2011 FORD KUGA pump
[x] Cancel search: pumpPage 1413 of 2057
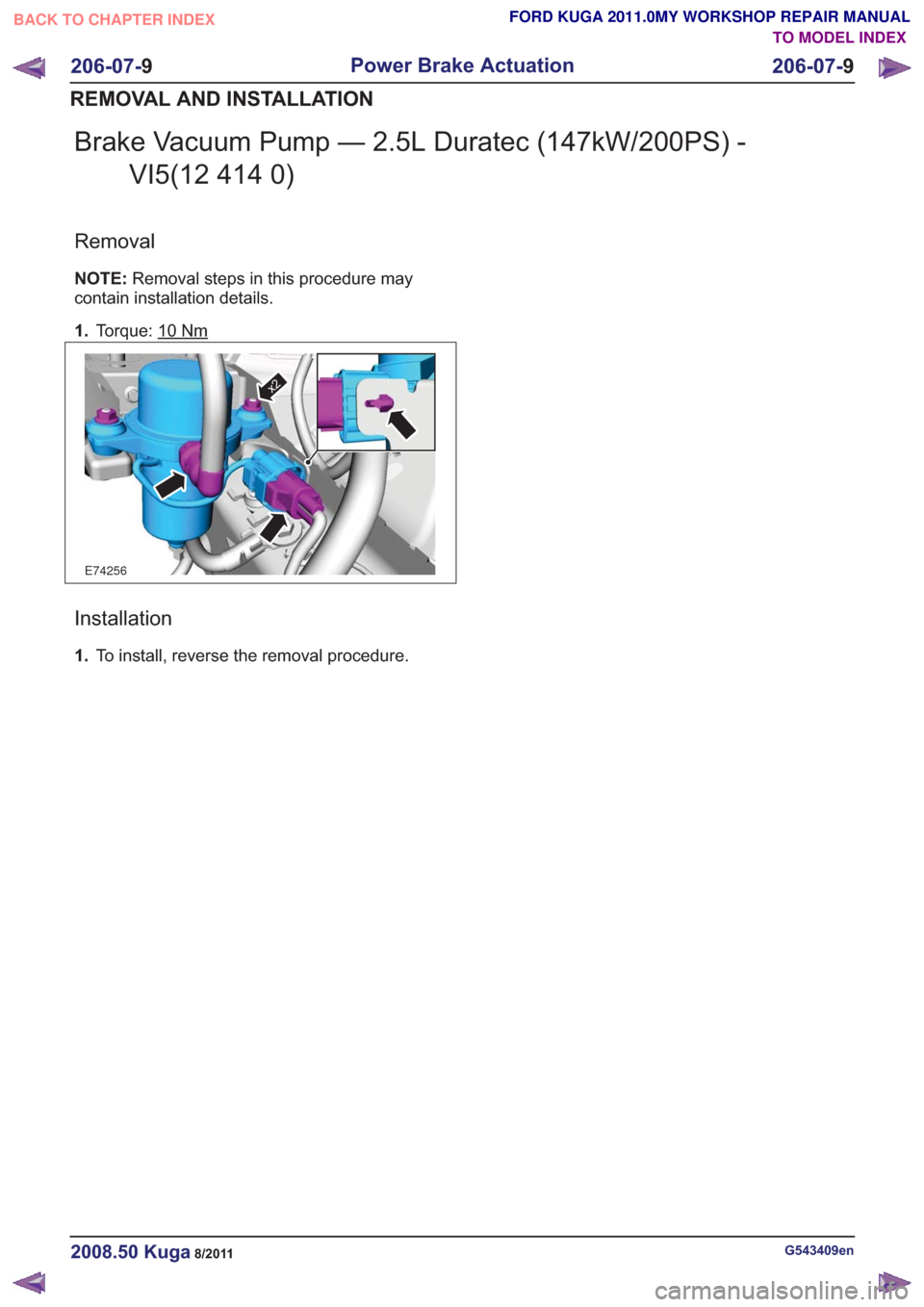
Brake Vacuum Pump — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -VI5(12 414 0)
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Torque: 10
Nm
E74256
x2
Installation
1.To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G543409en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 9
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1425 of 2057
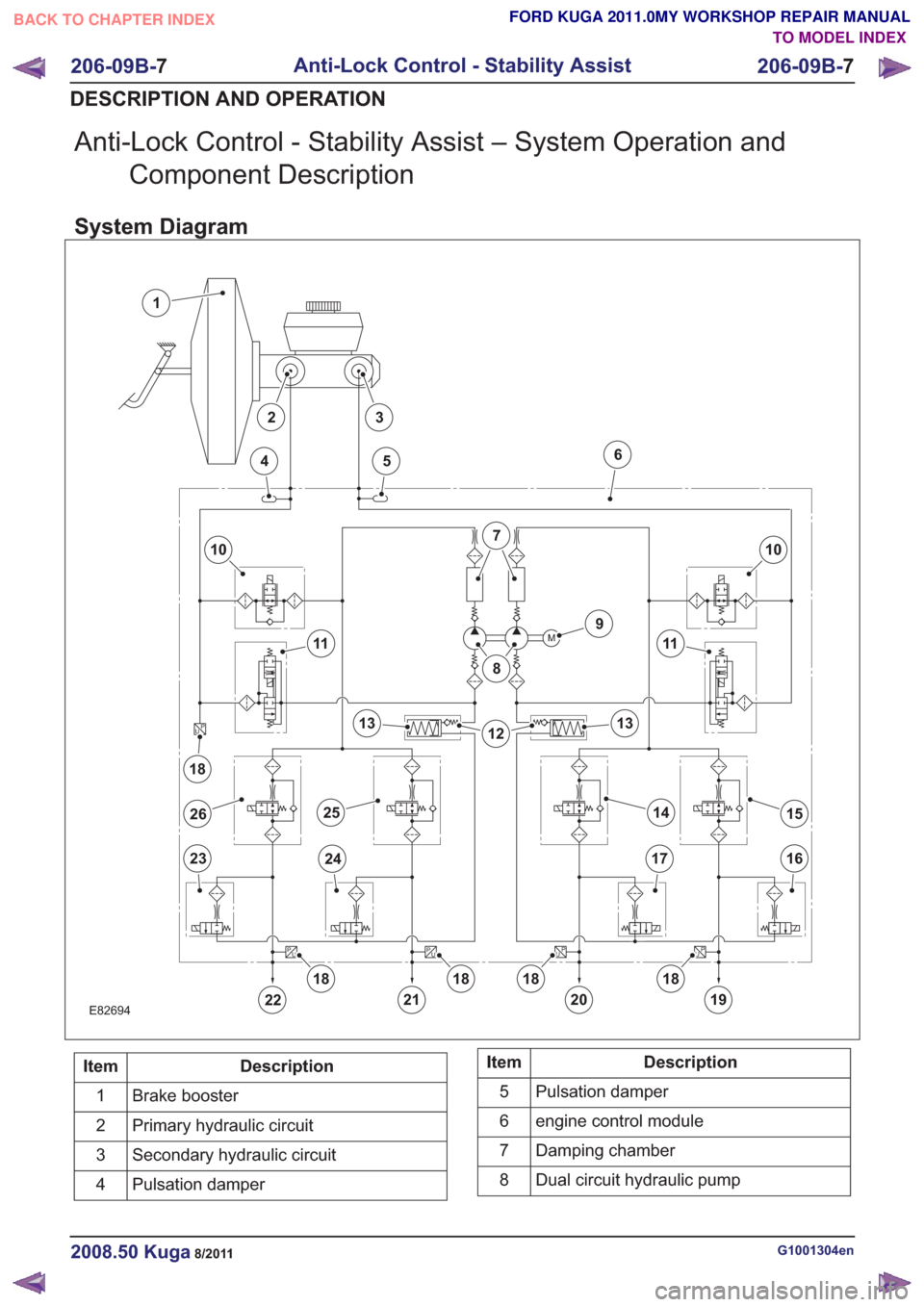
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist – System Operation andComponent Description
System Diagram
E82694
M
P
UP
U
P
U
P
U
P
U
1
10
22
23
456
7
8
9
11
1213
1415
1617
18
2324
13
11
10
19
2526
2120
181818
18
Description
Item
Brake booster
1
Primary hydraulic circuit
2
Secondary hydraulic circuit
3
Pulsation damper
4Description
Item
Pulsation damper
5
engine control module
6
Damping chamber
7
Dual circuit hydraulic pump
8
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 7
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1426 of 2057

Description
Item
D.C. motor
9
Solenoid-operated pilot valve (2 off)
10
Solenoid-operated priming valve (2 off)
11
One way check valve
12
Low-pressure accumulator (2 off)
13
Solenoid-operated inlet valve (RH rear
brake)
14
Solenoid-operated inlet valve (LH front
brake)
15
Solenoid-operated outlet valve (LH front
brake)
16
Solenoid-operated outlet valve (RH rear
brake)
17Description
Item
Pressure sensor (5 off)
18
LH front brake (secondary circuit)
19
RH rear brake (secondary circuit)
20
LH rear brake (primary circuit)
21
RH front brake (primary circuit)
22
Solenoid-operated outlet valve (RH front
brake)
23
Solenoid-operated outlet valve (LH rear
brake)
24
Solenoid-operated inlet valve (LH rear
brake)
25
Solenoid-operated inlet valve (RH front
brake)
26
System Operation
The HCU features 3 operating modes:
Normal braking:
Initially, no current is supplied to
any of the solenoid-operated valves. Operating the
brake pedal produces a corresponding increase
or decrease of pressure in the brakes, through the
open pilot valves and inlet valves. If the ABS
module determines that EBD is necessary, it
energizes the inlet valves for both the rear brakes,
to isolate the brakes from any further increase in
hydraulic pressure.
ABS braking: If the ABS module determines that
ABS braking is necessary, it actuates the inlet and
outlet valves of the relevant brake and starts the
hydraulic return pump. The inlet valve closes to
isolate the brake from pressurized fluid; the outlet
valve opens to release pressure from the brake
into the accumulator and the return pump circuit.
The brake releases slightly and the wheel starts to turn again. The ABS control unit then operates the
inlet and outlet valves to regulate the hydraulic
pressure acting on the brake in order to maximize
braking effect without the wheel locking up. Control
of the valves for each wheel takes place
individually.
Active braking:
With active braking, pressure is
generated for other braking functions than the
normal and ABS braking systems, e.g. for the ESP
and TCS systems. For active braking, the ABS
module energizes the pilot valves and priming
valves, starts the return pump and energizes all of
the inlet valves. Brake fluid, drawn from the
reservoir through the master cylinder and priming
valve, is pressurized by the return pump and
supplied to the inlet valves. The ABS control unit
then actuates the inlet and outlet valves in order
to regulate the pressure for the individual brakes.
Some noise may be generated during active
braking.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 8
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1430 of 2057

The opto-electronic steering wheel rotation sensors
use light barriers for contactless scanning of a
segment disk which is connected fixedly to the
steering shaft.
E54014
1
23
4
Description
Item
Segment disk
1
Photoelectric barrier
2
Electronics
3
Electrical connection
4
Use is made of opto-electronic types of sensors
with relative and absolute steering angle sensing.
For relative steering angle sensing, changes in the
steering angle are measured exclusively by the
sensor and transmitted to the ABS/ESP module.
With the aid of other vehicle status signals (e.g.
wheel speed sensors) the module calculates the
straight ahead position of the steering. For absolute
steering angle sensing, the sensor transmits a
specific signal to the module for each steering
angle position (in relation to one turn of the steering
wheel). The straight ahead position of the steering
is therefore defined in the sensor. On an absolute
steering angle sensor, several photoelectric barrier
modules are distributed around the segment disk
at varying distances. The gaps between segments
of the segment disk are also unequal. For each specific steering angle there is therefore a specific
switch status of all photoelectric barriers.
ABS/ESP module or hydraulic control unit
(HCU)
E97648
1
2
3
Description
Item
ABS Pump Motor
1
Valve block (with low-pressure
accumulators)
2
ABS module
3
The HCU comprises the ABS module, the valve
block (with low-pressure accumulators) and the
ABS pump.
The valve block combines all of the brake pressure
control valves in one unit. Depending on the
system, either simple changeover valves or
proportioning valves (e.g. on EBD (electronic brake
force distribution) systems) are installed. The
low-pressure accumulators store the brake fluid
that is returned from the wheel brakes during the
pressure reduction phase until it is drawn back into
the system by the ABS pump.
The ABS pump is designed as a dual piston pump.
This means that two separate pump elements
assure an increase in brake pressure during control
interventions. A direct current motor drives the
pump pistons via an eccentric shaft.
The ABS/ESP module monitors the input signals
of all sensors and actuates the electro-magnetic
brake pressure valves and the ABS pump as
required. For reasons of safety, the module is of
the redundant type, whereby processing of the
signals is carried out via two separate processors
that also monitor each other.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 12
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1443 of 2057

Steering System
Special Tool(s) / General EquipmentAlignment Pins, Subframe
205-316 (15-097A)
15097
Simulator, Driver and
Passenger Air Bags and Side
Air Curtains
501-073 (40-016)
501073
The Ford approved diagnostic tool
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanicalor electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart
Electrical
Mechanical
• Battery
• Battery cables
• Steering anglesensor electrical
connector
• Power steering pump control
module electrical
connectors
• Power steering pump control
module ground
cable
• Power steering pump control
module ground
cable retaining
screw
• Steering angle sensor warning
indicator
• Fuse(s)
• Tire pressure(s)
• Loose tie-rod end(s)
• Loose strut and
spring assemblies or
ball joints
• Loose pinch bolts on steering column
shaft flexible coup-
ling
• Wheels and tires
• Power steering line fluid leaks
• Steering gear bellows 3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported
concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the diagnostic tab within
the Ford approved diagnostic tool.
Components Tests
Steering Linkage
1. Grasp the steering wheel firmly and move it upand down and to the left and right without
turning the steering wheel to check the steering
column bearing for wear, steering column shaft
for wear, steering wheel for looseness and
steering column for looseness. If the steering
column bearing or the steering column shaft is
worn install a new steering column. If the
steering wheel or the steering column is loose,
tighten the steering wheel or the steering column
retaining bolts.
2. With the road wheels in the straight ahead position, gently turn the steering wheel to the
left and the right to check for free play in the
steering linkage.
3. There should be no excessive free play at the steering wheel rim. If there is excessive free
play, CHECK the tie-rod inner and outer ball
joints, REFER to Tie-Rod Component Test in
this procedure. CHECK the steering column
universal joint, REFER to Steering Column
Universal Joint Component Test in this
procedure. If there is no free play in the tie-rod
and the steering column, install a new steering
gear.
Tie-Rod
CAUTION: Steering gear boots must be
handled carefully to avoid damage. Use
new steering boot clamps when installing
the steering gear boots.
NOTE: Noises such as knocks, which may appear
to originate from the steering linkage, may also be
generated by front suspension components.
REFER to: Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH)
(100-04 Noise, Vibration and Harshness,
Diagnosis and Testing).
G1059437en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 2
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1447 of 2057

Steering Gear Checks After a Collision
General EquipmentFeeler gauge
Straight edge
Items to be observed when checking the steering
system
The following list of steering gear conditions and
the methods of testing should be taken into account
when carrying out checks to the steering system:
• If the steering gear has no faults after completing the following checks, do not install
a new steering gear.
• Surface corrosion and marks on the tie-rod are acceptable.
• When checking for turning effort torque peaks in the steering gear, turn the steering wheel from
steering lock stop to steering lock stop in
approximately 15 seconds.
• A steady increase of turning effort torque from steering center to steering lock stop is
acceptable.
• When checking for power steering fluid leaks, turn the steering wheel to the steering lock stop
in approximately 10 seconds.
• Noises from the power steering, for example the power steering pump relief valve, are
acceptable.
STEERING GEAR HOUSING
1. Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
2. Visually inspect the steering gear housing for cracks and damage. If the steering gear housing
is cracked or damaged, install a new steering
gear.
REFER to: Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
TIE-RODS
1. Using a straight edge and feeler gauge, check the tie-rods to see if they are straight. If the
distance between the tie-rod and straight edge is greater than 0.5 mm, install a new steering
gear.
REFER to:
Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
2. Check the tightening torque of the tie-rod end to wheel knuckle nut.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
3. Check the tightening torque of the tie-rod end locking nut.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
CHECK FOR TURNING EFFORT TORQUE
PEAKS IN THE STEERING GEAR
1. Lower and support the vehicle making sure that the road wheels are just clear of the floor.
2. With the ignition switch in position I, slowly turn the steering wheel from steering lock stop to
steering lock stop. If a turning effort torque peak
or judder is felt while turning the steering wheel,
detach the tie-rods from the wheel knuckles.
3. Slowly turn the steering wheel from steering lock stop to steering lock stop. If a turning effort
torque peak or judder is felt while turning the
steering wheel, install a new steering gear.
REFER to: Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
CHECK FOR POWER STEERING FLUID LEAKS
1. Lower the vehicle.
2. Run the engine at a fast idle and slowly turn the steering wheel to the left-hand steering lock
stop. Hold the steering wheel in this position for
5 seconds with a turning effort torque of 15 Nm
at the steering wheel rim.
3. Turn the steering wheel away from the left-hand steering lock stop for 30 seconds.
4. Run the engine at a fast idle and slowly turn the steering wheel to the right-hand steering lock
stop. Hold the steering wheel in this position for
5 seconds with a turning effort torque of 15 Nm
at the steering wheel rim.
5. Turn the steering wheel away from the right-hand steering lock stop.
6. Check for power steering fluid leaks at the steering gear housing and the power steering
line connections to the steering gear. If there is
G538091en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 6
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1450 of 2057

Power Steering System Filling
Special Tool(s)211-189
Adapter, Power Steering
Bleeding
13016
416-D001
Hand Vacuum
Pump/Pressure Pump
23036A
Materials
Specification
Name
WSS-M2C204-A2 /
5U7J-M2C204-AA
Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
1. Fill the power steering fluid reservoir to the MAX
mark.
Material: Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
(WSS-M2C204-A2 / 5U7J-M2C204-AA)
hydraulic fluid
2. Raise the vehicle until the road wheels are clear
of the floor. Support the vehicle.
Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
3. Slowly turn the steering wheel from lock to lock
and add power steering fluid until the power
steering fluid in the power steering fluid reservoir
stops dropping.
4. Start the engine and slowly turn the steering
wheel from lock to lock and add power steering
fluid until the power steering fluid in the power
steering fluid reservoir stops dropping. 5.
Switch the engine OFF and using the special
tools, create a vacuum of 62cm-Hg - 75cm-Hg
for 30 seconds.
Special Tool(s): 211-189, 416-D001
E73916
211-189
416-D001
6. Observe the vacuum gauge reading.
1.
2. If the vacuum decreases by more than
5cm-Hg in 5 minutes, the system should be
checked for leaks.
7. Remove the special tools. Fill the power steering
fluid reservoir to the MAX mark as necessary.
Material: Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
(WSS-M2C204-A2 / 5U7J-M2C204-AA)
hydraulic fluid
8. Lower the vehicle.
G543412en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 9
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 9
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1451 of 2057

Power Steering System Vacuum Bleeding
Special Tool(s)211-189
Adapter, Power Steering
Bleeding
13016
416-D001
Hand Vacuum
Pump/Pressure Pump
23036A
Materials
Specification
Name
WSA-M2C195-A / 9U7J-
M2C195-AA
Power Steering Fluid IW
Bleeding
9.
Refer to: Steering System Health and Safety
Precautions (100-00 General Information,
Description and Operation).
10.
E141054
11 . Material: Power Steering Fluid IW
(WSA-M2C195-A / 9U7J-M2C195-AA)
hydraulic fluid
G1467657en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 10
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 10
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL