TCS can be done, depending on equipment, in
one of the following ways. ▶ Infotainment » Owner´s Manual Infotainment , chapter CAR - vehicle set-
tings .
▶ By briefly pressing the symbol key
» Fig. 155 .
▶ By briefly pressing the symbol key
» Fig. 155 .
Upon deactivation, in the instrument cluster the indicator light
lights up and
the display shows the following message.Traction control (ASR) deactivated.ASR OFF
Upon activation, in the instrument cluster the indicator turns and the display
shows the following message.
Traction control (ASR) activated.ASR ON
The TCS should normally always be enabled. The system should be deactivated
only in the following situations, for example. ▶ When driving with snow chains.
▶ When driving in deep snow or on a very loose surface.
▶ When it is necessary to “rock” a car free when it has become stuck.
Note
On vehicles without the ESC system, the warning light does not illuminate
upon deactivation of the TCS system, but a message is only displayed on the
display of the instrument cluster.
Electronic differential lock (EDL and XDS)
Read and observe
on page 136 first.
EDL
EDL prevents the turning of the respective wheel of the driven axle. EDL
brakes the spinning wheel, if necessary, and transmits the driving force to the
other driving wheel. Driving becomes easier on road surfaces with different
traction under each wheel of the driven axle.
EDL switches off automatically to avoid excessive heat generation on the
brake of the wheel being braked. Once the brakes have cooled down, there is
an automatic re-activation of EDL.
XDS
XDS is an extension to the electronic differential lock. XDS does not respond to
traction, but to the load relief of the inner front wheel of the driving axle dur-
ing fast cornering.
The automatic brake intervention on the brake of the wheel with reduced load
prevents the wheel from spinning. Thus, the traction is improved and the vehi-
cle can continue to follow the desired track.
Driver Steering Recommendation (DSR)
Read and observe
on page 136 first.
The DSR indicates to the driver in critical situations a steering recommenda-
tion in order to stabilise the vehicle. The DSR is activated, for example, on the
right and left vehicle side when braking sharply on different road surfaces.
Brake Assist (HBA)
Read and observe
on page 136 first.
HBA increases the braking effect and helps to shorten the braking distance.
The HBA is activated by the very quick operation of the brake pedal. To ach-
ieve the shortest possible braking distance, the brake pedal must be applied
firmly until the vehicle has come to a complete standstill.
The HBA is automatically switched off when the brake pedal is released.
Hill Start Assist (HHC)
Read and observe
on page 136 first.
HHC allows you, when driving on slopes, to move your foot from the brake
pedal to the accelerator pedal without having to use the handbrake.
The system holds the brake pressure produced by the activation of the brake pedal for approx. 2 seconds after the brake pedal is released.
The HHC is active from a 5% slope if the driver's door is closed. HHC is always
active on slopes when in forward or reverse start off.
137Assist systems
Page 146 of 268

The area behind the vehicle is displayed when the following conditions are
met.
The ignition is switched on.
Reverse gear is engaged. 1)
The luggage compartment lid is completely closed.
The vehicle is not travelling at more than about 10 km/h.
Note
■ The display can be interrupted by pressing the symbol key » Fig. 158 on
page 141 .■
After disengaging the reverse gear, automatic display of the parking aid is
carried out (variant 2, 3) » page 141.
Guidelines and function keys
Fig. 163
Infotainment display: Orientation lines / function keys
Read and observe
and on page 143 first.
Orientation lines are shown along with the monitored area behind the vehicle
in the display.
Distance of the orientation lines behind the vehicle » Fig. 163
The distance is about 40 cm (safety distance limit).
The distance is approximately 100 cm.
The distance is approximately 200 cm.
The distance between the side lines corresponds approximately to the vehicle width including mirrors.
ABCFunction buttons » Fig. 163
Turns off the display of the area behind the vehicle.
Display settings - brightness, contrast, colour. Switching audible parking signals on/off.
Enabling and reduced park assistance display.
Change to park assistance display.
CAUTION
The objects shown in the display can be closer or even further away than they
appear. This is especially the case in the following situations.■
Protruding objects, such as a hitch, the rear of a truck and the like.
■
When driving from a horizontal surface into a slope or a depression.
■
When driving from a slope or a depression onto a horizontal surface.
Note
The orientation lines are immobile, and therefore the spacing of the bars be-
hind the vehicle will vary, depending on the vehicle load state and the road in-
clination.
Park Assist
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Functioning
145
Parking space search
146
Parking
146
Departing from a parallel parking space
147
Automatic brake assist
147
Information messages
147
Park Assist (hereinafter referred to as system) helps drivers park in suitable
parallel and perpendicular parking places or also to manoeuvre out of parallel
parking spaces.
The system takes over the steering movements when parking or leaving a
parking space. The driver operates the pedals and the shift lever or gear selec-
tor.
1)
The area behind the vehicle can be displayed for a few seconds more after disengaging the reverse gear.
144Driving
Page 152 of 268
NoteDuring control, speed can be increased by pressing the accelerator pedal. Re-
leasing the accelerator pedal will cause the speed to drop again to the set
speed.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
150
Automatic stop-start
151
Operation Overview
152
Start control
152
Stop/resume control
152
Set/change the desired speed
153
Set the clearance level
153
Special driving conditions
154
Information messages
155
The automatic distance control (hereinafter referred to as ACC) maintains the
set speed or the distance to the vehicle ahead without the accelerator or
brake pedal being pressed.
The front of the vehicle and the distance to the vehicle ahead is monitored by
a radar sensor » page 135.
The state in which the ACC maintains the speed or the proximity is described
as control from here on.
WARNING■
The general information relating to the use of assistance systems must
be observed » page 135, in section Introduction .■
The driver must always be ready to take over steering of the vehicle him-
self (accelerate or brake).
■
The ACC does not react when approaching a stationary obstacle, such as
traffic jams, vehicle breakdowns or vehicles waiting at a traffic light.
■
The ACC does not respond to crossing or oncoming objects.
■
If the ACC does not decelerate fast enough, immediately apply the vehi-
cle's foot brake.
WARNINGFor safety reasons, do not use the ACC under the following conditions.■When driving in turning lanes, motorway exits or construction sites, to
avoid an unwanted acceleration to the stored speed.■
When visibility is poor, (e.g. fog, heavy rain, thick snowfall).
■
When road conditions are poor (e.g. ice, slippery road, gravel, dirt road).
■
When driving around “sharp” bends.
■
When riding on a steep gradient / high slope.
■
When driving through places where metal objects (such as metal build-
ings, railroad tracks, etc.) can be found.
■
When driving through very divided and enclosed spaces (such as large-ca-
pacity garages, car ferries, tunnels and the like.).
Note
■ The ACC is designed primarily for use on motorways.■The ACC reduces the speed by automatically releasing the accelerator or by
means of a braking procedure as appropriate. If the brakes are used for an au-
tomatic speed reduction at any moments, then the brake light illuminates.■
In case of failure of more than one brake light on the vehicle or on the con-
nected trailer, the ACC becomes unavailable.
■
The control automatically cancels the engagement of the brake supportive
assistance systems (e.g. ESC) or when the maximum permitted engine speed is
exceeded.
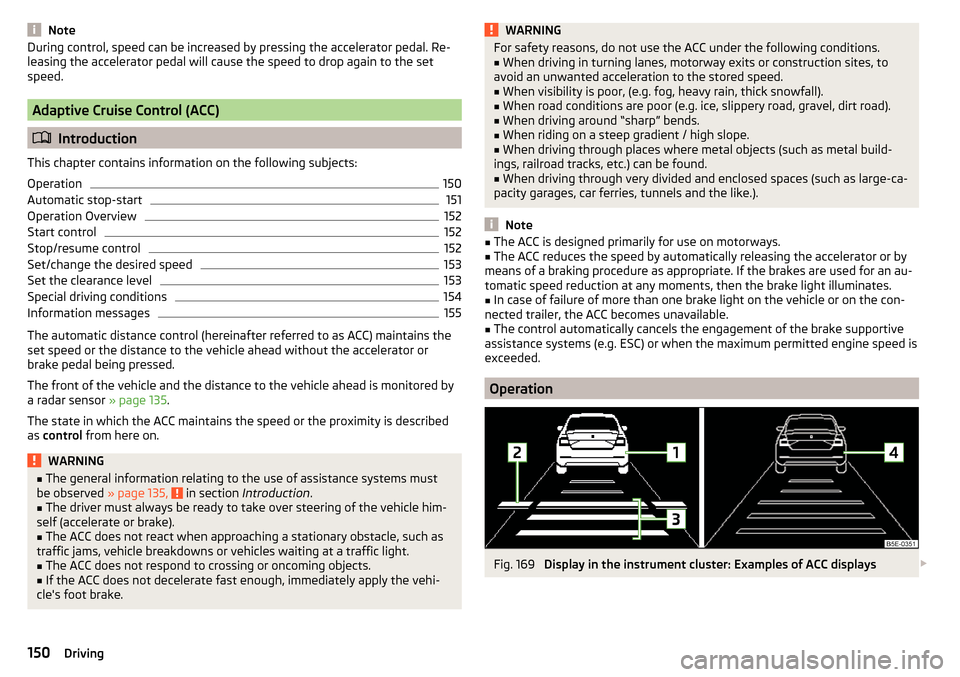
Operation
Fig. 169
Display in the instrument cluster: Examples of ACC displays
150Driving
Page 153 of 268

Fig. 170
Instrument cluster display: Examples of ACC status displays
Read and observe
on page 150 first.
The ACC allows a speed of 30 - 160 km/h to be set or a distance to the preced- ing vehicle to be very short of very long to be set.
The ACC adjusts the set speed with respect to the detected vehicle ahead,
thus maintaining the selected proximity.
The ACC can detect a vehicle that is up to approx. 120 m ahead using the radar sensor.
ACC display » Fig. 169
Vehicle detected (control active).
Line showing the displacement of the distance when setting » page 153,
Set the clearance level .
Set distance to the vehicle ahead.
Vehicle detected (control deactivated).
ACC status displays » Fig. 170
Regulation is inactive (in the colour display the digits of speed limits is
shown in grey).
Regulation active - no vehicle detected (in the colour display the digits of
the speed limits are highlighted).
Control deactivated - no speed stored.
Regulation active - vehicle detected (in the colour display the digits of the
speed limits are highlighted).
1234Note to reduce speed
If the delay of the ACC is insufficient in relation to the vehicle in front, in the
instrument cluster, the warning light
lights up and the display shows the
following message.Apply the brake!
Note
Some ACC notifications in the display of the instrument cluster may be hidden
by notifications for other functions. An ACC notification automatically appears
for a brief moment when there is a change in status of the ACC.
Automatic stop-start
Read and observe
on page 150 first.
Vehicles with an automatic transmission can decelerate to a standstill and
start moving again using the ACC.
Decelerate to a standstill
If a vehicle ahead decelerates to a standstill, the ACC will also decelerate your
vehicle to a standstill.
Starting to drive again after a holding period
As soon as the vehicle ahead starts moving again after a holding period, your
vehicle will also move and the speed will continue to be regulated. Control is
automatically disconnected in case of longer holding periods.
Depress the brake pedal.
151Assist systems
Page 154 of 268

Operation OverviewFig. 171
Operating lever
Read and observe
on page 150 first.
Overview of ACC functions operated with the lever » Fig. 1711Activate ACC (control deactivated)2Start control (resume) / increase speed by 1 km/h at a time
(sprung position)3Interrupt control (sprung position)4Deactivate ACC5 Increase speed by 10 km/h at a time6 Decrease speed by 10 km/h at a timeA Set proximity levelBStart control (adopt current speed) / Reduce speed by 1 km/h at
a time
Note
If the lever is set » Fig. 171 from the position directly into the sprung posi-
tion, the current speed is stored and the control process is started.
Start control
Read and observe
on page 150 first.
Basic requirements for start of control ACC is enabled.
TCS is enabled » page 135, Braking and stabilisation systems .
On vehicles with a manual transmission , the second gear or higher must
be engaged.
On vehicles with an automatic transmission , the selector lever must be in
the D/S position or in the Tiptronic position.
On vehicles with a manual transmission , the current speed must be higher
than approx. 25 km/h.
On vehicles with a automatic transmission , the current speed must be
higher than approx. 2 km/h.
The control be started with the key
or by adjusting the lever
» Fig. 171
on page 152 into the sprung position.
Button ›
Press press.
The ACC will adopt the current speed and execute control.
Lever position
›
Set the lever into the sprung position set.
The ACC will adopt the current speed and execute control. Should the speed be stored already, the ACC adopts this speed and executes control.
The warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster when the regulation
is switched on.
Note
■ If control is started at a speed of less than 30 km/h on vehicles with an auto-
matic transmission, the speed of 30 km/h is stored. The speed increases auto-
matically to 30 km/h or is regulated with respect to the speed of the vehicle
ahead.■
When TCS is disabled, it will be activated automatically upon starting control.
■
If the TCS is deactivated during control, control is stopped automatically.
Stop/resume control
Read and observe
on page 150 first.
Stop control
›
Set the lever into the sprung position
» Fig. 171 on page 152 set.
Or
›
Apply the brake.
Control stops, the speed remains stored.
152Driving
Page 156 of 268

Special driving conditionsFig. 172
Special conditions: Cornering / narrow vehicles or vehicles travel-
ling side by side
Fig. 173
Special conditions: Lane changes of other vehicles / stationary
vehicles
Read and observe
on page 150 first.
The following and similar situations require special attention of the driver.
When cornering
When driving around long bends the ACC may respond to a vehicle in the adja-
cent lane » Fig. 172 -
. Your own vehicle is regulated with respect to this vehi-
cle and will no longer respond to the vehicle ahead.
In such cases, control should be disabled by accelerating, applying the brake or
pressing the button on the operating lever .
» Fig. 171 on page 152 .
Narrow vehicles or vehicles travelling side by side
Narrow vehicles or vehicles travelling side by side are not detected by the ra-
dar sensor until they are within the sensor's range » Fig. 172 -
.
If necessary, slow down the car by applying the brake.
Other vehicles changing lanes
Vehicles that change onto the lane with a small proximity » Fig. 173 -
do not
have to be detected by the radar sensor in time. The result may be a delayed
ACC response.
If necessary, slow down the car by applying the brake.
Stationary vehicles
The ACC does not detect stationary objects! When a vehicle detected by the
ACC turns or sheers off and there is a stationary vehicle in front of this vehicle,
» Fig. 173 -
the ACC does not respond to the stationary vehicle.
In such cases, take over the steering and stop the vehicle by applying the foot
brake.
When overtaking
When your vehicle is being controlled (the speed is lower than that which is
stored) and the indicator is activated, the ACC interprets this situation as
meaning that the driver intends to overtake. The ACC automatically acceler-
ates the vehicle, thereby reducing the proximity to a vehicle ahead.
If the vehicle changes to the fast lane and no vehicle is detected ahead, the
ACC accelerates until the set speed is reached and then keeps it constant.
Acceleration can be cancelled at any time by touch on the brake pedal or
pressing the button on the lever
» Fig. 171 on page 152 .
Vehicles with special load or special body parts
Other vehicles with a load or with body parts protruding from the sides, back
or top of the vehicle contour may not be detected by the ACC.
Control should therefore be disabled whenever you are driving behind or over-
taking such a vehicle.
Towing a trailer
When towing, or in when another accessory is connected to the trailer socket
the ACC control is set with a lower rate. The manner of driving should there-
fore be adapted to this limitation.154Driving
Page 157 of 268

Information messagesRead and observe
on page 150 first.
The information messages are shown in the instrument cluster display.
ACC: no sensor view!
The sensor is soiled or covered.
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine and clean the sensor or remove the
item causing the lack of visibility » Fig. 154 on page 135 .
If the message appears again after starting the engine, the position of the lev- er should be
» Fig. 171 on page 152 adjusted.
ACC not available.
The ACC is not available for an unknown reason.
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine and then start it again. If the ACC is still
not available, push the lever into position . Seek help from a specialist ga-
rage.
Error: ACC
There is an ACC system error.
Push the lever into position . press. Seek help from a specialist garage.
Speed limit
Increase the speed accordingly and start control
» page 152.
Front Assist
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
155
Distance warning (dangerous distance)
156
Warning and automatic braking
156
Disable/enable
156
Information messages
157The Front Assist (hereinafter referred to as system) warns you of the danger of
a collision with a vehicle or another obstacle in front of the vehicle, and tries to
avoid a collision or mitigate its consequences by automatically applying the
brakes where necessary.
The area in front of the vehicle is monitored by a radar sensor » page 135.WARNING■
The general information relating to the use of assistance systems must
be observed » page 135, in section Introduction .■
The system does not respond to crossing or oncoming objects.
CAUTION
In case of failure of more than one brake light on the vehicle or on the electri-
cally connected trailer, the system becomes unavailable.
Operation
Read and observe
and on page 155 first.
The system support is provided in the following manner.▶ Alerts you about a dangerous proximity to the vehicle ahead.
▶ Warns you of an impending collision.
▶ Prepares the brakes for emergency braking prior to a detected danger.
▶ Assists with a brake action triggered by the driver.
▶ If the driver fails to respond to a detected danger, automatic braking is per-
formed.
The system can work only if the following basic conditions are met. The system is activated.
TCS is enabled » page 135, Braking and stabilisation systems .
The vehicle is travelling forwards at a speed of more than approx. 5 km/h.
Note
The system can be impaired or may not be available, for example when driving
in “sharp ”curves or with an ESC engagement » page 136.155Assist systems