2009 SKODA FABIA weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 88 of 259

Seats and Storage87
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
WARNING
Use the area ⇒page 86, fig. 115 of the storage compartment only for
storing objects which do not project so that the effectiveness of the side
airbag is not impaired.Removeable storage compartments in the luggage compartment*A removeable storage compartment*⇒fig. 116 is located on both sides in the side
trim panel of the luggage compartment.
The removeable storage compartments* are intended for storing small objects of
up to 2.5 kg in weight.
Flexible storage compartment*A flexible storage compartment is located on the right side of the luggage
compartment. The flexible storage compartment is foreseen for storing
small objects of up to 8 kg. in weight.
Removing
– Take hold of the flexible storage compartment at both upper corners.
– Press the upper corners to the inside and release the storage compart-
ment by pulling upwards.
– Take it out by pulling towards the middle of the vehicle.
Installing
– Insert both ends of the flexible storage compartment into the open-
ings of the right side trim panel of the luggage compartment and push
it downwards until it locks.
NoteIf the variable loading floor* is installed ⇒page 72 in the luggage compartment, no
flexible storage compartment can be installed.
AA
Fig. 116 Removeable
storage compartments
Fig. 117 Flexible storage
compartment
s3f4.1.book Page 87 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 106 of 259

Starting-off and Driving105
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
WARNING
•
The cruise control system must not, for safety reasons, be used in dense
traffic or on unfavourable road surfaces (such as icy roads, slippery roads or
loose chippings) - risk of accident!
•
In order to prevent unintentional use of the cruise control system, always
switch off the system after use.Note
•
Models fitted with a manual gearbox: Always depress the clutch pedal if you
switch on the cruise control system when the gearbox is in Neutral. Otherwise the
engine can rev up unintentionally.
•
The cruise control system is not able to maintain a constant speed when driving
on steep downhill sections. The weight of the vehicle increases the speed at which
it travels. One should shift down in good time to a lower gear or slow the vehicle
down by applying the foot brake.
•
It is not possible on vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox to switch on the
cruise control system if the selector lever is in the position P, N or R.
Storing a speed
The cruise control system is operated by means of the switch and
rocker button in the left lever of the multi-functional switch.
– Press the switch ⇒fig. 128 into the position ON.
– After the desired speed has been reached, press the rocker button
into the SET- position - the current speed is stored.After you have released the rocker button out of the position SET-, the speed
you have just stored is maintained at a constant speed without having to depress
the accelerator.
You can increase the speed by depressing the accelerator. Releasing the acceler-
ator will cause the speed to drop again to the set speed.
This does not apply, however, if you drive at a speed which is more than 10 km/h
higher than the set speed for a period of longer than 5 minutes. The stored speed
will be cancelled in the memory. You then have to re-store the desired speed.
One can reduce the speed in the usual manner. The system is switched off tempo-
rarily by actuating the brake or clutch pedal ⇒page 106.
WARNING
First ensure that it is not too high for the traffic conditions which exist at that
moment before resuming the stored speed.Changing a stored speed
You can also change the speed of the vehicle without depressing the
accelerator.Fa s t er
–You can increase the stored speed without depressing the acceler-
ator, by pressing the rocker button ⇒fig. 128 into the RES+ posi-
tion.
Fig. 128 Operating lever:
Rocker button and switch of
cruise control system
AA
AB
AA
AB
ABAB
s3f4.1.book Page 105 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 134 of 259
Seat belts133
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
The physical principle of a frontal collisionThe physical principle of a frontal accident can be explained quite simply:
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants. The magnitude of this kinetic energy
depends essentially on the speed at which the vehicle is travelling and on the
weight of the vehicle and the occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an acci-
dent.
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy
four times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor accident
with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces
acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/hour to 50 km/hour,
the forces which are produced on your body in the event of an accident can easily
exceed 10.000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of one tonne (1 000 kg).
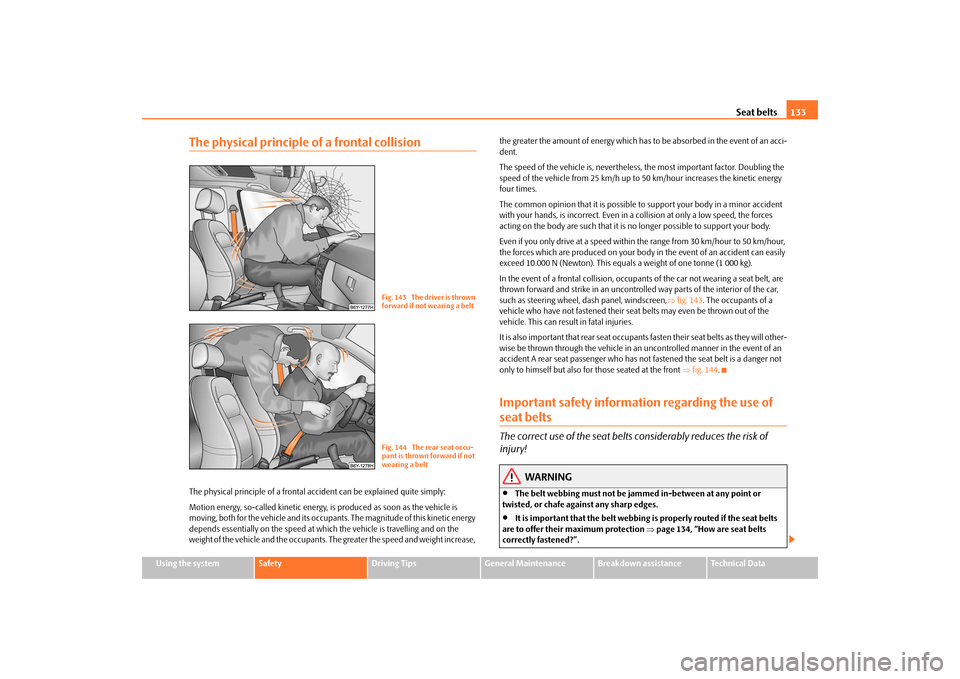
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt, are
thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the interior of the car,
such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen,⇒fig. 143. The occupants of a
vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may even be thrown out of the
vehicle. This can result in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will other-
wise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the event of an
accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a danger not
only to himself but also for those seated at the front ⇒fig. 144.
Important safety information regarding the use of seat beltsThe correct use of the seat belts considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or
twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
•
It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts
are to offer their maximum protection ⇒page 134, “How are seat belts
correctly fastened?”.
Fig. 143 The driver is thrown
forward if not wearing a beltFig. 144 The rear seat occu-
pant is thrown forward if not
wearing a belt
s3f4.1.book Page 133 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 148 of 259

Transporting children safely147
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Transporting children safelyWhat you should know about transporting children!An introduction to the subject
Accident statistics have revealed that children are generally more
safely transported on the rear seats than on the front passenger seat.Children younger than 12 years of age should normally travel on the rear seat of the
vehicle (take note of any national legal provisions which differ from this). They
should be secured there by means of a child restraint system or by using the existing
seat belts depending on their age, body size and weight. The child seat should be
mounted behind the front passenger seat for safety reasons.
The physical principle of an accident does, of course, also apply to children
⇒page 133, “The physical principle of a frontal collision”. They differ from adults in
that their muscles and bone structure of children are not yet fully developed. Thus
children are exposed to increased risk of injury.
Children should be transported by using special child safety seats in order to
reduce this risk of injury.
Only use child safety seats which are officially approved, suitable for children and
which comply with the standard ECE-R 44, which classifies child safety seats into 5
groups ⇒page 150, “Classification of child seats into groups”. Child restraint
systems which have been tested for conformity to ECE-R 44 standard have a non-
detachable test seal (a large E within a circle and below this the test number)
attached to the seat.
We recommend that you use child safety seats from the Škoda genuine accessories.
These child seats were developed and also tested for use in Škoda vehicles. They
fulfil the ECE-R 44 standard.
WARNING
Always comply with national legal provisions and instructions from the rele-
vant child safety seat manufacturer when installing and using a child seat ⇒ in “Important safety information regarding the use of child safety
seats”.
Note
National legal provisions, which deviate from the information contained in these
operating instructions, take precedence over the information contained in the
operating instructions.Important safety information regarding the use of child safety seats
Correct use of child safety seats considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•
All the occupants of the vehicle - particularly children - must wear a seat
belt when the vehicle is moving.
•
Children who are less than 1.50 m in height and who weigh less than 36
kg must not use a normal seat belt without a child restraint system other-
wise this may result in injuries to the stomach and neck areas. Comply with
the national legal requirements.
•
One should never carry children, and also not babies! - on one's lap.
•
You can transport a child safely in a suitable child safety seat ⇒page 150,
“Child seat”!
•
Only one child may be fastened with a seat belt into a child safety seat.
•
Never leave the child sitting unattended in the seat.
•
Certain outside climatic conditions can cause life-threatening tempera-
tures in the vehicle.WARNING (continued)
s3f4.1.book Page 147 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 151 of 259

Transporting children safely 150This applies particularly to children if they are not transported in accordance
with legal requirements.
The child is protected when seated in a child safety seat matching its age. Adequate
room is available between the child and the deployment area of the side airbag and
head airbag. The airbag offers optimal protection.
WARNING
•
It is essential to always switch off ⇒page 145 the front passenger airbag
when attaching a child safety seat on the front passenger seat where the
child is seated with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries
also when the child is facing the direction of travel). If this is not done, there
is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal injuries if the front
passenger airbag is deployed. In certain countries national legal provisions
also require that the front passenger side airbag or the front passenger head
airbag be deactivated. When transporting a child on the front passenger
seat, please comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
•
When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply
with the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child safety
seats.
•
Children must never be seated with their head in the deployment area of
the side airbag - risk of injury!
•
Do not place any objects within the deployment area of the side airbag -
risk of injury!
Child seatClassification of child seats into groups
Only child safety seats which have an official approval and are suit-
able for the child, may be used.ECE-R 44 standard applies to child safety seats. ECE-R means: Standard Economic
Commission of Europe - Regulation.Child safety seats which have been tested for conformity to ECE-R 44 standard have
a non-detachable test seal (a large E within a circle and below this the test number)
attached to the seat.
Child safety seats are classified in 5 groups:
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the vehicle
without a seat bolster.
Use of child seatsAn overview of the usefulness of child seats on each of the seats according to the
ECE-R 44 standard:
Universal category - seat is suitable for all approved types of child safety seats.
The seat can be fitted with fixing eyes for the “ISOFIX*”system.
The seat is equipped as standard with the fixing system “To p Te t h e r”.
Group
Weight
0
0 - 10 kg
⇒page 151
0+
up to 13 kg
⇒page 151
1
9 - 18 kg
⇒page 151
2
15 - 25 kg
⇒page 152
3
22 - 36 kg
⇒page 152
Child seat
groups
Front passenger
seat
Rear seat
outside
Rear seat
middle
0
0+
1
2 3
AU
AUA+AT
AU
AU
AUA+AT
AU
AU
AUA+AT
AU
AU
AU
AU
AUA+AT
s3f4.1.book Page 150 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 152 of 259

Transporting children safely151
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Child seats of group 0/0+The optimal solution for babies of up to about 9 months old weighing up to 10 kg
or children up to about 18 months old weighing up to 13 kg is a child safety seat
which is fastened in the opposite direction of travel ⇒fig. 162.
Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the direction of
travel should not be used on the front passenger seat when the vehicle is fitted
with a front passenger airbag ⇒page 148, “Use of child safety seats on the front
passenger seat”.
WARNING
•
It is essential to always switch off the front passenger airbag (airbags) at
a specialist garage or with the switch for front passenger airbag(s)* when
attaching in exceptional circumstances a child safety seat on the front
passenger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of
travel (in some countries also when the child is facing the direction of travel)
⇒page 146.
•
In certain countries national legal provisions require that besides the
front passenger airbag also the side or head passenger airbags are deacti-
vated. Please comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding
the use of child safety seats.
•
If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat may suffer
severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag or airbags are
deployed.
•
You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reactivated just
as soon as you no longer use a child safety seat on the front passenger seat.
Child safety seats in Group 1Child seats in Group 1 are for babies and small children up to 4 years of age with a
weight of between 9 and 18 kilograms. It is best for children in the lower range of
this group, to use a child seat which allows the child to sit with its back to the direc-
tion of travel. It is best for children in the upper range of the Group 0+, to use a child
seat which allows the child to sit ⇒fig. 163 in the direction of travel.
Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the direction of
travel should not be used on the front passenger seat when the vehicle is fitted
with a front passenger airbag ⇒page 148, “Use of child safety seats on the front
passenger seat”.
Fig. 162 Child seats of group
0/0+
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 163 Child seat with
padded table in Group 1
installed on rear seat bench
facing the direction of travel
s3f4.1.book Page 151 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 168 of 259

Driving and the Environment167
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data The engine and catalytic converter must first have reached their optimal operating
temperature in order to effectively reduce fuel consumption and pollutant emis-
sions.
The cold engine vehicle consumes approx. 15 - 20 litres/100 km of fuel immediately
after starting. Fuel consumption drops to 10 litres/100 km after just 1 kilometre. The
engine reaches its operating temperature (outside temperature and engine
dependent) only after about 4 to 10 kilometres and the fuel consumption then
stabilizes. You should therefore avoid driving short distances whenever possible.
An important factor in this connection is also the ambient temperature. The
⇒page 166, fig. 176 shows the different fuel consumptions for the same distance,
on the one hand at +20°C and on the other hand at -10°C. Your vehicle has a higher
fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressures
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.Always ensure that your tyres are inflated to the correct pressure at all times. The
rolling resistance will be increased if the tyre filling pressure is too low. This will not
only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and the driving behaviour will
worsen.
Always check the inflation pressure of the tyres when cold.
Do not drive with winter tyres all year round for this costs about 10 % more fuel.
Winter tyres are also louder.No unnecessary ballast
Transporting ballast costs fuel.The fact that every kilogram of extra weight increases your fuel consumption
means that it is worth taking a look in the luggage compartment to avoid trans-
porting any unnecessary ballast.
It is par ticularly i n town tra ffi c, whe n one is accelerating quite often, that the vehicle
weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption. A rule of thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will cause an increase in fuel
consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
You may frequently also leave a roof rack fitted on just out of convenience,
although you no longer need it. The increased aerodynamic drag of your vehicle
causes it to use about 1 l more fuel than normal at a speed of 100 - 120 km/h, even
when you are not carrying a load on the roof.
Saving electricity
Generating electricity costs fuel.– Switch off electrical components as soon as you no longer need them.When the engine is running, the alternator generates and supplies electrical power.
If more electrical components of the electrical system are switched on, more fuel is
needed to operate the alternator.Keeping a log of your fuel consumptionIf you really wish to keep a close check on your fuel consumption, it is best to enter
the figures in a logbook. This does not take much time but is a very worthwhile exer-
cise. It enables you to detect any change (positive and negative) at an early stage
and to take any appropriate action.
If you find that your fuel consumption is too high, you should reflect on how, where
and in what conditions you have driven the vehicle since you last refuelled.Environmental compatibilityEnvironmental protection has played a major role in the design, selection of mate-
rials and manufacture of your new Škoda. Particular emphasis has been paid to a
number of aspects, including:
Design measures•
Joints designed to be easily detached
s3f4.1.book Page 167 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM
Page 171 of 259

Towing a trailer 170Towing a trailerTo w i n g a t r a i l e rTechnical requirements
The towing device must satisfy certain technical requirements.Your vehicle is designed primarily for transporting persons and luggage. It can,
however, also be used for towing a trailer - provided certain technical equipment is
fitted.
If your vehicle has been equipped with a towing device from Škoda Original Acces-
sories, then the towing device satisfies all technical and legal requirements.
Your vehicle is fitted with a 13-pin power socket for the electrical connection
between the vehicle and trailer. If the trailer which you wish to tow has a 7-pin
connector, you can use a suitable adapter
8) from Škoda original accessories.
This work must be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications
if a towing device is retrofitted.
Specialist garages are familiar with details relating to retrofitting a towing device
and for any necessary modifications to the cooling system.
WARNING
We recommend that you have the towing device from Škoda original acces-
sories installed by a specialist garage. He is familiar with all the relevant
details relating to retrofitting such equipment. There is a risk of an accident
if the towing device is not properly fitted!
General Maintenance
There are a number of points to pay attention to when towing a
trailer.Trailer load
The permissible trailer load must on no account be exceeded.
You can negotiate appropriately steeper inclines and descents if you do not make
full use of the permissible trailer load.
The trailer loads specified only apply for altitudes up to 1 000 metres above mean
sea level. The fact that the engine power output drops with increasing height due to
a lowering of air pressure and thus the ability to climb, means that the trailer load
must be reduced by 10% for every further increase of 1 000 metres in height above
sea level. The towed weight is the weight of the (laden) vehicle and the (laden)
trailer together. One should take this into account before driving up to higher alti-
tudes.
The trailer and drawbar load information on the type plate of the towing
device are merely test data for the towing device The data relating to your
vehicle, which is often less than this test data, can be found in your vehicle
registration documents.
Distribution of the load
Distribute the load in the trailer in such a way that any heavy items are located as
close as possible to the axle. Secure the items to prevent them slipping.
Tyre pressure
Correct the tyre inflation pressure on your vehicle for that of “fully laden”,
⇒page 198. The inflation pressure of the tyres fitted to the trailer adjust in accord-
ance with the manufacturer's recommendation.
Exterior mirrors
You have to have additional exterior mirrors fitted if you are not able to see the
traffic behind the trailer with the standard rear-view mirrors. Both exterior mirrors
8)In some countries the adapter is supplied with the towing device.
s3f4.1.book Page 170 Thursday, June 18, 2009 11:07 AM