2014 FORD SUPER DUTY change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 2 of 82

The information contained in this publication was correct at the time of going to print. In the interest of
continuous development, we reserve the right to change specifications, design or equipment at any time
without notice or obligation. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, stored in a
retrieval system or translated into any language in any form by any means without our written permission.
Errors and omissions excepted.
© Ford Motor Company 2013
All rights reserved.
Part Number: 20130604200151
Page 8 of 82

The powertrain and glow plug control
modules electronically control the glow
plug system. After you switch the ignition
on the glow plug control module
immediately energizes the glow plugs. The
glow plug control module using the engine
coolant temperature, barometric pressure
sensor and environmental temperature
sensor will determine how long the glow
plugs stay energized. The required time for
the glow plugs to be energized decreases
as the coolant temperature, barometric
pressure and environmental temperature
increase.
Glow Plug
Engine and secondary cooling system
The cooling system contains a primary
cooling loop to cool the engine and
exhaust gases and a secondary cooling
loop to cool the transmission, exhaust
gases, charge air, and fuel. The coolant
serves three primary purposes: to provide
heat transfer, freeze point protection, and
corrosion protection using additives.
Vehicles with diesel engines typically are
used to carry heavy loads and accumulate
mileage rapidly. These two factors may
cause the additives in the coolant to wear
out in a shorter time. For more information
about coolant additives and coolant
change intervals See General
Maintenance Information (page 58). .
Operating the engine with insufficient
coolant or coolant additive can cause
severe engine damage
Selective catalytic reduction system
Your vehicle is equipped with a selective
catalytic reduction system designed to
reduce emission levels of nitrogen oxides
from the exhaust of your diesel engine. This
system relies on the use of diesel exhaust
fluid that you must replenish at certain intervals. Failure to maintain proper diesel
exhaust fluid levels or if the diesel exhaust
fluid becomes contaminated will result in
vehicle speed limitations or result in your
vehicle entering an idle-only mode. See
Selective Catalytic Reduction System
(page
20).
Speed control
If your vehicle speed goes outside a
predetermined range from the set speed,
the RSM (Resume) function will not reset
your vehicle speed. You will need to reset
your vehicle speed with the SET+ or SET-
button after reaching the desired speed
using the accelerator pedal.
Minor Troubleshooting Guide
If the engine won ’t crank WARNING
Battery posts, terminals and related
accessories contain lead and lead
compounds. Wash hands after
handling. Turn on the headlights. If the lights are dim,
do not go on at all or when the ignition is
turned to START the lights become dim or
go out, the battery connections may be
loose or corroded, or the battery may be
discharged. If there is a clicking or
stuttering sound coming from the engine
compartment when you turn the key to
START, this may also indicate a loose or
corroded battery connection.
Check the battery connections at the
battery posts, cable connection to the
engine grounding point and at the starter
connection.
If you suspect a discharged battery, have
it checked and corrected.
5
Super Duty (TFA) Introduction
Page 14 of 82

In order to operate the engine in
temperatures of 32°F (0°C) or lower, read
the following instructions:
•
Make sure that the batteries are of
sufficient size and are fully charged.
Check other electrical components to
make sure they are in optimum
condition
• Use the proper coolant solution at the
concentration recommended
protecting the engine against damage
from freezing
• Try to keep the fuel tank full as much
as possible at the end of operation to
prevent condensation in the fuel
system
• Make sure you use proper cold weather
engine oil and that it is at its proper
level. Also, if necessary, make sure to
follow the engine oil and filter change
schedule found under the Special
operating conditions section listed in
the scheduled maintenance
information
• At temperatures of -10°F (-23°C) or
below, it is recommended that you use
an engine block heater to improve cold
engine starting
• If operating in arctic temperatures of
-20°F (-29°C) or lower, consult your
truck dealer for information about
special cold weather equipment and
precautions
The following cold weather idling
guidelines are recommended:
• You can use Motorcraft® cetane
improvers or non-alcohol-based
cetane improvers from a reputable
manufacturer as needed.
• Maintain the engine cooling system
properly. •
Avoid shutting the engine down after
an extensive idling period. Drive your
vehicle for several miles with the
engine at normal operating
temperatures under a moderate load.
• Consider using an engine block heater.
• For extended idle times use an
approved idle speed increase device.
Winter Operating Tips for Arctic
Operation -20°F (-29°C) and Below
The following information is a guideline
only and is no to be the only source of
possible solutions in resolving extreme
cold temperature issues.
Starting Aids WARNING
Do not use starting fluid, such as
ether, in the air intake system (see
air filter decal). Such fluid could
cause immediate explosive damage to the
engine and possible personal injury. The use of the factory engine block heater
assists in engine starting in extreme cold
ambient temperatures. Refer to Engine
block heater in the Starting and Stopping
the Engine chapter of your Owner
’s
Manual.
Idle Control
Your vehicle may have a factory option for
a stationary elevated idle control through
dash-mounted upfitter switches that
allows the operator to elevate the idle rpm
for extended idle periods, as well as
aftermarket equipment such as PTO
operation. You must configure this feature
even if ordered from the factory. See your
authorized dealer for required upfitting.
11
Super Duty (TFA) Starting and Stopping the Engine
Page 21 of 82

filters at the same time. Regular fuel filter
changes are an important part of engine
maintenance; failing to keep with the
scheduled maintenance could lead to
engine performance issues and fuel
injection system damage. Refer to the
scheduled maintenance information of this
supplement for more information. See
General Maintenance Information
(page 58).
Refer to Motorcraft part numbers in the
Capacities and Specifications chapter for
the fuel filter replacement part number.
See Motorcraft Parts (page 54). This part
number includes filters and seals for both
the engine-mounted and frame-mounted
filters.
Removal - Diesel Fuel Conditioner
Module filter
The diesel fuel conditioner module filter is
located in the lower portion of the housing.
1. Drain the diesel fuel conditioner module. See Draining the Fuel and
Water Separator earlier in this chapter.
2. Remove the lower portion of the diesel
fuel conditioner module housing (filter
bowl) by turning it counterclockwise
using a 32 mm socket. Note:
Depending on the amount of seal
swelling, removal of the filter bowl may be
noisy and require some effort. Replace the
seal prior to reinstalling the filter bowl to
improve assembly.
3. Remove and discard the old fuel filter element.
4. Carefully clean the mating surfaces using a lint-free rag.
Installation – Diesel Fuel Conditioner
Module filter
1. Install the new filter into the filter bowl
tabs and replace the seal on the diesel
fuel conditioner module header (top
portion of separator). Refer to
Motorcraft part numbers in the
Capacities and Specifications chapter
for the fuel filter kit part number. See
Motorcraft Parts
(page 54).
2. Lube O-ring with lubricant packet in the filter kit. This will assist in making
sure the filter is properly tightened. 3. Reinstall the lower portion of the
housing by slowly turning it clockwise
onto diesel fuel conditioner module
housing, allowing fuel to soak into the
fuel filter element. Tighten the lower
housing until it contacts the
mechanical stop.
18
Super Duty (TFA) Fuel and RefuelingE163361 E163362
Page 31 of 82
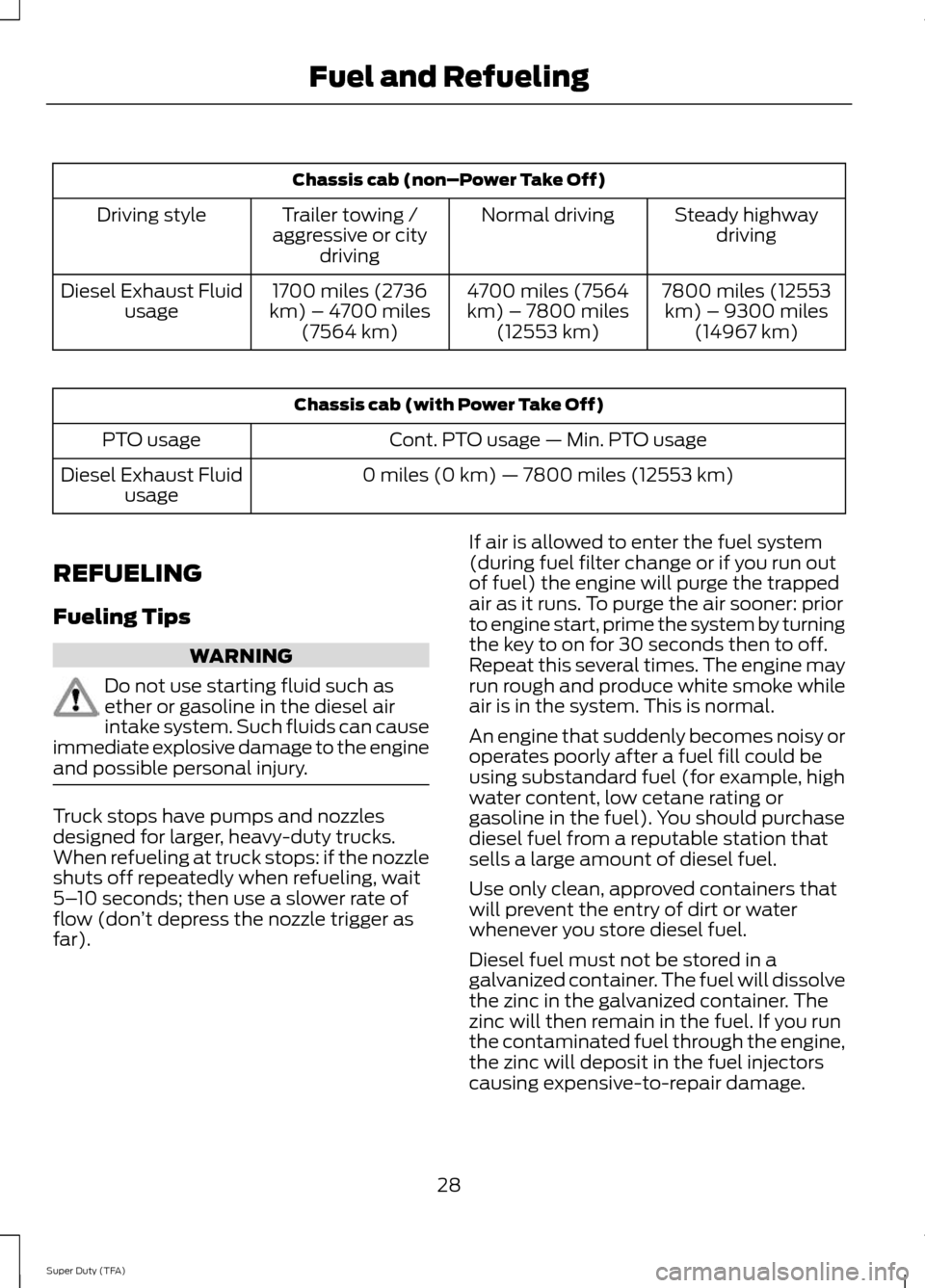
Chassis cab (non–Power Take Off)
Steady highwaydriving
Normal driving
Trailer towing /
aggressive or city driving
Driving style
7800 miles (12553km) – 9300 miles (14967 km)
4700 miles (7564
km) – 7800 miles (12553 km)
1700 miles (2736
km) – 4700 miles (7564 km)
Diesel Exhaust Fluid
usage Chassis cab (with Power Take Off)
Cont. PTO usage — Min. PTO usage
PTO usage
0 miles (0 km) — 7800 miles (12553 km)
Diesel Exhaust Fluid
usage
REFUELING
Fueling Tips WARNING
Do not use starting fluid such as
ether or gasoline in the diesel air
intake system. Such fluids can cause
immediate explosive damage to the engine
and possible personal injury. Truck stops have pumps and nozzles
designed for larger, heavy-duty trucks.
When refueling at truck stops: if the nozzle
shuts off repeatedly when refueling, wait
5–
10 seconds; then use a slower rate of
flow (don ’t depress the nozzle trigger as
far). If air is allowed to enter the fuel system
(during fuel filter change or if you run out
of fuel) the engine will purge the trapped
air as it runs. To purge the air sooner: prior
to engine start, prime the system by turning
the key to on for 30 seconds then to off.
Repeat this several times. The engine may
run rough and produce white smoke while
air is in the system. This is normal.
An engine that suddenly becomes noisy or
operates poorly after a fuel fill could be
using substandard fuel (for example, high
water content, low cetane rating or
gasoline in the fuel). You should purchase
diesel fuel from a reputable station that
sells a large amount of diesel fuel.
Use only clean, approved containers that
will prevent the entry of dirt or water
whenever you store diesel fuel.
Diesel fuel must not be stored in a
galvanized container. The fuel will dissolve
the zinc in the galvanized container. The
zinc will then remain in the fuel. If you run
the contaminated fuel through the engine,
the zinc will deposit in the fuel injectors
causing expensive-to-repair damage.
28
Super Duty (TFA) Fuel and Refueling
Page 32 of 82

Diesel fuel dispensing nozzle fill rate
Your truck is equipped with a fuel fill pipe
that is able to accept fuel up to 20 gallons
per minute from an 11⁄8 fuel-dispensing
nozzle. Pumping fuel at greater flow rates
may result in premature nozzle shut-off or
spit back.
Fuel filler cap
WARNINGS
The fuel system may be under
pressure. If the fuel filler cap is
venting vapor or if you hear a hissing
sound, wait until it stops before completely
removing the fuel filler cap. Otherwise, fuel
may spray out and injure you or others. If you do not use the proper fuel filler
cap, excessive pressure or vacuum
in the fuel tank may damage the fuel
system or cause the fuel cap to disengage
in a collision, which may result in possible
personal injury. Note:
If you must replace the fuel filler cap,
replace it with a fuel filler cap designed for
your vehicle. The vehicle warranty may be
void for any damage to the fuel tank or fuel
system if the correct genuine Ford or
Motorcraft® fuel filler cap is not used.
Your fuel tank filler cap has an indexed
design with a 1/4 turn on/off feature.
When fueling your vehicle:
1. Turn the engine off.
2. Carefully turn the filler cap counterclockwise until it spins off.
3. Pull to remove the cap from the fuel filler pipe.
4. To install the cap, align the tabs on the
cap with the notches on the filler pipe.
5. Turn the filler cap clockwise 1/4 of a turn until it clicks at least once. EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
Diesel Exhaust System: Oxidation
Catalyst And Diesel Particulate
Filter System (If Equipped)
Your vehicle is equipped with a diesel
particulate filter. The diesel particulate
filter is an inline filter in the exhaust system
that reduces carbon emissions by trapping
exhaust particles before they reach the
tailpipe. The diesel particulate filter looks
similar to a traditional exhaust catalyst,
except larger, and is part of the exhaust
system under the vehicle. The filter couples
to a diesel oxidation catalyst that reduces
the amount of harmful exhaust emitted
from the tailpipe. As soot gathers in the
system, it begins to restrict the filter. You
need to periodically clean the soot that
gathers inside the. You can clean the soot
in two different ways, passive regeneration
and active regeneration. Both methods
occur automatically and require no actions
from the driver. During either one of these
regeneration methods, you may notice a
change in exhaust tone. At certain times,
the information display will display various
messages related to the diesel particulate
filter. See the Information Displays chapter
in the Owner Guide for more information.
Passive regeneration
In passive regeneration, the high
temperature of the exhaust system
automatically cleans the filter, or reduces
the soot level, by burning (oxidizing) the
soot. This high exhaust temperature occurs
naturally because of normal engine
operating conditions (at varying levels, due
to driving patterns.
29
Super Duty (TFA) Fuel and Refueling
Page 35 of 82

Information display procedure
Start with your vehicle engine fully warmed
and then press the Info button on the
steering wheel until the information display
reads one of the following choices:
If you have warmed your vehicle up and
the diesel particulate filter needs cleaning,
a message requesting permission to initiate
filter cleaning will be displayed EXHST
XX% FULL CLEAN? Y/N or EXHAUST
FULL CLEAN? Y/N. Answer yes to this
prompt and then follow the prompts
regarding exhaust position as needed to
initiate Operator Commanded
Regeneration. Be sure to understand each
prompt. If you are not sure what is being
asked by each prompt, contact an
authorized dealer. The display will confirm
the operation has started and when it has
finished. If you have warmed your vehicle
up and the diesel particulate
filter is near or at saturation, the
powertrain fault indicator will illuminate
and message requesting permission to
initiate filter cleaning will be displayed
EXH AT LIMIT CLEAN? Y/N. Answer yes
to this prompt and then follow the
prompts regarding exhaust position as
needed to initiate Operator Commanded
Regeneration. Be sure to understand each
prompt. If you are not sure what is being
asked by each prompt, contact an
authorized dealer. The display will confirm
the operation has started and when it has
finished. You can also drive to clean the
filter. See Active regeneration earlier in this
chapter. The service engine soon light will
illuminate and the following
message
EXH OVER LIMIT
SERVICE NOW will appear when the
system is at the point of oversaturation.
You will not be able to allow cleaning. You
must have your vehicle serviced by an
authorized dealer. Once operator commanded regeneration
starts, the engine
’s rpm will rise to
approximately 2,000 - 2,400 rpm and the
cooling fan will increase speed; you will
hear a change in audible sound due to the
fan and engine speed increase.
It is not necessary to open the hood on the
engine compartment. Once operator
commanded regeneration is complete, the
engine rpm and fan will return to normal
idling. The exhaust system will remain very
hot for several minutes even after
regeneration is complete. Do not reposition
the vehicle over materials that could burn
until the exhaust system has had sufficient
time to cool. Depending on the amount of
soot collected by the diesel particulate
filter, ambient temperature, and altitude,
operator commanded regeneration may
last from 10 to 25 minutes.
How to interrupt or cancel Operator
Commanded Regeneration
If you need to cancel the operator
commanded regeneration, pressing the
brake, accelerator, or shutting off the
vehicle will stop the procedure. Depending
on the amount of time you allowed the
operator commanded regeneration to
operate, soot may not have had sufficient
time to be eliminated, but the exhaust
system and exhaust gas may still be hot.
If you shut your vehicle off during operator
commanded regeneration, you will notice
turbo flutter. This is a normal consequence
caused by shutting off a diesel engine
during boosted operation and is considered
normal.
Filter service and maintenance
Over time, a slight amount of ash will build
up in the diesel particulate filter, which is
not removed during the regeneration
process. The filter may need to be removed
for ash cleaning at approximately 120,000
miles (193,000 km) or greater (actual
mileage can vary greatly depending upon
32
Super Duty (TFA) Fuel and Refueling
Page 45 of 82

Scheduled Maintenance
The scheduled maintenance services in
the scheduled maintenance information
of this supplement are required because
they are considered essential to the life
and performance of your vehicle. See
General Maintenance Information
(page 58).
Use only recommended fuel, lubricants,
fluids and service parts conforming to Ford
specifications. Motorcraft® parts are
designed and built for best performance
in your vehicle.
ENGINE OIL CHECK
Because it is normal to add some oil
between oil changes, check your engine oil
level each time you stop for fuel. To check
the engine oil level consistently and
accurately, the following procedure is
recommended:
1. Have engine at normal operating temperature (at least into the NORMAL
range on the engine coolant
temperature gauge).
2. Park the vehicle on a level surface, then
turn off the engine and open the hood.
3. Allow at least 20 minutes after engine
shutdown to ensure that the oil
contained in the upper parts of the
engine has returned to the oil pan.
4. Protecting yourself from engine heat, pull out the dipstick, wipe it clean and
reinsert fully.
5. Read oil level on both sides of dipstick
and use highest level (reading) for the
actual engine oil level. 6. Maintain the oil level within the
crosshatch area on the dipstick by
adding oil as required. Do not overfill
the oil past the maximum line as
depicted by the arrow.
Engine Oil Specifications
To help achieve acceptable engine
performance and durability, it is important
that only engine oils of good quality are
used in your diesel engine and it is changed
at the recommended interval. For normal
or severe service, use Motorcraft® oil or an
equivalent oil conforming to Ford
specifications as listed in the Capacities
and Specifications chapter. See
Technical Specifications
(page 56). It
is important to use these oils because they
are compatible with the emission control
equipment of your vehicle to meet the
more stringent emission standards.
The use of correct oil viscosities for diesel
engines is important for satisfactory
operation. Determine which oil viscosity
best suits the temperature range you
expect to encounter for the next service
interval from the following SAE viscosity
grade chart.
42
Super Duty (TFA) MaintenanceE163369