2009 YAMAHA YZ450F run flat
[x] Cancel search: run flatPage 67 of 190
3-21
CHASSIS
A tight spoke will emit a clear, ringing
tone; a loose spoke will sound flat.
2. Tighten:
• Spokes
(with a spoke nipple wrench "1")
Be sure to tighten the spokes before
and after break-in.
CHECKING THE WHEELS
1. Inspect:
• Wheel runout
Elevate the wheel and turn it.
Abnormal runout→ Replace.
2. Inspect:
• Bearing free play
Exist play→Replace.
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING THE
STEERING HEAD
1. Place a stand under the engine to
raise the front wheel off the
ground. WARNING! Securely
support the vehicle so that
there is no danger of it falling
over.
2. Check:
• Steering stem
Grasp the bottom of the forks and
gently rock the fork assembly
back and forth.
Free play→Adjust steering head.3. Check:
• Steering smooth action
Turn the handlebar lock to lock.
Unsmooth action→Adjust steer-
ing ring nut.
4. Adjust:
• Steering ring nut
Steering ring nut adjustment
steps:
a. Remove the number plate.
b. Remove the handlebar and upper
bracket.
c. Loosen the steering ring nut "1"
using the steering nut wrench "2".
d. Tighten the steering ring nut "3"
using steering nut wrench "4".
• Apply the lithium soap base grease
on the thread of the steering stem.
• Set the torque wrench to the steer-
ing nut wrench so that they form a
right angle.
e. Loosen the steering ring nut one
turn.
f. Retighten the steering ring nut us-
ing the steering nut wrench.
Avoid over-tightening.
g. Check the steering stem by turn-
ing it lock to lock. If there is any
binding, remove the steering stem
assembly and inspect the steer-
ing bearings.
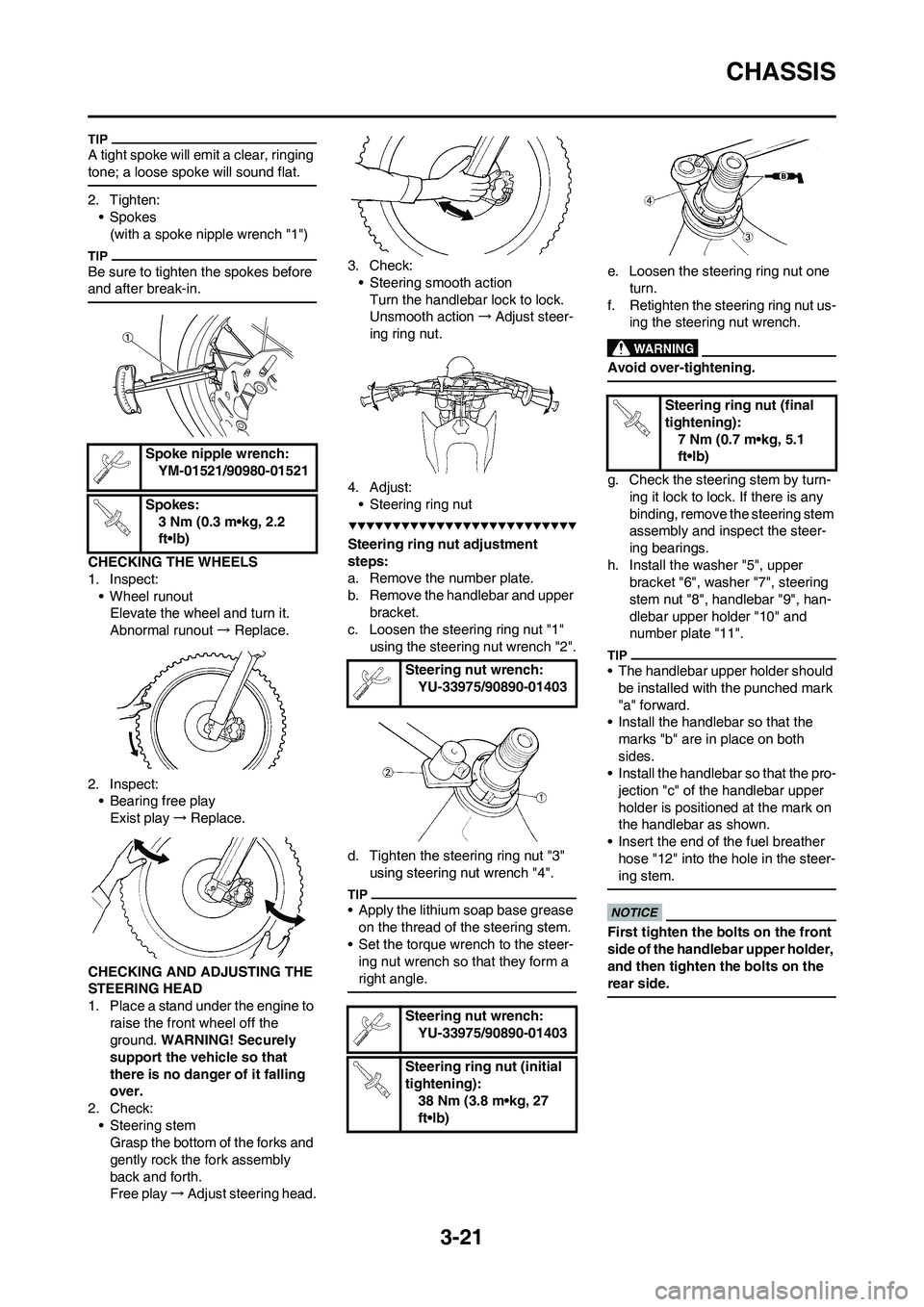
h. Install the washer "5", upper
bracket "6", washer "7", steering
stem nut "8", handlebar "9", han-
dlebar upper holder "10" and
number plate "11".
• The handlebar upper holder should
be installed with the punched mark
"a" forward.
• Install the handlebar so that the
marks "b" are in place on both
sides.
• Install the handlebar so that the pro-
jection "c" of the handlebar upper
holder is positioned at the mark on
the handlebar as shown.
• Insert the end of the fuel breather
hose "12" into the hole in the steer-
ing stem.
First tighten the bolts on the front
side of the handlebar upper holder,
and then tighten the bolts on the
rear side.
Spoke nipple wrench:
YM-01521/90980-01521
Spokes:
3 Nm (0.3 m•kg, 2.2
ft•lb)
Steering nut wrench:
YU-33975/90890-01403
Steering nut wrench:
YU-33975/90890-01403
Steering ring nut (initial
tightening):
38 Nm (3.8 m•kg, 27
ft•lb)
Steering ring nut (final
tightening):
7 Nm (0.7 m•kg, 5.1
ft•lb)
Page 118 of 190

4-48
CDI MAGNETO
REMOVING THE ROTOR
1. Remove:
• Nut (rotor) "1"
• Washer
2. Remove:
• Rotor "1"
Use the rotor puller 2.
CHECKING THE CDI MAGNETO
1. Inspect:
• Rotor inner surface "a"
• Stator outer surface "b"
Damage→Inspect the crankshaft
runout and crankshaft bearing.
If necessary, replace CDI magne-
to and/or stator.
CHECKING THE WOODRUFF KEY
1. Inspect:
• Woodruff key "1"
Damage→Replace.
INSTALLING THE CDI MAGNETO
1. Install:
• Stator "1"
• Screw (stator) "2"
• Apply the sealant on the grommet
of the CDI magneto lead.
• Tighten the screws using the T30
bit.
2. Install:
• Woodruff key "1"
•Rotor "2"
• Degrease the contact surfaces of
the tapered portions of the crank-
shaft and rotor.
• When installing the woodruff key,
make sure that its flat surface "a" is
in parallel with the crankshaft center
line "b".
• When installing the rotor, align the
keyway "c" of the rotor with the
woodruff key.
3. Install:
•Washer
• Nut (rotor) "1"
4. Connect:
• CDI magneto lead
Refer to "CABLE ROUTING DIA-
GRAM" section in the CHAPTER
2.5. Install:
• Dowel pin
• O-ring
• Gasket (left crankcase cover)
• Left crankcase cover "1"
• Hose guide (cylinder head breath-
er hose) "2"
• Bolt (left crankcase cover)
• Apply the lithium soap base grease
on the O-ring.
• Tighten the bolts in stage, using a
crisscross pattern.
Rotor puller:
YM-04151/90890-04151
Screw (stator):
10 Nm (1.0 m•kg,
7.2ft•lb)
YAMAHA Bond No. 1215
(ThreeBond® No. 1215):
90890-85505
Nut (rotor):
56 Nm (5.6 m•kg, 40
ft•lb)
Bolt (left crankcase cov-
er):
10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Page 126 of 190

4-56
CRANKCASE AND CRANKSHAFT
DISASSEMBLING THE
CRANKCASE
1. Separate:
• Right crankcase
• Left crankcase
Separation steps:
a. Remove the crankcase bolts,
hose guide and clutch cable hold-
er.
Loosen each bolt 1/4 of a turn at a
time and after all the bolts are loos-
ened, remove them.
b. Remove the right crankcase "1".
• Place the crankcase with its left
side downward and split it by insert-
ing a screwdriver tip into the split-
ting slit "a" in the crankcase.
• Lift the right crankcase horizontally
while lightly patting the case split-
ting slit and engine mounting boss
using a soft hammer, and leave the
crankshaft and transmission with
the left crankcase.
Use soft hammer to tap on the
case half. Tap only on reinforced
portions of case. Do not tap on
gasket mating surface. Work slow-
ly and carefully. Make sure the
case halves separate evenly. If the
cases do not separate, check for a
remaining case bolt or fitting. Do
not force.
c. Remove the dowel pins and O-
ring.
REMOVING THE BALANCER
SHAFT
1. Remove:
• Balancer shaft "1"
Remove the balancer shaft with its
flat side "a" facing the crankshaft.
REMOVING THE CRANKSHAFT
1. Remove:
• Crankshaft "1"
Use the crankcase separating
tool "2".
Install the crankcase separating tool
as shown.
Do not use a hammer to drive out
the crankshaft.
REMOVING THE CRANKCASE
BEARING
1. Remove:
• Bearing "1"
• Remove the bearing from the
crankcase by pressing its inner
race.
• Do not use the removed bearing.
CHECKING THE TIMING CHAIN
AND TIMING CHAIN GUIDE
1. Inspect:
• Timing chain
Cracks/stiff→Replace the timing
chain and camshaft sprocket as a
set.
2. Inspect:
• Timing chain guide
Wear/damage→Replace.
CHECKING THE CRANKCASE
1. Inspect:
• Contacting surface "a"
Scratches→Replace.
• Engine mounting boss "b", crank-
case
Cracks/damage→Replace.
2. Inspect:
• Bearing
Rotate inner race with a finger.
Rough spot/seizure→Replace.
3. Inspect:
•Oil seal
Damage→Replace.
CHECKING THE CRANKSHAFT
1. Measure:
• Runout limit "a"
• Small end free play limit "b"
• Connecting rod big end side
clearance "c"
Crankcase separating
tool:
YU-A9642/90890-04152
Page 179 of 190

7-1
ENGINE
TUNING
ENGINE
CARBURETOR SETTING
• The air/fuel mixture will vary de-
pending on atmospheric conditions.
Therefore, it is necessary to take
into consideration the air pressure,
ambient temperature, humidity,
etc., when adjusting the carburetor.
• Perform a test run to check for prop-
er engine performance (e.g., throt-
tle response) and spark plug(-s)
discoloration or fouling. Use these
readings to determine the best pos-
sible carburetor setting.
It is recommended to keep a record of
all carburetor settings and external
conditions (e.g., atmospheric condi-
tions, track/surface conditions, lap
times) to make future carburetor set-
ting easier.
• The carburetor is a part of the
fuel line. Therefore, be sure to in-
stall it in a wellventilated area,
away from flammable objects
and any sources of fire.
• Never look into the carburetor in-
take. Flames may shoot out from
the pipe if the engine backfires
while it is being started. Gasoline
may be discharged from the ac-
celerator pump nozzle when the
carburetor has been removed.
• The carburetor is extremely sen-
sitive to foreign matter (dirt,
sand, water, etc.). During instal-
lation, do not allow foreign mat-
ter to get into the carburetor.
• Always handle the carburetor
and its components carefully.
Even slight scratches, bends or
damage to carburetor parts may
prevent the carburetor from
functioning correctly. Carefully
perform all servicing with the ap-
propriate tools and without ap-
plying excessive force.
• When the engine is stopped or
when riding at no load, do not
open and close the throttle un-
necessarily. Otherwise, too
much fuel may be discharged,
starting may become difficult or
the engine may not run well.• After installing the carburetor,
check that the throttle operates
correctly and opens and closes
smoothly.
ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONS AND
CARBURETOR SETTINGS
The air density (i.e., concentration of
oxygen in the air) determines the rich-
ness or leanness of the air/fuel mix-
ture.
• Higher temperature expands the air
with its resultant reduced density.
• Higher humidity reduces the
amount of oxygen in the air by so
much of the water vapor in the
same air.
• Lower atmospheric pressure (at a
high altitude) reduces the density of
the air.
EFFECT OF SETTING PARTS IN
RELATION TO THROTTLE VALVE
OPENING
A. Closed
B. Fully open
1. Pilot screw/pilot jet
2. Throttle valve cutaway
3. Jet needle
4. Main jetCONSTRUCTION OF
CARBURETOR AND SETTING
PARTS
The FLATCR carburetor has a prima-
ry main jet. This type of main jet is
perfect for racing machines since it
supplies an even flow of fuel, even at
full load. Use the main jet and the jet
needle to set the carburetor.
The FLATCR carburetor is manufac-
tured with a pilot screw. The pilot
screw adjustment ranges from fully
closed throttle to 1/4 open throttle.
1. Jet needle
2. Pilot air jet
3. Needle jet
4. Main jet
5. Pilot jet
6. Pilot screw
ADJUSTING THE MAIN JET
The richness of the air-fuel mixture at
full throttle can be set by changing the
main jet "1".
If the air-fuel mixture is too rich or too
lean, the engine power will drop, re-
sulting in poor acceleration.
Effects of changing the main jet
(reference)
A. Idle
B. Fully open
1. #162
2. #158
3. #160 Air
tem
p.Hu-
midi-
tyAir
pres-
sure
(alti-
tude)Mix-
tureSet-
ting
High HighLow
(high)Rich-
erLean-
er
Low LowHigh
(low)Lean-
erRich-
er
Standard main jet #160
7
Page 184 of 190

7-6
CHASSIS
CHASSIS
SELECTION OF THE SECONDARY
REDUCTION RATIO (SPROCKET)
• It is generally said that the second-
ary gear ratio should be reduced for
a longer straight portion of a speed
course and should be increased for
a course with many corners. Actual-
ly, however, as the speed depends
on the ground condition of the day
of the race, be sure to run through
the circuit to set the machine suit-
able for the entire course.
• In actuality, it is very difficult to
achieve settings suitable for the en-
tire course and some settings may
be sacrificed. Thus, the settings
should be matched to the portion of
the course that has the greatest ef-
fect on the race result. In such a
case, run through the entire course
while making notes of lap times to
find the best balance; then, deter-
mine the secondary reduction ratio.
• If a course has a long straight por-
tion where a machine can run at
maximum speed, the machine is
generally set such that it can devel-
op its maximum revolutions toward
the end of the straight line, with care
taken to avoid the engine over-rev-
ving.
Riding technique varies from rider to
rider and the performance of a ma-
chine also vary from machine to ma-
chine. Therefore, do not imitate other
rider's settings from the beginning but
choose your own setting according to
the level of your riding technique.
DRIVE AND REAR WHEEL
SPROCKETS SETTING PARTS
TIRE PRESSURE
Tire pressure should be adjust to suit
the road surface condition of the cir-
cuit.
• Under a rainy, muddy, sandy, or
slippery condition, the tire pressure
should be lower for a larger area of
contact with the road surface.
• Under a stony or hard road condi-
tion, the tire pressure should be
higher to prevent a flat tire.
FRONT FORK SETTING
The front fork setting should be made
depending on the rider's feeling of an
actual run and the circuit conditions.The front fork setting includes the fol-
lowing three factors:
1. Setting of air spring characteris-
tics
• Change the fork oil amount.
2. Setting of spring preload
• Change the spring.
3. Setting of damping force
• Change the compression damp-
ing.
• Change the rebound damping.
The spring acts on the load and
the damping force acts on the
cushion travel speed.
CHANGE IN AMOUNT AND
CHARACTERISTICS OF FORK OIL
Damping characteristic near the final
stroke can be changed by changing
the fork oil amount.
Adjust the oil amount in 5 cm3 (0.2
Imp oz, 0.2 US oz) increments or
decrements. Too small oil amount
causes the front fork to produce a
noise at full rebound or the rider to
feel some pressure on his hands
or body. Alternatively, too large oil
amount will cause the air spring
characteristics to have a tendency
to be stiffer with the consequent
deteriorated performance and
characteristics. Therefore, adjust
the front fork within the specified
range.
Secondary reduction ratio =
Number of rear wheel sprocket
teeth/Number of drive sprocket
teeth
Standard secondary
reduction ratio49/13
(3.769)
Part name Size Part number
Drive
sprocket "1"
(STD) 13T 9383B-13233
Rear wheel
sprocket "2"
47T 1C3-25447-00
48T 1C3-25448-00
(STD) 49T 1C3-25449-00
50T 1C3-25450-00
51T 1C3-25451-00
52T 1C3-25452-00
Standard tire pressure:
100 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm
2,
15 psi)
Extent of adjustment:
60–80 kPa (0.6–0.8 kgf/
cm
2, 9.0–12 psi)
Extent of adjustment:
100–120 kPa (1.0–1.2
kgf/cm
2, 15–18 psi)
Standard oil amount:
350 cm3 (12.3 Imp oz,
11.8 US oz)
* 340 cm
3 (12.0 Imp oz,
11.5 US oz)
Extent of adjustment:
300–375 cm
3(10.6–13.2
Imp oz, 10.1–12.7 US
oz)
* Except for USA and CDN