Page 43 of 128

41
Shifting
■
■Driving mode-specific shift characteristics
The driving mode selector switch allows the driver to choose the automatically shifted
AUTO mode or a manually shifted SPORT, NORMAL or WET mode and their
corresponding default shift speed level. The driver may perform gear changes using the
paddle shift switches while driving in a manually shifted driving mode. While the shift speed
is adjustable using the shift speed selector, each driving mode has its own default shift
speed setting. Shift speeds are determined by how quickly the following operations are
carried out: Clutch disengagement, gear select, gear shift and clutch engagement.
Selecting a faster shift speed will shorten the time it takes from the moment the paddle shift
switch is pulled until the shift is totally completed. Faster shift speeds allow for enhanced
response and near-seamless power delivery, but will also result in a greater amount of shift
shock due to the speed at which the aforementioned operations are carried out. Selecting
a slower shift speed will allow the clutch and gear shift/select mechanisms to operate at a
more gentle pace, leading to a smoother application of torque and less shift shock.
Driving modeDriving mode default shift speed
AUTO ■■
2/7 (Non-adjustable)
SPORT ■■■■■□□
5/7
NORMAL ■■■□□□□
3/7
WET ■□□□□□□
1/7
Shift characteristicsLevel 1 n Level 7
Shift speed Slow (approx. 1 sec.) n
Fast (approx. 0.15 sec.)
Shift shock Less n
More
Shift speed selector
When in a manually shif ted driving
mode (SPORT, NORMAL or WET),
the shift speed can be adjusted from
l e v e l 1 t o 7 u s i n g t h e s h i f t s p e e d
selector.
Shift speed is also determined by the
accelerator pedal angle. The more the
accelerator pedal is depressed, the
shorter the shift times will be.
S106-04
Fast
Slow
Fully released Fully
depress
Level 1
Level 2 Level 7
Accelerator
pedal angle
Shift speed
Page 46 of 128
44
Steering
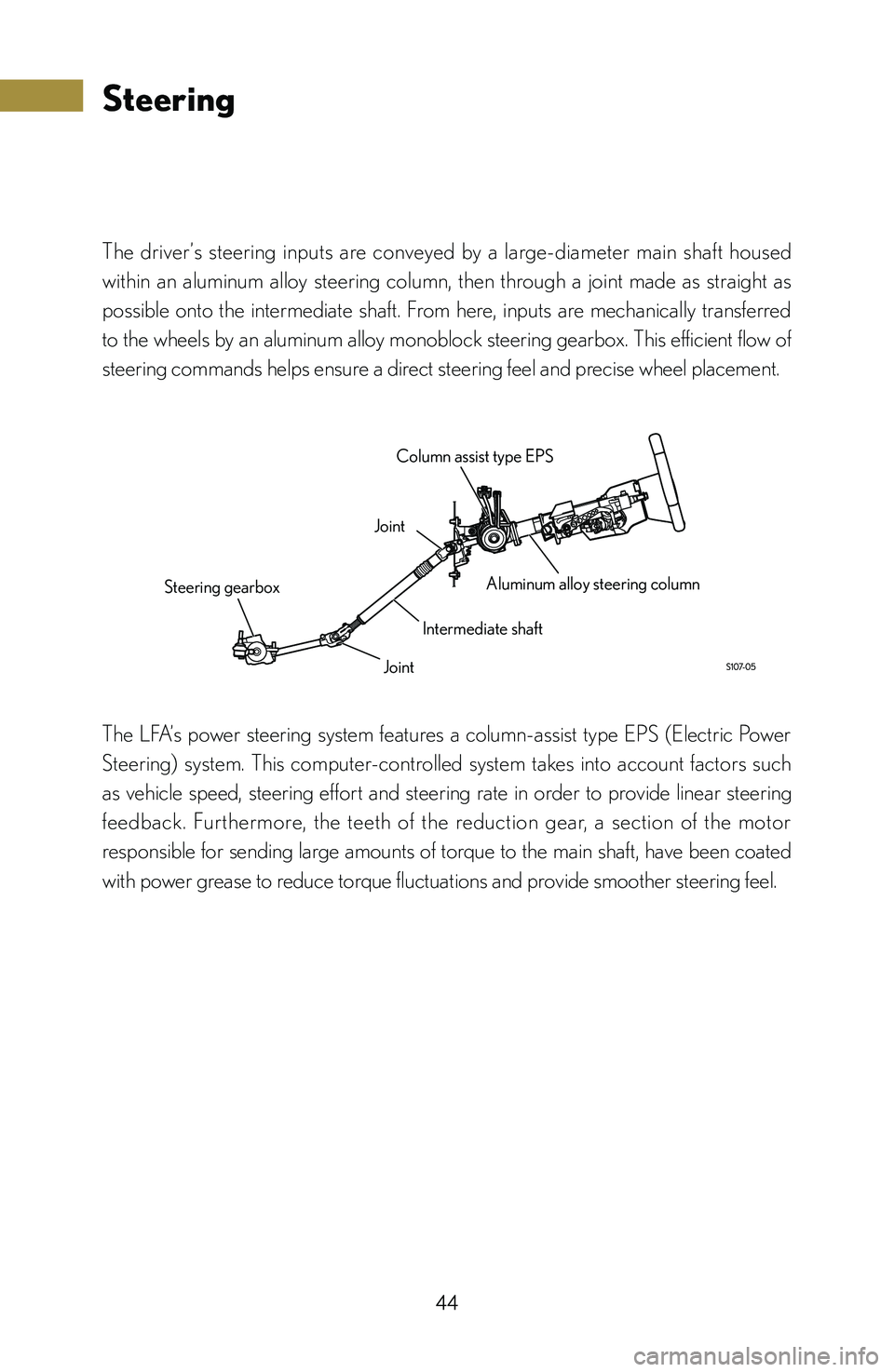
The driver’s steering inputs are conveyed by a large-diameter main shaft housed
within an aluminum alloy steering column, then through a joint made as straight as
possible onto the intermediate shaft. From here, inputs are mechanically transferred
to the wheels by an aluminum alloy monoblock steering gearbox. This efficient flow of
steering commands helps ensure a direct steering feel and precise wheel placement.
Joint Column assist type EPS
Aluminum alloy steering column
Intermediate shaft
Joint
Steering gearbox
The LFA’s power steering system features a column-assist type EPS (Electric Power
Steering) system. This computer-controlled system takes into account factors such
as vehicle speed, steering effort and steering rate in order to provide linear steering
feedback. Furthermore, the teeth of the reduction gear, a section of the motor
responsible for sending large amounts of torque to the main shaft, have been coated
with power grease to reduce torque fluctuations and provide smoother steering feel.
Page 47 of 128
45
Steering
■
■Steering wheel
The steering wheel features a flat-bottomed design that has 1.10 in. (28 mm) of the
lower half cut away. This reduces the steering wheel’s inertial moment and locates
the wheel’s rotational center and its center of gravity in almost the same place, almost
completely eliminating any imbalance within the steering wheel itself, reducing the
amount of steering fluctuations imparted by lateral and vertical forces. Ultimately
this provides the driver with a more natural and accurate steering feel. Furthermore,
the use of an aluminum alloy frame and hollow CFRP rim reduces the inertial force
generated by steering inputs.
H o l l o w C F R P
steering wheel rim
Center of rotation
Center of gravity
Turns lock-to-lock: 2.35
Aluminum alloy frame
Steering wheel center
Page 48 of 128
46
■
■Steering rack and gearbox
The steering gearbox consists of a monoblock aluminum alloy rack and pinion unit
mounted to the front suspension member using four rigid mounts. This allows the
driver to feel as if they are solidly connected to the road. An overall steering ratio of
14.3:1 allows the driver to precisely follow their intended line through a corner.
S107-06The joint between the steering shaft and gearbox is set at a narrow angle (approx. 10˚)
for a highly efficient connection that allows even subtle steering inputs to be accurately
conveyed, keeping the LFA directly on the driver’s intended path no matter what the
situation, whether it be a winding road or an extremely fast straightaway. Joint angle: Approx. 10˚
Page 52 of 128

50
Braking
The LFA is equipped with an ECB (Electronically Controlled Brake) system.
When the brake pedal is depressed, information on how much force is being used to
depress the pedal and the amount it is depressed is sent to the ECB computer. This
computer takes into account the vehicle’s overall condition using inputs from various
sensors and distributes the optimal amount of brake force to each individual wheel.
The ECB system uses an electric pump to generate hydraulic pressure, thereby
providing braking power without relying on engine vacuum. The use of this
technology ensures a consistent supply of effective braking power.
However, the detail behind the LFA brake system does not end with the ECB system.
Monoblock calipers and CCM (Carbon Ceramic Material) discs are just a few of the
other components that give the LFA its generous braking power. Furthermore, large
brake ducts have been proactively integrated in order to feed the brakes fresh, cold
air to keep them working at their optimum temperature for consistent performance.
Regarding the brake override system:
If the driver depresses the brake and accelerator pedals at the same time or if
the ECU judges that both acceleration and braking commands are being issued,
braking will be prioritized. The system will ignore the signal from the accelerator
pedal, close all throttle valves and provide the appropriate amount of braking force
demanded by the driver’s braking effort.
Page 54 of 128
52
■
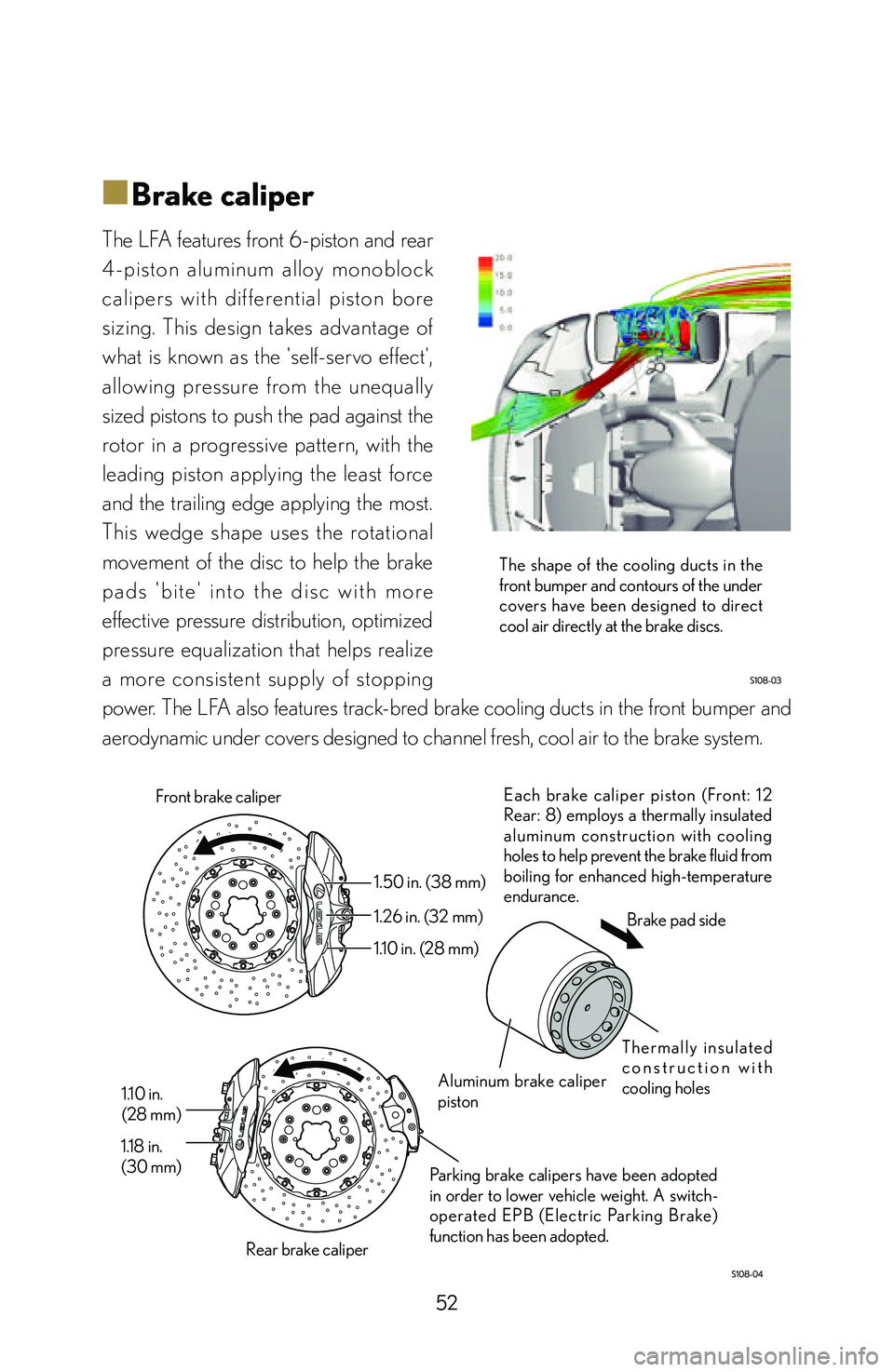
■Brake caliper
The LFA features front 6-piston and rear
4-piston aluminum alloy monoblock
calipers with dif ferential piston bore
sizing. This design takes advantage of
what is known as the 'self-servo effect',
allowing pressure from the unequally
sized pistons to push the pad against the
rotor in a progressive pattern, with the
leading piston applying the least force
and the trailing edge applying the most.
This wedge shape uses the rotational
movement of the disc to help the brake
p a d s ' b i t e ' i n t o t h e d i s c w i t h m o r e
effective pressure distribution, optimized
pressure equalization that helps realize
a more consistent supply of stopping
power. The LFA also features track-bred brake cooling ducts in the front bumper and
aerodynamic under covers designed to channel fresh, cool air to the brake system.
Each brake caliper piston (Front: 12
Rear: 8) employs a thermally insulated
aluminum construction with cooling
holes to help prevent the brake fluid from
boiling for enhanced high-temperature
endurance.
Parking brake calipers have been adopted
in order to lower vehicle weight. A switch-
operated EPB (Electric Parking Brake)
function has been adopted.
1.50 in. (38 mm)
1.26 in. (32 mm)
1.10 in. (28 mm)
1.10 in.
(28 mm)
1.18 in.
(30 mm) Front brake caliper
Rear brake caliper Aluminum brake caliper
piston
T h e r m a l l y i n s u l a t e d
c o n s t r u c t i o n w i t h
cooling holesBrake pad side
The shape of the cooling ducts in the
front bumper and contours of the under
covers have been designed to direct
cool air directly at the brake discs.
Page 58 of 128

56
Checking the engine
Components expected to operate at high speeds have been made as light and
precise as possible, realizing a superfast engine capable of revving from idle to 9,000
rpm in only 0.6 seconds.
In order to ensure adequate lubrication under high G-loads, a dry sump lubrication
system has been adopted.
The engine oil is cooled by a liquid-cooled oil cooler located in the valley between
each bank of cylinders and an air-cooled oil cooler housed within the front overhang.
In addition, two high-per formance radiators have been housed within the rear
overhang for an optimal front-rear weight balance.
A TFT LCD panel has been adopted to accurately transmit various information from
the engine to the driver. An analog-style digital tachometer displays engine speed
while other real-time engine information is displayed digitally for both superior visual
clarity and response.
An acrylic lens with a metal ring is positioned at the center of the meter to clearly
display the primary instruments and to create a three-dimensional appearance.
Page 65 of 128

63
Checking the engine
■
■Fuel gauge
The fuel gauge displays the amount of fuel remaining on a scale of 0 to 1/1. The
saddle-shaped fuel tank consists of a main tank compartment and a sub-tank
compartment. When the fuel level drops to approximately 2.9 gal. (11 L, 2.4 Imp. gal.)
between both compartments, the bar display will blink in amber to inform the driver
that the remaining fuel level is low. In this state, the remaining amount of fuel is directed
into the main tank compartment in order to ensure a stable supply of fuel to the engine
even under high cornering G-loads.
S109-14Main tank
compartment Sub-tank compartment
Fuel
Remaining fuel directed to main tank
compartment
Blinks when remaining fuel drops to approx. 2.9 gal. (11 L, 2.4 Imp. gal.)
The main tank compar tment and sub-tank compar tment each have their own
individual sender gauges to monitor the fuel levels. The ECU calculates the total
amount of fuel remaining from both of these sensors and informs the driver using
the fuel gauge. The ECU digitally processes the fuel level data in order to display a
clear and accurate fuel level even when the fuel level fluctuates under high cornering
G-loads.