2012 Seat Alhambra fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 272 of 388

270Checking and refilling levels
WARNING
Driving with insufficient fuel reserve could result in the vehicle breaking
down in traffic and a serious accident.
● If the fuel level is too low then the fuel supply to the engine can be-
come irregular especially on slopes.
● If the engine “is choked” or stalls due to lack of or irregularity of the
fuel supply, the power steering as well as all of the driver assistance sys-
tems including braking assistance will stop working.
● Always refuel when there is only one quarter of the fuel tank left to
avoid running out of fuel.
CAUTION
● Always pay attention to any lit lamps and to the corresponding descrip-
tions and instructions to avoid damage to the vehicle.
● Never run the tank completely dry. An irregular fuel supply may lead to
ignition faults and unburnt fuel could enter the exhaust system. This could
damage the catalytic converter filter or the diesel particulate filter!
Note
The arrow next to the fuel pump symbol on the instrument panel ⇒ fig. 164
indicates the side of the vehicle on which the tank flap is located. Filling the tank with petrol or diesel
Fig. 165 Open tank flap
with tank cap attached to
the holder.
Before refuelling, always turn off the engine, the ignition, mobile tele-
phones, auxiliary heating and keep them off during refuelling.
Unscrewing the tank cap
● The tank flap is at the rear of the vehicle on the right.
● Press the rear of the tank flap to open it.
● Unscrew the tank cap anti-clockwise and insert it in the hole in the tank
flap hinge ⇒ fig. 165.
Refilling
The correct petrol type for the vehicle is located on a sticker inside the fuel
tank flap ⇒ page 271.
● If the automatic filler nozzle is operated correctly, it will switch itself off
as soon as the tank is full ⇒
.
● Do not continue to refuel if it is turned off! Otherwise, this will fill the ex-
pansion chamber and fuel may leak out if the ambient conditions are warm.
Page 275 of 388

273
Checking and refilling levels
● If, in exceptional circumstances, petrol with a lower octane rating to that
recommended is used, only use moderate engine speeds and a light throt-
tle. Avoid using full throttle and overloading the engine. Otherwise you may
damage the engine. Fill up with fuel of a suitable octane rating as soon as
possible.
● Do not refuel if the filler indicates that the fuel contains metal. LRP (lead
replacement petrol) fuels also contain high concentrations of metal addi-
tives. This could damage the engine!
● Just one full tank of leaded fuel would seriously impair the efficiency of
the catalytic converter and could damage it.
Diesel
Diesel fuel
Diesel fuel must correspond to European standard EN 590 (In Germany,
EN 590 or DIN 51628).
The use of diesel fuel with a high sulphur percentage requires shorter serv-
ice intervals ⇒ Booklet Maintenance Programme ⇒
. Your Technical Serv-
ice will be able to tell you which countries have diesel with a high sulphur
content.
Do not mix fuel additives (thinners, or similar additives) with diesel fuel.
Winter-grade diesel
When using “summer-grade diesel fuel”, difficulties may be experienced at
temperatures below 0 °C (+32 °F) because the fuel thickens due to wax sep-
aration. For this reason, “winter-grade diesel fuel” is available in Germany,
for example, during the cold months. It can be used at temperatures as low
as -20 °C (-4 °F).
In countries with different climatic conditions, other types of diesel fuel are
available that are suitable to local temperatures. Technical Services and fill-
ing stations in the country concerned will inform you on the type of diesel
fuels available. A cold diesel engine makes more noise during winter temperatures than
summer temperatures. Furthermore, the exhaust fumes may turn slightly
bluish while the engine is heating. The quantity of exhaust gases will de-
pend on the outside temperature.
Filter pre-heater
Vehicles with a diesel engine are fitted with a fuel filter pre-heater. This en-
sures that the fuel system remains operational to approx. -24 °C (-11.2 °F),
provided you use winter-grade diesel which is safe to -15 °C (+5 °F).
However, if the fuel has waxed to such an extent that the engine will not
start at temperatures of under -24 °C (-11,2 °F), simply place the vehicle in a
warm garage or workshop for a while to heat up.
Auxiliary heater
Vehicles with a diesel engine may be fitted with an auxiliary heater. The
heater runs off the fuel from the fuel tank. On doing so, smells and steam
may be noticed outside the vehicle for a short period. This is normal and it
is not an indication of a fault in the vehicle.
Whenever there is little fuel in the tank (reserve), the auxiliary heater auto-
matically switches off.
WARNING
Never use start boosters. An aerosol start booster could explode or cause
a sudden rise in engine speed leading to engine damage and serious in-
jury.
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 276 of 388

274Checking and refilling levels
CAUTION
● The vehicle is not prepared for the use of biodiesel. Never, under any
circumstances refuel with biodiesel. It could damage the fuel system and
subsequently lead to engine faults!
● The addition of biodiesel to diesel by the diesel producer according to
Standard EN 590 or other equivalent (DIN 51628 in Germany, for example)
is authorised and causes no type of damage to the engine or the fuel
system.
● The diesel engine has been designed for to use diesel fuel exclusively.
Therefore, never use petrol, fuel oil or other unsuitable fuels. The composi-
tion of these fuels may significantly damage the fuel system and the en-
gine.
● The use of diesel fuels with a high sulphur percentage could considera-
bly reduce the service life of the diesel particulate filter. Your Technical Serv-
ice will be able to tell you which countries have diesel with a high sulphur
content.
Information on fuel consumption
The consumption and emission values indicated do not refer to one specific
vehicle. They are only to be used to compare the values of the different ve-
hicle versions. The fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions of a vehicle not on-
ly depend on the effective use of fuel. They also depend on your driving
style and other non-technical factors.
Calculation of fuel consumption
Fuel consumption and emission values are determined according to the cur-
rent version of the 715/2007/EC or 80/1268/EEC regulation and are valid
for the vehicle kerb weight. The specifications do not refer to an individual
vehicle. Two measuring cycles are carried out on a rolling road test bed. The
test criteria are as follows:
Urban cycleMeasurement of the urban cycle starts with an engine cold
start. City driving is then simulated at between 0 and 50 km/
h.
Road cycleIn the road cycle simulation, the car undergoes frequent ac-
celeration and braking in all gears, as in normal everyday
driving. The road speed ranges from 0 to 120 km/h.
CombinedThe average combined consumption is calculated with a
weighting of around 37 % for the urban cycle and 63 % for
the road cycle.
CO 2 emis-
sions of the
combinationThe exhaust gases are collected during both driving cycles
to calculate carbon dioxide emissions (urban and road). The
gas composition is then analysed to evaluate the CO 2 con-
tent and other emissions.
Note
● The kerb weight may vary according to the vehicle equipment. This
could raise consumption and the CO 2 emissions slightly.
● In practice, consumption values could be different to the values calcula-
ted based on the 715/2007/EC or 80/1268/EEC regulations.
Page 356 of 388

354Technical specifications
Trailer weight Trailer without brakes 750
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 1800
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 1800
Engine oil capacity
Approximate engine oil capacity with oil filter change 3,6
Petrol engine 1.4 110 kW (150 PS) Automatic
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 110 (150)/ 5800
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 240/ 1500-4000
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
4/ 1390
Fuel Super 95 RON a)
a)
Research Octane Number = Anti-detonation rating of the petrol.
Performance Maximum speed in km/h 197
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h in sec. 6,6
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h in sec. 9,9
Consumption (litres/100 km)/ CO
2 (g/km)
Urban cycle 9,4/218
Extra-urban cycle 6,6/154
Combined 7,6/178
Page 357 of 388

355
Technical specifications
Weights 5 seats 7 seats
Gross vehicle weight in kg 2310 2500
Weight in running order (with driver) in kg 1742 1790
Gross front axle weight in kg 1190/1240 1190/1240
Gross rear axle weight in kg 1070/1120 1260/1310
Permitted roof load in kg 100 100
Trailer weight
Trailer without brakes 750
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 1800
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 1800
Engine oil capacity
Approximate engine oil capacity with oil filter change 3,6
Petrol engine 2.0 147 kW (200 PS) Automatic
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 147 (200)/ 5100
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 280/ 1700-5000
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
4,6/ 1984
Fuel Super 95 RON a)
a)
Research Octane Number = Anti-detonation rating of the petrol.
Performance Maximum speed in km/h 221
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h in sec. 5,8
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h in sec. 8,3
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 360 of 388

358Technical specifications
Trailer weight Trailer without brakes 750
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 2000
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 2000
Engine oil capacity
Approximate engine oil capacity with oil filter change 4,0
Diesel engine 2.0 TDI CR 100 kW (136 PS)
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 100 (136)/ 4200
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 320/1750-2500
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
4/1968
Fuel Min. 51 CN a)
a)
Cetane Number (cetane index) = Measure of the combustion power of the diesel
Performance Maximum speed in km/h 192
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h in sec. 7,8
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h in sec. 11,1
Consumption (litres/100 km)/ CO
2 (g/km)
5 seats 7 seats
Urban cycle 6,8/179 6,9/182
Extra-urban cycle 4,8/127 4,9/130
Combined 5,5/143 5,6/146
Page 361 of 388

359
Technical specifications
Weights 5 seats 7 seats
Gross vehicle weight in kg 2340 2510
Weight in running order (with driver) in kg 1174 1822
Gross front axle weight in kg 1190/1240 1200/1250
Gross rear axle weight in kg 1100/1150 1260/1310
Permitted roof load in kg 100 100
Trailer weight
Trailer without brakes 750
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 2200
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 2200
Engine oil capacity
Approximate engine oil capacity with oil filter change 4,0
Diesel engine 2.0 TDI CR 100 kW (136 PS) Automatic
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 100 (136)/ 4200
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 320/1750-2500
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
4/1968
Fuel Min. 51 CN a)
a)
Cetane Number (cetane index) = Measure of the combustion power of the diesel
Performance Maximum speed in km/h 189
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h in sec. 7,8
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h in sec. 11,1
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 362 of 388
360Technical specifications
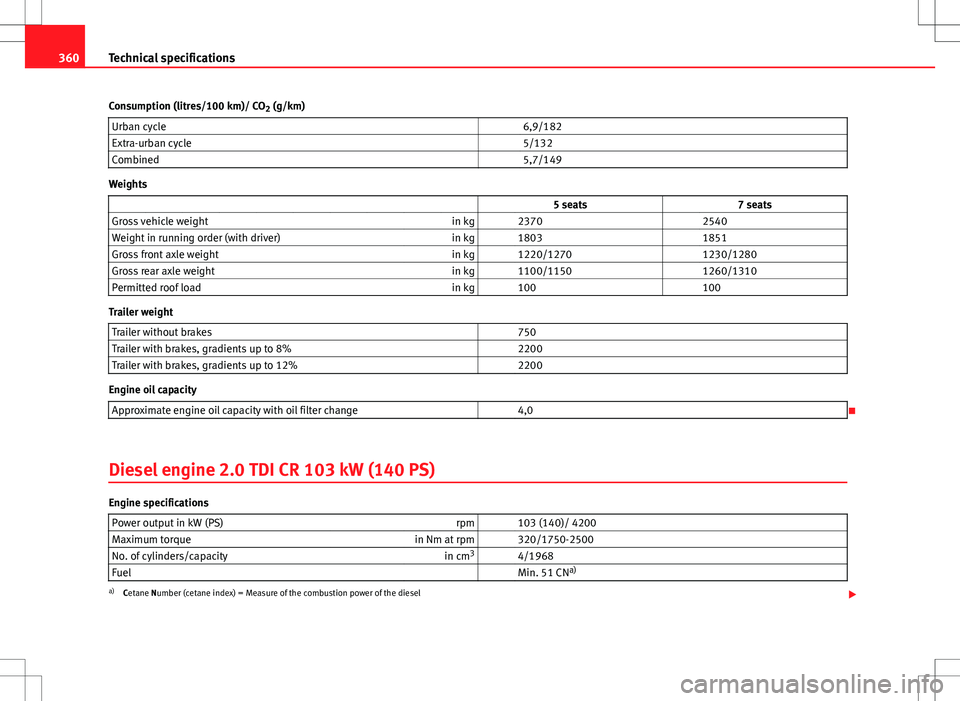
Consumption (litres/100 km)/ CO 2 (g/km)
Urban cycle 6,9/182
Extra-urban cycle 5/132
Combined 5,7/149
Weights
5 seats 7 seats
Gross vehicle weight in kg 2370 2540
Weight in running order (with driver) in kg 1803 1851
Gross front axle weight in kg 1220/1270 1230/1280
Gross rear axle weight in kg 1100/1150 1260/1310
Permitted roof load in kg 100 100
Trailer weight
Trailer without brakes 750
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 2200
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 2200
Engine oil capacity
Approximate engine oil capacity with oil filter change 4,0
Diesel engine 2.0 TDI CR 103 kW (140 PS)
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 103 (140)/ 4200
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 320/1750-2500
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
4/1968
Fuel Min. 51 CN a)
a)
Cetane Number (cetane index) = Measure of the combustion power of the diesel