2009 PONTIAC G6 light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 201 of 410

Radio Reception
Frequency interference and static can occur during
normal radio reception if items such as cell phone
chargers, vehicle convenience accessories, and external
electronic devices are plugged into the accessory power
outlet. If there is interference or static, unplug the item
from the accessory power outlet.
AM
The range for most AM stations is greater than for FM,
especially at night. The longer range can cause station
frequencies to interfere with each other. For better radio
reception, most AM radio stations boost the power levels
during the day, and then reduce these levels during the
night. Static can also occur when things like storms and
power lines interfere with radio reception. When this
happens, try reducing the treble on the radio.
FM Stereo
FM signals only reach about 10 to 40 miles (16 to 65 km).
Although the radio has a built-in electronic circuit that
automatically works to reduce interference, some static
can occur, especially around tall buildings or hills,
causing the sound to fade in and out.
XM Satellite Radio Service
XM Satellite Radio Service gives digital radio reception
from coast-to-coast in the 48 contiguous United States,
and in Canada. Just as with FM, tall buildings or hills can
interfere with satellite radio signals, causing the sound to
fade in and out. In addition, traveling or standing under
heavy foliage, bridges, garages, or tunnels may cause
loss of the XM signal for a period of time.
Cellular Phone Usage
Cellular phone usage may cause interference with the
vehicle’s radio. This interference may occur when
making or receiving phone calls, charging the phone’s
battery, or simply having the phone on. This interference
causes an increased level of static while listening to
the radio. If static is received while listening to the radio,
unplug the cellular phone and turn it off.
Fixed Mast Antenna
The �xed mast antenna can withstand most car washes
without being damaged as long as it is securely attached
to the base. If the mast becomes slightly bent, straighten
it out by hand. If the mast is badly bent, replace it.
Occasionally check to make sure the antenna is
tightened to its base. If tightening is required,
tighten by hand.
3-69
Page 206 of 410

Braking
SeeBrake System Warning Light on page 3-34.
Braking action involves perception time and reaction
time. Deciding to push the brake pedal is perception
time. Actually doing it is reaction time.
Average reaction time is about three-fourths of a
second. But that is only an average. It might be less
with one driver and as long as two or three seconds or
more with another. Age, physical condition, alertness,
coordination, and eyesight all play a part. So do alcohol,
drugs, and frustration. But even in three-fourths of a
second, a vehicle moving at 60 mph (100 km/h) travels
66 feet (20 m). That could be a lot of distance in an
emergency, so keeping enough space between
the vehicle and others is important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road, whether it is pavement or
gravel; the condition of the road, whether it is wet, dry, or
icy; tire tread; the condition of the brakes; the weight of
the vehicle; and the amount of brake force applied.Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive
in spurts — heavy acceleration followed by heavy
braking — rather than keeping pace with traffic. This is
a mistake. The brakes might not have time to cool
between hard stops. The brakes will wear out much
faster with a lot of heavy braking. Keeping pace with
the traffic and allowing realistic following distances
eliminates a lot of unnecessary braking. That means
better braking and longer brake life.
If the engine ever stops while the vehicle is being
driven, brake normally but do not pump the brakes.
If the brakes are pumped, the pedal could get harder
to push down. If the engine stops, there will still be some
power brake assist but it will be used when the brake
is applied. Once the power assist is used up, it can
take longer to stop and the brake pedal will be harder
to push.
Adding non-dealer/non-retailer accessories can affect
vehicle performance. SeeAccessories and Modifications
on page 5-4.
4-4
Page 207 of 410

Antilock Brake System (ABS)
This vehicle has the Antilock Brake System (ABS),
an advanced electronic braking system that will
help prevent a braking skid.
When the engine is started and the vehicle begins to
drive away, ABS checks itself. A momentary motor
or clicking noise might be heard while this test is going
on, and it might even be noticed that the brake pedal
moves a little. This is normal.
If there is a problem with
ABS, this warning light
stays on. SeeAntilock
Brake System (ABS)
Warning Light on
page 3-35.Let us say the road is wet and you are driving safely.
Suddenly, an animal jumps out in front of you. You slam
on the brakes and continue braking. Here is what
happens with ABS:
A computer senses that the wheels are slowing down.
If one of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer
will separately work the brakes at each wheel.
ABS can change the brake pressure to each wheel, as
required, faster than any driver could. This can help
the driver steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As the brakes are applied, the computer keeps
receiving updates on wheel speed and controls braking
pressure accordingly.
Remember: ABS does not change the time needed to get
a foot up to the brake pedal or always decrease stopping
distance. If you get too close to the vehicle in front of you,
there will not be enough time to apply the brakes if that
vehicle suddenly slows or stops. Always leave enough
room up ahead to stop, even with ABS.
4-5
Page 208 of 410

Using ABS
Do not pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal
down �rmly and let antilock work. The antilock pump or
motor might be heard operating and the brake pedal
might be felt to pulsate, but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
ABS allows the driver to steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help more than
even the very best braking.
StabiliTrak®System
The vehicle may have the StabiliTrak system which
combines antilock brake, traction and stability control
systems and helps the driver maintain directional control
of the vehicle in most driving conditions.
StabiliTrak activates when the computer senses a
discrepancy between the intended path and the direction
the vehicle is actually traveling. StabiliTrak selectively
applies braking pressure at any one of the vehicle’s
brakes to help steer the vehicle in the intended direction.This symbol will appear
when the StabiliTrak
system is activated.
When you �rst start the vehicle and begin to drive away,
the system performs several diagnostic checks to ensure
there are no problems. The system may be heard or felt
while it is working. This is normal and does not mean
there is a problem with the vehicle.
This light is located on the
instrument panel cluster.
When the system is on, this light will come on if there
is a problem, or if the system has been turned off.
StabiliTrak comes on automatically whenever the
vehicle is started. To help assist with directional control
of the vehicle, the system should always be left on.
4-6
Page 209 of 410

The Traction Control System (TCS) and StabiliTrak can
be turned off if needed by pressing and holding the
StabiliTrak/TCS button. Press the button again to turn
StabiliTrak and Traction Control back on. SeeTraction
Control System (TCS) on page 4-7for more information.
If cruise control is being used when the system
activates, the StabiliTrak light will �ash and cruise
control will automatically disengage. Cruise control may
be reengaged when road conditions allow. See
Cruise Control on page 3-10.
Traction Control System (TCS)
The vehicle has a Traction Control System (TCS) that
limits wheel spin. This is especially useful in slippery road
conditions. The system operates only if it senses that one
or both of the front wheels are spinning or beginning to
lose traction. When this happens, the system reduces
engine power and may also upshift the transmission to
limit wheel spin. Also, the traction control system
activates the appropriate corner brakes to gain even
quicker control to limit wheel spin.This light, located on the
instrument panel, will come
on when the TCS is
limiting wheel spin.
The system may be heard or felt while it is working, but
this is normal.
If the vehicle is in cruise control when TCS begins to
limit wheel spin, the cruise control will automatically
disengage. The cruise control may be re-engaged when
road conditions allow. SeeCruise Control on page 3-10.
TCS operates in all transmission shift lever positions
except park or neutral. But the system can upshift the
transmission only as high as the shift lever position that is
chosen, so use the lower gears only when necessary.
SeeAutomatic Transmission Operation on page 2-26.
4-7
Page 210 of 410

This light is located on the
instrument panel cluster.
This light comes on if there is a problem, or if the
system has been turned off.
When this warning light is on, the system will not limit
wheel spin. Adjust your driving accordingly.
TCS automatically comes on whenever the vehicle is
started. To limit wheel spin, especially in slippery
road conditions, always leave the system turned on.
TCS can be turned off if needed.
To turn the system on or
off, press the TCS button
located under the
climate controls.
It is recommended to leave the system on for normal
driving conditions, but it may be necessary to turn
the system off if the vehicle is stuck in sand, mud, ice orsnow, and you want to “rock” the vehicle to attempt to
free it. SeeIf Your Vehicle is Stuck in Sand, Mud, Ice, or
Snow on page 4-19.
If the TCS button is pressed once, the traction control
system will turn off and the traction control system
warning light comes on. The StabiliTrak system will stay
on. Press the TCS button again to turn the system
back on. The traction control system warning light will
go off. Press and hold the TCS button and the
StabiliTrak system and the traction control system will
turn off. Press the TCS button again to turn StabiliTrak
and the traction control system back on. For more
information, seeStabiliTrak
®System on page 4-6.
When the system is off, the Traction Control System
warning light will come on and stay on. If the Traction
Control System is limiting wheel spin and the button
is pressed to turn the system off, the warning light will
come on and the system will stop limiting wheel
spin. The system will not provide traction assistance
until the system is turned back on.
Adding non-dealer/non-retailer accessories can affect
the vehicle’s performance. SeeAccessories and
Modifications on page 5-4for more information.
4-8
Page 213 of 410
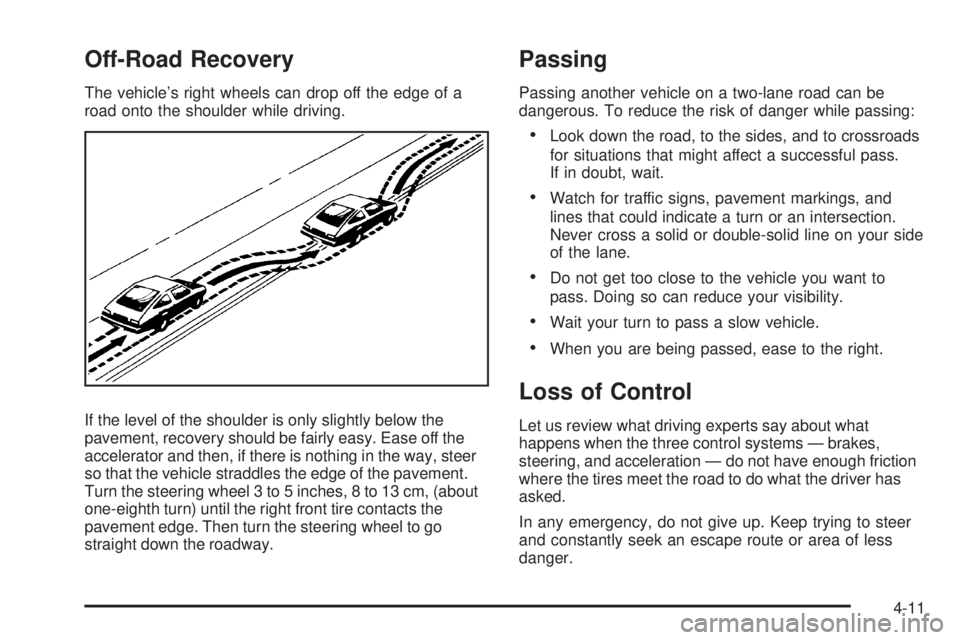
Off-Road Recovery
The vehicle’s right wheels can drop off the edge of a
road onto the shoulder while driving.
If the level of the shoulder is only slightly below the
pavement, recovery should be fairly easy. Ease off the
accelerator and then, if there is nothing in the way, steer
so that the vehicle straddles the edge of the pavement.
Turn the steering wheel 3 to 5 inches, 8 to 13 cm, (about
one-eighth turn) until the right front tire contacts the
pavement edge. Then turn the steering wheel to go
straight down the roadway.
Passing
Passing another vehicle on a two-lane road can be
dangerous. To reduce the risk of danger while passing:
Look down the road, to the sides, and to crossroads
for situations that might affect a successful pass.
If in doubt, wait.
Watch for traffic signs, pavement markings, and
lines that could indicate a turn or an intersection.
Never cross a solid or double-solid line on your side
of the lane.
Do not get too close to the vehicle you want to
pass. Doing so can reduce your visibility.
Wait your turn to pass a slow vehicle.
When you are being passed, ease to the right.
Loss of Control
Let us review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems — brakes,
steering, and acceleration — do not have enough friction
where the tires meet the road to do what the driver has
asked.
In any emergency, do not give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of less
danger.
4-11
Page 215 of 410

Driving at Night
Night driving is more dangerous than day driving
because some drivers are likely to be impaired — by
alcohol or drugs, with night vision problems, or by fatigue.
Night driving tips include:
Drive defensively.
Do not drink and drive.
Reduce headlamp glare by adjusting the inside
rearview mirror.
Slow down and keep more space between you and
other vehicles because headlamps can only light up
so much road ahead.
Watch for animals.
When tired, pull off the road.
Do not wear sunglasses.
Avoid staring directly into approaching headlamps.
Keep the windshield and all glass on your vehicle
clean — inside and out.
Keep your eyes moving, especially during turns or
curves.
No one can see as well at night as in the daytime.
But, as we get older, these differences increase.
A 50-year-old driver might need at least twice as much
light to see the same thing at night as a 20-year-old.
4-13