2011 Seat Ibiza ST belt
[x] Cancel search: beltPage 49 of 280

47
Child safety
WARNING
● The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie approximately on the cen-
tre of the shoulder, never across the neck or the arm. The seat belt must
lie close to the upper part of the body. The lap belt part must lie across
the pelvis, not across the stomach, and always fit closely. Pull the belt
tight if necessary to take up any slack ⇒ page 25, Seat belts.
● Read and always observe information and warnings concerning the
use of child seats ⇒
in Safety notes on using child seats on page 44.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 50 of 280

48Child safety
Securing child seats
Ways to secure a child seat
A child seat can be secured differently on the rear seat and
on the front passenger seat. You can secure a child seat to the rear seat or front passenger seat in the
following ways:
● Child seats in groups 0 to 3 can be secured with a seat belt.
● Child seats for groups 0, 0+ and 1 with the ISOFIX system can be se-
cured, without fastening seat belts, with the ISOFIX securing rings
⇒ page 48.
CategoryWeightSeat locationsFront passen- gerRear outerRear centre
Group 0<10 kgU*UUGroup 0+<13 kgU*UUGroup 19-18 kgU*U/LUGroup 2 / 315-36 kgXUFUF
Suitable for universal approved restraining systems for use in this age
category (universal retention systems are those fitted using the adult
seat belt).
Suitable for universal forward-facing retention systems approved for
use with this age group.
Move the front passenger seat as far back as possible, as high as pos-
sible and always deactivate the airbag.
Suitable for retention systems using the ISOFIX anchors.
Seat position not suitable for children in this age group.
U:
UF
*:
L:
X
WARNING
● When travelling, children must be secured in the vehicle with a re-
straint system suitable for age, weight and size.
● Never install a child seat facing backwards on the front passenger
seat unless the front passenger airbag has been disabled. This could
cause fatal injuries to the child! However, if, in exceptional cases, it is
necessary to transport a child in the front passenger seat, the front pas-
senger airbag ⇒ page 41, Deactivating airbags* must always be disabled
and the seat adjusted to its highest position, where possible.
● Read and always observe information and warnings concerning the
use of child seats ⇒
in Safety notes on using child seats on page 44.
Securing a child seat with the ISOFIX system
Child seats can be secured quickly, easily and safely on the
rear outer seats with the ISOFIX system.
Fig. 26 ISOFIX securing
rings
Page 51 of 280

49
Child safety
When removing or fitting the child seat, please be sure to follow
the manufacturer's instructions.
– Press the child seat onto the ISOFIX retaining rings until the
child seat can be heard to engage securely. If the child seat is
fitted with any other anti-rotation system, follow the manufac-
turer instructions carefully.
– Pull on both sides of the child seat to ensure that it is secure.
Two ISOFIX retaining rings are fitted on each rear seat. In some vehicles, the
rings are secured to the seat frame and, in others, they are secured to the
rear floor. The access to the ISOFIX rings is between the rear seat backrest
and the seat cushioning.
Child seats with ISOFIX mountings are available in your Authorised Service
Centres.
WARNING
● The retaining rings are designed to only be used with ISOFIX child
seats.
● Never secure child seats without the ISOFIX system, retaining belts or
objects to the fastening rings – this can result in potentially fatal injuries
to the child.
● Ensure that the child seat is secured correctly to the ISOFIX anchor
points.
Top Tether retainer straps
Some child restraint seats have a third Top Tether anchoring
point, apart from both ISOFIX anchoring points, which allow
better child retention.
Fig. 27 Position of the
Top Tether rings on the
back of the rear seat
Child seats with the Top Tether system come with a strap for securing the
seat to the vehicle anchor point, located at the back of the rear backrest.
The retainer strap is used to reduce forwards movements of the safety seat
in a crash, helping reduce the risk of injuries to the head from hitting the
inside of the vehicle.
It is foreseen that an EU Directive will introduce requirements related to the
retention of child restraint systems by means of ISOFIX and Top Tether an-
chorages (probably compulsory for new types from 2010), which will entail
improved retention of the child restraint seat and less head movement in
case of frontal collisions.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 52 of 280
50Child safety
Use of retainer straps on rear-facing seats
At present there are very few rear-facing child safety seats fitted with a re-
tainer strap. Please carefully read and follow the safety seat manufacturer's
instructions for information on how to install the retainer strap properly.
WARNING
An undue installation of the safety seat will increase the risk of injury in
the event of a crash.
● Never tie the retainer strap to a hook in the luggage compartment.
● Never secure or tie luggage or other items to the lower anchorages
(ISOFIX) or the upper ones (Top Tether).
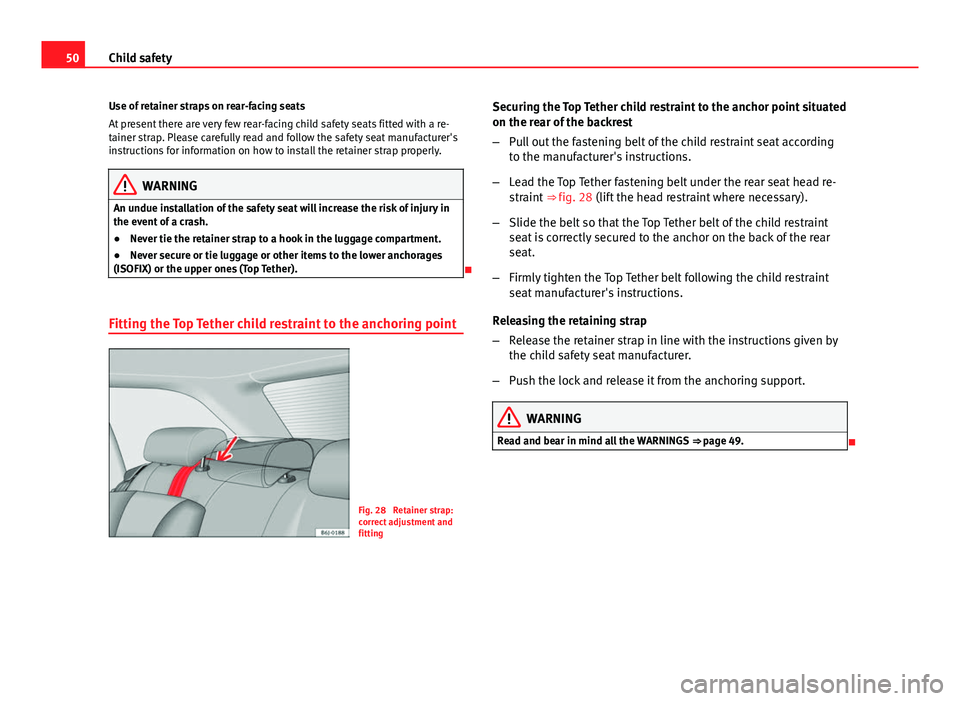
Fitting the Top Tether child restraint to the anchoring point
Fig. 28 Retainer strap:
correct adjustment and
fitting Securing the Top Tether child restraint to the anchor point situated
on the rear of the backrest
–
Pull out the fastening belt of the child restraint seat according
to the manufacturer's instructions.
– Lead the Top Tether fastening belt under the rear seat head re-
straint ⇒ fig. 28 (lift the head restraint where necessary).
– Slide the belt so that the Top Tether belt of the child restraint
seat is correctly secured to the anchor on the back of the rear
seat.
– Firmly tighten the Top Tether belt following the child restraint
seat manufacturer's instructions.
Releasing the retaining strap
– Release the retainer strap in line with the instructions given by
the child safety seat manufacturer.
– Push the lock and release it from the anchoring support.
WARNING
Read and bear in mind all the WARNINGS ⇒ page 49.
Page 66 of 280

64Cockpit
ItemSymbolMeaning of warning and indicator
lampsFurther infor-mation
1Engine fault (petrol engine)⇒ page 67
1Glow plug system for diesel engine
If lit: glow plug system active
If flashing: engine fault⇒ page 68
2Soot accumulation in the diesel en-
gine particulate filter⇒ page 68
3
Red:
Engine oil pressure
⇒ page 68Yellow:
If flashing: engine oil sensor faulty
If it remains lit: insufficient engine
oil
4Bulb defective⇒ page 69
5Level of liquid for washing windows
too low.⇒ page 69
6Rear fog light switched on⇒ page 69
7Seat belt warning lamp*⇒ page 20
8Anti-lock brake system (ABS) *⇒ page 69
9
If flashing: Electronic Stability Pro-
gramme (ESP) or the TCS is working
If it remains lit: ESP or TCS faulty⇒ page 70
⇒ page 70
10Brake fluid required or
serious fault in brake system⇒ page 71
11Handbrake on⇒ page 159
ItemSymbolMeaning of warning and indicator
lampsFurther infor-mation
12Cruise speed activated (Cruise con-
trol)⇒ page 71
13Tyre pressure*⇒ page 71
14Selector lever lock (automatic gear-
box)⇒ page 72
15Fuel level / reserve⇒ page 72
16Doors open⇒ page 72
17Tailgate open⇒ page 72
18Airbag or belt tensioner system fault
or airbag disabled⇒ page 31
19Main beam switched on⇒ page 73
20Start-Stop system switched off⇒ page 148
21Electro-hydraulic steering⇒ page 73
22Fault in the emission control system⇒ page 73
23Coolant level / coolant temperature⇒ page 73
24Alternator fault⇒ page 74
25If it stays lit: TCS disabled⇒ page 70
⇒ page 70
Page 115 of 280

113
Seats and storage compartments
Seats and storage compartments The importance of correct seat adjustment
Proper seat adjustment optimises the level of protection of-
fered by seat belts and airbags.
Your vehicle has five seats, two in the front and three in the rear. Each seat
is equipped with a three-point seat belt.
The driver seat and the front passenger seat can be adjusted in many ways
to suit the physical requirements of the vehicle occupants. The correct seat
position is very important for:
● a fast and easy operation of all controls on the instrument panel,
● a relaxed posture which does not cause drowsiness,
● a safe driving ⇒ page 7,
● ensuring that the seat belts and airbag system provide maximum pro-
tection ⇒ page 19.
WARNING
● If the driver and passengers assume improper sitting positions, they
may sustain critical injuries.
● More people than available seats must never be transported in your
vehicle.
● Every passenger in the vehicle must properly fasten and wear the
seat belt belonging to his or her seat. Children must be protected with an
appropriate child restraint system ⇒ page 43, Child safety.
● The front seats and all head restraints must always be adjusted to
body size and the seat belt must always be properly adjusted to provide
you and your passengers with optimum protection.
WARNING (Continued)
● Always keep your feet on the footwell when the vehicle is moving;
never rest them on the dash panel, out of the window or on the seat. This
is also applied to passengers. An incorrect sitting position exposes you
to an increased risk of injury in case of a sudden braking or an accident.
If the airbag is triggered, you could sustain severe injuries due to an in-
correct sitting position.
● It is important for the driver and front passenger to keep a distance of
at least 25 cm from the steering wheel and dash panel. Failure to respect
the minimum distance means that the airbag will not protect you. Risk of
fatal injury. The distance between the driver and the steering wheel or
between the front passenger and the dash panel should always be as
great as possible.
● Adjust the driver or front passenger seat only when the vehicle is sta-
tionary. Otherwise, your seat could move unexpectedly while the vehicle
is moving. This could increase the risk of an accident and therefore, in-
jury. In addition, while adjusting your seat, you will assume an incorrect
sitting position. Risk of fatal accidents.
● Special guidelines apply to installing a child seat on the front passen-
ger seat. When installing a child seat, please observe the warnings de-
scribed in ⇒ page 43, Child safety.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 116 of 280

114Seats and storage compartments
Head restraints
Correct adjustment of head restraints
Properly adjusted head restraints are an important part of
passenger protection and can reduce the risk of injuries in
most accident situations.
Fig. 69 Front view: head
restraints and seat belts
correctly adjusted
Fig. 70 Side view: head
restraints and seat belts
correctly adjusted
– Adjust the head restraint so that the top is at the same level as
the top of your head or as close as possible to the same level as
the top of your head, at least at eye level ⇒ fig. 69 and
⇒ fig. 70.
Adjusting the head restraints ⇒ page 115
WARNING
● Travelling with the head restraints removed or improperly adjusted
increases the risk of severe injuries.
● Improperly adjusted head restraints could lead to death in the event
of a collision or accident.
● Incorrectly adjusted head restraints also increase the risk of injury
during sudden or unexpected driving or braking manoeuvres.
● The head restraints must always be adjusted according to the pas-
senger's height.
Page 118 of 280

116Seats and storage compartments
Front seats
Adjustment of the front seats
Fig. 72 Front left seat
controls
1
Adjusting the seat forwards and backwards
– Pull up the grip and move the seat forwards or backwards.
– Then release the grip 1
and move the seat further until the
catch engages.
2
Adjusting seat height
– Pull the lever up or push down (several times if necessary) from
its home position. This adjusts the seat height in stages.
3
Adjusting the backrest angle
– Take your weight off the backrest and turn the hand wheel.
WARNING
● Never adjust the driver or front passenger seat while the vehicle is in
motion. While adjusting your seat, you will assume an incorrect sitting
position. Risk of fatal accidents. Adjust the driver or front passenger seat
only when the vehicle is stationary.
● To reduce the risk of injury to the driver and front passenger in case of
a sudden braking or an accident, never drive with the backrest tilted to-
wards the rear. The maximum protection of the seat belt can be achieved
only when the backrests are in an upright position and the driver and
front passenger have properly adjusted their seat belts. The further the
backrests are tilted to the rear, the greater the risk of injury due to im-
proper positioning of the belt web!
● Exercise caution when securing the seat height into forwards/back-
wards position. Injuries can be caused if the seat height is adjusted with-
out due care and attention.
● To move the seat lengthways, pull upwards and not sideways on the
lever, as the force exerted on it in this position could damage it.