Page 306 of 828
15-30000-00
1. ENGINE DATA LIST
Data Unit Value
Coolant temperature℃ 0.436 V (130℃) to 4.896 V (-40℃)
Intake air temperature℃ -40 to 130℃ (varies by ambient air
temperature or engine mode)
Idle speed rpm750 ± 20
Engine load % 18~25%
Mass air flow kg/h 16 to 25 kg/h
Throttle position angle°TA 0° (Full Open) to 78° (Close)
Engine torque Nm varies by engine conditions
Injection time ms 3 to 5ms
Battery voltage V 13.5 V to 14.1 V
Accelerator pedal position 1 V 0.4. to 4.8V
Accelerator pedal position 2 V 0.2 to 2.4 V
Throttle position 1 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Throttle position 2 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Oxygen sensor mV 0 to 5 V
A/C compressor switch 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Full load 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Gear selection (A/T) 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Knocking control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Brake switch 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Cruise control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Page 307 of 828
15-4
Glow plug
Differential pressure
sensor
Camshaft position
sensor
1. MAJOR COMPONENTS
Rear EGT sensor
Oxygen sensor
Front EGT sensor
HFM (air mass/
temperature)
Injector (C3I)
Variable swirl valve
actuator
IMV
Page 308 of 828
15-50000-00
Fuel rail pressure
sensorEGR valveFuel temperature
sensor
Electric throttle bodyKnock sensor
(2 ea)
Coolant temperature
sensor
T-MAP sensorD20DTR ECU
E-VGT actuator
Water sensorGCU (Preglow control
unit)
E-EGR bypass valve
Page 310 of 828
15-70000-00
Fuel rail pressure
sensor
(2) Components for ECU Input
CAN
- ABS & ESP
- GCU
- Instrument
cluster
- TCUSwirl valve position
sensor
Differential
pressure sensorE-EGR valve
position sensorCamshaft position
sensorCoolant
temperature senso
r
Exhaust gas
temperature senso
r
HFM sensorOxygen sensorT-MAP sensor
Crankshaft position
sensor
Accelerator pedal
sensorThrottle position
sensorKnock sensor
-Auto cruise switch
- Rear right wheel
speed (without ABS)
- Refrigerant pressure
sensor
- Clutch pedal signal
- Blower switch signal
- Brake pedal signal
Water sensor
Page 311 of 828
15-8
(3) Components for ECU Output
CAN
E-EGR cooler
bypass valve
- Instrument cluster
- TCU
- Self diagnosis
PTC heaterCooling fan
E-EGR valve
Variable swirl valveE-VGT actuatorIMV valve
A/C compressorInjectorThrottle position
sensor
- Glow plug unit
- ABS & ESP unit
- GCU
Page 312 of 828

15-90000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston
speed and crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine
power and emission gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure
and activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so
controls various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted
to reduce emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences.
For example, there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer
and adopted CAN communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M
and brake system) in the vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status
and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied
instantly so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector
drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and
hold-current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working
condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper
injection volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and
engine cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to
ignition position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel
and engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum
engine power. -
-
-
Page 322 of 828
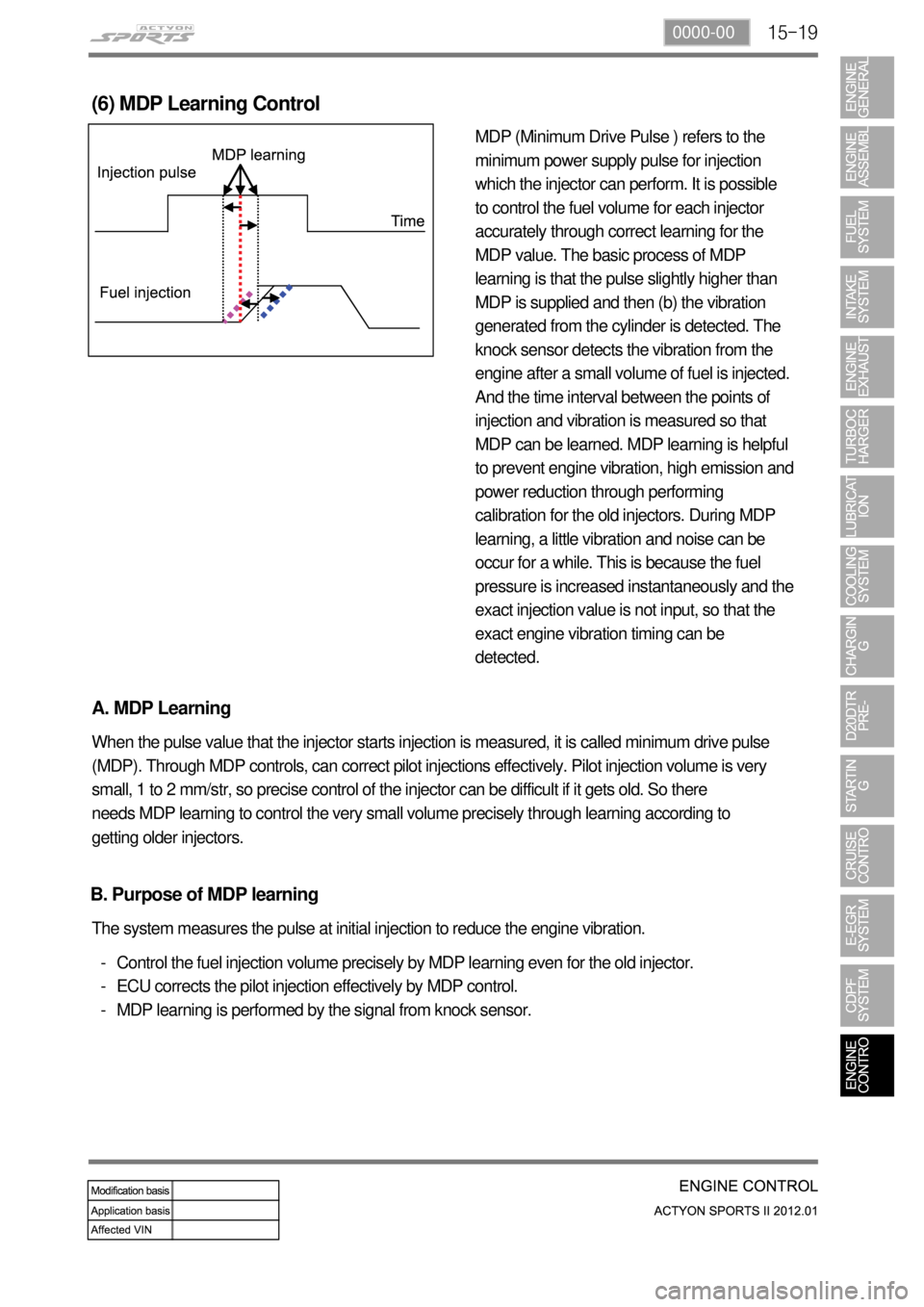
15-190000-00
MDP (Minimum Drive Pulse ) refers to the
minimum power supply pulse for injection
which the injector can perform. It is possible
to control the fuel volume for each injector
accurately through correct learning for the
MDP value. The basic process of MDP
learning is that the pulse slightly higher than
MDP is supplied and then (b) the vibration
generated from the cylinder is detected. The
knock sensor detects the vibration from the
engine after a small volume of fuel is injected.
And the time interval between the points of
injection and vibration is measured so that
MDP can be learned. MDP learning is helpful
to prevent engine vibration, high emission and
power reduction through performing
calibration for the old injectors. During MDP
learning, a little vibration and noise can be
occur for a while. This is because the fuel
pressure is increased instantaneously and the
exact injection value is not input, so that the
exact engine vibration timing can be
detected.
(6) MDP Learning Control
A. MDP Learning
When the pulse value that the injector starts injection is measured, it is called minimum drive pulse
(MDP). Through MDP controls, can correct pilot injections effectively. Pilot injection volume is very
small, 1 to 2 mm/str, so precise control of the injector can be difficult if it gets old. So there
needs MDP learning to control the very small volume precisely through learning according to
getting older injectors.
Control the fuel injection volume precisely by MDP learning even for the old injector.
ECU corrects the pilot injection effectively by MDP control.
MDP learning is performed by the signal from knock sensor. -
-
- The system measures the pulse at initial injection to reduce the engine vibration.
B. Purpose of MDP learning
Page 324 of 828
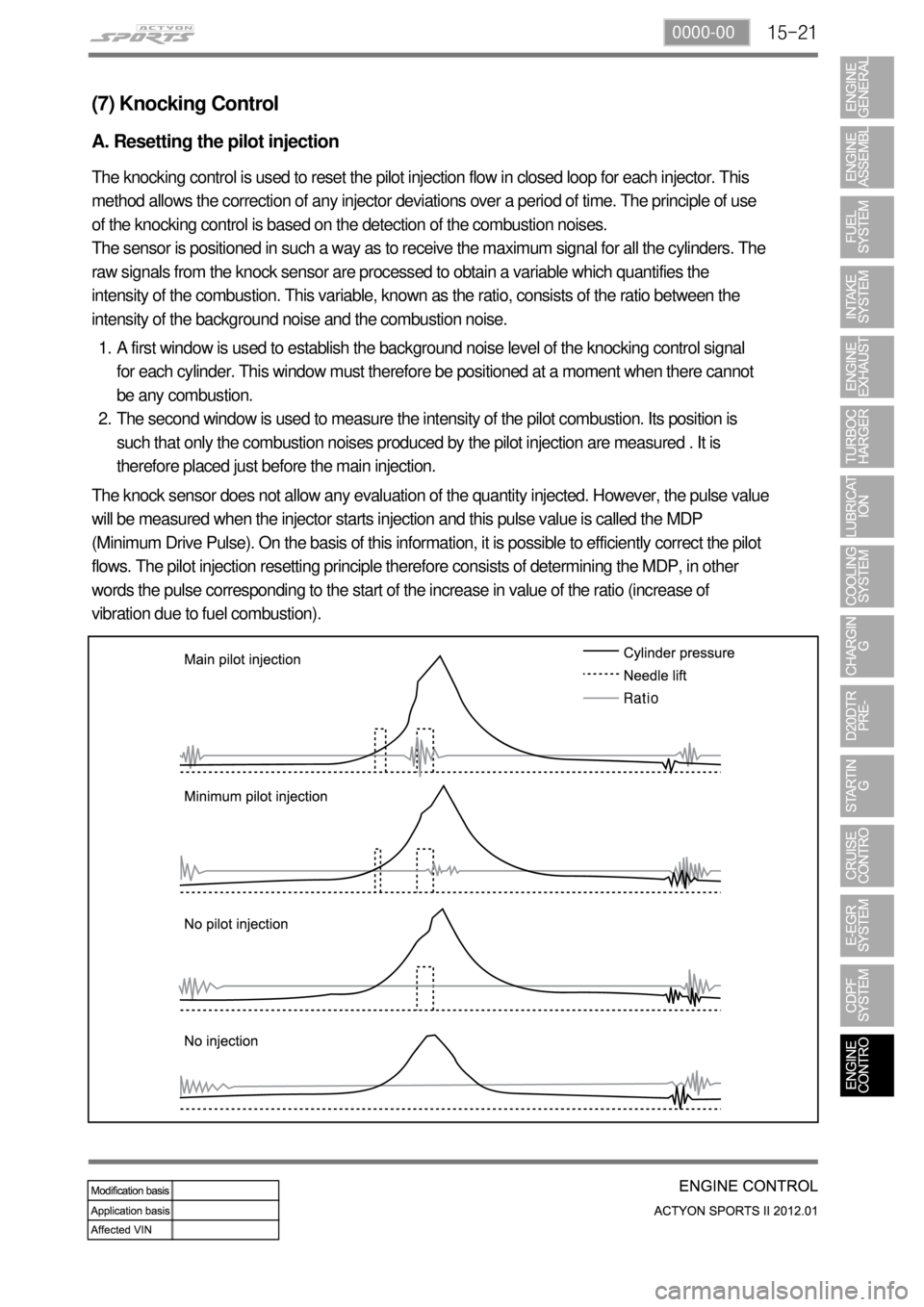
15-210000-00
(7) Knocking Control
A. Resetting the pilot injection
The knocking control is used to reset the pilot injection flow in closed loop for each injector. This
method allows the correction of any injector deviations over a period of time. The principle of use
of the knocking control is based on the detection of the combustion noises.
The sensor is positioned in such a way as to receive the maximum signal for all the cylinders. The
raw signals from the knock sensor are processed to obtain a variable which quantifies the
intensity of the combustion. This variable, known as the ratio, consists of the ratio between the
intensity of the background noise and the combustion noise.
A first window is used to establish the background noise level of the knocking control signal
for each cylinder. This window must therefore be positioned at a moment when there cannot
be any combustion.
The second window is used to measure the intensity of the pilot combustion. Its position is
such that only the combustion noises produced by the pilot injection are measured . It is
therefore placed just before the main injection. 1.
2.
The knock sensor does not allow any evaluation of the quantity injected. However, the pulse value
will be measured when the injector starts injection and this pulse value is called the MDP
(Minimum Drive Pulse). On the basis of this information, it is possible to efficiently correct the pilot
flows. The pilot injection resetting principle therefore consists of determining the MDP, in other
words the pulse corresponding to the start of the increase in value of the ratio (increase of
vibration due to fuel combustion).