Page 901 of 1082
04-50000-00
1. OVERVIEW
The hydraulic clutch transmits the force required to operate the clutch pedal to the concentric slave
cylinder fitted to the clutch housing as a hydraulic pressure.
(The hydraulic pressure is transmitted in the following order: Clutch pedal - Clutch master cylinder -
Clutch pipe - Clutch damper - Clutch pipe and hose - Concentric slave cylinder - Pressure plate -
Flywheel.)
If a driver depress the clutch pedal, the hydraulic pressure is generated in the master cylinder. It is
transmitted to the concentric slave cylinder through the pipe, resulting in the cylinder being forced out. At
this time, the clutch disc is forced against the cylinder by pushing the cover. This, in turn, remove the
flywheel from the pressure plate. As a consequence, the power from the engine will be cut off and the
gear change can be carried out.
Page 903 of 1082

04-70000-00
Operating Elements ▶
The clutch "release" system consists of the clutch pedal and clutch release cylinder.
This system directly releases the clutch by using hydraulic pressure while the conventional clutch system
releases the clutch by using release lever and release fork. This system provides higher efficiency than
conventional clutch system, and its durability is superior.
Clutch master cylinder (mounted on clutch pedal)
Concentric slave cylinder pipe (mounted inside of transmission) -
-Driving elements ▶
The driving elements consist of two flat surfaces machined to a smooth finish.
One of these is the rear face of the engine flywheel and the other is the clutch pressure plate. The clutch
pressure plate is fitted into a clutch steel cover, which is bolted to the flywheel.
Driven elements ▶
The driven element is the clutch disc with a splined hub which is free to slide lengthwise along the splines
of the input shaft.
The driving and driven elements are held in contact by spring pressure. This pressure is exerted by a
diaphragm spring in the clutch cover pressure plate assembly.
2) Overview
Page 904 of 1082
04-8
3) Layout
Clutch discClutch cover assembly
Concentric slave cylinderDual mass flywheel (DMF)
Clutch setting jig
Page 905 of 1082
04-90000-00
3. DUAL MASS FLYWHEEL (DMF)
The dual mass flywheel (DMF) is of having a mass divided into two halves.
While one mass is connected to the engine crankshaft, which is affected by the mass moment of inertia
of the engine, the other mass is affected by one of the transmission.
The divided dual masses are connected to the coil spring and damping system internally.
The DMF has the following benefits: ▶
Reducing fuel consumption by lowering engine speed
Reducing rattling noise and vehicle vibration in all driving ranges
Reducing synchronization wear
Facilitating gear change
Protecting power train parts by preventing excessive load from being delivered -
-
-
-
-
Primary flywheel
Secondary flywheel
Arc damper spring
Torque limiter
Ring gear 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Page 911 of 1082
06-54110-01
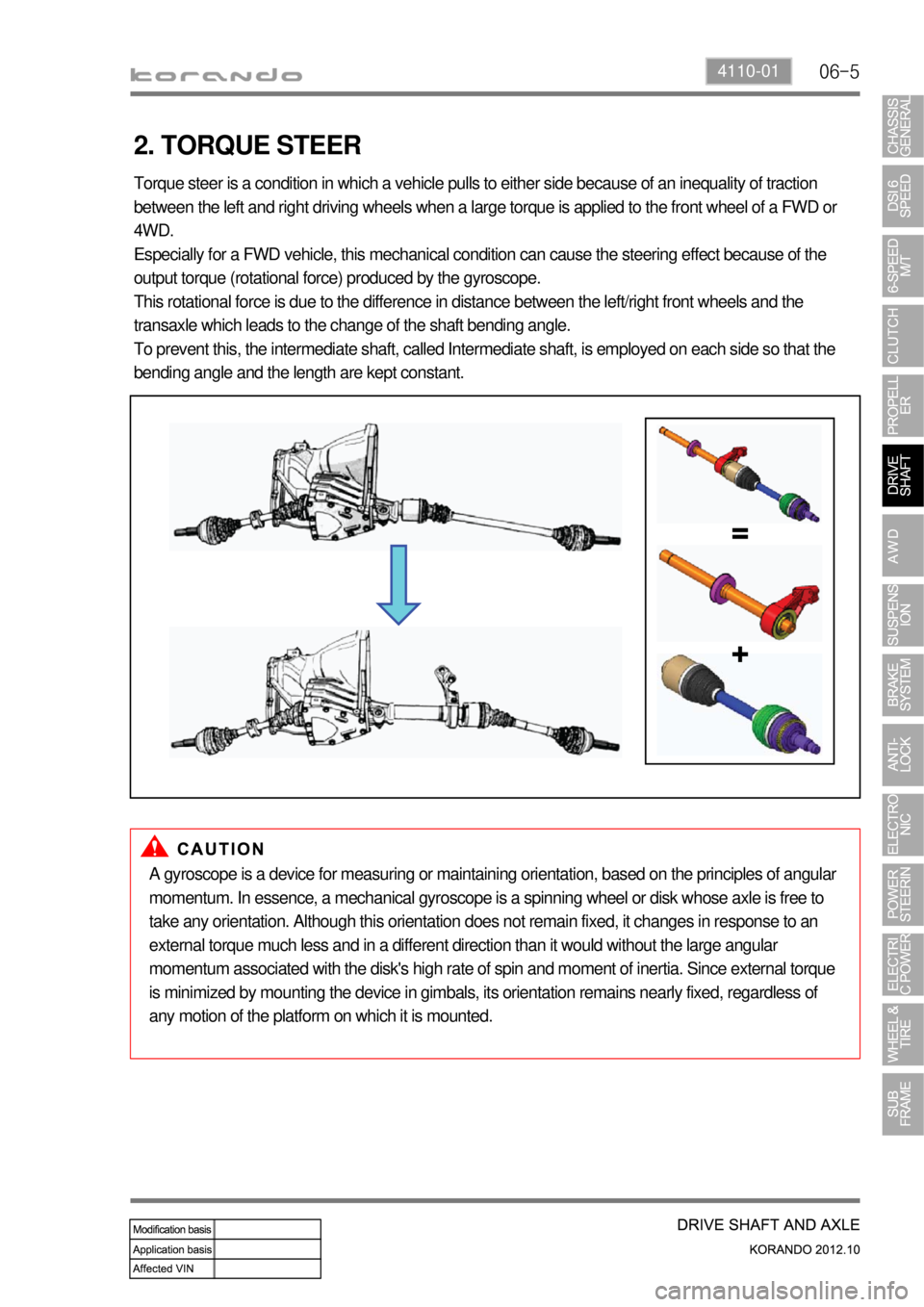
2. TORQUE STEER
Torque steer is a condition in which a vehicle pulls to either side because of an inequality of traction
between the left and right driving wheels when a large torque is applied to the front wheel of a FWD or
4WD.
Especially for a FWD vehicle, this mechanical condition can cause the steering effect because of the
output torque (rotational force) produced by the gyroscope.
This rotational force is due to the difference in distance between the left/right front wheels and the
transaxle which leads to the change of the shaft bending angle.
To prevent this, the intermediate shaft, called Intermediate shaft, is employed on each side so that the
bending angle and the length are kept constant.
A gyroscope is a device for measuring or maintaining orientation, based on the principles of angular
momentum. In essence, a mechanical gyroscope is a spinning wheel or disk whose axle is free to
take any orientation. Although this orientation does not remain fixed, it changes in response to an
external torque much less and in a different direction than it would without the large angular
momentum associated with the disk's high rate of spin and moment of inertia. Since external torque
is minimized by mounting the device in gimbals, its orientation remains nearly fixed, regardless of
any motion of the platform on which it is mounted.
Page 912 of 1082
06-6
3. REAR AXLE
The rear axle installed in this car is a removable axle, called IRDA (Independent Rear Differential Axle).
The rear differential carrier is installed directly on the sub frame,
and there is an independent suspension that allows each wheel on the same axle to move vertically and
independently of each other with the universal joint and the slip joint.
Page 914 of 1082
07-4
1. OVERVIEW
The AWD system in this vehicle is the electronic 4WD system and controls the traction to rear wheels
according to the driving conditions.
1) Driving Mode
(1) AUTO mode (Normal driving mode)
Normally the vehicle is in 2WD mode.
Automatically change to this mode when the vehicle needs higher traction.
(2) LOCK mode (when pressing 4WD LOCK switch)
This mode provides the highest traction. Use
this mode when driving on unpaved, rugged,
steep, sandy, wet or slippery roads.
In 4WD LOCK mode, if the rear wheel speed
exceeds 40 km/h, 4WD LOCK mode is
canceled and 4WD AUTO mode is activated
(Indicator OFF). If the speed is decreased
below 35 km/h, 4WD LOCK mode is resumed
(Indicator ON again). -
-
Mode table ▶
4WD LOCK switch Vehicle speed Driving mode
Not pressed (4WD AUTO) No conditions 4WD AUTO
Pressed (4WD LOCK) over 40 km/h 4WD AUTO
Pressed (4WD LOCK) below 35 km/h 4WD LOCK
Page 915 of 1082
07-50000-00
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
1) Components
(1) PTU (Power Transfer Unit)
<007b008f008c004700970096009e008c00990047009b009900880095009a008d008c00990047009c00950090009b0047009000950047009b008f008c0047008d009900960095009b0047009e008f008c008c00930047008b00990090009d008c0047009400
96008b008c00930047008a008f00880095008e008c009a0047>the angle of engine torque to 90°
and transfer it to E-coupling to distribute the torque to rear wheels.
(2) E-Coupling (Electronic Coupling)
E-Coupling transfer the engine torque from PTU to rear axle and controls to distribute it between front
wheels and rear wheels.
(3) E-Coupling Control Unit (ECU)
E-Coupling controls the current (clutch engagement force) of EMCD in E-Coupling according to CAN
signals (wheel speed, engine torque, pedal position, ABS/ESP signals).
* EMCD: Electro-Magnetic Control Device PTU assemblyE-coupling control unit
(located on the floor under driver seat)E-coupling