Page 982 of 1082
12-50000-00
3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HPS AND EPS
HPS EPS
1 Crankshaft pulley (DDU)
2 Auto tensioner
3 Tensioner pulley
4 Vacuum pump
5 A/C compressor pulley
6 Alternator pulley
7 Water pump pulley
8 No.1 idle pulley
9 No.2 idle pulley
10 Power steering pump -
HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Page 983 of 1082
12-6
4. MAJOR CHANGES
1) Steering Heating System
Steering wheel heating unit
Old New
The steering wheel heated wire and the heating unit are
installed in the steering wheel assembly.Lower switch cluster
Old
New
The steering wheel heating switch has
been added on the lower switch cluster.
Specifications ▶
Description Specification
Power consumption Below 95W
Rated voltage 12V
Operating voltage 9V~16V
Rated current6±2.0A
Steering wheel
heating unit
Steering wheel
heating switch
Page 984 of 1082

12-70000-00
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering
system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing hydraulic fluid. The fluid increases pressure in
the power steering pump and aids the movement of the steering mechanism.
The power steering system consists of pump, oil reservoir, rack and gear box.
The power steering pump is a vane type and delivers hydraulic pressure to operate the power steering
system.
The pressure relief valve in the pump controls the discharging pressure.
The rotary valve in the rack and the pinion gear directs the oil from the power steering pump to one side
of the rack piston. The integrated rack piston converts the hydraulic pressure to linear movement. The
operating force of the rack moves the wheels through the tie rod, the tie rod end and the steering knuckle.
Even though the hydraulic pressure cannot be generated, a driver can steer the vehicle without power
assist but it needs very high steering force.
In this case, the operating force of the steering wheel is conveyed to the pinion, and the movement of the
pinion moves the rack through the pinion gear combined to the rack gear.
Page 985 of 1082
12-8
Installation of steering
gear box and pipeInstallation of pipe
Installation of reservoir and hoseInstallation of power steering pump
and pipe
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
The steering pump is driven by the engine power through a belt. This pump circulates the power steering
oil from the reservoir -> steering pump -> oil supply pipe -> steering gear box -> oil return pipe ->
reservoir to perform steering operations.
Return pipe
Supply pipe
Page 986 of 1082
13-34610-00
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Description Specification
System operationOperating type Motor driven power steering system
Operating temperature- 40°C to 80°C
Rated voltage 12 V
Rated current 85 A
Operating voltageNetwork 8 to 16 V
C-EPS ECU 8 to 16 V
Full Performance 10 to 16 V
MotorType 3-Phase BLAC (Brushless AC)
Rated current/voltage 85 A / 12 V (at idle 0.5 A)
Position sensor type Hall sensor type
Torque & angle sensorType Non-contact type
Steering columnOperating type Manual tilting & telescoping
Lower shaftType Sliding (Ball slip) type
Steering gearGear ratio 46.94 mm/rev
Rack stroke 146 mm
Maximum steering angleInner wheel39°
Outer wheel31.24°
Page 988 of 1082
13-54610-00
3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HPS AND EPS
HPS EPS
1 Crankshaft pulley (DDU)
2 Auto tensioner
3 Tensioner pulley
4 Vacuum pump
5 A/C compressor pulley
6 Alternator pulley
7 Water pump pulley
8 No.1 idle pulley
9 No.2 idle pulley
10 Power steering pump -
HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Page 989 of 1082
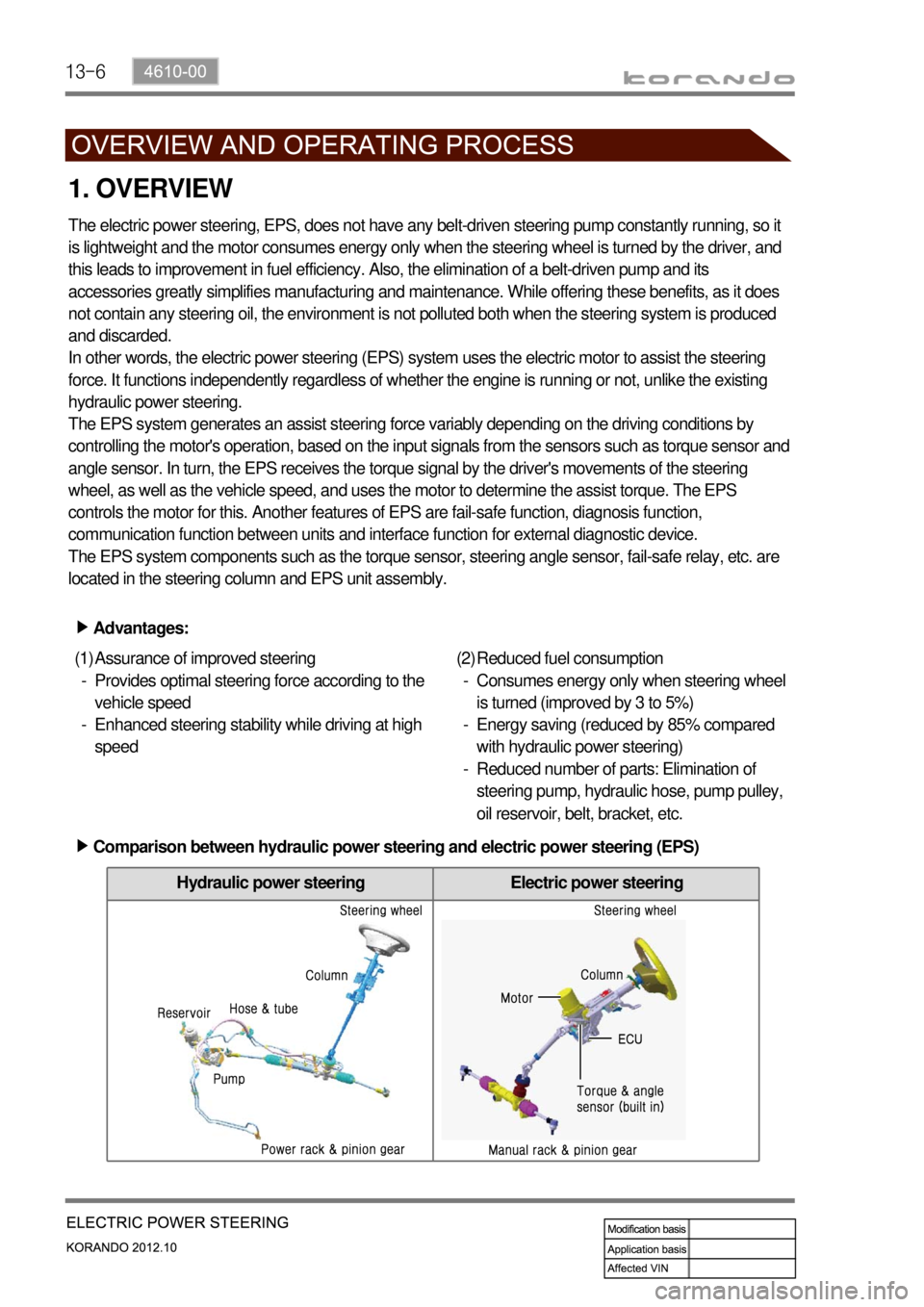
13-6
Hydraulic power steering Electric power steering
1. OVERVIEW
The electric power steering, EPS, does not have any belt-driven steering pump constantly running, so it
is lightweight and the motor consumes energy only when the steering wheel is turned by the driver, and
this leads to improvement in fuel efficiency. Also, the elimination of a belt-driven pump and its
accessories greatly simplifies manufacturing and maintenance. While offering these benefits, as it does
not contain any steering oil, the environment is not polluted both when the steering system is produced
and discarded.
In other words, the electric power steering (EPS) system uses the electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently regardless of whether the engine is running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The EPS system generates an assist steering force variably depending on the driving conditions by
controlling the motor's operation, based on the input signals from the sensors such as torque sensor and
angle sensor. In turn, the EPS receives the torque signal by the driver's movements of the steering
wheel, as well as the vehicle speed, and uses the motor to determine the assist torque. The EPS
controls the motor for this. Another features of EPS are fail-safe function, diagnosis function,
communication function between units and interface function for external diagnostic device.
The EPS system components such as the torque sensor, steering angle sensor, fail-safe relay, etc. are
located in the steering column and EPS unit assembly.
Advantages: ▶
Assurance of improved steering
Provides optimal steering force according to the
vehicle speed
Enhanced steering stability while driving at high
speed (1)
-
-Reduced fuel consumption
Consumes energy only when steering wheel
is turned (improved by 3 to 5%)
Energy saving (reduced by 85% compared
with hydraulic power steering)
Reduced number of parts: Elimination of
steering pump, hydraulic hose, pump pulley,
oil reservoir, belt, bracket, etc. (2)
-
-
-
Comparison between hydraulic power steering and electric power steering (EPS) ▶
Page 990 of 1082
13-74610-00
2. OPERATION
When the driver turns the steering wheel, a torque is generated and the torque sensor and the steering
angle sensor in the EPS system detect the rotation of the steering column to run the electric motor. At
this time, the worm gear connected to the motor drives the helical gear mounted to the steering column
to generate the assist torque for the steering column. This allows the driver to operate the steering wheel
easier.Output torque = 1) Steering force (manual torque) + 2) Assist torque