2012 YAMAHA YZ450F oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 173 of 228
5-34
SWINGARM
HANDLING NOTE
Support the machine securely so
there is no danger of it falling over.
REMOVING THE BEARING
1. Remove:
• Bearing "1"
Remove the bearing by pressing its
outer race.
CHECKING THE SWINGARM
1. Inspect:
• Bearing "1"
• Bushing "2"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust →Replace bearing and
bushing as a set.
2. Inspect:
• Oil seal "3"
Damage→Replace.
CHECKING THE RELAY ARM
1. Inspect:
• Bearing "1"
•Collar "2"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust → Replace bearing and
collar as a set.
2. Inspect:
• Oil seal "3"
Damage→Replace.CHECKING THE CONNECTING
ROD
1. Inspect:
•Bearing "1"
• Collar "2"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust →Replace bearing and
collar as a set.
2. Inspect:
• Oil seal "3"
Damage→Replace.
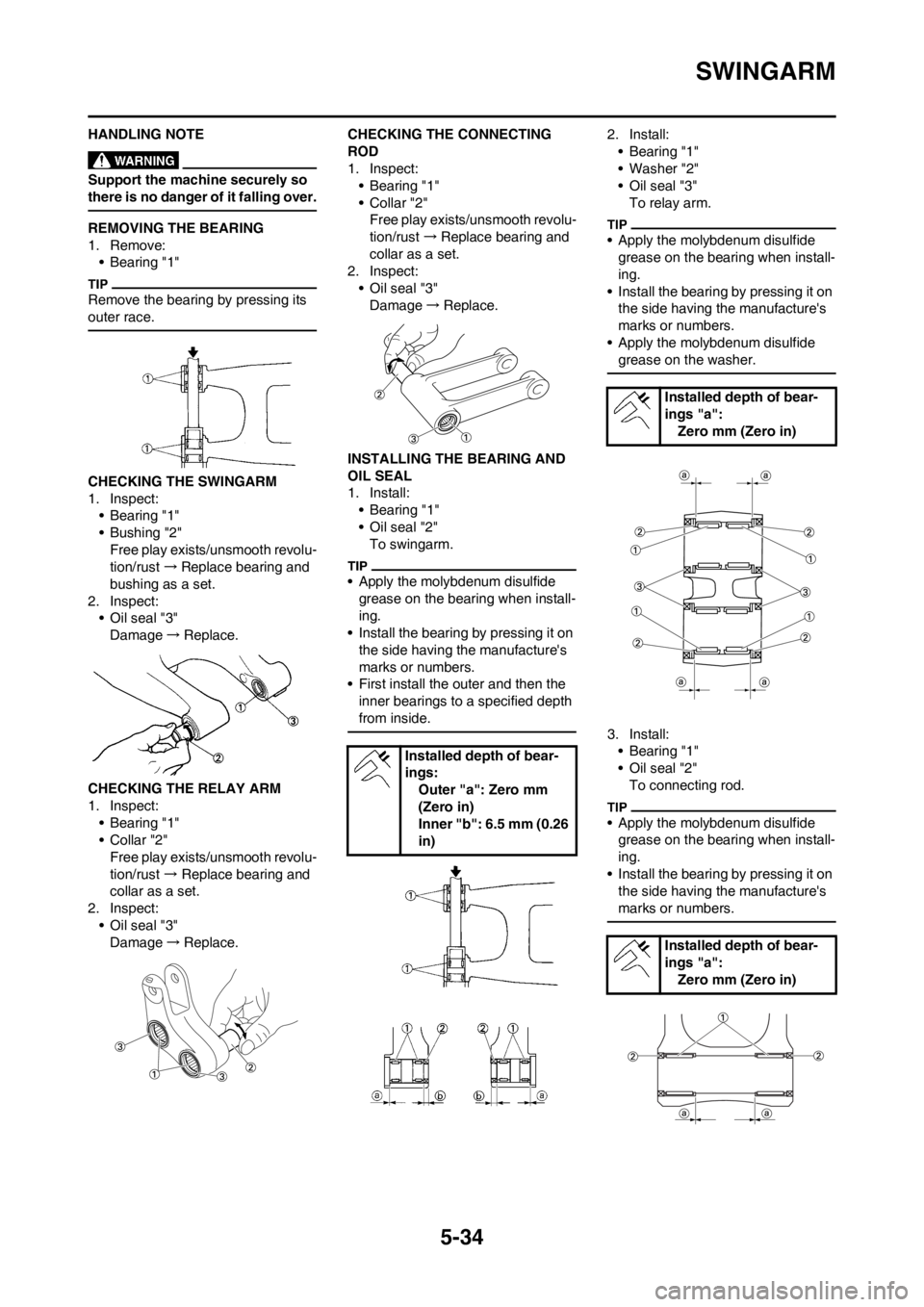
INSTALLING THE BEARING AND
OIL SEAL
1. Install:
•Bearing "1"
• Oil seal "2"
To swingarm.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bearing when install-
ing.
• Install the bearing by pressing it on
the side having the manufacture's
marks or numbers.
• First install the outer and then the
inner bearings to a specified depth
from inside.
2. Install:
• Bearing "1"
• Washer "2"
• Oil seal "3"
To relay arm.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bearing when install-
ing.
• Install the bearing by pressing it on
the side having the manufacture's
marks or numbers.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the washer.
3. Install:
• Bearing "1"
• Oil seal "2"
To connecting rod.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bearing when install-
ing.
• Install the bearing by pressing it on
the side having the manufacture's
marks or numbers.
Installed depth of bear-
ings:
Outer "a": Zero mm
(Zero in)
Inner "b": 6.5 mm (0.26
in)
Installed depth of bear-
ings "a":
Zero mm (Zero in)
Installed depth of bear-
ings "a":
Zero mm (Zero in)
Page 174 of 228

5-35
SWINGARM
INSTALLING THE SWINGARM
1. Install:
• Bushing "1"
• Thrust bearing "2"
• Oil seal "3"
•Collar "4"
To swingarm "5".
Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bushings, thrust bear-
ings, oil seal lips and contact surfaces
of the collar and thrust bearing.
2. Install:
•Collar "1"
• Washer "2"
To relay arm "3".
Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the collars and oil seal lips.
3. Install:
•Collar "1"
To connecting rod "2".
Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the collar and oil seal lips.
4. Install:
• Connecting rod "1"
• Bolt (connecting rod) "2"
• Washer "3"
• Nut (connecting rod) "4"
To relay arm "5".
Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bolt.
5. Install:
• Relay arm "1"
• Bolt (relay arm) "2"
• Washer "3"
• Nut (relay arm) "4"
To swingarm.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bolt circumference
and threaded portion.
• Do not tighten the nut yet.
6. Install:
• Swingarm "1"
• Pivot shaft "2"
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the pivot shaft.
• Insert the pivot shaft from right side.
7. Check:
• Swingarm side play "a"
Free play exists→Replace thrust
bearing.
• Swingarm up and down move-
ment "b"
Unsmooth movement/binding/
rough spots →Grease or replace
bearings, bushings and collars.
8. Install:
• Bolt (connecting rod) "1"
• Washer "2"
• Nut (connecting rod) "3"
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bolt.
• Do not tighten the nut yet.
9. Install:
• Bolt (rear shock absorber-relay
arm) "1"
• Nut (rear shock absorber-relay
arm) "2"
Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bolt.
Nut (connecting rod):
80 Nm (8.0 m•kg, 58
ft•lb)
Pivot shaft:
85 Nm (8.5 m•kg, 61
ft•lb)
Nut (rear shock absorb-
er-relay arm):
53 Nm (5.3 m•kg, 38
ft•lb)
Page 177 of 228

5-38
REAR SHOCK ABSORBER
HANDLING NOTE
• Support the machine securely so
there is no danger of it falling
over.
• This rear shock absorber is pro-
vided with a separate type tank
filled with high-pressure nitro-
gen gas. To prevent the danger
of explosion, read and under-
stand the following information
before handling the shock ab-
sorber. The manufacturer can
not be held responsible for prop-
erty damage or personal injury
that may result from improper
handling.
• Never tamper or attempt to dis-
assemble the cylinder or the
tank.
• Never throw the rear shock ab-
sorber into an open flame or
other high heat. The rear shock
absorber may explode as a re-
sult of nitrogen gas expansion
and/ or damage to the hose.
• Be careful not to damage any
part of the gas tank. A damaged
gas tank will impair the damp-
ing performance or cause a
malfunction.
• Take care not to scratch the
contact surface of the piston
rod with the cylinder; or oil
could leak out.
• Never attempt to remove the
plug at the bottom of the nitro-
gen gas tank. It is very danger-
ous to remove the plug.
• When scrapping the rear shock
absorber, follow the instruc-
tions on disposal.
NOTES ON DISPOSAL (YAMAHA
DEALERS ONLY)
Before disposing the rear shock ab-
sorber, be sure to extract the nitrogen
gas from valve "1". Wear eye protec-
tion to prevent eye damage from es-
caping gas and/or metal chips.
To dispose of a damaged or worn-
out rear shock absorber, take the
unit to your Yamaha dealer for this
disposal procedure.
REMOVING THE BEARING
1. Remove:
• Stopper ring (upper bearing) "1"
Press in the bearing while pressing its
outer race and remove the stopper
ring.
2. Remove:
• Upper bearing "1"
Remove the bearing by pressing its
outer race.
3. Remove:
• Lower bearing "1"
Remove the bearing by pressing its
outer race.
CHECKING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER
1. Inspect:
• Damper rod "1"
Bends/damage→Replace rear
shock absorber assembly.
• Shock absorber "2"
Oil leaks→Replace rear shock
absorber assembly.
Gas leaks→Replace rear shock
absorber assembly.
• Spring "3"
Damage→Replace spring.
Fatigue→Replace spring.
Move spring up and down.
• Spring guide "4"
Wear/damage→Replace spring
guide.
• Bearing "5"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust →Replace.
INSTALLING THE BEARING
1. Install:
• Upper bearing "1"
Install the bearing parallel until the
stopper ring groove appears by
pressing its outer race.
Do not apply the grease on the
bearing outer race because it will
wear the rear shock absorber sur-
face on which the bearing is press
fitted.
Page 185 of 228

7-1
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS AND WIRING DIAGRAM
ELECTRICAL
This section is intended for those who have basic knowledge and skill concerning the servicing of Yamaha motorcycles
(e.g., Yamaha dealers, service engineers, etc.) Those who have little knowledge and skill concerning servicing are request-
ed not to undertake inspection, adjustment, disassembly, or reassembly only by reference to this manual. It may lead to
servicing trouble and mechanical damage.
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS AND WIRING DIAGRAM
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
1. Crankshaft position sensor
2. AC magneto
3. Rectifier/regulator
4. Condenser
5. Fuel pump
6. Engine stop switch
7. ECU
8. Ignition coil9. Spark plug
10. Fuel injector
11. Intake air temperature sensor
12. Intake air pressure sensor
13. Throttle position sensor
14. Atmospheric pressure sensor
15. Coolant temperature sensor
16. Coupler for connecting optional part
7
Page 186 of 228

7-2
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS AND WIRING DIAGRAM
WIRING DIAGRAM
1. Crankshaft position sensor
2. AC magneto
3. Rectifier/regulator
4. Condenser
5. Fuel pump
6. Engine stop switch
7. ECU
8. Ignition coil
9. Spark plug
10. Fuel injector
11. Intake air temperature sensor
12. Intake air pressure sensor
13. Throttle position sensor
14. Atmospheric pressure sensor
15. Coolant temperature sensor
16. Coupler for connecting optional part COLOR CODE
BBlack
Br Brown
Gy Gray
LBlue
Lg Light green
O Orange
PPink
RRed
WWhite
YYellow
B/L Black/Blue
B/R Black/Red
B/W Black/White
B/Y Black/Yellow
Br/W Brown/White
P/W Pink/White
R/B Red/Black
R/W Red/White
STOPON
Gy
Gy
B
B/L
W1
W2
W2 O
R/B
R RR
R
R
R R
Lg
Lg Lg L
P/W
P
YB/RB
B B
BB BB
BB/W
B/W B/W Br/WGyB/L
W1 W1
W2 W2 B/Y
B/Y Br
B/R
R/W
OO
R/B RR
R
L
P/W
PYL
L
LY
Br/WB/L
B/L B/L
B
B/L
B/L
Br
W1
Br/W
W2
R
R O
B/L
L
Y
B/L
Br
R
P
Gy
Gy
B/R
B/R
R/WB/Y
B/L
W1
W2
W1 R
R R
B
B/Y
Lg Lg
O
R/B R/B
Br/W
P/W P/W
LL
Y
B/L B/L
B/L
Br
B
B/W
B/W
B
B
B L
B/L P
Page 187 of 228

7-3
IGNITION SYSTEM
IGNITION SYSTEM
INSPECTION STEPS
Use the following steps for checking the possibility of the malfunctioning engine being attributable to ignition system failure
and for checking the spark plug which will not spark.
*marked: Only when the ignition checker is used.
• Remove the following parts before inspection.
1. Seat
2. Fuel tank
• Use the following special tools in this inspection.
Spark gap testSpark→• *Clean or replace spark plug.
• Check the connection of the spark plug cap to the
spark plug.
No spark↓
Check entire ignition system for connection.
(couplers, leads and ignition coil)No good→
Repair or replace.
OK↓
Check engine stop switch. No good→Replace.
OK↓
Check ignition coil. (primary coil and secondary
coil)No good→
Replace.
OK↓
Check AC magneto. (crankshaft position sensor
and stator coil)No good→
Replace.
OK↓
Replace ECU.
Dynamic spark tester:
YM-34487
Ignition checker:
90890-06754
Pocket tester:
YU-03112-C/90890-03112
Page 188 of 228

7-4
IGNITION SYSTEM
SPARK GAP TEST
1. Disconnect the spark plug cap
from spark plug.
2. Connect the dynamic spark tester
"1" (ignition checker "2") as
shown.
• Spark plug cap "3"
• Spark plug "4"
A. For USA and CDN
B. Except for USA and CDN
3. Kick the kickstarter crank.
4. Check the ignition spark gap.
5. Start engine, and increase spark
gap until misfire occurs. (for USA
and CDN only)
6. Inspect:
• Sealed portion of spark plug cap
"a"
• Spark plug terminal pin "b"
• Threaded portion of spark plug "c"
7. Inspect:
• Installed condition of spark plug
and spark plug cap
Push in the spark plug cap, mak-
ing sure that it is securely fitted
into the hole in the cylinder head
cover.CHECKING THE COUPLERS AND
LEADS CONNECTION
1. Check:
• Couplers and leads connection
Rust/dust/looseness/short-circuit
→Repair or replace.
CHECKING THE ENGINE STOP
SWITCH
1. Inspect:
• Engine stop switch conduction
Not conductive while it is pushed→
Replace.
Conductive while it is freed→Re-
place.
Set the tester selection position to "Ω
× 1".
CHECKING THE IGNITION COIL
1. Remove the ignition coil cap.
2. Inspect:
• Primary coil resistance
Out of specification→Replace.3. Inspect:
• Secondary coil resistance
Out of specification→Replace.
Disconnect the spark plug cap before
measuring the secondary coil resis-
tance.
CHECKING THE AC MAGNETO
1. Inspect:
• Crankshaft position sensor resis-
tance
Out of specification→Replace.
Minimum spark gap:
6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Tester (+) lead→Black lead "1"
Tester (-) lead→Black lead "2"
Result
Conductive (while the
engine stop switch is
pushed)
Tester (+) lead→Orange lead "1"
Tester (-) lead→Red lead "2"
Primary
coil resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
3.57–4.83
Ω at 20°C
(68°F) Ω × 1
BB
Tester (+) lead→Orange lead "1"
Tester (-) lead→Spark plug termi-
nal "2"
Secondary
coil resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
10.71–14.49
kΩ at 20°C
(68°F) kΩ × 1
Tester (+) lead→Gray lead "1"
Tester (-) lead→Black lead "2"
Crankshaft
position
sensor re-
sistanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
248–372 Ω
at 20°C
(68°F)Ω × 100
GyB
Page 189 of 228

7-5
IGNITION SYSTEM
2. Inspect:
• Stator coil resistance
Out of specification→Replace.
CHECKING THE ECU
1. Check:
• All electrical components.
2. Check:
• ECU installation status
Make sure that the ECU is in-
stalled correctly.
• The lean angle sensor is built into
the ECU.
• The lean angle sensor stops the en-
gine in case of a turnover.
• To ensure that the lean angle sen-
sor operates correctly, do not
change the installation position of
the sensor.
3. Check:
•ECU
If no fault is found, replace the
ECU. Tester (+) lead→White lead "1"
Tester (-) lead→White lead "2"
Stator coil
resistanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
0.60–0.90
Ω at 20°C
(68°F)Ω × 10
W1 W2