2014 SKODA CITIGO lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 5 of 164

Table of Contents
Board literature4
Notes
5
Structure and more information about the
Owner's Manual
6
Abbreviations
Safety
Passive Safety
8
General information
8
Correct and safe seated position
9
Seat belts
11
Using seat belts
11
Inertia reels and belt tensioners
14
Airbag system
15
Description of the airbag system
15
Airbag overview
16
Deactivating airbags
18
Transporting children safely
19
Child seat
19
Fastening systems
22
Using the system
Cockpit
27
Overview
26
Instruments and control lights
28
Instrument cluster
28
Multi-function display (MFD)
30
Warning lights
33
Unlocking and opening
39
Unlocking and locking
39
Luggage compartment lid
43Electric Windows44Mechanical windows45
Panorama sliding/tilting roof
46
Lights and visibility
48
Lights
48
Indoor Lighting
51
Visibility
52
Windscreen wipers and washers
52
Rear mirror
54
Seats and head restraints
55
Seats and head restraints
55
Seat features
57
Transporting and practical equipment
60
Useful equipment
60
Luggage compartment
65
Roof rack
68
Heating and air conditioning
70
Heating, ventilation, cooling
70
Communication and multimedia
73
Telephone and Move & Fun
73
Driving
Starting-off and Driving
76
Starting and turning off the engine
76
Brakes and parking
77
Manual gear changing and pedals
79
Automated transmission
80
Running in and economical driving
82
Driving through water and driving off of
made-up roads
83
Assist systems
84
Braking and stabilisation systems
84
Parking aid
85
Cruise Control System
87
START-STOP
88City Safe Drive90Tyre pressure monitoring92
General Maintenance
Care and maintenance
93
Modifications, adjustments and technical alterations
93
Washing vehicle
96
Cleaning vehicle exterior
97
Interior care
101
Inspecting and replenishing
103
Fuel
103
Engine compartment
107
Engine oil
110
Coolant
111
Brake fluid
113
Vehicle battery
113
Wheels
117
Tyres and wheel rims
117
Approved tyre / rim combinations
120
Winter operation
121
Do-it-yourself
Emergency equipment and self-help
122
Emergency equipment
122
Reserve and temporary spare
123
Changing a wheel
124
Puncture repair kit
127
Jump-starting
130
Towing the vehicle
131
Remote control
132
Emergency unlocking/locking
133
Replacing windscreen wiper blades
134
Fuses and light bulbs
135
Fuses
135
Replacing bulbs
1382Table of Contents
Page 10 of 164
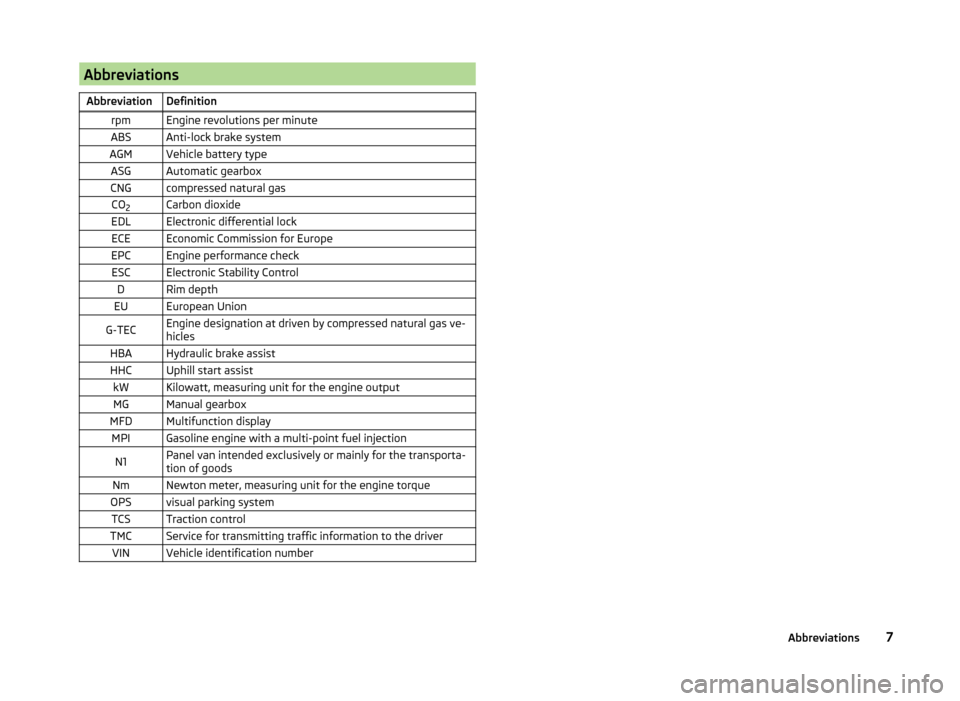
AbbreviationsAbbreviationDefinitionrpmEngine revolutions per minuteABSAnti-lock brake systemAGMVehicle battery typeASGAutomatic gearboxCNGcompressed natural gasCO2Carbon dioxideEDLElectronic differential lockECEEconomic Commission for EuropeEPCEngine performance checkESCElectronic Stability ControlDRim depthEUEuropean UnionG-TECEngine designation at driven by compressed natural gas ve-
hiclesHBAHydraulic brake assistHHCUphill start assistkWKilowatt, measuring unit for the engine outputMGManual gearboxMFDMultifunction displayMPIGasoline engine with a multi-point fuel injectionN1Panel van intended exclusively or mainly for the transporta-
tion of goodsNmNewton meter, measuring unit for the engine torqueOPSvisual parking systemTCSTraction controlTMCService for transmitting traffic information to the driverVINVehicle identification number7Abbreviations
Page 13 of 164

WARNING (Continued)■When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the out-
er edge in the “9 o'clock” and “3 o'clock” position. Never hold the steering
wheel in the “12 o'clock” position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or
inner edge of the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure
the arms, hands and head when the driver airbag is deployed.■
Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell as they may get
caught behind the pedals when driving or applying the braking. You would
then no longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or acceleration pedals.
Adjusting the steering wheel position
Fig. 2
Adjusting the steering wheel po-
sition
Read and observe on page 9 first.
The height of the steering wheel can be adjusted.
›
Swivel the lever underneath the steering wheel downwards » Fig. 2.
›
Adjust the steering wheel to the desired position.
›
Push the lever upwards to the stop.
WARNING■
The lever for adjusting the steering wheel must be locked while you are
driving so that the position of the steering wheel cannot accidentally
change during the journey – risk of accident!■
Never adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is moving only when
the vehicle is stationary!
Correct seated position for the front passenger
Read and observe
on page 9 first.
For passenger safety and to reduce the risk of injury in an accident, the follow-ing instructions must be observed.
Position the front passenger seat back as far as possible. The front pas-
senger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel so
that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety if it is deployed.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 13.
Front passenger adjustment » page 56, Adjusting the front seats .
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactiva-
ted » page 18 , Deactivating airbags .
WARNING■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you – hazard!■
Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven – nev-
er place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the
surfaces of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it be-
comes necessary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an air-
bag is deployed, you could suffer fatal injuries by adopting an incorrect
seated position!
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
Read and observe
on page 9 first.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or anaccident, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 13.
Use a suitable child restraint system if transporting children in the vehi- cle » page 19 , Transporting children safely .
Adjust head restraints » page 56.
10Safety
Page 15 of 164

WARNING■Fasten your seat belt before each journey – even when driving in town!
This also applies to the passengers seated at the rear – risk of injury!■
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way
of ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child » page 13, Fastening
and unfastening seat belts .
■
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if you are correctly seat-
ed » page 9 , Correct and safe seated position .
■
The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
WARNINGInformation on the correct routing of the belt■Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even
in minor accidents.■
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
■
The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. specta-
cles, ball-point pens, bunches of keys etc.). Such objects can cause injury.
WARNINGInformation on dealing with the safety belts■The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twis-
ted, or chafe against any sharp edges.■
Make sure you do not catch the seat belt when closing the door.
WARNINGInformation on the proper use of the safety belts■Never use one seat belt to secure two persons (including children). The
seatbelt must not be placed over a child who is sitting on the lap of another
passenger.■
The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to
protect and the risk of injury increases.
■
The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked, otherwise the belt
tongue will not lock in place properly.
WARNING (Continued)■ Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jack-
et) do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of
the seat belts.■
Do not use clamps or similar items, which inhibit the safety belt locking
function. A seat belt which is too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
■
The seat belts for the rear seats can only fulfil their function reliably
when the seat backrests are correctly locked into position » page 59, Seat
backrests .
WARNINGInformation on the care and maintenance of the safety belts■The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may im-
pair proper operation of the inertia reel » page 103, Safety belts .■
The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not at-
tempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
■
Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis. If any damage
to the seat belts, seat belt connections, inertia reel or the lock is detected,
the relevant seat belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
■
Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident
and were therefore stretched, must be replaced – this is best done by a
specialist garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspec-
ted. The anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
Note
The national legal requirements must be observed when using seat belts.12Safety
Page 16 of 164

The physical principle of a frontal collisionFig. 4
Driver without a fastened seat belt/rear seat passenger without a
fastened seat belt
Read and observe
on page 12 first.
As soon as the vehicle is moving, so-called kinetic energy (the energy of mo-
tion) is produced both in terms of the car as well as in terms of the occupants.
The magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on the speed at
which the vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle including the
occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the
amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an accident.
The speed of the vehicle is the most important factor. Doubling the speed of
the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy four
times.
The idea that it is possible to support your body with your hands in a minor ac-
cident is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces acting on
the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed of 30-50 km/h, the forces that your body is
exposed to in the event of an accident can exceed a metric ton (1000 kg).
For example, a person's weight of 80 kg “increases” to 4.8 tons (4800 kg) at
50 km/h.
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt
are thrown forward and strike parts of the interior of the car, such as the
steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen in ways which cannot be control-
led » Fig. 4 -
. In certain circumstances you could even be thrown out of the
vehicle, which could cause life threatening or even fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear passengers fasten their seat belts, as they could
otherwise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the
event of an accident.
A rear seat passenger who has not fastened their seat belt is a danger not on-
ly to himself but also for those seated at the front » Fig. 4 –
.
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
Fig. 5
Fastening/unfastening the seat belt
Fig. 6
Routing of belt webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt/Rout-
ing of belt webbing for an expectant mother
Read and observe
on page 12 first.
Fastening
›
Correctly adjust the front seat before fastening the seat belt » page 9, Cor-
rect and safe seated position .
›
Use the lock tongue to slowly pull the webbing over your chest and pelvis.
13Seat belts
Page 17 of 164

›Insert the lock tongue into the belt buckle
» Fig. 5 – that is part of the seat
until it clicks into place.›
Pull on the belt to check that it has engaged correctly in the lock.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is
easy to get hold of.
It is important that the belt is properly routed to ensure seat belts offer the
maximum protection.
The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across the neck but must
roughly run over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
The lap part of the belt must run across the pelvis, must not be positioned
across the stomach and must always fit snugly » Fig. 6 –
.
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child.
On expectant mothers, the lap part of the belt must be positioned as low as possible on the pelvis to avoid exerting any pressure on the lower abdo-
men » Fig. 6 –
.
Releasing
Release the seat belt only when the vehicle is stationary.
›
Press the red button in the belt buckle » Fig. 5 –
, the lock tongue pops
out.
›
Manually guide the belt back so that it is easier to fully roll up the webbing,
the seat belt does not twist.
CAUTION
When releasing the seatbelt ensure that the tongue of the lock does not dam-
age the door trim or other parts of the interior.
Inertia reels and belt tensioners
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Inertia reels
14
Belt tensioners
14
Inertia reels
Each seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel.
When pulling slowly on the seat belt, the belt can move freely. When pulling
sharply on the seat belt, the movement is locked by the inertia reel.
The belts also lock when full braking, when the car accelerates, when driving
downhill and when cornering.WARNINGIf the seat belt does not lock when pulling sharply on it, have it inspected
immediately by a specialist garage.
Belt tensioners
Safety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced
by the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat
belts.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal
collision of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the
seat belts are not fastened.
The seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a collision of a cer-
tain severity.
Belt tensioners are not activated in the event of minor frontal collisions, side
and rear-end collisions, in the case of a rollover and also not in accidents in
which no major forces are produced from the front.
WARNING■ Any work on the belt tensioner system including removal and installation
of system components because of other repair work, must only be carried
out by a specialist garage.■
The protective function of the system is only adequate for a single acci-
dent. If the belt tensioners have been deployed, it is then necessary to re-
place the entire system.
Note
■ Smoke is generated when the belt tensioners are deployed. This is not an in-
dication of a fire in the vehicle.■
When disposing of the vehicle or parts of the belt tensioner system, it is im-
portant to comply with national legal requirements. ŠKODA service partners
are familiar with these regulations and will be able to provide you with de-
tailed information.
14Safety
Page 19 of 164

Deployment factors
It is not possible to generally determine which deployment conditions apply to
the airbag system in every situation. An important role is played by factors
such as the type of object that the vehicle hits (hard/soft), the impact angle,
vehicle speed etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which
occurs. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates the
relevant restraint system.
If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is measured during the collision
remains below the prescribed reference values specified in the control unit,
the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suffer severe dam-
age to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe frontal
collision.
› Driver’s front airbag.
› Front passenger airbag.
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe side collision.
› Head-Thorax side airbag on the crash side.
When an airbag is deployed, the following events occur.
› The interior lighting illuminates (if the switch for the interior light is in the
door contact position).
› The hazard warning lights are switched on.
› All doors are unlocked.
› The fuel supply to the engine is interrupted.
Airbag overview
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Front airbags
16
Side airbags Head-Thorax
17Front airbagsFig. 7
Driver airbag in the steering wheel/front passenger airbag in the
dashboard
Fig. 8
Safe distance to steering wheel/gas-filled airbags
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the front airbag system offers addi-
tional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and front passenger.
The front airbag for the driver is housed in the steering wheel » Fig. 7 –
.
The front airbag for the front seat passenger is located in the dash panel
above the stowage compartment » Fig. 7 –
.
When the airbags are deployed, they inflate in front of the driver and front
passenger » Fig. 8 -
. The forward movement of the driver and of the front
passenger is cushioned when they make contact with the fully inflated airbag
and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus reduced.
16Safety
Page 27 of 164

The attachment points for attaching the belt for a child seat with the
system are located on the back of the rear seat backrests » Fig. 16.WARNING■
Always refer to the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat
when installing and removing a child seat with the system.■
Only use child seats with the
system on the seats with the at-
tachment points.
■
Only ever attach one belt from the child seat to a locking eye.
■
On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other
anchorage points.
24Safety