Page 968 of 1082
11-16
5) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection)
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch is
needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is only
a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation overcomes
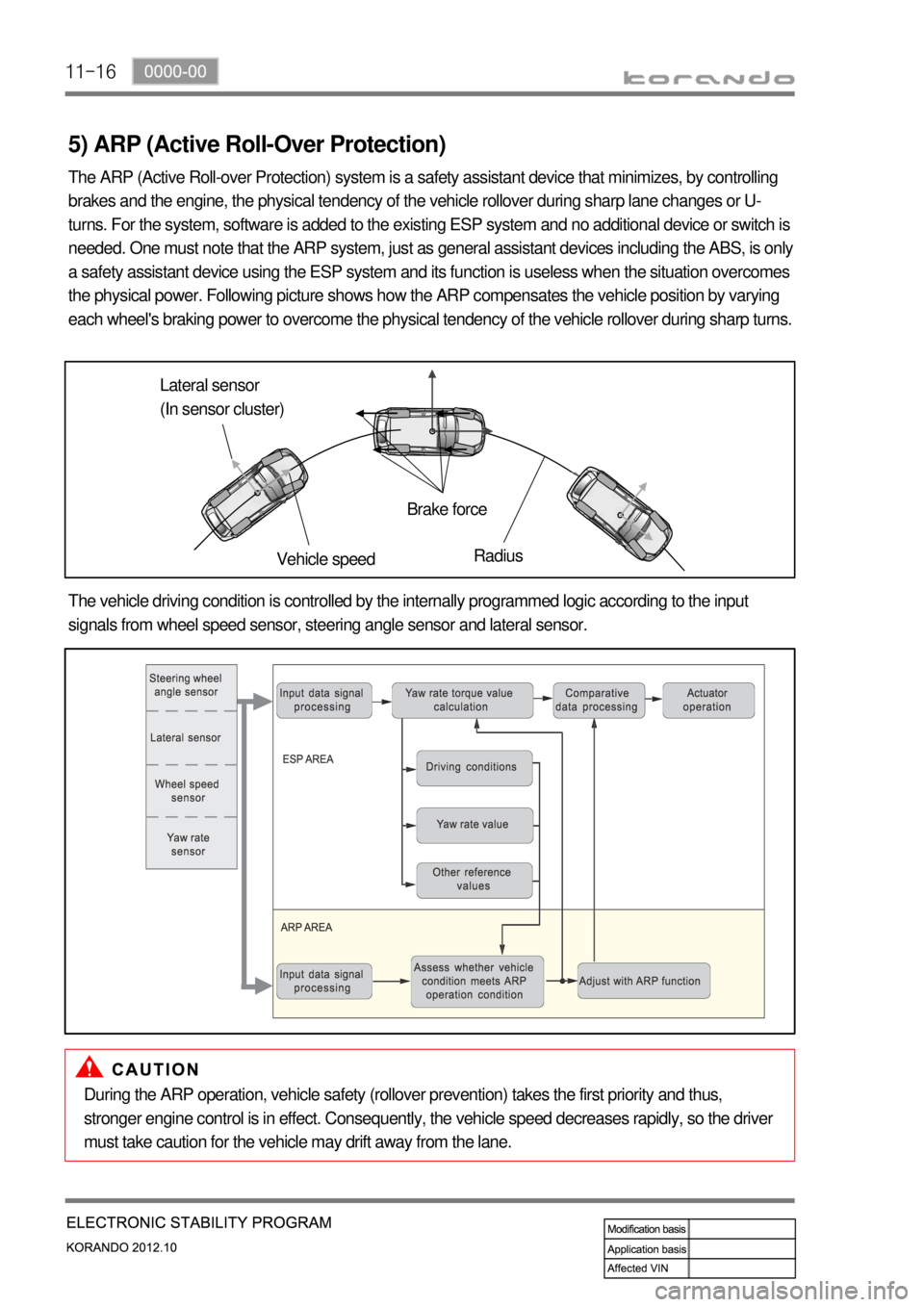
the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle position by varying
each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp turns.
Lateral sensor
(In sensor cluster)
Vehicle speedBrake force
Radius
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver
must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Page 969 of 1082
11-170000-00
6) HSA (Hill Start Assist)
The HSA (Hill Start Assist) prevents the vehicle from rolling backward by supplying the hydraulic
pressure to the wheels by the HECU after the brake pedal is released when starting off on uphill.
Page 973 of 1082

11-210000-00
Circuit description ▶
When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic circuit has a
normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in secondary circuit.
When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when applying the non-ABS operating
brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve are open, whereas the normally-closed
shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet and outlet
valves will be closed or open depending on the braking pressure RISE, HOLD or DUMP conditions.
Flashing warning lamp and warning sound during ESP operation ▶
When the ESP operates while the vehicle is moving, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flickers and the buzzer sounds at every 0.1 second. The ESP lamp operation is to inform a driver that the
vehicle is extremely unstable.
The ESP system is just a supplementary system for the vehicle and it cannot control the vehicle over the
physical limit. Do not solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
Drive feeling during ESP operation ▶
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions. For example, it will feel different when the ESP system is activated while the ABS is operated
by depressing the brake pedal and when the ESP system is in control without the brake pedal
depressed on the same curve.
If the ESP system operates with the brake applied, the brake pressure will be increased on the
corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls. In other words, the ESP
system would make the driver feel more abruptly braked compared to the situation that the braking
pressure is applied to wheel which had no braking force.
Noise and vibration that driver senses during ESP operation ▶
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to a driver due to the pressure changes caused by the
motor and valve operations in a very short period of time.
Extreme cornering will trigger the ESP operation and this will make the driver sense noise and vibration
due to sudden brake application.
Also, the ESP system controls the engine power. Therefore, the driver may notice the engine power
decreases even when the accelerator pedal is depressed.
Page 974 of 1082
11-22
1) Idling and Normal Braking Condition
In this position, the separation valve and the inlet valve are open (normal open), the electrically operated
shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the brake is applied under these conditions, the brake fluid will be sent to each wheel via the
separation valve and inlet valve.
Page 978 of 1082
11-26
5) Hydraulic Circuit of HBA
The above figure shows one front and one rear wheel and the same hydraulic circuit forms as in the ESP
operation. When HECU recognizes that it is an emergency and it is required for hard braking, depending
on the pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and pressure changes caused by the pressure sensor
timing, it operates the pump immediately to apply the brake pressure at the wheels. Then, the pressure in
the pump increases until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked. The motor still keeps rotating
and the outlet valve and the separation valve will stay closed. When the wheel starts to lock, the HBA
function cancels and switches to ABS operation.
Page 992 of 1082

14-4
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct line from
one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap under the tread
surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire distortion while the radial
structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time,
transmits the power to propel, brake and steer on the road. It also functions to maintain a
<009d008c008f0090008a0093008c02c5009a004700940096009d008c0094008c0095009b0055004700700095004700960099008b008c00990047009b00960047008a0096009400970093008c009b008c0047009a009c008a008f0047009b0088009a009200
9a0053004700880047009b00900099008c00470094009c009a>t be structured to be a resilient
vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6 mm from
<009b008f008c0047008e009900960096009d008c004700890096009b009b0096009400550047007b008f0090009a0047009e008c0088009900470093009000940090009b0047009400880099009200470090009a004700950096009b0047009a008c008c00
950047008d0099009600940047009b008f008c00470096009c>tside so there is additional "▲"
mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire groove depth,
measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire inflation
pressure, changed tire location, etc.
1) Structure of Tire
Tread
This thick layer of rubber provides the interface
between the tire and the road. Wear-resistant
rubber is used to protect the carcass and belt
against fractures and impacts and to deliver a
long driving life.
Shoulder
Located between the tread and sidewall, the
shoulder rubber is the thickest so that the design
must allow for the easy diffusion of heat
generated within the tire while driving.
Sidewall
The part between the shoulder and bead, the
flexible sidewall protects the carcass and
enhances the ride. A tire’s type, size,
structure, pattern, manufacturing company,
product name and various characters are
indicated here. Bead
The bead attaches the tire to the rim and wraps
the end of the cord fabric. Comprised of the bead
wire, core, flipper and other parts, the bead is
generally designed to be slightly tight around the
rim so that in the case of a sudden drop in inflation
pressure, the tire will not fall off the rim.
Carcass
As the most important framework of a tire, the
entire inner layer of cord fabric is called the
carcass. The carcass acts to support air pressure,
vertical load and absorb shocks.
Valve
Belt
Bead core
Page 995 of 1082
14-74170-00
When the vehicle is driven on a road surface covered with water at high speed, tires do not contact with
the road surface but rotate floating on a thin film of water.
It causes brake failure, lower traction force and losing the steering performance.
To prevent this, increase the tire inflation pressure, use tires with leaf shape tread which is not worn.
However, it is a best measure to drive slowly.
2) Hydro Planing