2012 CHEVROLET CORVETTE weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 244 of 434

Black plate (24,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
9-24 Driving and Operating
Leaving the Vehicle with
the Engine Running
(Automatic Transmission)
{WARNING
It can be dangerous to leave the
vehicle with the engine running.
The vehicle could move suddenly
if the shift lever is not fully in
P (Park) with the parking brake
firmly set. And, if you leave the
vehicle with the engine running, it
could overheat and even catch
fire. You or others could be
injured. Do not leave the vehicle
with the engine running.If you have to leave the vehicle with
the engine running, be sure the
vehicle is in P (Park) and the
parking brake is firmly set before
you leave it. After you have moved
the shift lever into P (Park), hold
down the regular brake pedal. See if
you can move the shift lever away
from P (Park) without first pushing
the button on the lever. If you can, it
means that the shift lever was not
fully locked into P (Park).
Torque Lock (Automatic
Transmission)
If you are parking on a hill and you
do not shift the transmission into
P (Park) properly, the weight of
the vehicle may put too much
force on the parking pawl in the
transmission. You may find it difficult
to pull the shift lever out of P (Park). This is called
“torque lock.”
To prevent torque lock, set the
parking brake and then shift into
P (Park) properly before you leave
the driver seat. To find out how, see
“Shifting Into P (Park)” previously in
this section.
When you are ready to drive, move
the shift lever out of P (Park) before
you release the parking brake.
If torque lock does occur, you may
need to have another vehicle push
yours a little uphill to take some of
the pressure from the transmission
parking pawl, so you can pull the
shift lever out of P (Park).
Page 314 of 434

Black plate (40,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
10-40 Vehicle Care
The ZR1, Z06, and Grand Sport
models also have an electronic
brake pad wear sensor system.
When pads are worn, the CHANGE
BRAKE PADS message displays
in the Driver Information Center.
SeeBrake System Messages on
page 5‑37.
Some driving conditions or climates
can cause a brake squeal when the
brakes are first applied or lightly
applied. This does not mean
something is wrong with the brakes.
Brake linings should always be
replaced as complete axle sets. Brake Rotor Wear
ZR1 models have, and Z06 and
Grand Sport models may have,
ceramic brake rotors. Rotors should
be visually inspected whenever the
brake pads are replaced. Rotors
also need to be weighed before
brake pads are replaced to confirm
that the rotor mass is greater than
the wear‐out mass printed on the
rotor. The rotor can be reused if the
weight of the rotor is above the
mass limit. Rotor inspection and
weighing methods can be found in
the service manual. See
Service
Publications Ordering Information
on page 13‑17. Brake Rotor Protector
{WARNING
Ceramic rotors will be very hot
after operation and touching them
may cause burns. Be sure brake
system is completely cool prior to
installation of protector, or coming
in contact with them.
Notice: Rotors may be chipped if
hard contact is made with the
wheel during wheel installation or
removal. Always use the rotor
protectors. Be sure to carefully
follow wheel removal and
installation instructions.
Page 337 of 434
Black plate (63,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
Vehicle Care 10-63
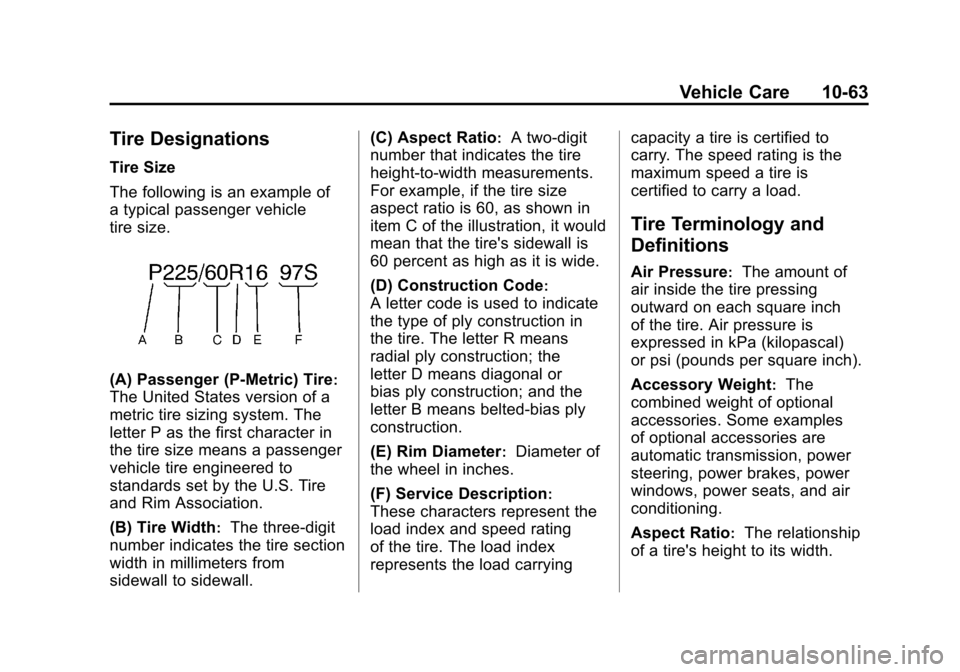
Tire Designations
Tire Size
The following is an example of
a typical passenger vehicle
tire size.
(A) Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire:
The United States version of a
metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in
the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to
standards set by the U.S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width
:The three‐digit
number indicates the tire section
width in millimeters from
sidewall to sidewall. (C) Aspect Ratio
:A two‐digit
number that indicates the tire
height‐to‐width measurements.
For example, if the tire size
aspect ratio is 60, as shown in
item C of the illustration, it would
mean that the tire's sidewall is
60 percent as high as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code
:
A letter code is used to indicate
the type of ply construction in
the tire. The letter R means
radial ply construction; the
letter D means diagonal or
bias ply construction; and the
letter B means belted‐bias ply
construction.
(E) Rim Diameter
:Diameter of
the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description
:
These characters represent the
load index and speed rating
of the tire. The load index
represents the load carrying capacity a tire is certified to
carry. The speed rating is the
maximum speed a tire is
certified to carry a load.
Tire Terminology and
Definitions
Air Pressure:The amount of
air inside the tire pressing
outward on each square inch
of the tire. Air pressure is
expressed in kPa (kilopascal)
or psi (pounds per square inch).
Accessory Weight
:The
combined weight of optional
accessories. Some examples
of optional accessories are
automatic transmission, power
steering, power brakes, power
windows, power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio
:The relationship
of a tire's height to its width.
Page 338 of 434

Black plate (64,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
10-64 Vehicle Care
Belt:A rubber coated layer of
cords that is located between
the plies and the tread. Cords
may be made from steel or other
reinforcing materials.
Bead
:The tire bead contains
steel wires wrapped by steel
cords that hold the tire onto
the rim.
Bias Ply Tire
:A pneumatic tire
in which the plies are laid at
alternate angles less than
90 degrees to the centerline of
the tread.
Cold Tire Pressure
:The
amount of air pressure in a tire,
measured in kPa (kilopascal)
or psi (pounds per square inch)
before a tire has built up heat
from driving. See Tire Pressure
on page 10‑66. Curb Weight
:The weight of a
motor vehicle with standard and
optional equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil,
and coolant, but without
passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings
:A code
molded into the sidewall of a
tire signifying that the tire is in
compliance with the U.S.
Department of Transportation
(DOT) Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards. The DOT code
includes the Tire Identification
Number (TIN), an alphanumeric
designator which can also
identify the tire manufacturer,
production plant, brand, and
date of production.
GVWR
:Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating. See Vehicle Load Limits
on page 9‑14. GAWR FRT
:Gross Axle
Weight Rating for the front axle.
See Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9‑14.
GAWR RR
:Gross Axle
Weight Rating for the rear axle.
See Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9‑14.
Intended Outboard Sidewall
:
The side of an asymmetrical tire,
that must always face outward
when mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa)
:The metric
unit for air pressure.
Light Truck (LT‐Metric) Tire
:
A tire used on light duty trucks
and some multipurpose
passenger vehicles.
Load Index
:An assigned
number ranging from 1 to 279
that corresponds to the load
carrying capacity of a tire.
Page 339 of 434

Black plate (65,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
Vehicle Care 10-65
Maximum Inflation Pressure:
The maximum air pressure to
which a cold tire can be inflated.
The maximum air pressure is
molded onto the sidewall.
Maximum Load Rating
:
The load rating for a tire at the
maximum permissible inflation
pressure for that tire.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle
Weight
:The sum of curb
weight, accessory weight,
vehicle capacity weight, and
production options weight.
Normal Occupant Weight
:
The number of occupants a
vehicle is designed to seat
multiplied by 68 kg (150 lbs).
See Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9‑14.
Occupant Distribution
:
Designated seating positions. Outward Facing Sidewall
:
The side of an asymmetrical tire
that has a particular side that
faces outward when mounted on
a vehicle. The side of the tire
that contains a whitewall,
bears white lettering, or bears
manufacturer, brand, and/or
model name molding that is
higher or deeper than the same
moldings on the other sidewall
of the tire.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire
:
A tire used on passenger cars
and some light duty trucks and
multipurpose vehicles.
Recommended Inflation
Pressure
:Vehicle
manufacturer's recommended
tire inflation pressure as shown
on the tire placard. See Tire
Pressure on page 10‑66
andVehicle Load Limits on
page 9‑14. Radial Ply Tire
:A pneumatic
tire in which the ply cords that
extend to the beads are laid at
90 degrees to the centerline of
the tread.
Rim
:A metal support for a tire
and upon which the tire beads
are seated.
Sidewall
:The portion of a tire
between the tread and the bead.
Speed Rating
:An
alphanumeric code assigned to
a tire indicating the maximum
speed at which a tire can
operate.
Traction
:The friction between
the tire and the road surface.
The amount of grip provided.
Tread
:The portion of a tire
that comes into contact with
the road.
Page 340 of 434

Black plate (66,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
10-66 Vehicle Care
Treadwear Indicators:Narrow
bands, sometimes called wear
bars, that show across the tread
of a tire when only 1.6 mm
(1/16 in) of tread remains.
See When It Is Time for New
Tires on page 10‑73.
UTQGS (Uniform Tire Quality
Grading Standards)
:A tire
information system that
provides consumers with
ratings for a tire's traction,
temperature, and treadwear.
Ratings are determined by
tire manufacturers using
government testing procedures.
The ratings are molded into
the sidewall of the tire. See
Uniform Tire Quality Grading on
page 10‑76. Vehicle Capacity Weight
:
The number of designated
seating positions multiplied by
68 kg (150 lbs) plus the rated
cargo load. See
Vehicle Load
Limits on page 9‑14.
Vehicle Maximum Load on the
Tire
:Load on an individual tire
due to curb weight, accessory
weight, occupant weight, and
cargo weight.
Vehicle Placard
:A label
permanently attached to a
vehicle showing the vehicle
capacity weight and the
original equipment tire size
and recommended inflation
pressure. See “Tire and Loading
Information Label” underVehicle
Load Limits on page 9‑14.
Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount
of air pressure to operate
effectively.
Notice: Neither tire
underinflation nor
overinflation is good.
Underinflated tires, or tires
that do not have enough air,
can result in:
.Tire overloading and
overheating which could
lead to a blowout.
.Premature or
irregular wear.
.Poor handling.
.Reduced fuel economy.
Page 341 of 434

Black plate (67,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
Vehicle Care 10-67
Overinflated tires, or tires
that have too much air, can
result in:
.Unusual wear.
.Poor handling.
.Rough ride.
.Needless damage from
road hazards.
The Tire and Loading
Information label on the
vehicle indicates the original
equipment tires and the correct
cold tire inflation pressures.
The recommended pressure is
the minimum air pressure
needed to support the vehicle's
maximum load carrying capacity.
For additional information
regarding how much weight
the vehicle can carry, and an
example of the Tire and Loading Information label, see
Vehicle
Load Limits on page 9‑14.
How the vehicle is loaded
affects vehicle handling and ride
comfort. Never load the vehicle
with more weight than it was
designed to carry.
When to Check
Check the tires once a month
or more.
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type
gauge to check the tire
pressure. Proper tire inflation
cannot be determined by looking
at the tire. Check the tire
inflation pressure when the tires
are cold, meaning the vehicle
has not been driven for at least
three hours or no more than
1.6 km (1 mi). Remove the valve cap from the
tire valve stem. Press the tire
gauge firmly onto the valve to
get the pressure measurement.
If the cold tire inflation pressure
matches the recommended
pressure on the Tire and
Loading Information label, no
further adjustment is necessary.
If the inflation pressure is low,
add air until the recommended
pressure is reached. If the
inflation pressure in high, press
on the metal stem in the center
of the tire valve to release air.
Re‐check the tire pressure with
the tire gauge.
Return the valve caps on the
valve stems to keep out dirt and
moisture and prevent leaks.
Page 348 of 434

Black plate (74,1)Chevrolet Corvette Owner Manual - 2012
10-74 Vehicle Care
The rubber in tires ages over time.
This also applies for the spare tire,
if the vehicle has one, even if it is
never used. Multiple conditions
including temperatures, loading
conditions, and inflation pressure
maintenance affect how fast aging
takes place. Tires will typically need
to be replaced due to wear before
they may need to be replaced due
to age. Consult the tire
manufacturer for more information
on when tires should be replaced.
Vehicle Storage
Tires age when stored normally
mounted on a parked vehicle.
Park a vehicle that will be stored for
at least a month in a cool, dry, clean
area away from direct sunlight to
slow aging. This area should be
free of grease, gasoline, or other
substances that can deteriorate
rubber.Parking for an extended period can
cause flat spots on the tires that
may result in vibrations while
driving. When storing a vehicle for
at least a month, remove the tires
or raise the vehicle to reduce the
weight from the tires.
Buying New Tires
GM has developed and matched
specific tires for the vehicle. The
original equipment tires installed
were designed to meet General
Motors Tire Performance Criteria
Specification (TPC Spec) system
rating. When replacement tires are
needed, GM strongly recommends
buying tires with the same TPC
Spec rating.
GM's exclusive TPC Spec system
considers over a dozen critical
specifications that impact the
overall performance of the
vehicle, including brake systemperformance, ride and handling,
traction control, and tire pressure
monitoring performance. GM's TPC
Spec number is molded onto the
tire's sidewall near the tire size.
If the tires have an all‐season
tread design, the TPC Spec
number will be followed by MS for
mud and snow. See
Tire Sidewall
Labeling on page 10‑62, for
additional information.
GM recommends replacing all the
tires at the same time. Uniform tread
depth on all tires will help to
maintain the performance of the
vehicle. Braking and handling
performance may be adversely
affected if all the tires are not
replaced at the same time. See Tire
Inspection on page 10‑72 andTire
Rotation on page 10‑72.