2010 CADILLAC ESCALADE height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 173 of 616

SBZA Detection Zones
The SBZA sensor covers a zone of approximatelyone lane over from both sides of the vehicle,3.5 m (11 ft). This zone starts at each side mirror andgoes back approximately 16 ft. (5.0 m). The height ofthe zone is approximately between 0.5 m (1.5 ft) and2.0 m (6 ft) off the ground.
Use caution while changing lanes when towing a trailer,as the SBZA detection zones do not change when atrailer is towed.
How the System Works
Left Side Mirror DisplayRight Side Mirror Display
When the vehicle is started, both outside mirrordisplays will briefly come on to indicate that the systemis operating. When the vehicle is moving forward, theleft or right side mirror SBZA display will light up if avehicle is detected in that blind zone.
If the turn signal is activated and a vehicle is alsodetected on the same side, the SBZA display will flashto give you extra warning not to change lanes.
SBZA displays do not come on while the vehicle isapproaching or passing other vehicles. At speedsgreater then 32 km/h (20 mph), SBZA displays maycome on when a vehicle you have passed remains in ordrops back into the detection zone.
SBZA can be disabled through the Driver InformationCenter (DIC). SeeDriver Information Center (DIC)onpage 4!41for more information. If the SBZA is disabledby the driver, the SBZA mirror displays will not light upduring normal driving.
When the System Does Not Seem To Work
Properly
Occasional missed alerts can occur under normalcircumstances and will increase in wet conditions.The system does not need to be serviced due to anoccasional missed alert. The number of missed alertswill increase with increased rainfall or road spray.
If the SBZA displays do not light up when the system ison and vehicles are in the blind zone, the system mayneed service. Take the vehicle to your dealer/retailer.
3-49
Page 427 of 616

If you put things inside your vehicle—like
suitcases, tools, packages, or anything
else—they will go as fast as the vehicle goes.
If you have to stop or turn quickly, or if there is a
crash, they will keep going.
{WARNING:
Things you put inside your vehicle can strike
and injure people in a sudden stop or turn,
or in a crash.
.Put things in the cargo area of your
vehicle. Try to spread the weight evenly.
.Never stack heavier things, like
suitcases, inside the vehicle so that some
of them are above the tops of the seats.
.Do not leave an unsecured child restraint
in your vehicle.
.When you carry something inside the
vehicle, secure it whenever you can.
.Do not leave a seat folded down unless
you need to.
There is also important loading information for
off-road driving in this manual. See“Loading Your
Vehicle for Off-Road Driving”underOff-Road
Drivingon page 6!13.
Add-On Equipment
When you carry removable items, you may need
to put a limit on how many people you can carry
inside your vehicle. Be sure to weigh your vehicle
before you buy and install the new equipment.
Notice :Overloading the vehicle may cause
damage. Repairs would not be covered by the
vehicle warranty. Do not overload the vehicle.
Remember not to exceed the Gross Axle Weight
Rating (GAWR) of the front or rear axle.
Automatic Level Control
The automatic level control rear suspension
comes as a part of the Road Sensing Suspension.
SeeRoad Sensing Suspensionon page 6!9.
This type of level control is fully automatic and will
provide a better leveled riding position as well as
better handling under a variety of passenger and
loading conditions. An air compressor connected
to the rear shocks will raise or lower the rear of
the vehicle to maintain proper vehicle height.
6-37
Page 428 of 616

The system is activated when the ignition key
is turned to RUN and will automatically adjust
vehicle height thereafter. The system may exhaust
(lower vehicle height) for up to 10 minutes after
the ignition key has been turned to LOCK. You
may hear the air compressor operating when the
height is being adjusted.
If a weight-distributing hitch is being used, it is
recommended to allow the shocks to inflate,
thereby leveling the vehicle prior to adjusting the
height. See“Weight distributing Hitches and
Weight Carrying Hitches”underTowing a Trailer
on page 6!42.
Towing
Towing Your Vehicle
To avoid damage, the disabled vehicle should betowed with all four wheels off the ground. Consult yourdealer/retailer or a professional towing service if thedisabled vehicle must be towed. SeeRoadside Serviceo n p a g e 9!8.
To tow the vehicle behind another vehicle forrecreational purposes (such as behind a motorhome),see“Recreational Vehicle Towing”following.
Recreational Vehicle Towing
If the vehicle has a two–mode hybrid engine, see theTwo–mode Hybrid manual for more information.
Recreational vehicle towing means towing the vehiclebehind another vehicle–such as behind a motorhome.The two most common types of recreational vehicletowing are known as“dinghy towing”(towing the vehiclewith all four wheels on the ground) and“dolly towing”(towing the vehicle with two wheels on the ground andtwo wheels up on a device known as a“dolly”).
Here are some important things to consider beforerecreational vehicle towing:
.What is the towing capacity of the towing vehicle?Be sure to read the tow vehicle manufacturer'srecommendations.
.What is the distance that will be travelled? Somevehicles have restrictions on how far and how longthey can tow.
.Is the proper towing equipment going to be used?See your dealer/retailer or trailering professionalfor additional advice and equipmentrecommendations.
.Is the vehicle ready to be towed? Just as preparingthe vehicle for a long trip, make sure the vehicle isprepared to be towed. SeeBefore Leaving on aLong Trip on page 6!26.
6-38
Page 431 of 616
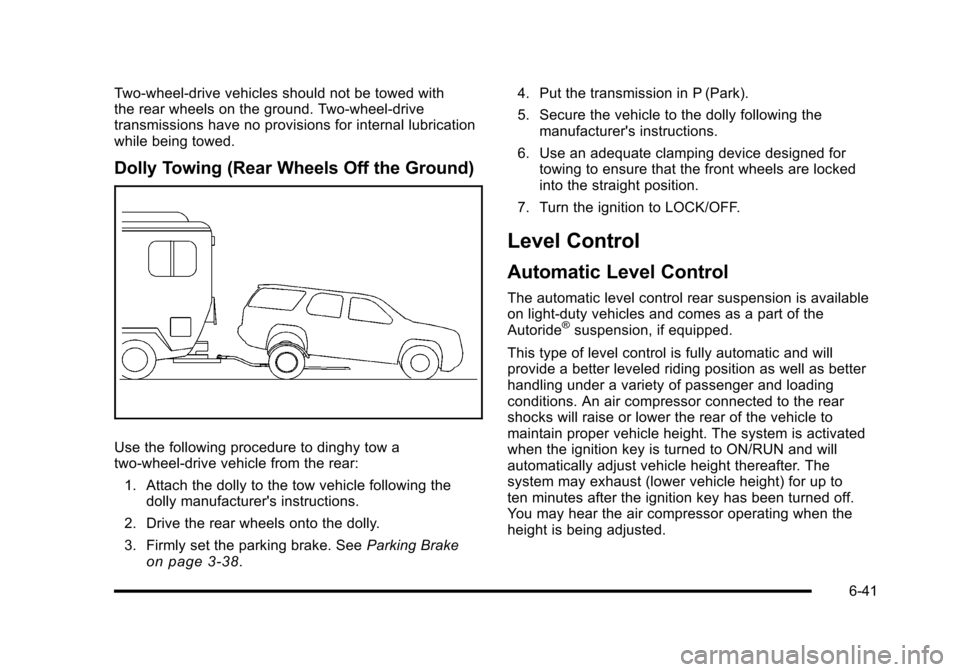
Two-wheel-drive vehicles should not be towed withthe rear wheels on the ground. Two-wheel-drivetransmissions have no provisions for internal lubricationwhile being towed.
Dolly Towing (Rear Wheels Off the Ground)
Use the following procedure to dinghy tow atwo-wheel-drive vehicle from the rear:
1. Attach the dolly to the tow vehicle following thedolly manufacturer's instructions.
2. Drive the rear wheels onto the dolly.
3. Firmly set the parking brake. SeeParking Brakeon page 3!38.
4. Put the transmission in P (Park).
5. Secure the vehicle to the dolly following themanufacturer's instructions.
6. Use an adequate clamping device designed fortowing to ensure that the front wheels are lockedinto the straight position.
7. Turn the ignition to LOCK/OFF.
Level Control
Automatic Level Control
The automatic level control rear suspension is availableon light!duty vehicles and comes as a part of theAutoride®suspension, if equipped.
This type of level control is fully automatic and willprovide a better leveled riding position as well as betterhandling under a variety of passenger and loadingconditions. An air compressor connected to the rearshocks will raise or lower the rear of the vehicle tomaintain proper vehicle height. The system is activatedwhen the ignition key is turned to ON/RUN and willautomatically adjust vehicle height thereafter. Thesystem may exhaust (lower vehicle height) for up toten minutes after the ignition key has been turned off.You may hear the air compressor operating when theheight is being adjusted.
6-41
Page 488 of 616

Brake Wear
This vehicle has disc brakes. Disc brake pads havebuilt-in wear indicators that make a high-pitchedwarning sound when the brake pads are worn and newpads are needed. The sound can come and go or beheard all the time the vehicle is moving, except whenapplying the brake pedal firmly.
{WARNING:
The brake wear warning sound means that soon
the brakes will not work well. That could lead to
an accident. When the brake wear warning sound
is heard, have the vehicle serviced.
Notice:Continuing to drive with worn-out brakepads could result in costly brake repair.
Some driving conditions or climates can cause a brakesqueal when the brakes are first applied or lightlyapplied. This does not mean something is wrong withthe brakes.
Properly torqued wheel nuts are necessary to helpprevent brake pulsation. When tires are rotated, inspectbrake pads for wear and evenly tighten wheel nuts inthe proper sequence to torque specifications inCapacities and Specifications on page 7!115.
Brake linings should always be replaced as completeaxle sets.
Brake Pedal Travel
See your dealer/retailer if the brake pedal does notreturn to normal height, or if there is a rapid increase inpedal travel. This could be a sign that brake servicemight be required.
Brake Adjustment
Every brake stop, the disc brakes adjust for wear.
7-42
Page 499 of 616

4. At a wall, measure from the ground upward (A) tothe recorded distance from Step 3 and mark it.
5. Draw or tape a horizontal line (B) on the wall thewidth of the vehicle at the height of the mark inStep 4.
Notice:Do not cover a headlamp to improve beamcut-off when aiming. Covering a headlamp maycause excessive heat build-up which may causedamage to the headlamp.
6. Turn on the low-beam headlamps and place apiece of cardboard or equivalent in front of theheadlamp not being adjusted. This allows only thebeam of light from the headlamp being adjusted tobe seen on the flat surface.
7. Locate the vertical headlamp aiming screws, whichare under the hood near each headlamp assembly.
The adjustment screw can be turned with aE8 Torx®socket.
8. Turn the vertical aiming screw until the headlampbeam is aimed to the horizontal tape line. Turn itclockwise or counterclockwise to raise or lower theangle of the beam.
7-53
Page 506 of 616

Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire is molded into the
sidewall. The following illustration is an example
of a typical P!Metric tire sidewall.
Passenger (P!Metric) Tire
(A) Tire Size:The tire size code is a combination
of letters and numbers used to define a particular
tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type,
and service description. See the“Tire Size”
illustration later in this section for more detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria
Specification):Original equipment tires designed
to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a
TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all
federal safety guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of Transportation):The
Department of Transportation (DOT) code
indicates that the tire is in compliance with the
U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number (TIN):The letters
and numbers following DOT code are the Tire
Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date
the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded
onto both sides of the tire, although only one side
may have the date of manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material:The type of cord and
number of plies in the sidewall and under the
tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG):Tire
manufacturers are required to grade tires based
on three performance factors: treadwear, traction,
and temperature resistance. For more information,
seeUniform Tire Quality Gradingon page 7!76.
7-60
Page 507 of 616

(G) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit:
Maximum load that can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed to support that load.
For information on recommended tire pressure
seeInflation - Tire Pressureon page 7!65and
Loading the Vehicleon page 6!32.
Tire Size
The following examples show the different parts of
a tire size.
Passenger (P!Metric) Tire
(A) Passenger (P!Metric) Tire:The United
States version of a metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in the tire size means
a passenger vehicle tire engineered to standards
set by the U.S. Tire and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width:The three!digit number indicates
the tire section width in millimeters from sidewall
to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio:A two!digit number that
indicates the tire height!to!width measurements.
For example, if the tire size aspect ratio is 75, as
shown in item C of the light truck (LT!Metric) tire
illustration, it would mean that the tire's sidewall is
75% as high as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code:A letter code is used to
indicate the type of ply construction in the tire.
The letter R means radial ply construction; the
letter D means diagonal or bias ply construction;
and the letter B means belted!bias ply
construction.
(E) Rim Diameter:Diameter of the wheel in
inches.
(F) Service Description:These characters
represent the load index and speed rating of the
tire. The load index represents the load carry
capacity a tire is certified to carry. The speed
rating is the maximum speed a tire is certified to
carry a load.
7-61