2012 SMART FORTWO COUPE weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 115 of 228

B‑pillar (Y page 214). In addition, the
load must be distributed in such a way so
that the weight on each axle never exceeds
the
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) for the
front and rear axle. The GVWR and GAWR for
your vehicle are indicated on the
certification label which can be found on
the driver’s door B‑pillar.
For more information, see “Loading the
vehicle” ( Y page 130).
The handling characteristics of a fully
loaded vehicle depend greatly on the load
distribution. It is therefore recommended
to load the vehicle with the heaviest items
being placed towards the front of the
vehicle.
Please pay attention to and comply with the
following instructions when loading the
vehicle and transporting cargo:
R Always place items being carried
against seat backrests, and fasten them
as securely as possible.
R The heaviest portion of the cargo should
always be kept as low as possible against
seat backrests.
R Do not stack loads higher than the top
edge of the head restraints.
R Make sure no luggage/cargo items can get
above or next to the driver’s and/or
passenger seat into the passenger
compartment.
R Make sure luggage/cargo is properly
secured.
R Always use, if so equipped, cargo net*
when transporting cargo.
Do not carry any unnecessary weight in the
vehicle. This increases vehicle weight,
which results in increased energy
consumption. Useful features
Sun visors
The sun visors protect you from sun glare
while driving. Glare through the windshield
X
Swing sun visor : down.
Glare through a side window X
Swing sun visor : down.
X Disengage sun visor : from
mounting ;.
X Pivot sun visor : to the side. Sun screen*
The sun screen provides protection from
sun rays and from heat generated by the
panorama roof*.
The sun screen can be adjusted to any
desired position. X
Opening or closing: Move sun screen :
forward or backward using the handle. Useful features
113
>> Controls.
* optional Z
Page 128 of 228

The Tire and Loading Information placard
lists the recommended cold tire inflation
pressures
: for maximum loaded vehicle
weight.
The tire inflation pressures listed
apply to the tires installed as original
equipment.
Important notes on tire inflation
pressure G
WARNING
If the tire inflation pressure drops
repeatedly, check the tires for punctures
from
foreign objects and/or whether air is
leaking from the valves or from around the
rim.
Tire temperature and tire inflation
pressure are also increased while driving,
depending on the driving speed and the
tire load.
Potential problems associated with
underinflated and overinflated tires Underinflated tires
G
WARNING
Follow recommended tire inflation
pressures.
Do not underinflate tires. Underinflated
tires wear excessively and/or unevenly,
adversely affect handling and fuel
economy, and are more likely to fail from
being overheated. Underinflated tires can
R
cause excessive and uneven tire wear
R adversely affect fuel economy
R lead to tire failure from being
overheated
R adversely affect handling
characteristics
Overinflated tires G
WARNING
Follow recommended tire inflation
pressures.
Do not overinflate tires. Overinflated
tires can adversely affect handling and
ride comfort, wear unevenly, increase
stopping distance, and result in sudden
deflation (blowout) because they are more
likely to become punctured or damaged by
road debris, potholes etc.
Overinflated tires can
R adversely affect handling
characteristics
R cause uneven tire wear
R be more prone to damage from road
hazards
R adversely affect ride comfort
R increase stopping distance Checking tire inflation pressure
Safety notes G
WARNING
Follow recommended tire inflation
pressures.
Do not underinflate tires. Underinflated
tires wear excessively and/or unevenly,
adversely affect handling and fuel
economy, and are more likely to fail from
being overheated.
Do not overinflate tires. Overinflated
tires can adversely affect handling and
ride comfort, wear unevenly, increase 126
Tires and wheels
>> Operation.
Page 132 of 228

Always follow the recommended tire
inflation pressure (
Y page 125) for proper
tire inflation. Loading the vehicle
Two labels on your vehicle show how much
weight it may properly carry.
1) The Tire and Loading Information placard can be found on the driver’s
door B‑pillar. This placard tells you
important information about the
number of people that can be in the
vehicle
and the total weight that can be
carried in the vehicle. It also contains
information on the proper size and
recommended tire inflation pressures
for the original equipment tires on
your vehicle.
2) The certification label, also found on the driver’s door B‑pillar, tells you
about
the gross weight capacity of your
vehicle, called the Gross Vehicle
Weight Rating (GVWR). The GVWR
includes the weight of the vehicle, all
occupants, fuel and cargo. The
certification label also tells you about
the front and rear axle weight capacity,
called the Gross Axle Weight Rating
(GAWR). The GAWR is the total allowable
weight that can be carried by a single
axle (front or rear). Never exceed the
GVWR or GAWR for either the front axle
or rear axle. :
Driver’s door B‑pillar Following is a discussion on how to work
with
the information contained on the Tire
and Loading Information placard with
regards to loading your vehicle.
Tire and Loading Information G
WARNING
Do not overload the tires by exceeding the
specified load limit as indicated on the
Tire and Loading Information placard on
the
driver’s door B‑pillar. Overloading the
tires can overheat them, possibly causing
a blowout. Overloading the tires can also
result in handling or steering problems, or
brake failure.
Tire and Loading Information placard
i Data shown on Tire and Loading
Information placard example are for
illustration purposes only. Load limit
data are specific to each vehicle and may
vary from data shown in the following
illustration. Refer to Tire and Loading
Information placard on vehicle for
actual data specific to your vehicle. The Tire and Loading Information placard
showing load limit information
: is
located on the driver’s door B‑pillar
(Y page 130).
X Locate the statement “The combined
weight of occupants and cargo should
never
exceed XXXX kg or XXXX lbs.” on the
Tire and Loading Information placard. 130
Tires and wheels
>> Operation.
Page 133 of 228

The combined weight of all occupants and
cargo/luggage should never exceed the
weight referenced in that statement.
Seating capacity The seating capacity gives you important
information on the number of occupants
that can be in the vehicle. The Tire and
Loading Information placard showing
seating capacity : is located on the
driver’s door B‑pillar (
Y page 130).
i Data shown on Tire and Loading
Information placard example are for
illustration purposes only. Seating
capacity data are specific to each
vehicle and may vary from data shown in
the
following illustration. Refer to Tire
and Loading Information placard on
vehicle for actual data specific to your
vehicle.
Steps for determining correct load limit
The following steps have been developed as
required of all manufacturers under
Title 49, Code of U.S. Federal Regulations,
Part 575 pursuant to the “National Traffic
and Motor Vehicle Safety Act of 1966”.
X Step 1: Locate the statement “The
combined weight of occupants and cargo
should never exceed XXXX kg or
XXXX lbs.” on your vehicle’s Tire and
Loading Information placard.
X Step 2:
Determine the combined weight of
the driver and passenger that will be
riding in your vehicle. X
Step 3: Subtract the combined weight of
the driver and passenger from
XXXX kilograms or XXXX lbs.
X Step 4: The resulting figure equals the
available amount of cargo and luggage
load
capacity. For example, if the “XXXX”
amount equals 540 lbs and there will be
one 150 lbs passenger in your vehicle, the
amount of available cargo and luggage
load capacity is 390 lbs
(540 lbs - 150 lbs = 390 lbs).
X Step 5:
Determine the combined weight of
luggage and cargo being loaded on the
vehicle. That weight may not safely
exceed the available cargo and luggage
load capacity calculated in step 4.
i The maximum cargo compartment load
is 110 lbs (50 kg).
The
following table shows examples on how
to calculate total and cargo load
capacities with varying seating
configurations and number and size of
occupants. The following examples use a
load limit of 540 lbs. This is for
illustration purposes only . Make sure you
are using the actual load limit for your
vehicle stated on the vehicle’s Tire and
Loading Information placard (Y page 130).
The higher the weight of all occupants, the
less cargo and luggage load capacity is
available. Tires and wheels
131>> Operation. Z
Page 134 of 228
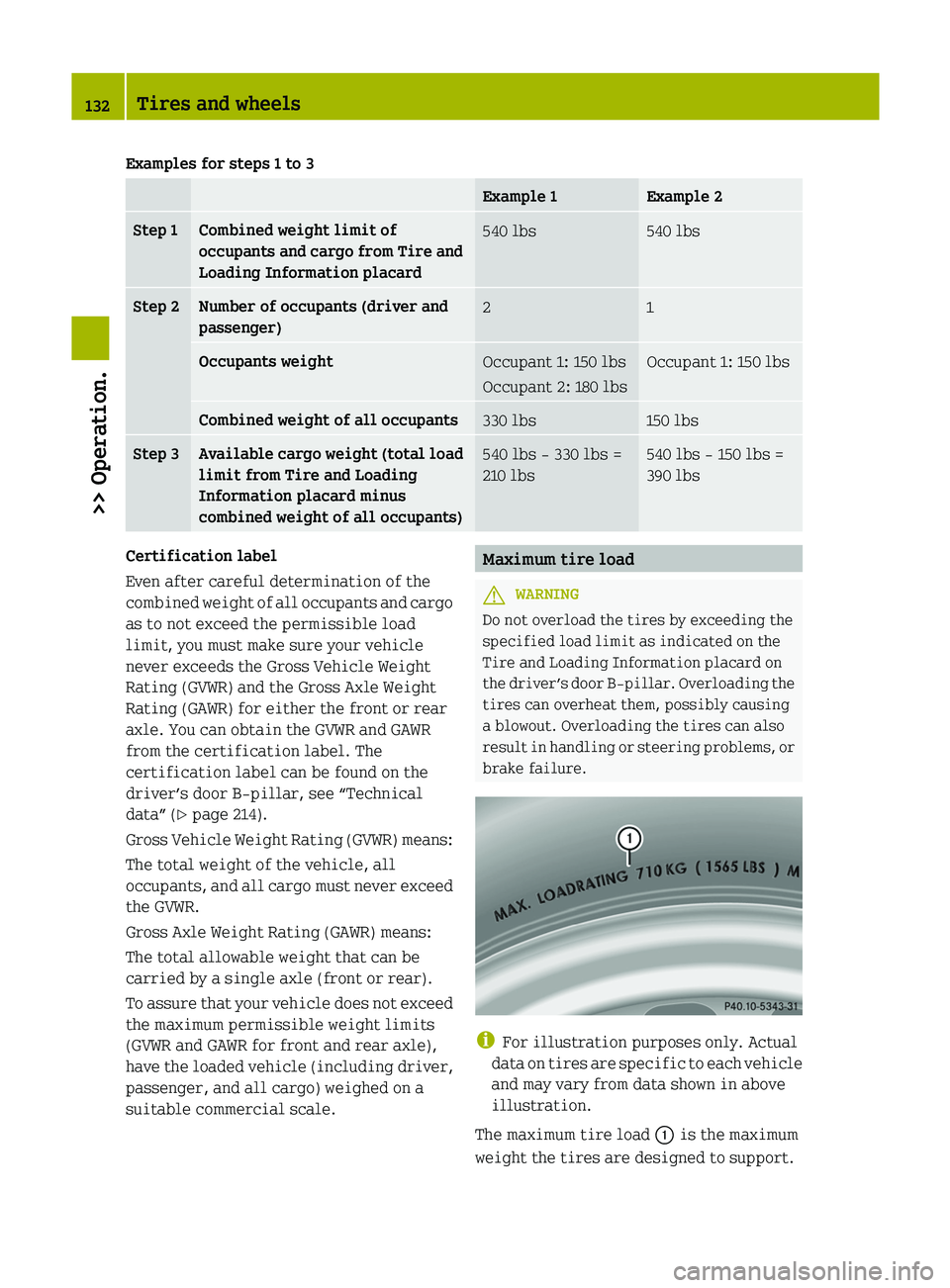
Examples for steps 1 to 3
Example 1 Example 2
Step 1 Combined weight limit of
occupants
and cargo from Tire and
Loading Information placard 540 lbs 540 lbs
Step 2 Number of occupants (driver and
passenger)
2 1
Occupants weight
Occupant 1: 150 lbs
Occupant 2: 180 lbs Occupant 1: 150 lbs
Combined weight of all occupants
330 lbs 150 lbs
Step 3 Available cargo weight (total load
limit from Tire and Loading
Information placard minus
combined weight of all occupants)
540 lbs - 330 lbs =
210 lbs 540 lbs - 150 lbs =
390 lbs
Certification label
Even after careful determination of the
combined
weight of all occupants and cargo
as to not exceed the permissible load
limit, you must make sure your vehicle
never exceeds the Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating (GVWR) and the Gross Axle Weight
Rating (GAWR) for either the front or rear
axle. You can obtain the GVWR and GAWR
from the certification label. The
certification label can be found on the
driver’s door B‑pillar, see “Technical
data” (Y page 214).
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) means:
The total weight of the vehicle, all
occupants, and all cargo must never exceed
the GVWR.
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) means:
The total allowable weight that can be
carried by a single axle (front or rear).
To assure that your vehicle does not exceed
the maximum permissible weight limits
(GVWR and GAWR for front and rear axle),
have the loaded vehicle (including driver,
passenger, and all cargo) weighed on a
suitable commercial scale. Maximum tire load
G
WARNING
Do not overload the tires by exceeding the
specified load limit as indicated on the
Tire and Loading Information placard on
the
driver’s door B‑pillar. Overloading the
tires can overheat them, possibly causing
a blowout. Overloading the tires can also
result in handling or steering problems, or
brake failure. i
For illustration purposes only. Actual
data
on tires are specific to each vehicle
and may vary from data shown in above
illustration.
The maximum tire load : is the maximum
weight the tires are designed to support. 132
Tires and wheels
>> Operation.
Page 141 of 228

The TIN is a unique identifier which
facilitates
efforts by tire manufactures to
notify purchasers in recall situations or
other safety matters concerning tires and
gives purchasers the means to easily
identify such tires.
The TIN is comprised of “Manufacturer’s
identification mark” ;, “Tire size” =,
“Tire type code” ?, and “Date of
manufacture” A.
i For illustration purposes only. Actual
data on tires are specific to each vehicle
and may vary from data shown in above
illustration.
DOT (Department of Transportation) Tire branding symbol
:
which denotes the
tire meets requirements of the U.S.
Department of Transportation.
Manufacturer’s identification mark Manufacturer’s identification mark
;
denotes the tire manufacturer.
New tires have a mark with two symbols.
Retreaded tires have a mark with four
symbols. For more information on
retreaded tires ( Y page 124).
Tire size Code = indicates the tire size. Tire type code Tire type code
? may, at the option of the
manufacturer, be used as a descriptive
code for identifying significant
characteristics of the tire.
Date of manufacture Date of manufacture
A
identifies the week
and year of manufacture.
The first two figures identify the week,
starting with “01” to represent the first
full week of the calendar year. The second
two figures represent the year.
For example, “3202” represents the 32nd
week of 2002. Tire ply material
i
For illustration purposes only. Actual
data
on tires are specific to each vehicle
and may vary from data shown in above
illustration.
This marking tells you about the type of
cord and number of plies in the
sidewall : and under the tread ;. Tire and loading terminology
Accessory weight The combined weight (in excess of those
standard items which may be replaced) of
automatic transmission, power steering,
power brakes, power windows, power seats, Tires and wheels
139
>> Operation. Z
Page 142 of 228

radio, and heater, to the extent that these
items are available as factory-installed
equipment (whether installed or not).
Air pressure
The amount of air inside the tire pressing
outward
on each square inch of the tire. Air
pressure is expressed in pounds per square
inch (psi), or kilopascal (kPa) or bars.
Aspect ratio Dimensional relationship between tire
section
height and section width expressed
in percentage.
Bar Another metric unit for air pressure. There
are
14.5038 pounds per square inch (psi) to
1 bar; there are 100 kilopascals (kPa) to
1 bar.
Bead The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped
by steel cords that hold the tire onto the
rim.
Cold tire inflation pressure
Tire inflation pressure when your vehicle
has been sitting for at least 3 hours or
driven no more than 1 mile (1.6 km).
Curb weight
The weight of a motor vehicle with standard
equipment including the maximum
capacity of fuel, oil, and coolant, and, if
so equipped, air conditioning and
additional optional equipment, but
without passengers and cargo.
DOT (Department of Transportation)
A tire branding symbol which denotes the
tire meets requirements of the U.S.
Department of Transportation. GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating) The GAWR is the maximum permissible axle
weight. The gross vehicle weight on each
axle must never exceed the GAWR for the
front and rear axle indicated on the
certification
label located on the driver’s
door B‑pillar.
GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight) The GVW comprises the weight of the
vehicle including fuel, tools, installed
accessories, passengers and cargo. The
GVW
must never exceed the GVWR indicated
on the certification label located on the
driver’s door B‑pillar.
GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) This is the maximum permissible vehicle
weight of the fully loaded vehicle (weight
of the vehicle including all options,
passengers,
fuel, and cargo. It is indicated
on certification label located on the
driver’s door B‑pillar.
Kilopascal (kPa) The metric unit for air pressure. There are
6.9
kPa to 1 psi; another metric unit for air
pressure is bars. There are
100 kilopascals (kPa) to 1 bar.
Maximum load rating The maximum load in kilograms and pounds
that can be carried by the tire.
Maximum loaded vehicle weight
The sum of curb weight, accessory weight,
total load limit and production options
weight.
Maximum permissible tire inflation
pressure
This number is the greatest amount of air
pressure
that should ever be put in the tire.140
Tires and wheels
>> Operation.
Page 143 of 228

Normal occupant weight
The number of occupants the vehicle is
designed to seat, multiplied by
68 kilograms (150 lbs).
Occupant distribution
The distribution of occupants in a vehicle
at their designated seating positions.
Production options weight
The combined weight of those installed
regular production options weighing over
5 lbs (2.3 kilograms) in excess of those
standard items which they replace, not
previously considered in curb weight or
accessory weight, including heavy duty
brakes,
ride levelers, roof rack, heavy duty
battery, and special trim.
PSI (Pounds per square inch) A standard unit of measure for air
pressure.
Recommended tire inflation pressure
The recommended tire inflation pressure
for
normal driving conditions is listed on
the Tire and Loading Information placard
located on driver’s door B‑pillar and
provides best handling, tread life and
riding comfort.
Rim A metal support for a tire or a tire and tube
assembly upon which the tire beads are
seated.
Sidewall
The portion of a tire between the tread and
the bead. TIN (Tire Identification Number) Unique identifier which facilitates
efforts by tire manufacturers to notify
purchasers in recall situations or other
safety matters concerning tires and gives
purchasers the means to easily identify
such tires. The TIN is comprised of
“Manufacturer’s identification mark”,
“Tire size”, “Tire type code” and “Date of
manufacture”.
Tire load rating
Numerical code associated with the
maximum load a tire can support.
Tire ply composition and material used
This indicates the number of plies or the
number of layers of rubber-coated fabric
in the tire tread and sidewall. Tire
manufacturers also must indicate the ply
materials in the tire and sidewall, which
include
steel, nylon, polyester, and others.
Tire speed rating Part of tire designation; indicates the
speed range for which a tire is approved.
Total load limit
Rated cargo and luggage load plus
68 kilograms (150 lbs) times the vehicle’s
designated seating capacity.
Traction
Force exerted by the vehicle on the road via
the tires. The amount of grip provided.
Tread
The portion of a tire that comes into
contact with the road. Tires and wheels
141
>> Operation. Z