2014 Alfa Romeo MiTo height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 48 of 280
SEATSFRONT SEATS
All adjustments must be made with the car stationary.
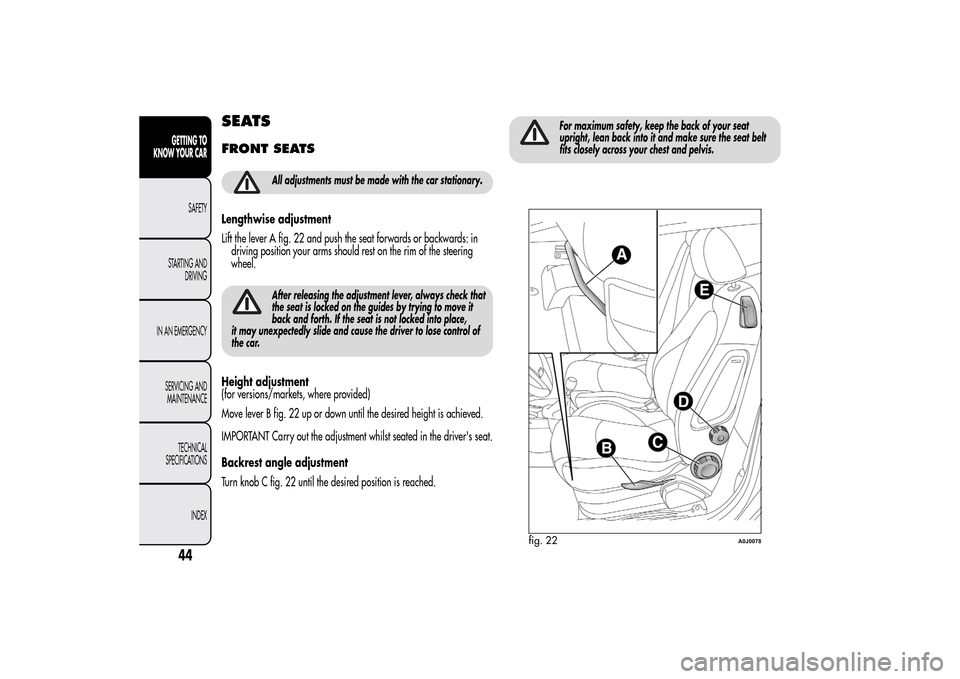
Lengthwise adjustment
Lift the lever A fig. 22 and push the seat forwards or backwards: in
driving position your arms should rest on the rim of the steering
wheel.
After releasing the adjustment lever, always check that
the seat is locked on the guides by trying to move it
back and forth. If the seat is not locked into place,
it may unexpectedly slide and cause the driver to lose control of
the car.
Height adjustment
(for versions/markets, where provided)
Move lever B fig. 22 up or down until the desired height is achieved.
IMPORTANT Carry out the adjustment whilst seated in the driver's seat.
Backrest angle adjustment
Turn knob C fig. 22 until the desired position is reached.
For maximum safety, keep the back of your seat
upright, lean back into it and make sure the seat belt
fits closely across your chest and pelvis.
fig. 22
A0J0078
44GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 51 of 280

HEAD RESTRAINTSFRONTHead restraints are adjustable in height and they lock automatically
into the desired position:
❒upwards adjustment: raise the head restraint until it clicks into place;
❒downwards adjustment: press button A fig. 25 and lower the head
restraint.
Head restraints must be adjusted so that the head,
rather than the neck, rests on them. Only in this case
can they protect your head correctly.
To remove the head restraints:
❒raise the head restraints to their maximum height;
❒press buttons A and B fig. 25, then remove the head restraints by
pulling them upwards.
“Anti-Whiplash” device
The head restraints are equipped with an “Anti-Whiplash” device,
which reduces the distance between head and head restraint in the
event of a rear impact, thus mitigating the “whiplash” effect.
The head restraint may move when the backrest is pressed by the
occupant's torso or hand: this behaviour is caused by the system and
should not be considered a malfunction.
fig. 25
A0J0130
47GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CARSAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 52 of 280

REARTwo height-adjustable head restraints are provided for the back seats
(to adjust the height see the previous paragraph).
On some versions a head restraint is also provided for the central seat.
To remove the head restraints:
❒raise the head restraints to their maximum height;
❒press buttons A fig. 26, then remove the head restraints by pulling
them upwards.
STEERING WHEELIt can be adjusted axially and vertically.
To adjust, release A fig. 27 by pushing it forwards (position 1) and
adjust the steering wheel. Then lock lever A by pulling it towards
the steering wheel (position 2).
All adjustments must be carried out only with the
vehicle stationary and engine off.It is absolutely forbidden to carry out any after-market
operation involving steering system or steering column
modifications (e.g. installation of anti-theft device)
that could badly affect performance and safety, invalidate the
warranty and also result in the car not meeting type-approval
requirements.
fig. 26
A0J0083
fig. 27
A0J0034
48GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 90 of 280

Folding the seatsProceed as follows:
❒raise the head restraints to the maximum height, press both the
buttons A fig. 66 to the side of the two supports, then remove the
head restraints by sliding them upwards;❒move the seat belts to the side, making sure that they are correctly
extended and not twisted;
❒lift the backrest retaining levers A fig. 67 and fold the desired
cushion forwards (a red band indicates that lever A is raised).
Repositioning the rear seat
Move the seat belts to the side making sure that they are correctly
extended and not twisted.
Raise the previously folded backrest until you hear the click of the
locking mechanism, visually checking that the red band on lever A fig.
67 has disappeared. The red band indicates that the backrest is not
secured.
Finally, reposition the head restraints, inserting them into their
housings.
fig. 65
A0J0081
fig. 66
A0J0083
fig. 67
A0J0082
86GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 122 of 280

If the belt has been subjected to high levels of stress,
for example after an accident, it should be changed
completely together with the attachments, attachment
fixing screws and the pretensioner. In fact, even if the belt has no
visible defects, it may have lost its resilience.
SEAT BELT MAINTENANCE❒Always use the belt with the strap well stretched and never twisted;
make sure that it is free to run without obstructions;
❒replace the belt after an accident of a certain severity even if it does
not appear to be damaged. Always replace the belt if the
pretensioners were deployed;
❒hand wash the seat belts with water and neutral soap, rinse and
leave to dry in the shade. Do not use strong detergents, bleach,
colourants or any other substance which could damage the belt
fibres;
❒prevent the reels from getting wet: their correct operation is only
guaranteed if water does not get inside;
❒replace the seat belt when there is wear or cuts.
CARRYING CHILDREN SAFELYFor optimal protection in the event of an impact, all occupants must be
seated and wearing adequate restraint systems, including newborn
and other children!
This prescription is compulsory in all EC countries according to EC
Directive 2003/20/EC.
Compared with an adult, a child's head is larger and heavier in
proportion to his/her body and the child's muscular and bone
structures are not fully developed. Therefore, correct restraint systems
other than adult seat belts are necessary to reduce as much as possible
the risk of injuries in case of accident, braking or sudden manoeuvre.
Children must be seated safely and comfortably. As far as the
characteristics of the child restraint systems used allow, you are
advised to keep children in rear facing restraint systems for as long as
possible (at least until 2 years old), since this is the most protected
position in the event of an impact.
The choice of the most suitable child restraint device depends on the
weight of the child; there are various types of child restraint systems
and you are advised always to choose the one that is most suitable for
the child.
When over 1.50 m in height, from the point of view of restraint
systems, children are considered as adults and wear seat belts
normally.
118GETTING TO KNOW
YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 125 of 280
GROUP 2
The diagram is indicative and for assembly purposes
only. Fit the child seat according to the instructions,
which must be included.
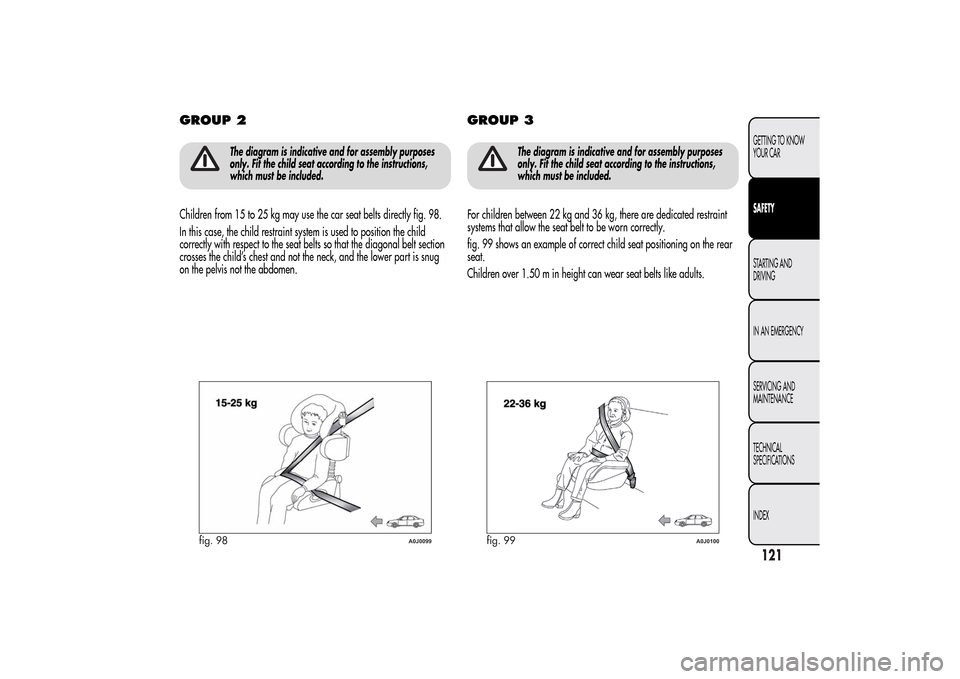
Children from 15 to 25 kg may use the car seat belts directly fig. 98.
In this case, the child restraint system is used to position the child
correctly with respect to the seat belts so that the diagonal belt section
crosses the child’s chest and not the neck, and the lower part is snug
on the pelvis not the abdomen.
GROUP 3
The diagram is indicative and for assembly purposes
only. Fit the child seat according to the instructions,
which must be included.
For children between 22 kg and 36 kg, there are dedicated restraint
systems that allow the seat belt to be worn correctly.
fig. 99 shows an example of correct child seat positioning on the rear
seat.
Children over 1.50 m in height can wear seat belts like adults.
fig. 98
A0J0099
fig. 99
A0J0100
121GETTING TO KNOW
YOUR CARSAFETYSTARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 213 of 280

WHEELSRIMS AND TYRESPressed steel or alloy rims. Tubeless radial carcass tyres. The vehicle
registration document also lists all type-approved tyres.
For safe driving, the car must be fitted with tyres of the same make and
type on all wheels.
IMPORTANT If there are any discrepancies between the Owner
handbook and the registration document, take the information from the
latter.
IMPORTANT Do not use tubes with tubeless tires.SPACE-SAVER WHEELPressed steel rim. Tubeless tyre.READING THE TYRE CODEExample fig. 173: 195/55 R 16 87H195
Rated width (S, distance in mm between sidewalls)
55
Height/width ratio (H/S) as a percentage
RRadial tyre16
Rim diameter in inches (Ø)
91
Load rating (capacity)
VMaximum speed indexMaximum speed index
Qup to 160 km/hRup to 170 km/hSup to 180 km/hTup to 190 km/hUup to 200 km/hHup to 210 km/hVup to 240 km/hW
up to 270 km/h
Yup to 300 km/h
Maximum speed index for snow tyresQM+S
up to 160 km/h
TM+S
up to 190 km/h
HM+S
up to 210 km/h
fig. 173
A0J0139
209GETTING TO KNOW
YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCETECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONSINDEX
Page 220 of 280

DIMENSIONSDimensions are expressed in mm and refer to the vehicle equipped with its original tyres. Height is measured with car unladen.
LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT VOLUMEUnladen capacity (V.D.A. standards): = 270 dm
3
AB CD E FGH
4063 904 2511 648 14461475
(*)/1483(**)
17201469
(*)/1475(**)
(*)With 195/55 R16 tyres
(**)With 215/40 R18 tyresSmall variations in size are possible depending on the dimensions of the rims
fig. 175
A0J0202
216GETTING TO KNOW
YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX