Page 20 of 360
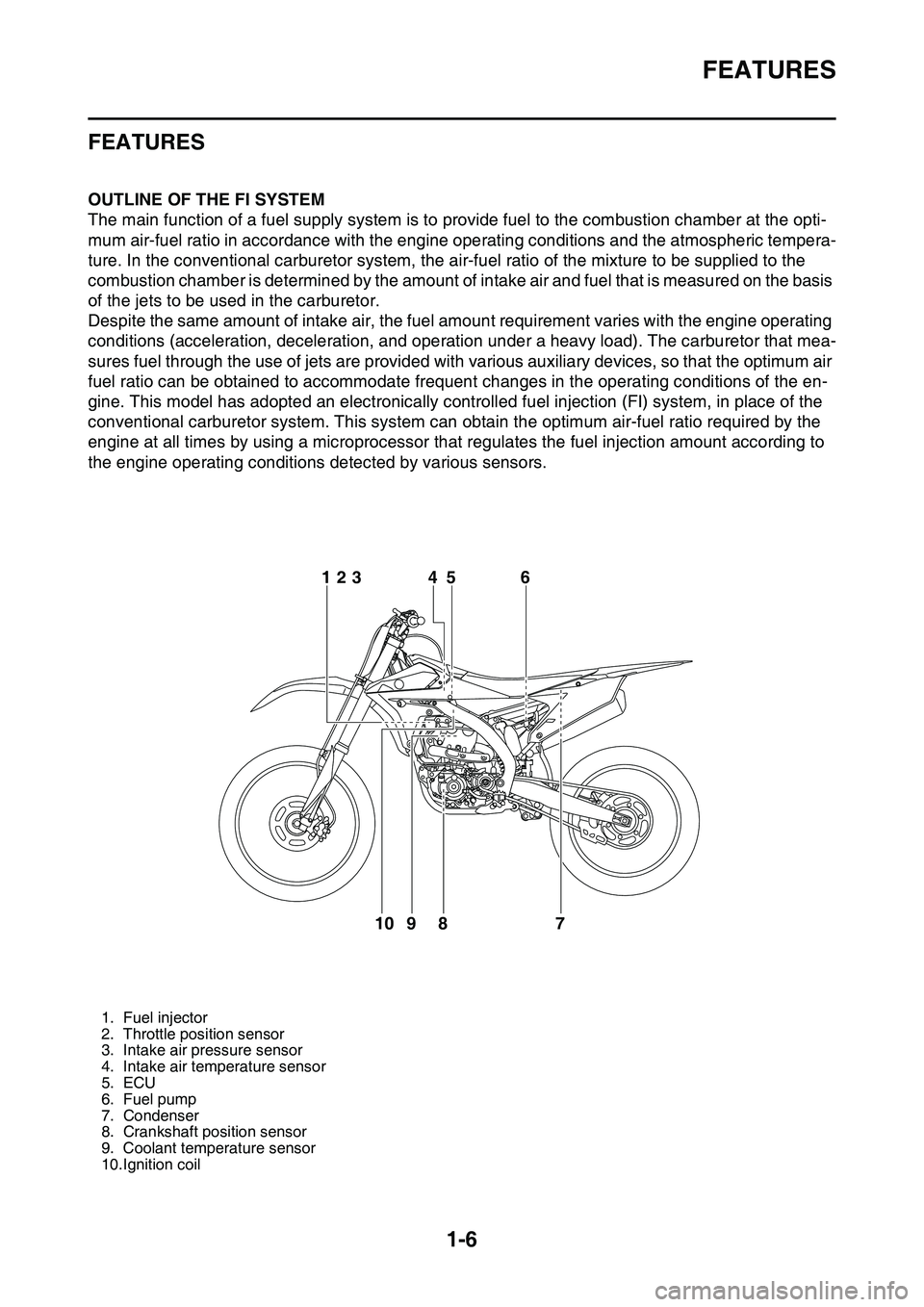
FEATURES
1-6
EAS20170
FEATURES
EAS1SL1014OUTLINE OF THE FI SYSTEM
The main function of a fuel supply system is to provide fuel to the combustion chamber at the opti-
mum air-fuel ratio in accordance with the engine operating conditions and the atmospheric tempera-
ture. In the conventional carburetor system, the air-fuel ratio of the mixture to be supplied to the
combustion chamber is determined by the amount of intake air and fuel that is measured on the basis
of the jets to be used in the carburetor.
Despite the same amount of intake air, the fuel amount requirement varies with the engine operating
conditions (acceleration, deceleration, and operation under a heavy load). The carburetor that mea
-
sures fuel through the use of jets are provided with various auxiliary devices, so that the optimum air
fuel ratio can be obtained to accommodate frequent changes in the operating conditions of the en
-
gine. This model has adopted an electronically controlled fuel injection (FI) system, in place of the
conventional carburetor system. This system can obtain the optimum air-fuel ratio required by the
engine at all times by using a microprocessor that regulates the fuel injection amount according to
the engine operating conditions detected by various sensors.
EAS1SL1015
1. Fuel injector
2. Throttle position sensor
3. Intake air pressure sensor
4. Intake air temperature sensor
5. ECU
6. Fuel pump
7. Condenser
8. Crankshaft position sensor
9. Coolant temperature sensor
10.Ignition coil
6
7 8 95 4 123
10
Page 31 of 360

SPECIAL TOOLS
1-17
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
This tool is used to measure
the voltage, current, and re
-
sistance of electrical compo-
nents.
Timing light
90890-03141
YU-03141
This tool is used to measure
the ignition timing.
Pressure gauge
90890-03153
YU-03153
This tool is used to measure
the fuel pressure.
Yamaha diagnostic tool
90890-03215
This tool is used to check er-
ror codes or carry out self-di-
agnosis.
Fuel pressure adapter
90890-03186
YM-03186
This tool is used to mount the
pressure gauge.
Test harness S-pressure
sensor (3P)
90890-03207
YU-03207
This tool is used to check the
throttle position sensor input
voltage.
FI diagnostic tool sub-lead
90890-03212
YU-03212
This tool is used to connect
the Yamaha diagnostic tool
to a battery.
Valve guide remover & in-
staller set (ø5.5)
90890-04016
This tool is used to replace
the valve guide.
Valve guide remover (5.5
mm)
YM-01122
Valve guide installer (5.5
mm)
YM-04015
Valve guide reamer (5.5 mm)
YM-01196
Tool name/Part number How to use Illustration
Page 33 of 360
SPECIAL TOOLS
1-19
Crankcase separating tool
90890-04152
YU-A9642
This tool is used to remove
the crankshaft.
Ignition checker
90890-06754
Oppama pet-4000 spark
checker
YM-34487
This tool is used to check the
spark performance of the ig
-
nition coil.
Digital tachometer
90890-06760
YU-39951-B
This tool is used to measure
the engine speed.
Three bond No.1215®
90890-85505
This sealant (Bond) is used
for crankcase mating sur
-
face, etc.
Tool name/Part number How to use Illustration
Page 55 of 360
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
2-12
EAS1SL1055
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Voltage
System voltage 12 V
Ignition system
Ignition system TCI
Advancer type Digital
Ignition timing (B.T.D.C.) 10.0 ° at 2000 r/min
Engine control unit
Model/manufacturer 1SL0/YAMAHA (USA) (CAN)
1SL1/YAMAHA (EUR) (JPN) (AUS) (NZL)
(ZAF)
Ignition coil
Minimum ignition spark gap 6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Primary coil resistance 2.16–2.64
Secondary coil resistance 8.64–12.96 k
AC magneto
Standard output 14.0 V, 95 W at 5000 r/min
Stator coil resistance 0.624–0.936
Rectifier/regulator
Regulator type Semi conductor-short circuit
No load regulated voltage 14.1–14.9 V
Rectifier capacity (DC) 23.0 A
Page 59 of 360
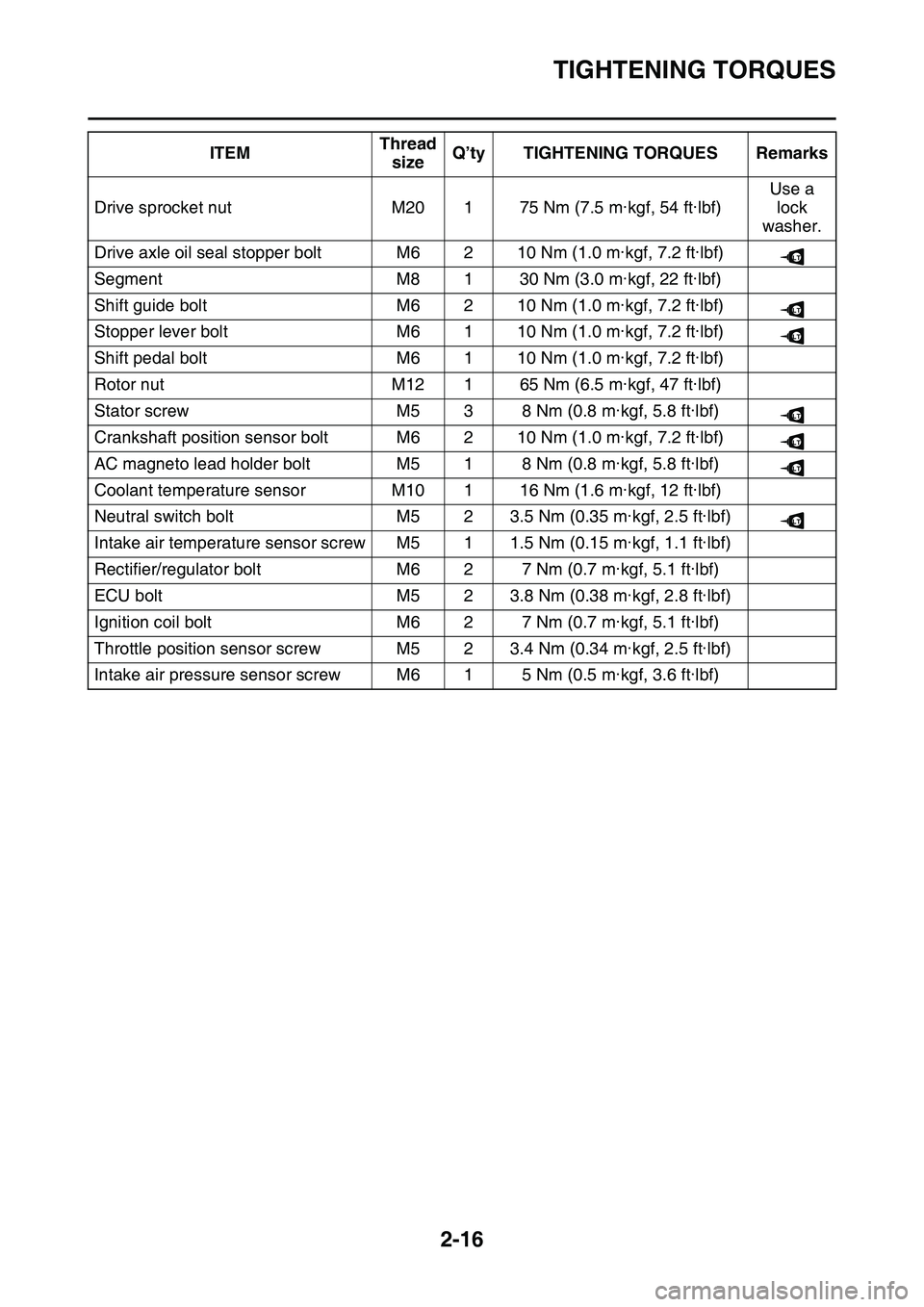
TIGHTENING TORQUES
2-16
Drive sprocket nutM20175 Nm (7.5 m·kgf, 54 ft·lbf)
Use a
lock
washer.
Drive axle oil seal stopper boltM6210 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
SegmentM8130 Nm (3.0 m·kgf, 22 ft·lbf)
Shift guide boltM6210 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Stopper lever boltM6110 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Shift pedal boltM6110 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Rotor nutM12165 Nm (6.5 m·kgf, 47 ft·lbf)
Stator screwM538 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Crankshaft position sensor boltM6210 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
AC magneto lead holder boltM518 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Coolant temperature sensorM10116 Nm (1.6 m·kgf, 12 ft·lbf)
Neutral switch boltM523.5 Nm (0.35 m·kgf, 2.5 ft·lbf)
Intake air temperature sensor screwM511.5 Nm (0.15 m·kgf, 1.1 ft·lbf)
Rectifier/regulator boltM627 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
ECU boltM523.8 Nm (0.38 m·kgf, 2.8 ft·lbf)
Ignition coil boltM627 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Throttle position sensor screwM523.4 Nm (0.34 m·kgf, 2.5 ft·lbf)
Intake air pressure sensor screwM615 Nm (0.5 m·kgf, 3.6 ft·lbf)
ITEMThread
sizeQ’ty TIGHTENING TORQUES Remarks
LT
LT
LT
LT
LT
LT
LT
Page 88 of 360
CHECKING THE WHEEL BEARINGS ..................................................... 3-33
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING THE STEERING HEAD .......................... 3-33
LUBRICATING THE LEVERS .................................................................. 3-34
LUBRICATING THE PEDAL .................................................................... 3-34
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM.................................................................................. 3-35
CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG .............................................................. 3-35
CHECKING THE IGNITION TIMING ........................................................ 3-35
Page 95 of 360

PRE-OPERATION INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
3-7
EAS1SL1067
PRE-OPERATION INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
Before riding for break-in operation, practice or a race, make sure the machine is in good operating
condition.
Before using this machine, check the following points.
EAS1SL1068GENERAL INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
TIP
Perform usual maintenance enough so that, in the race course, a confirmation of that and simple set-
ting adjustments may only be left, in order to get enough time to use effectively.
ITEMinspectPage
CoolantCheck that coolant is filled up to the radiator cap.
Check the cooling system for leakage.3-8 – 10
FuelCheck that a fresh gasoline is filled in the fuel tank.
Check the fuel line for leakage.1-22
Engine oilCheck that the oil level is correct. Check the crank-
case and oil line for leakage.3-14 – 16
Gear shifter and clutchCheck that gears can be shifted correctly in order and
that the clutch operates smoothly.3-10 – 11
Throttle grip/Housing
Check that the throttle grip operation and free play
are correctly adjusted. Lubricate the throttle grip and
housing, if necessary.
3-11 – 12
BrakesCheck the play of front brake and effect of front and
rear brake.3-21 – 27
Drive chainCheck drive chain slack and alignment. Check that
the drive chain is lubricated properly.3-27
4-64 – 65
WheelsCheck for excessive wear and tire pressure. Check
for loose spokes and have no excessive play.3-32 – 33
SteeringCheck that the handlebar can be turned smoothly and
have no excessive play.3-33 – 34
Front forks and rear
shock absorberCheck that they operate smoothly and there is no oil
leakage.3-28 – 32
Cables (wires)
Check that the clutch and throttle cables move
smoothly. Check that they are not caught when the
handlebars are turned or when the front forks travel
up and down.
—
Exhaust pipeCheck that the exhaust pipe is tightly mounted and
has no cracks.3-13 – 14
Rear wheel sprocketCheck that the rear wheel sprocket tightening bolt is
not loose.4-8 – 9
LubricationCheck for smooth operation. Lubricate if necessary. 3-12 , 3-34
Bolts and nutsCheck the chassis and engine for loose bolts and
nuts.1-25 – 26
Lead connectorsCheck that the AC magneto, ECU and ignition coil are
connected tightly.1-12 – 14
Settings
Is the machine set suitably for the condition of the rac-
ing course and weather or by taking into account the
results of test runs before racing? Are inspection and
maintenance completely done?10-1 – 8
Page 105 of 360

ENGINE
3-17
TIP
Get the high tension cord “1” of the ignition coil
pinched in the detector “a” of the digital tachom
-
eter.
4. Measure:
• Engine idling speed
Out of specification Regulate.
5. Adjust:
• Engine idling speed
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Turn the starter knob/idle screw “1” in the di-
rection of “a” or “b” to make an adjustment.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS1SL1088ADJUSTING THE VALVE CLEARANCE
TIP
• This section is intended for those who have
basic knowledge and skill concerning the ser
-
vicing of Yamaha motorcycles (e.g., Yamaha
dealers, service engineers, etc.). Those who
have little knowledge and skill concerning ser
-
vicing are requested not to undertake inspec-
tion, adjustment, disassembly, or reassembly
only by reference to this manual. It may lead to servicing trouble and mechanical damage.
• Make sure that the valve clearance is
checked or adjusted while the engine is cold
(at room temperature).
• While the valve clearance is checked or ad-
justed, make sure that the piston is positioned
in the top dead center (TDC).
1. Remove:
• Seat
• Side cover (left/right)
• Air scoop (left/right)
Refer to “GENERAL CHASSIS” on page 4-
1.
• Fuel tank
Refer to “FUEL TANK” on page 7-1.
•ECU
2. Remove:
• Spark plug
• Cylinder head cover
Refer to “CAMSHAFT” on page 5-11.
3. Remove:
• Timing mark accessing screw “1”
• Crankshaft end accessing screw “2”
• O-ring
4. Check:
• Valve clearance
Out of specification Regulate.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Turn the crankshaft counterclockwise with a
wrench.
b. Align the top dead center (TDC) mark “a” on
the rotor with the alignment mark “b” on the
crankcase cover.
Engine idling speed
1900–2100 r/min
Direction “a”Engine idling speed De-
creases.
Direction “b”Engine idling speed In-
creases.
1 1
a a
1 b
a
Valve clearance (cold)
Exhaust
0.20–0.25 mm (0.0079–0.0098 in)
1
2