2011 FORD KUGA fuel rail
[x] Cancel search: fuel railPage 1709 of 2057

Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
• CHECK for signs of contamina-tion such as strange odors from
the fuel tank.
• If contaminated fuel is found, DRAIN the complete fuel
system. FLUSH the fuel system
through with clean gasoline.
REFER to: Fuel Tank Draining
(310-00 Fuel System -
General Information, General
Procedures).
INSTALL a new fuel filter.
• INSPECT the fuel injectors. CLEAN the fuel injectors or
INSTALL a new set of injectors
as required only after the
checks have been carried out.
REFER to: Fuel Injectors (303-
04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5,
Removal and Installation).
• INSTALL a new fuel rail.
REFER to: Fuel Rail(303-04
Fuel Charging and Controls -
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS)
- VI5, Removal and Installa-
tion).
• Incorrect or contaminated fuel.
• Carry out a full enginediagnosis using the guided
diagnostic menu in the Ford
diagnostic equipment.
• KS.
• Carry out a full enginediagnosis using the guided
diagnostic menu in the Ford
diagnostic equipment.
• CKP sensor.
• INSPECT the fuel injectors.CLEAN the fuel injectors or
INSTALL a new set of injectors
as required only after the
checks have been carried out.
REFER to: Fuel Injectors (303-
04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5,
Removal and Installation).
• Fuel injector(s).
G1183441en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04A-
18
Fuel Charging and Controls
— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -
VI5
303-04A- 18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1712 of 2057

Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
• Carry out a full enginediagnosis using the guided
diagnostic menu in the Ford
diagnostic equipment.
• Fuel rail fuel pressure sensor.
• Check the fuel system pres-sure.
• Low fuel system pressure.
G1183441en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04A-
21
Fuel Charging and Controls
— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -
VI5
303-04A- 21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1713 of 2057
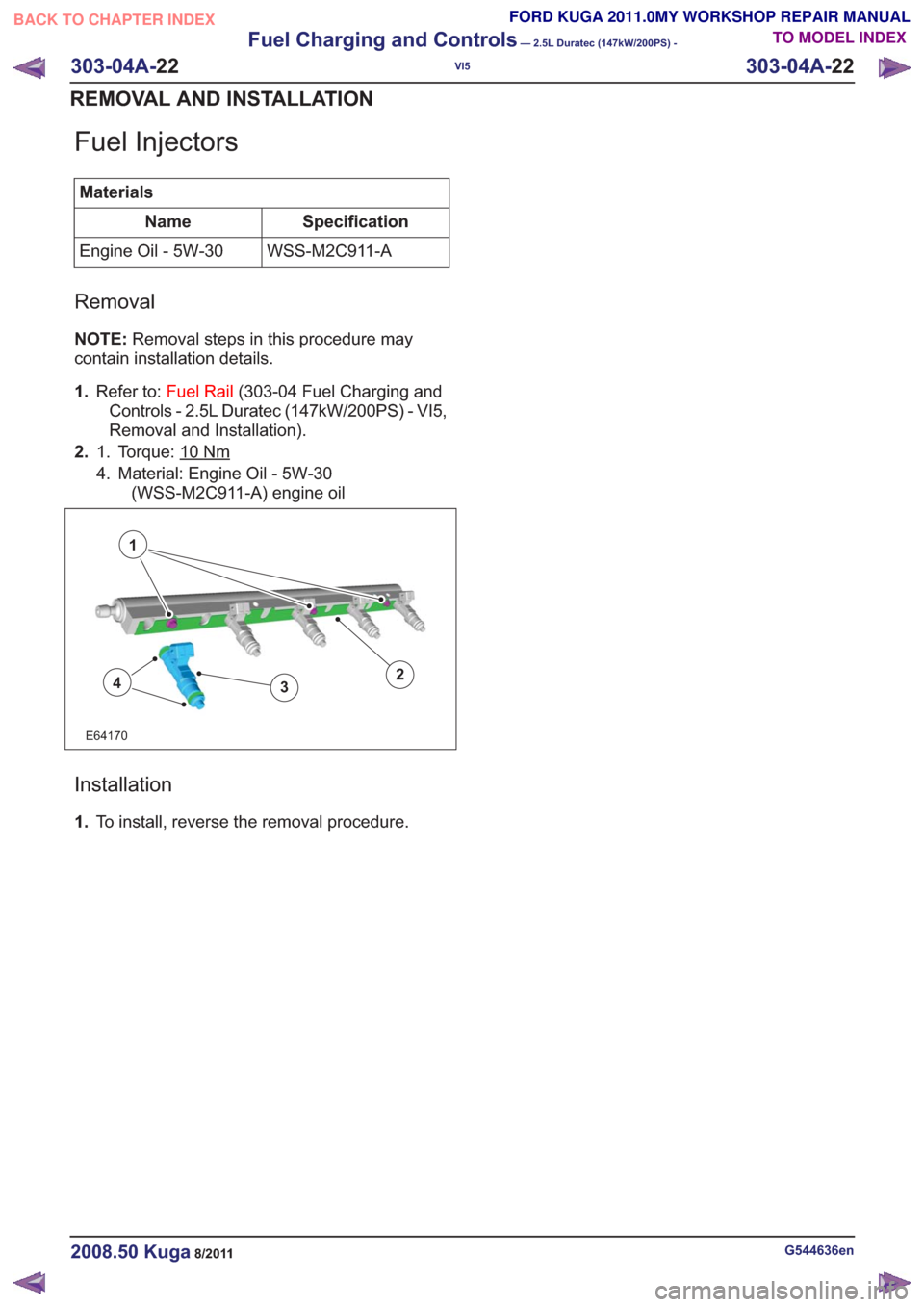
Fuel Injectors
MaterialsSpecification
Name
WSS-M2C911-A
Engine Oil - 5W-30
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Fuel Rail (303-04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5,
Removal and Installation).
2. Torque: 10
Nm1.
4. Material: Engine Oil - 5W-30
(WSS-M2C911-A) engine oil
E64170
1
243
Installation
1.To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G544636en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04A- 22
Fuel Charging and Controls
— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -
VI5
303-04A- 22
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1715 of 2057

Fuel Rail
Removal
NOTE:Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel
Systems Health and Safety Precautions
(100-00 General Information, Description and
Operation).
2. Refer to: Fuel System Pressure Release
(310-00 Fuel System - General Information,
General Procedures).
3. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect
(414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables,
General Procedures).
4. Refer to: Air Cleaner (303-12 Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Removal and
Installation).
5. Torque: 10
Nm
x2x2
E92954
6. CAUTION: Make sure that the inside of
the pipe ends are clean and free of oil
residue.
Torque: 4Nm
E63576
7. CAUTION: Make sure that the inside ofthe pipe ends are clean and free of oil
residue.
E64164
8. CAUTION: Make sure that the inside ofthe pipe ends are clean and free of oil
residue.
E64165
G1079057en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04A- 24
Fuel Charging and Controls
— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -
VI5
303-04A- 24
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1794 of 2057
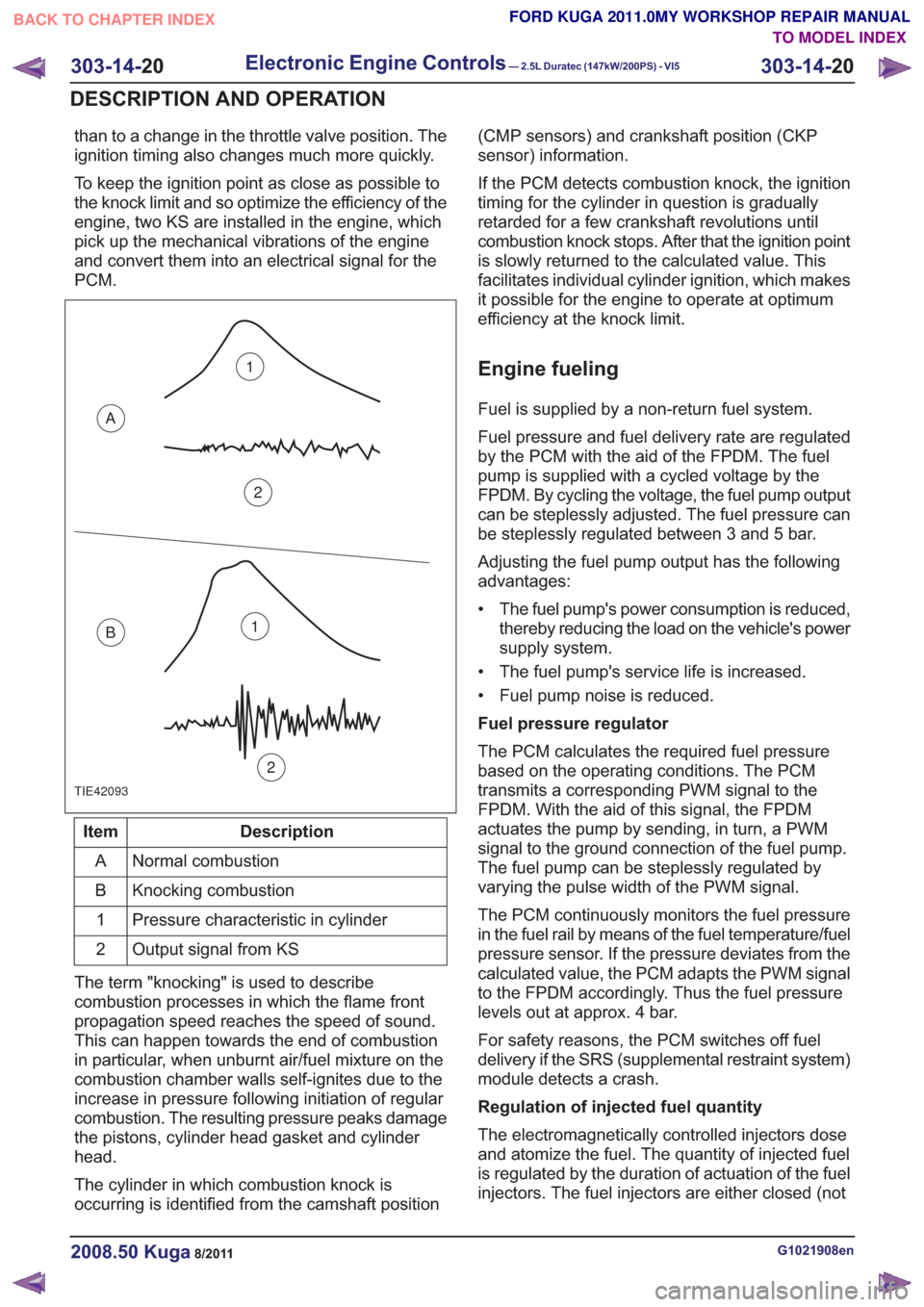
than to a change in the throttle valve position. The
ignition timing also changes much more quickly.
To keep the ignition point as close as possible to
the knock limit and so optimize the efficiency of the
engine, two KS are installed in the engine, which
pick up the mechanical vibrations of the engine
and convert them into an electrical signal for the
PCM.
TIE42093
1
2
A
B1
2
Description
Item
Normal combustion
A
Knocking combustion
B
Pressure characteristic in cylinder
1
Output signal from KS
2
The term "knocking" is used to describe
combustion processes in which the flame front
propagation speed reaches the speed of sound.
This can happen towards the end of combustion
in particular, when unburnt air/fuel mixture on the
combustion chamber walls self-ignites due to the
increase in pressure following initiation of regular
combustion. The resulting pressure peaks damage
the pistons, cylinder head gasket and cylinder
head.
The cylinder in which combustion knock is
occurring is identified from the camshaft position (CMP sensors) and crankshaft position (CKP
sensor) information.
If the PCM detects combustion knock, the ignition
timing for the cylinder in question is gradually
retarded for a few crankshaft revolutions until
combustion knock stops. After that the ignition point
is slowly returned to the calculated value. This
facilitates individual cylinder ignition, which makes
it possible for the engine to operate at optimum
efficiency at the knock limit.
Engine fueling
Fuel is supplied by a non-return fuel system.
Fuel pressure and fuel delivery rate are regulated
by the PCM with the aid of the FPDM. The fuel
pump is supplied with a cycled voltage by the
FPDM. By cycling the voltage, the fuel pump output
can be steplessly adjusted. The fuel pressure can
be steplessly regulated between 3 and 5 bar.
Adjusting the fuel pump output has the following
advantages:
• The fuel pump's power consumption is reduced,
thereby reducing the load on the vehicle's power
supply system.
• The fuel pump's service life is increased.
• Fuel pump noise is reduced.
Fuel pressure regulator
The PCM calculates the required fuel pressure
based on the operating conditions. The PCM
transmits a corresponding PWM signal to the
FPDM. With the aid of this signal, the FPDM
actuates the pump by sending, in turn, a PWM
signal to the ground connection of the fuel pump.
The fuel pump can be steplessly regulated by
varying the pulse width of the PWM signal.
The PCM continuously monitors the fuel pressure
in the fuel rail by means of the fuel temperature/fuel
pressure sensor. If the pressure deviates from the
calculated value, the PCM adapts the PWM signal
to the FPDM accordingly. Thus the fuel pressure
levels out at approx. 4 bar.
For safety reasons, the PCM switches off fuel
delivery if the SRS (supplemental restraint system)
module detects a crash.
Regulation of injected fuel quantity
The electromagnetically controlled injectors dose
and atomize the fuel. The quantity of injected fuel
is regulated by the duration of actuation of the fuel
injectors. The fuel injectors are either closed (not
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 20
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
20
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1807 of 2057
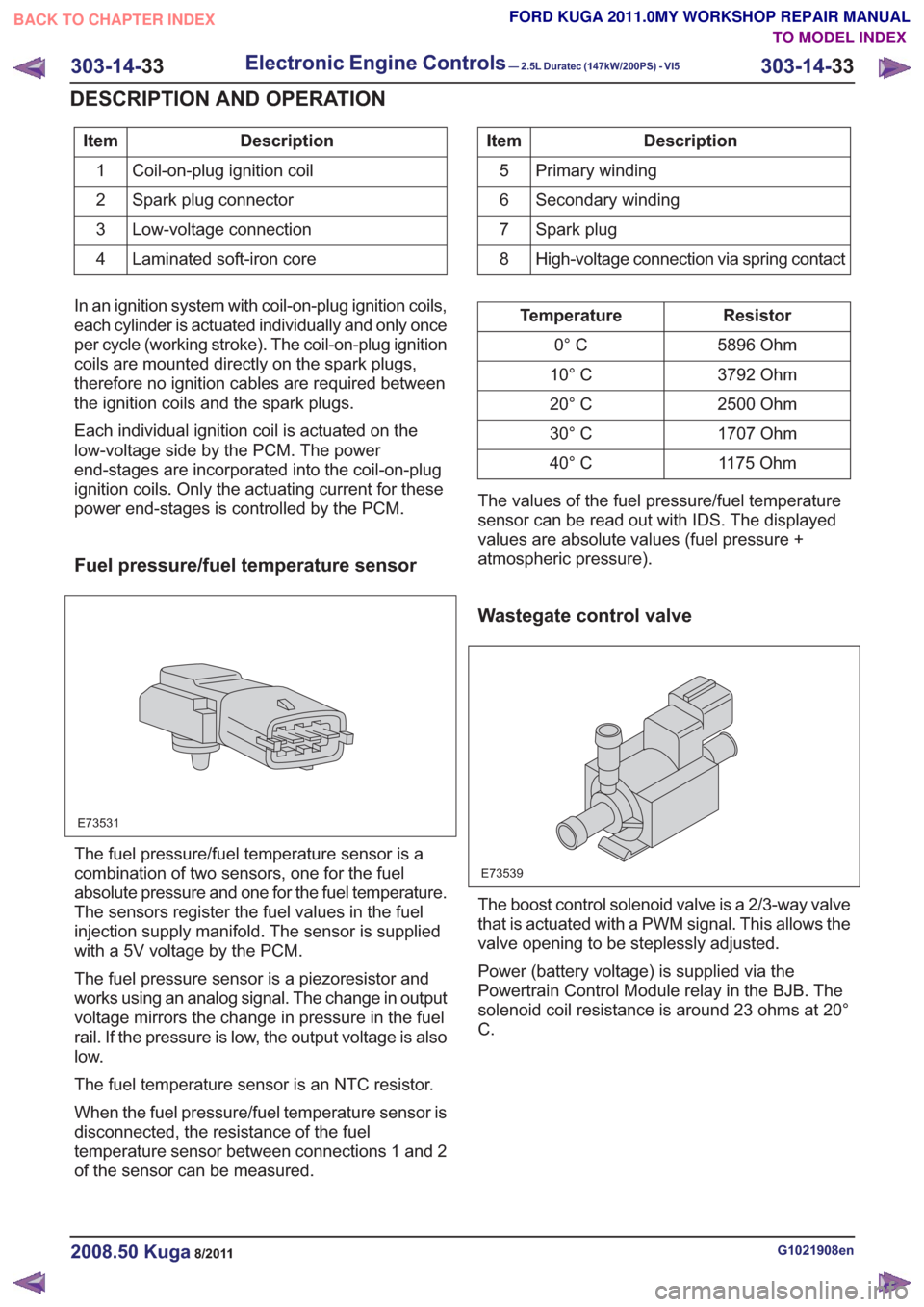
Description
Item
Coil-on-plug ignition coil
1
Spark plug connector
2
Low-voltage connection
3
Laminated soft-iron core
4Description
Item
Primary winding
5
Secondary winding
6
Spark plug
7
High-voltage connection via spring contact
8
In an ignition system with coil-on-plug ignition coils,
each cylinder is actuated individually and only once
per cycle (working stroke). The coil-on-plug ignition
coils are mounted directly on the spark plugs,
therefore no ignition cables are required between
the ignition coils and the spark plugs.
Each individual ignition coil is actuated on the
low-voltage side by the PCM. The power
end-stages are incorporated into the coil-on-plug
ignition coils. Only the actuating current for these
power end-stages is controlled by the PCM.
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor
E73531
The fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor is a
combination of two sensors, one for the fuel
absolute pressure and one for the fuel temperature.
The sensors register the fuel values in the fuel
injection supply manifold. The sensor is supplied
with a 5V voltage by the PCM.
The fuel pressure sensor is a piezoresistor and
works using an analog signal. The change in output
voltage mirrors the change in pressure in the fuel
rail. If the pressure is low, the output voltage is also
low.
The fuel temperature sensor is an NTC resistor.
When the fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor is
disconnected, the resistance of the fuel
temperature sensor between connections 1 and 2
of the sensor can be measured.
Resistor
Temperature
5896 Ohm
0° C
3792 Ohm
10° C
2500 Ohm
20° C
1707 Ohm
30° C
1175 Ohm
40° C
The values of the fuel pressure/fuel temperature
sensor can be read out with IDS. The displayed
values are absolute values (fuel pressure +
atmospheric pressure).
Wastegate control valve
E73539
The boost control solenoid valve is a 2/3-way valve
that is actuated with a PWM signal. This allows the
valve opening to be steplessly adjusted.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is around 23 ohms at 20°
C.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 33
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
33
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1978 of 2057
Fuel System Pressure Release
Release
1.Refer to: Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel
Systems Health and Safety Precautions
(100-00 General Information, Description and
Operation).
2. Remove the fuel pump and sender unit fuse.
3. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the
engine stalls.
4. Crank the engine for approximately five seconds
to make sure that the fuel rail pressure is
released.
5. Install the fuel pump and sender unit fuse.
G551380en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-00- 10
Fuel System - General Information
310-00- 10
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL