2013 SKODA ROOMSTER seats
[x] Cancel search: seatsPage 78 of 219
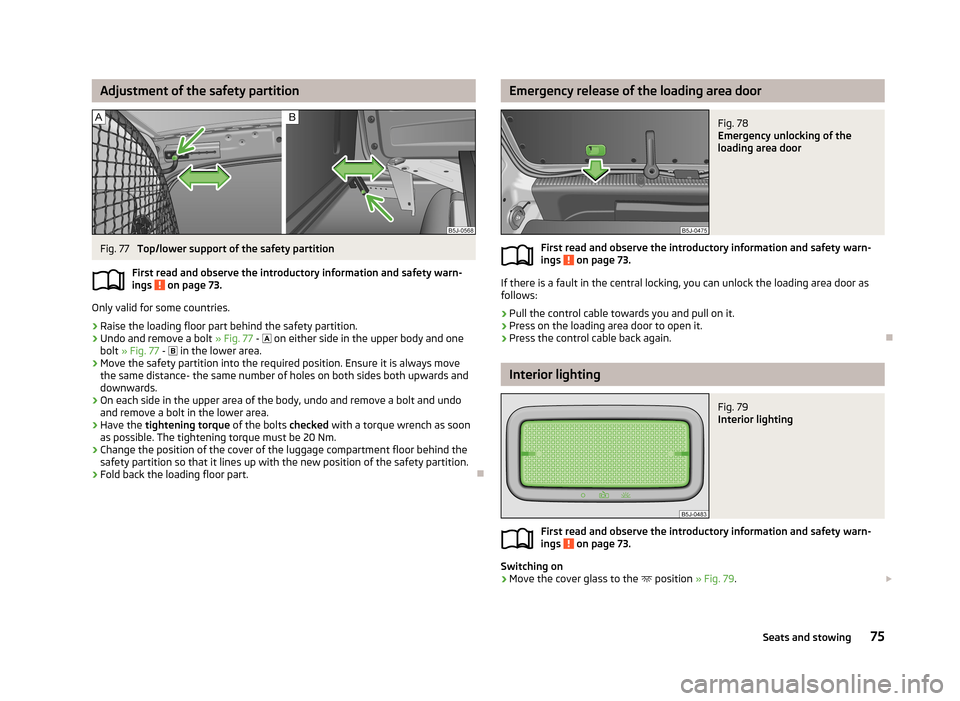
Adjustment of the safety partitionFig. 77
Top/lower support of the safety partition
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 73.
Only valid for some countries.
›
Raise the loading floor part behind the safety partition.
›
Undo and remove a bolt » Fig. 77 -
on either side in the upper body and one
bolt » Fig. 77 -
in the lower area.
›
Move the safety partition into the required position. Ensure it is always move
the same distance- the same number of holes on both sides both upwards anddownwards.
›
On each side in the upper area of the body, undo and remove a bolt and undoand remove a bolt in the lower area.
›
Have the tightening torque of the bolts checked with a torque wrench as soon
as possible. The tightening torque must be 20 Nm.
›
Change the position of the cover of the luggage compartment floor behind the safety partition so that it lines up with the new position of the safety partition.
›
Fold back the loading floor part.
Emergency release of the loading area doorFig. 78
Emergency unlocking of the
loading area door
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 73.
If there is a fault in the central locking, you can unlock the loading area door as
follows:
›
Pull the control cable towards you and pull on it.
›
Press on the loading area door to open it.
›
Press the control cable back again.
Interior lighting
Fig. 79
Interior lighting
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn- ings on page 73.
Switching on
›
Move the cover glass to the position
» Fig. 79.
75Seats and stowing
Page 98 of 219

Driving
Starting-off and Driving
Steering
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Adjusting the steering wheel position
95
Power steering
95WARNING■ When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer
edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering wheel in
the 12 o'clock position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or inner edge of
the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure the arms, hands
and head when the driver airbag is deployed.■
Never adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is moving only when the
vehicle is stationary!
■
Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance
1
» Fig. 88 on page 95
between the steering wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - there is a risk that you could be killed.
■
If the steering wheel is adjusted further towards the head, the protection
provided by the driver airbag in the event of an accident is reduced. Check
that the steering wheel is aligned to the chest.
Adjusting the steering wheel positionFig. 88
Adjustable steering wheel: Lever below the steering column/safe
distance to the steering wheel
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 95.
The height and forward/back position of the steering wheel can be adjusted.
›
First of all adjust the driver's seat » page 52, Front seats .
›
Pull the lever below the steering wheel down » Fig. 88 -
.
›
Adjust the steering wheel to the desired position (with regard to the height and
forward/back position).
›
Push the lever upwards to the stop.
WARNINGThe lever for adjusting the steering wheel must be locked whilst driving so
that the position of the steering wheel cannot accidentally change during the
journey – risk of accident!
Power steering
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 95.
The power steering enables you to steer the vehicle with less physical force.
The power steering only works when the engine is running.
95Starting-off and Driving
Page 126 of 219
Safety
Passive Safety
General information
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Safety equipment
123
Before setting off
123
What influences the driving safety?
124
In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the subject
of passive safety in your vehicle.
We have combined everything here which you should be familiar with, for exam- ple, regarding seat belts, airbags, child seats and safety of children.
WARNING■ This chapter contains important information on how to use the vehicle for
the driver and his occupants.■
You can find further information on safety concerning you and those travel-
ling with you in the following chapters of this owner's manual.
■
The complete on-board literature should always be in the vehicle. This ap-
plies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Safety equipment
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 123.
The following list contains only part of the safety equipment in your vehicle.
› Three-point seat belts for all the seats.
› Belt force limiters for the front seats.
› Belt tensioners for the front seats.
› Seat belt height adjusters for the front seats.
›
Front airbag for the driver and the front passenger.
› Side airbags.
› Head airbags.
› Anchoring points for child seats using the ISOFIX system.
› Anchoring points for child seats using the TOP TETHER system.
› Head restraints adjustable for height.
› Adjustable steering column.
The specified safety equipment works together, in order to optimally protect you
and those travelling with you in accident situations.
The safety equipment does not protect you or the people travelling with you, if
you or your occupants adopt an incorrect seated position or the equipment is not
correctly adjusted or used.
If the seat belt is not fastened properly, this may result in injuries if an airbag is
activated in the event of an accident.
Before setting off
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 123.
For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you, please pay
attention to the following points before setting off.
› Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal system are functioning properly.
› Check the tyre inflation pressure.
› Ensure that all of the windows offer good visibility to the outside.
› Secure all items of luggage
» page 57.
› Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedals.
› Adjust the mirrors, the front seat and head restraint to your body size.
› Advise your passengers to adjust the head restraints to their body size.
› Protect children in suitable child seats with correctly fastened seat
belts » page 139 , Transporting children safely .
› Adopt the correct seated position
» page 124. Tell your passengers to assume
the correct seated position.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt. Also inform passengers to fasten the seat belt
correctly » page 127 , Using seat belts .
123Passive Safety
Page 127 of 219

What influences the driving safety?First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 123.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving safety is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
The following guidelines must therefore be observed. › Do not become distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g. by
your passengers or mobile phone calls.
› Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. due to medication, alcohol
or drugs.
› Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
› Always adjust the driving speed to the road, traffic and weather conditions.
› Take regular breaks on long journeys – at least every two hours.
Correct seated position
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Correct seated position for the driver
125
Correct seated position for the front passenger
125
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
125
Examples of incorrect seated positions
125WARNINGGeneral information■The front seats and head restraints must be adjusted to match the body
size at all times and the seat belt must always be fastened properly to provide the most effective levels of protection to the passengers.■
If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
■
If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury is
increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
■
The seat backrests must not be tilted too far back when driving, as this will
impair the function of the seat belts and of the airbag system – risk of injury!
WARNINGInformation for the driver■Always assume the correct seated position before setting off and do not
change this position while driving. Also advise your passengers to adopt the
correct seated position and not to change this position while the car is mov-
ing.■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering wheel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - hazard!
■
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer
edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering wheel in
the 12 o'clock position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or inner edge of
the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure the arms, hands
and head when the driver airbag is deployed.
■
Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell, as these may get
caught in the pedal apparatus when driving or braking. You would then no longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or acceleration pedals.
WARNINGInformation for the front seat passenger■Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from the dash panel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - there is a risk that you could be killed.■
Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven - never
place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the seats.
You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply
the brakes or in the event of an accident. You may suffer fatal injuries when
an airbag is deployed if you have adopted an incorrect seating position.
124Safety
Page 128 of 219
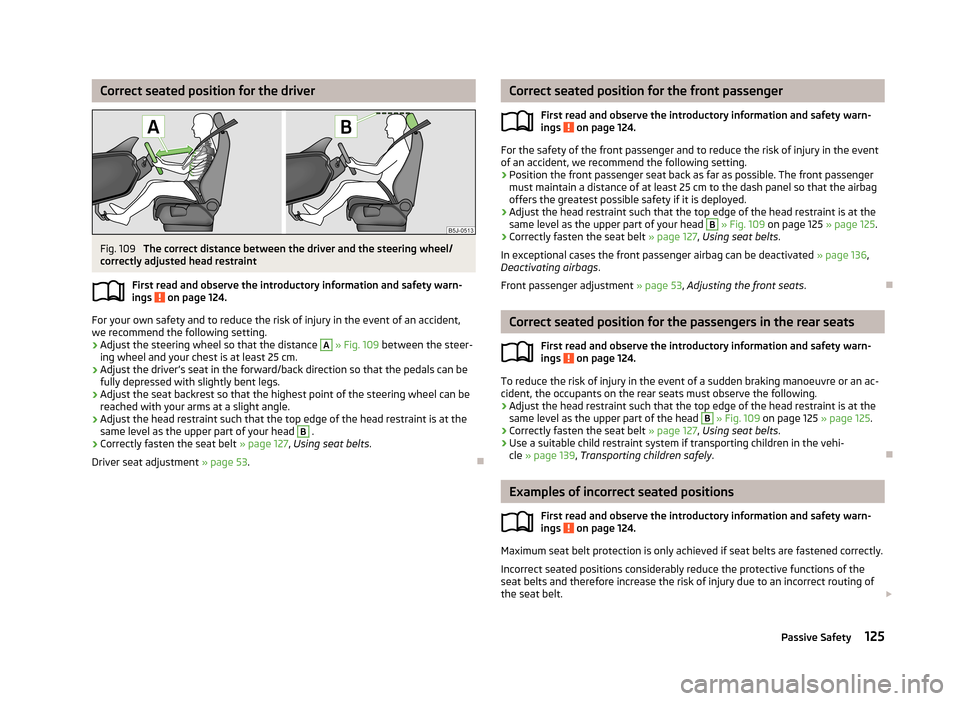
Correct seated position for the driverFig. 109
The correct distance between the driver and the steering wheel/
correctly adjusted head restraint
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 124.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident,
we recommend the following setting.
› Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance
A
» Fig. 109 between the steer-
ing wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm.
› Adjust the driver’s seat in the forward/back direction so that the pedals can be
fully depressed with slightly bent legs.
› Adjust the seat backrest so that the highest point of the steering wheel can be
reached with your arms at a slight angle.
› Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head
B
.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt
» page 127, Using seat belts .
Driver seat adjustment » page 53.
Correct seated position for the front passenger
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 124.
For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event
of an accident, we recommend the following setting.
› Position the front passenger seat back as far as possible. The front passenger
must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel so that the airbag
offers the greatest possible safety if it is deployed.
› Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head
B
» Fig. 109 on page 125 » page 125.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt
» page 127, Using seat belts .
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactivated » page 136,
Deactivating airbags .
Front passenger adjustment » page 53, Adjusting the front seats .
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 124.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an ac-
cident, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
› Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of the head
B
» Fig. 109 on page 125 » page 125.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt
» page 127, Using seat belts .
› Use a suitable child restraint system if transporting children in the vehi-
cle » page 139 , Transporting children safely .
Examples of incorrect seated positions
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 124.
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if seat belts are fastened correctly.
Incorrect seated positions considerably reduce the protective functions of the
seat belts and therefore increase the risk of injury due to an incorrect routing of
the seat belt.
125Passive Safety
Page 129 of 219

The driver is fully responsible for himself and passengers, especially children.
Never allow a passenger to adopt an incorrect seated position when the car is
moving.
The following list contains instructions which, if not observed, may cause serious injuries or death. This list is not complete, however we would like you to familiar-
ise yourself with this subject.
Observe the following instructions while driving. › Do not stand up.
› Do not stand on the seats.
› Do not kneel on the seats.
› Do not tilt the seat backrest too far back.
› Do not lean against the dash panel.
› Do not lie on the rear seats.
› Do not sit only on the front part of the seat.
› Do not sit facing to the side.
› Do not lean out of the window.
› Do not put your feet out of the window.
› Do not put your feet on the dash panel.
› Do not put your feet on the seat cushion.
› Do not allow anybody to travel in the footwell.
› Do not drive without fastening your seat belt.
› Do not delay in the luggage compartment.
126Safety
Page 130 of 219

Seat belts
Using seat belts
Introduction
Fig. 110
Driver wearing seat belt
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
The physical principle of a frontal collision
128
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
129
Seat belt height adjuster on the front seats
130
Seat belt for the rear middle seat
130
Seat belts that are fastened correctly offer good protection in the event of an ac-
cident. They reduce the risk of an injury and increase the chance of survival in the
event of a major accident.
Correctly fastened seat belts hold occupants of the car in the correct seated posi-
tion » Fig. 110 .
The seat belts reduce the kinetic energy (energy of motion) to a considerable ex-
tent. They also prevent uncontrolled movements which, in turn, may well result in
severe injuries.
Occupants of a vehicle who have correctly fastened their seat belts have the ma-
jor benefit of the fact that the kinetic energy is absorbed as effectively as possi-
ble by the belts.
The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other passive safety measures,
such as the airbag system, also contribute to the kinetic energy being reduced as
effectively as possible. The energy produced is thus absorbed and there is less
risk of injury.
Particular safety aspects must be observed when transporting children in the ve-
hicle » page 139 , Transporting children safely .WARNING■
Fasten your seat belt before each journey - even when driving in town! This
also applies to the passengers seated at the rear – risk of injury!■
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of
ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child » page 129, Fastening and
unfastening seat belts .
■
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if you are correctly seat-
ed » page 124 , Correct seated position .
■
The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
WARNINGObserve the following instructions for the correct routing of the seat belt.■Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in
minor accidents.■
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the belt
is roughly positioned across the middle of your shoulder - on no account across your neck.
■
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then sud-
denly held firm by the belt.
■
The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. specta-
cles, ball-point pens, bunches of keys etc.). Such objects can cause injury.
WARNINGObserve the following instructions for handling the seat belts.■The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted,
or chafe against any sharp edges.■
Make sure you do not catch the seat belt when closing the door.
127Seat belts
Page 131 of 219

WARNINGObserve the following instructions for the proper use of the seat belts.■Never use one seat belt to secure two persons (including children). The
seatbelt must not be placed over a child who is sitting on the lap of another
passenger.■
The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to pro-
tect and the risk of injury increases.
■
The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked, otherwise the belt tongue
will not lock in place properly.
■
Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jacket)
do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of the
seat belts.
■
It is prohibited to use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e. g. for
shortening the belts for smaller persons).
■
The seat belts for the rear seats can only fulfil their function reliably when
the seat backrests are correctly locked into position » page 55.
WARNINGObserve the following instructions for proper maintenance of the seat belts.■The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may im-
pair proper operation of the inertia reel » page 156.■
The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not attempt
to repair the seat belts yourself.
■
Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis. If any damage to
the seat belts, seat belt connections, inertia reel or the lock is detected, the
relevant seat belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
■
Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident and
were therefore stretched, must be replaced - this is best done by a specialist
garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The an-
chorage points for the belts should also be checked.
Note
The national legal requirements must be observed when using seat belts.
The physical principle of a frontal collisionFig. 111
Driver without a fastened seat belt/rear passenger without a fas-
tened seat belt
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 127.
As soon as the vehicle is moving, so-called kinetic energy (the energy of motion)
is produced both in terms of the car as well as in terms of the occupants.
The magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on the speed at which
the vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle including the occupants.
The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the amount of energy
which has to be absorbed in the event of an accident.
The speed of the vehicle is the most important factor. Doubling the speed of the
vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy four times.
The idea that it is possible to support your body with your hands in a minor acci- dent is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces acting on the
body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed of 30-50 km/h, the forces that your body is ex-
posed to in the event of an accident can exceed a metric ton (1000 kg).
For example, a person's weight of 80 kg “increases” to 4.8 tons (4800 kg) at
50 km/h.
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt are thrown forward in an uncontrolled way and strike parts of the interior of the car,
such as the steering wheel, dash panel or windscreen » Fig. 111 -
. In certain cir-
cumstances you could even be thrown out of the vehicle, which could cause life threatening or even fatal injuries.
128Safety