2010 GMC TERRAIN air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 315 of 410
Vehicle Care 9-41
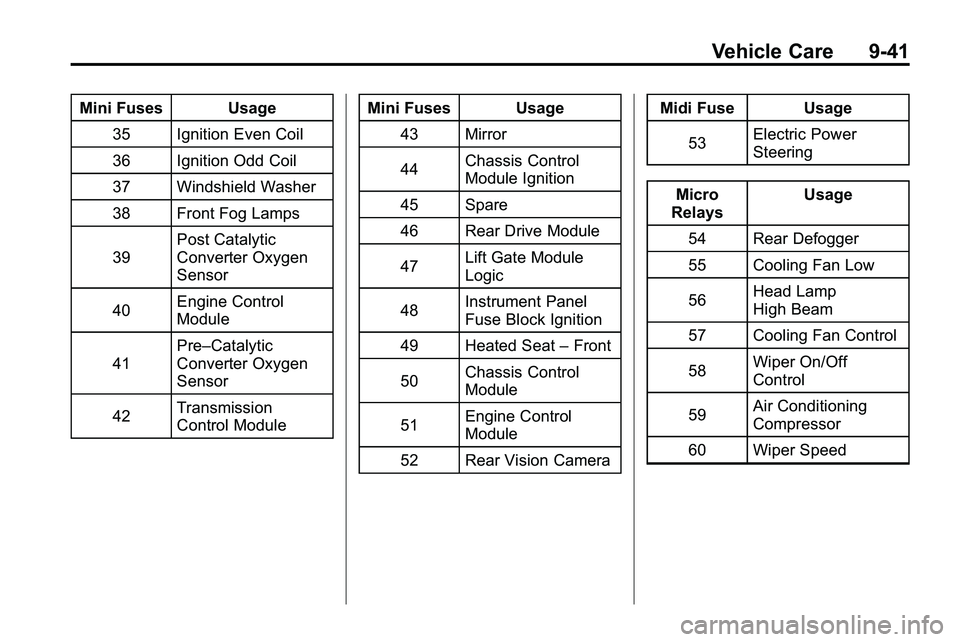
Mini Fuses Usage35 Ignition Even Coil
36 Ignition Odd Coil
37 Windshield Washer
38 Front Fog Lamps
39 Post Catalytic
Converter Oxygen
Sensor
40 Engine Control
Module
41 Pre–Catalytic
Converter Oxygen
Sensor
42 Transmission
Control Module Mini Fuses Usage
43 Mirror
44 Chassis Control
Module Ignition
45 Spare
46 Rear Drive Module
47 Lift Gate Module
Logic
48 Instrument Panel
Fuse Block Ignition
49 Heated Seat –Front
50 Chassis Control
Module
51 Engine Control
Module
52 Rear Vision Camera Midi Fuse Usage
53 Electric Power
Steering
Micro
Relays Usage
54 Rear Defogger
55 Cooling Fan Low
56 Head Lamp
High Beam
57 Cooling Fan Control
58 Wiper On/Off
Control
59 Air Conditioning
Compressor
60 Wiper Speed
Page 317 of 410

Vehicle Care 9-43
Instrument Panel Fuse Block
Mini Fuses Usage 1 Steering Wheel DM
2 Spare
3 Spare
4 Body Control
Module 1 Mini Fuses Usage
5 Infotainment
6 Body Control
Module 7
7 Noise Control
Module Mini Fuses Usage
8 Body Control
Module 4
9 Radio
10 SEO Battery
11 Ultrasonic Rear
Parking Aid Module
12 Heater, Ventilation
and Air Conditioning
Battery
13 Auxiliary Power
Front
14 Heater, Ventilation
and Air Conditioning
Ignition
15 Display
16 Body Control
Module 5
17 Auxiliary
Power Rear
18 Instrument Panel
Cluster Ignition
Page 323 of 410

Vehicle Care 9-49
Tire Terminology and
Definitions
Air Pressure:The amount of
air inside the tire pressing
outward on each square inch
of the tire. Air pressure is
expressed in psi (pounds per
square inch) or kPa (kilopascal).
Accessory Weight
:This
means the combined weight
of optional accessories.
Some examples of optional
accessories are, automatic
transmission, power steering,
power brakes, power windows,
power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio
:The relationship
of a tire's height to its width. Belt
:A rubber coated layer of
cords that is located between
the plies and the tread. Cords
may be made from steel or other
reinforcing materials.
Bead
:The tire bead contains
steel wires wrapped by steel
cords that hold the tire onto
the rim.
Bias Ply Tire
:A pneumatic tire
in which the plies are laid at
alternate angles less than
90 degrees to the centerline of
the tread.
Cold Tire Pressure
:The
amount of air pressure in a tire,
measured in psi (pounds per
square inch) or kPa (kilopascal)
before a tire has built up heat
from driving. See Tire Pressure
on page 9‑52. Curb Weight
:The weight of a
motor vehicle with standard and
optional equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil,
and coolant, but without
passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings
:A code molded
into the sidewall of a tire
signifying that the tire is in
compliance with the U.S.
Department of Transportation
(DOT) motor vehicle safety
standards. The DOT code
includes the Tire Identification
Number (TIN), an alphanumeric
designator which can also
identify the tire manufacturer,
production plant, brand, and
date of production.
GVWR
:Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating. See Vehicle Load Limits
on page 8‑22.
Page 329 of 410

Vehicle Care 9-55
Tire Pressure Monitor
Operation
This vehicle may have a Tire
Pressure Monitor System (TPMS).
The TPMS is designed to warn the
driver when a low tire pressure
condition exists. TPMS sensors are
mounted onto each tire and wheel
assembly, excluding the spare tire
and wheel assembly. The TPMS
sensors monitor the air pressure in
the vehicle's tires and transmit the
tire pressure readings to a receiver
located in the vehicle.
When a low tire pressure condition
is detected, the TPMS illuminates
the low tire pressure warning light
located on the instrument panel
cluster. If the warning light comes
on, stop as soon as possible andinflate the tires to the recommended
pressure shown on the tire loading
information label. See
Vehicle Load
Limits on page 8‑22.
At the same time a message to
check the pressure in a specific tire
appears on the Driver Information
Center (DIC) display. The low tire
pressure warning light and the DIC
warning message come on at each
ignition cycle until the tires are
inflated to the correct inflation
pressure. Using the DIC, tire
pressure levels can be viewed by
the driver. For additional information
and details about the DIC operation
and displays see Driver Information
Center (DIC) on page 4‑25.
The low tire pressure warning light
may come on in cool weather when
the vehicle is first started, and then
turn off as you start to drive. This
could be an early indicator that the
air pressure in the tire(s) are getting
low and need to be inflated to the
proper pressure. A Tire and Loading Information
label, attached to your vehicle,
shows the size of your vehicle's
original equipment tires and the
correct inflation pressure for your
vehicle's tires when they are cold.
See
Vehicle Load Limits
on
page 8‑22, for an example of the
Tire and Loading Information label
and its location on your vehicle.
Also see Tire Pressure
on
page 9‑52.
Your vehicle's TPMS can warn you
about a low tire pressure condition
but it does not replace normal tire
maintenance. See Tire Inspection
on page 9‑58,Tire Rotationon
page 9‑58and Tires on page 9‑45.
Notice: Liquid tire sealants could
damage the Tire Pressure Monitor
System (TPMS) sensors. Sensor
damage caused by using a tire
sealant is not covered by your
warranty. Do not use liquid tire
sealants.
Page 334 of 410

9-60 Vehicle Care
The vehicle needs new tires if any
of the following statements are true:
.You can see the indicators at
three or more places around
the tire.
.You can see cord or fabric
showing through the tire's
rubber.
.The tread or sidewall is cracked,
cut, or snagged deep enough to
show cord or fabric.
.The tire has a bump, bulge,
or split.
.The tire has a puncture, cut,
or other damage that cannot be
repaired well because of the size
or location of the damage.
The rubber in tires degrades over
time. This is also true for the spare
tire, if the vehicle has one, even
if it is not being used. Multiple
conditions affect how fast this aging
takes place, including temperatures,
loading conditions, and inflation
pressure maintenance. With proper
care and maintenance tires typically wear out before they degrade due to
age. If you are unsure about the
need to replace the tires as they get
older, consult the tire manufacturer
for more information.
Buying New Tires
GM has developed and matched
specific tires for your vehicle.
The original equipment tires
installed on your vehicle,
when it was new, were designed
to meet General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification (TPC Spec)
system rating. If you need
replacement tires, GM strongly
recommends that you get tires
with the same TPC Spec rating.
This way, your vehicle will
continue to have tires that are
designed to give the same
performance and vehicle safety,
during normal use, as the
original tires.
GM's exclusive TPC Spec
system considers over a dozen
critical specifications that impact
the overall performance of your
vehicle, including brake system
performance, ride and handling,
traction control, and tire
pressure monitoring
performance. GM's TPC Spec
number is molded onto the tire's
sidewall near the tire size. If the
tires have an all‐season tread
design, the TPC Spec number
will be followed by an MS for
mud and snow. See
Tire
Sidewall Labeling
on page 9‑46
for additional information.
GM recommends replacing tires
in sets of four. This is because
uniform tread depth on all tires
will help keep your vehicle
performing most like it did when
the tires were new. Replacing
less than a full set of tires can
affect the braking and handling
performance of your vehicle.
Page 339 of 410

Vehicle Care 9-65
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent,
cracked, or badly rusted or
corroded. If wheel nuts keep coming
loose, the wheel, wheel bolts, and
wheel nuts should be replaced.
If the wheel leaks air, replace it
(except some aluminum wheels,
which can sometimes be repaired).
See your dealer/retailer if any of
these conditions exist.
Your dealer/retailer will know the
kind of wheel you need.
Each new wheel should have the
same load-carrying capacity,
diameter, width, offset, and be
mounted the same way as the
one it replaces.If you need to replace any of the
wheels, wheel bolts, wheel nuts,
or Tire Pressure Monitor System
(TPMS) sensors, replace them only
with new GM original equipment
parts. This way, you will be sure to
have the right wheel, wheel bolts,
wheel nuts, and TPMS sensors for
the vehicle.
{WARNING
Using the wrong replacement
wheels, wheel bolts, or wheel
nuts on your vehicle can be
dangerous. It could affect the
braking and handling of your
vehicle, make your tires lose air
and make you lose control. You
could have a collision in which
you or others could be injured.
Always use the correct wheel,
wheel bolts, and wheel nuts for
replacement.Notice:
The wrong wheel can
also cause problems with bearing
life, brake cooling, speedometer
or odometer calibration,
headlamp aim, bumper height,
vehicle ground clearance, and
tire or tire chain clearance to the
body and chassis.
See If a Tire Goes Flat
on
page 9‑67for more information.
Page 361 of 410

Vehicle Care 9-87
Wheels and Trim—Aluminum
or Chrome
The vehicle may have either
aluminum or chrome-plated wheels.
Keep the wheels clean using a soft
clean cloth with mild soap and
water. Rinse with clean water. After
rinsing thoroughly, dry with a soft
clean towel. A wax may then be
applied.
Notice: Chrome wheels and other
chrome trim may be damaged if
the vehicle is not washed after
driving on roads that have been
sprayed with magnesium, calcium
or sodium chloride. These
chlorides are used on roads for
conditions such as ice and dust.
Always wash the vehicle's
chrome with soap and water after
exposure. Notice:
Using strong soaps,
chemicals, abrasive polishes,
cleaners, brushes, or cleaners
that contain acid on aluminum or
chrome-plated wheels, could
damage the surface of the
wheel(s). The repairs would not
be covered by the vehicle
warranty. Use only approved
cleaners on aluminum or
chrome-plated wheels.
The surface of these wheels is
similar to the painted surface of the
vehicle. Do not use strong soaps,
chemicals, abrasive polishes,
abrasive cleaners, cleaners with
acid, or abrasive cleaning brushes
on them because the surface could
be damaged. Do not use chrome
polish on aluminum wheels. Notice:
Using chrome polish on
aluminum wheels could damage
the wheels. The repairs would
not be covered by the vehicle
warranty. Use chrome polish on
chrome wheels only.
Use chrome polish only on
chrome-plated wheels, but avoid
any painted surface of the wheel,
and buff off immediately after
application.
Notice: Driving the vehicle
through an automatic car wash
that has silicone carbide tire
cleaning brushes, could damage
the aluminum or chrome-plated
wheels. The repairs would not be
covered by the vehicle warranty.
Never drive a vehicle that has
aluminum or chrome-plated
wheels through an automatic car
wash that uses silicone carbide
tire cleaning brushes.
Page 362 of 410

9-88 Vehicle Care
Windshield and Wiper Blades
Clean the outside of the windshield
with glass cleaner.
Clean the rubber blades using a lint
free cloth or paper towel soaked
with windshield washer fluid or a
mild detergent. Wash the windshield
thoroughly when cleaning the
blades. Bugs, road grime, sap, and
a buildup of vehicle wash/wax
treatments may cause wiper
streaking. Replace the wiper blades
if they are worn or damaged.
Wipers can be damaged by:
.Extreme dusty conditions
.Sand and salt
.Heat and sun
.Snow and ice, without proper
removal
Tires
Use a stiff brush with tire cleaner to
clean the tires.
Notice:Using petroleum-based
tire dressing products on the
vehicle may damage the paint
finish and/or tires. When applying
a tire dressing, always wipe off
any overspray from all painted
surfaces on the vehicle.
Sheet Metal Damage
If the vehicle is damaged and
requires sheet metal repair or
replacement, make sure the body
repair shop applies anti-corrosion
material to parts repaired or
replaced to restore corrosion
protection.
Original manufacturer replacement
parts will provide the corrosion
protection while maintaining the
vehicle warranty.
Finish Damage
Any stone chips, fractures or deep
scratches in the finish should be
repaired right away. Bare metal will
corrode quickly and may develop
into major repair expense.
Minor chips and scratches can be
repaired with touch-up materials
available from your dealer/retailer.
Larger areas of finish damage can
be corrected in your dealer's/
retailer's body and paint shop.
Underbody Maintenance
Chemicals used for ice and snow
removal and dust control can collect
on the underbody. If these are not
removed, corrosion and rust can
develop on the underbody parts
such as fuel lines, frame, floor pan,
and exhaust system even though
they have corrosion protection.