2013 VOLKSWAGEN PASSAT Pressure
[x] Cancel search: PressurePage 321 of 379

Section width
The linear distance between the exteriors of the sidewalls of an inflated tire, excluding elevations due
to labeling decoration, or protective bands.
Sidewall
The portion of a tire between the bead and the tread.
Sidewall separation
The parting of the rubber compound from the cord material in the sidewall.
Speed rating (letter code)
A standardized letter code indicating the maximum speed at which a tire is designed to be driven for
extended periods of time. The ratings range from 93 mph or 150 km/h (“P”) to 186 mph or (300 km/h)
“Y”.
The speed rating letter code, where applicable, is molded on the tire sidewall. You may not find this
information on all tires because it is not required by law.
Tire Pressure Monitoring System
A system that detects when at least one of a vehicle's tires is underinflated and illuminates a low tire-
pressure warning light.
Tread
The portion of a tire that normally touches the road.
Tread rib
A tread section running circumferentially around a tire.
Tread separation
Tire failure caused by the tread pulling away from the tire carcass.
Tread wear indicators (TWI)
Raised areas within the main tread grooves that show, visually, when tires are worn and near the end
of their useful life.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG)
A tire information system developed by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA) that is designed to help buyers compare tires. UTQG is not a safety rating, nor is it a
guarantee that a tire will last for a certain number of miles or perform a certain way. It gives tire buyers
more information to compare with factors such as price, brand loyalty and dealer recommendations.
Under UTQG, tires are graded by the tire manufacturers in 3 areas: tread wear, traction and
temperature resistance. UTQG information is molded into the tire sidewalls.
U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number (TIN)
A tire's serial number. It begins with the letters “DOT” (“Department of Transportation”) and indicates
that the tire meets all federal standards. The next two numbers or letters indicate the plant where the
tire was manufactured. The last four numbers represent the week and year of manufacture.
For example, the numbers 1709 mean that the tire was produced in the 17th week of 2009. Any other
numbers are marketing codes used by the tire manufacturer. This information is used to help identify
affected consumers if a tire defect requires a recall.
Vehicle capacity weight
The total rated cargo, luggage and passenger load. Passenger load is 150 lbs (68 kilograms) times the
vehicle's total seating capacity (as listed on the label inside the driver door).
Page 323 of 379

Cord separation
The parting of cords from adjacent rubber compounds.
Cracking
Any parting within the tread, sidewall, or inner liner of the tire extending to cord material.
Cold tire inflation pressure
The tire pressure recommended by the vehicle manufacturer for a tire of a specified size that has not
been driven for more than a couple of miles (kilometers) at low speeds in the 3 hour period before the
tire pressure is measured or adjusted.
Curb weight
The weight of a motor vehicle with standard equipment including the maximum capacity of fuel, oil,
and coolant, air conditioner, and additional weight of optional equipment.
Extra load tire
A tire designed to operate at higher loads and at higher inflation pressures than the corresponding
standard tire.
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR)
The load-carrying capacity of a single axle system, measured where the tire contacts the ground.
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
The maximum loaded weight of the vehicle.
Groove
The space between 2 adjacent tread ribs.
Load rating (code)
The maximum load that a tire is rated to carry for a given inflation pressure. You may not find this
information on all tires because it is not required by law.
Maximum load rating
The load rating for a tire at the maximum permissible inflation pressure for that tire.
Maximum loaded vehicle weight
The total of:
�x Curb weight
�x Accessory weight.
�x Vehicle capacity weight.
�x Production options weight.
Maximum (permissible) inflation pressure
The maximum cold inflation pressure to which a tire may be inflated. Also called “maximum inflation
pressure.”
Normal occupant weight
Means 150 lbs (68 kilograms) times the number of occupants seated in the vehicle up to the total
seating capacity of your vehicle.
Occupant distribution
The placement of passengers in a vehicle.
Page 324 of 379

Outer diameter
The diameter of a new, properly inflated tire.
Overall width
Total width measured at the exterior sidewalls of an inflated tire, including the additional width of
labeling, decorations, or protective bands or ribs.
Passenger car tire
A tire intended for use on passenger cars, multipurpose passenger vehicles, and trucks, that have a
gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of 10,000 pounds or less.
Ply
A layer of rubber-coated parallel cords.
Ply separation
A parting of rubber compound between adjacent plies.
Pneumatic tire
A mechanical device made of rubber, chemicals, fabric, and steel or other materials, that, when
mounted on an automotive wheel, provides the traction and contains the gas or fluid that sustains the
load.
Production options weight
The combined weight of installed regular production options weighing over 5 lbs (2.3 kg) more then the
standard items they replace, and not previously considered as curb weight or accessory weight. These
include, for example, heavy-duty brakes, ride levelers, heavy-duty battery, and special trim.
Radial ply tires
A pneumatic tire in which the ply cords that extend to the beads are laid at substantially 90 degrees to
the centerline of the tread.
Recommended inflation pressure
The tire pressure recommended by the vehicle manufacturer for a tire of a specified size that has not
been driven for more than a couple of miles (kilometers) at low speeds in the 3 hour period before the
tire pressure is measured or adjusted.
Reinforced tire
A tire designed to operate at higher loads and at higher inflation pressures than the corresponding
standard tire.
Rim
The outer edge of a wheel upon which the tire beads are seated.
Rim diameter
The nominal diameter of the wheel's tire bead seating surface. If you change your wheel size, to
wheels of a different diameter, you will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheels.
Rim size
Designation means rim diameter and width.
Rim type designation
The industry or manufacturer's designation for a rim by style or code.
Rim width
The nominal distance between wheel rim flanges.
Page 325 of 379

Section width
The linear distance between the exteriors of the sidewalls of an inflated tire, excluding elevations due
to labeling decoration, or protective bands.
Sidewall
The portion of a tire between the bead and the tread.
Sidewall separation
The parting of the rubber compound from the cord material in the sidewall.
Speed rating (letter code)
A standardized letter code indicating the maximum speed at which a tire is designed to be driven for
extended periods of time. The ratings range from 93 mph or 150 km/h (“P”) to 186 mph or (300 km/h)
“Y”.
The speed rating letter code, where applicable, is molded on the tire sidewall. You may not find this
information on all tires because it is not required by law.
Tire Pressure Monitoring System
A system that detects when at least one of a vehicle's tires is underinflated and illuminates a low tire-
pressure warning light.
Tread
The portion of a tire that normally touches the road.
Tread rib
A tread section running circumferentially around a tire.
Tread separation
Tire failure caused by the tread pulling away from the tire carcass.
Tread wear indicators (TWI)
Raised areas within the main tread grooves that show, visually, when tires are worn and near the end
of their useful life.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG)
A tire information system developed by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA) that is designed to help buyers compare tires. UTQG is not a safety rating, nor is it a
guarantee that a tire will last for a certain number of miles or perform a certain way. It gives tire buyers
more information to compare with factors such as price, brand loyalty and dealer recommendations.
Under UTQG, tires are graded by the tire manufacturers in 3 areas: tread wear, traction and
temperature resistance. UTQG information is molded into the tire sidewalls.
U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number (TIN)
A tire's serial number. It begins with the letters “DOT” (“Department of Transportation”) and indicates
that the tire meets all federal standards. The next two numbers or letters indicate the plant where the
tire was manufactured. The last four numbers represent the week and year of manufacture.
For example, the numbers 1709 mean that the tire was produced in the 17th week of 2009. Any other
numbers are marketing codes used by the tire manufacturer. This information is used to help identify
affected consumers if a tire defect requires a recall.
Vehicle capacity weight
The total rated cargo, luggage and passenger load. Passenger load is 150 lbs (68 kilograms) times the
vehicle's total seating capacity (as listed on the label inside the driver door).
Page 344 of 379

Description Possible causes, among
others Possible remedy
Electrical loads switched on. Switch off unnecessary loads.
Engine control malfunctioning. Have the malfunction corrected.
Tire pressure too low. Adjust tire pressure.
Driving in the mountains. No direct corrective action possible.
Towing a trailer. – Check use.
– Remove if not in use.
Driving with heavy payload. No direct corrective action possible.
Driving at high engine speed. Select a higher gear.
Applicable only in Mexico, the AGCC, and South Korea
Frequently asked questions
If you suspect a malfunction or vehicle damage, read and follow the following advice before contacting
an authorized Volkswagen dealer or an authorized Volkswagen Service Facility. You may also find
helpful information under “Characteristics” and “Checklist” in the index.
Description Possible causes among
others Possible remedy
Engine does not start.
Vehicle battery dead. – Perform jump-start.
– Charge vehicle battery.
The wrong vehicle key is used. Use a valid vehicle key.
Fuel level too low. Refuel.
Vehicle cannot be locked
or unlocked using vehicle
key.
– Battery in the remote control
vehicle key is dead.
– Too far away from vehicle.
– Buttons pressed outside
operating range.
– Replace the battery in the remote
control vehicle key.
– Move closer to vehicle.
– Synchronize vehicle key.
– Lock or unlock vehicle manually.
Unusual noises.
Cold engine, braking assist
systems, and electronic
steering column lock.
Check the “Noises” entry in the index.
Odd driving behavior.
Assistance systems activated. Check the “Assistance systems” entry
in the index.
DSG® Direct Shift Gearbox too
hot.
Stop vehicle as soon as you can do so
safely
Outside mirrors move
when vehicle is unlocked.
Convenience settings are
stored. Correct convenience settings.
Front seats cannot be
adjusted with power
controls.
Vehicle battery dead. Charge vehicle battery.
Fuse blown. Check fuse and replace if necessary.
No jack or spare tire in
vehicle.
Equipment differs depending
on vehicle.
No direct corrective action possible
because this depends on the
Page 345 of 379
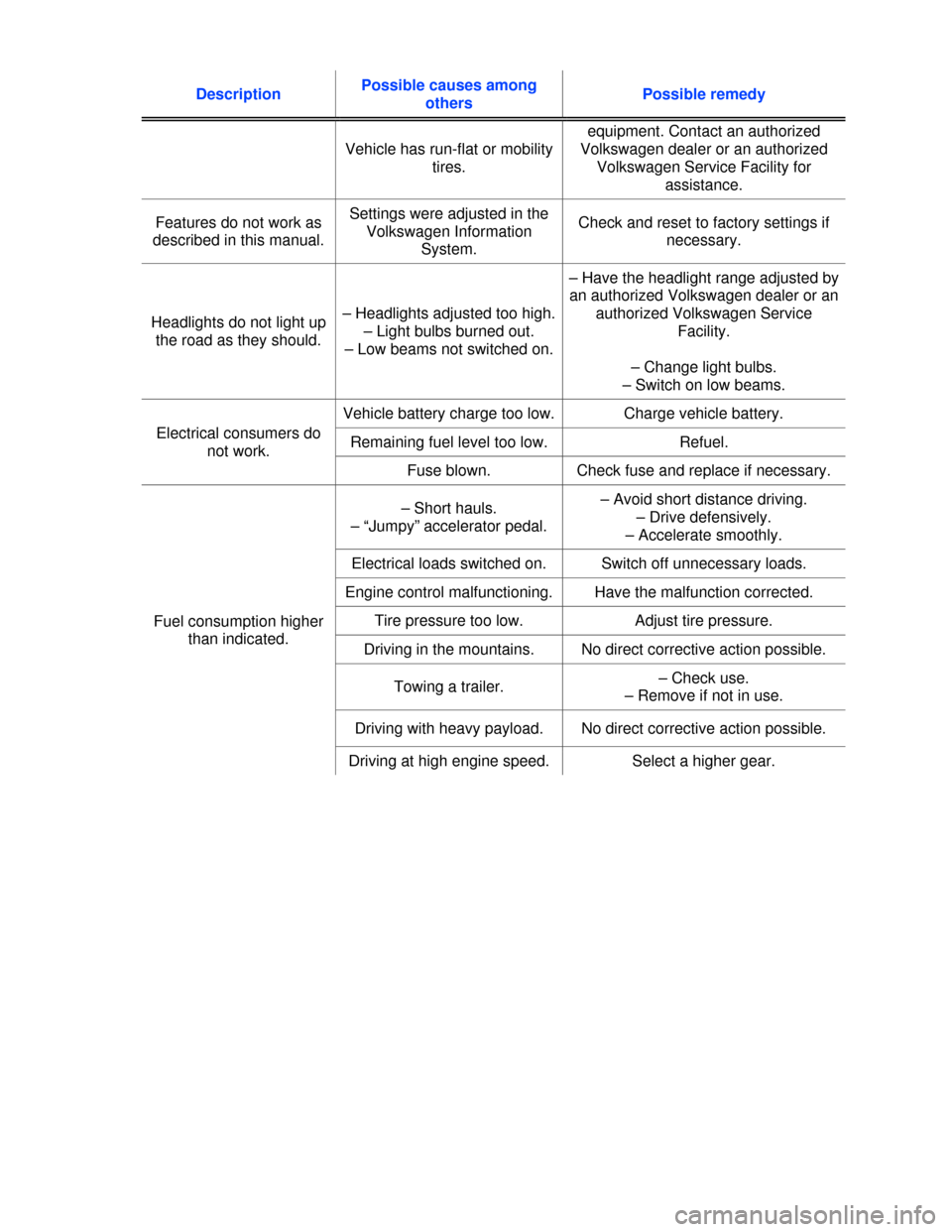
Description Possible causes among
others Possible remedy
Vehicle has run-flat or mobility
tires.
equipment. Contact an authorized
Volkswagen dealer or an authorized
Volkswagen Service Facility for
assistance.
Features do not work as
described in this manual.
Settings were adjusted in the
Volkswagen Information
System.
Check and reset to factory settings if
necessary.
Headlights do not light up
the road as they should.
– Headlights adjusted too high.
– Light bulbs burned out.
– Low beams not switched on.
– Have the headlight range adjusted by
an authorized Volkswagen dealer or an
authorized Volkswagen Service
Facility.
– Change light bulbs.
– Switch on low beams.
Electrical consumers do
not work.
Vehicle battery charge too low. Charge vehicle battery.
Remaining fuel level too low. Refuel.
Fuse blown. Check fuse and replace if necessary.
Fuel consumption higher
than indicated.
– Short hauls.
– “Jumpy” accelerator pedal.
– Avoid short distance driving.
– Drive defensively.
– Accelerate smoothly.
Electrical loads switched on. Switch off unnecessary loads.
Engine control malfunctioning. Have the malfunction corrected.
Tire pressure too low. Adjust tire pressure.
Driving in the mountains. No direct corrective action possible.
Towing a trailer. – Check use.
– Remove if not in use.
Driving with heavy payload. No direct corrective action possible.
Driving at high engine speed. Select a higher gear.
Page 349 of 379
Fire extinguisher
A fire extinguisher may be located in a holder in the footwell in front of or under the front passenger
seat.
The fire extinguisher must comply with the valid legal requirements. It must be fully functional and
checked regularly. See the testing label on the fire extinguisher.
WARNING
In the event of a sudden driving or braking maneuver or accident, loose objects could be
flung though the vehicle and cause severe injuries.
�x Always secure the fire extinguisher, high-visibility vest, first-aid kit, and warning triangle
safely in the vehicle.
Only applicable in the AGCC
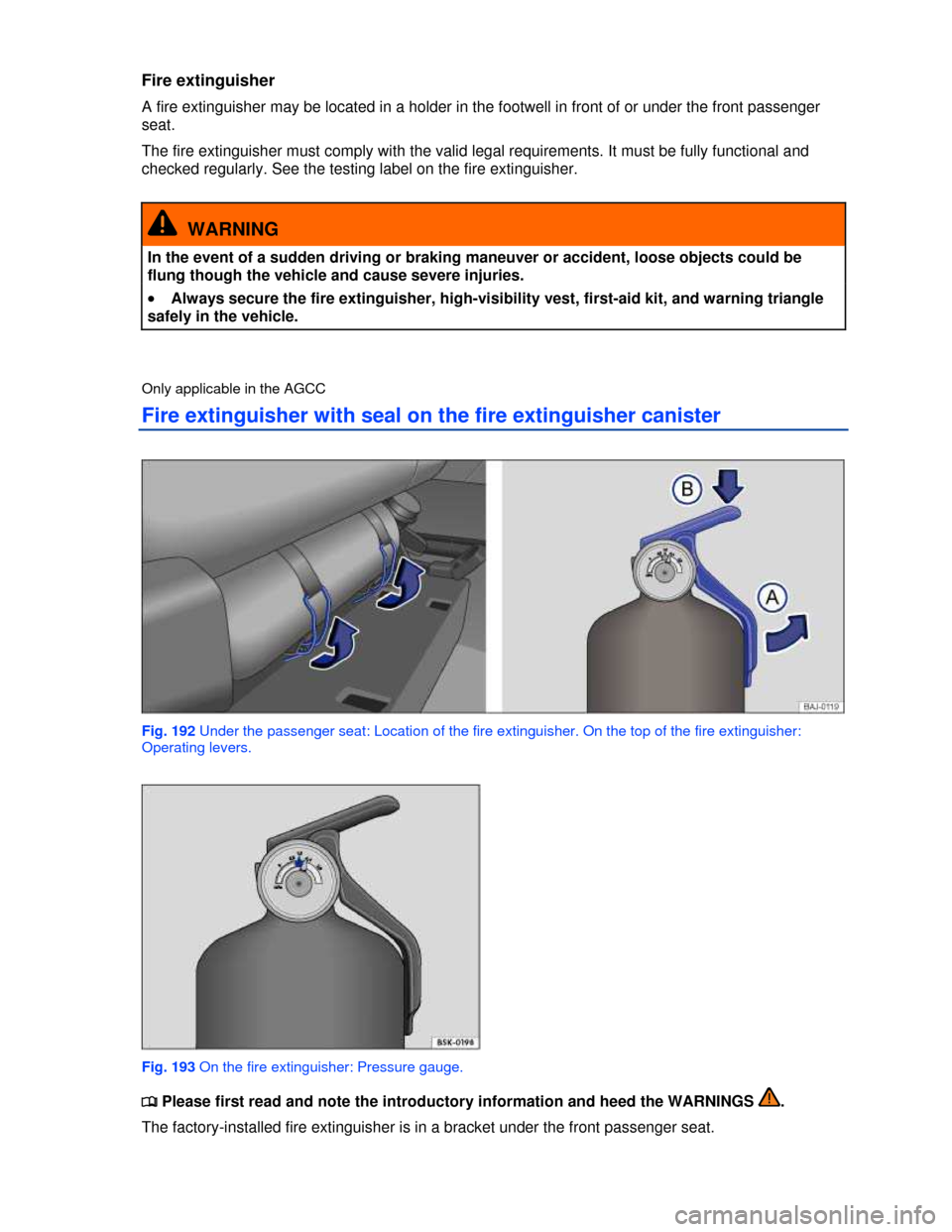
Fire extinguisher with seal on the fire extinguisher canister
Fig. 192 Under the passenger seat: Location of the fire extinguisher. On the top of the fire extinguisher:
Operating levers.
Fig. 193 On the fire extinguisher: Pressure gauge.
�
Page 350 of 379
It is important to know where the fire extinguisher is stored, how to remove and how to use it before
you need it to put out a fire.
Please be sure to read the operating instructions and heed the other important information on the fire
extinguisher label before you have to use it in a later emergency.
Using the fire extinguisher
�x Release the retaining tab on the fire extinguisher bracket upward, in the direction of the arrow
⇒ fig. 192.
�x Remove the fire extinguisher from the bracket.
�x Lift the lever on the fire extinguisher in the direction of the arrow (A) to break the seal on the
extinguisher canister.
�x While holding the fire extinguisher upright, direct the nozzle at the source of the fire.
�x Press the release in the direction of the arrow (B) to release the extinguishing agent.
�x Extinguish the fire from the bottom up.
�x Stop extinguishing the fire only when the flames are quenched.
�x If possible, have another fire extinguisher or other extinguishing agent available in case the fire
reignites!
Installing the fire extinguisher
�x Guide the fire extinguisher into the attachment straps.
�x Place the fire extinguisher on the bracket.
�x When locking the attachment strap, always make sure that the locking bars engage securely.
Fire extinguisher maintenance
Check the following on the fire extinguisher regularly:
�x Expiration date: do not exceed the expiration date on the fire extinguisher.
�x Pressure gauge: the needle ⇒ fig. 193 must be in the green area (ready for use).
�x General inspection: make sure the components are secure and check for rust, dents or other
damage.
�x Intact tamper-resistant seal: shows that the fire extinguisher has not been used.
WARNING
A loose fire extinguisher in the passenger can be thrown around the passenger compartment
and cause serious personal injury during hard braking, an emergency maneuver or during a
crash
�x Always make sure that the fire extinguisher is properly and firmly secured in bracket
provided.