Page 467 of 621
457
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
This illustration indicates typical tire
symbols.
1. Tire size— F or det ails, see “— Ti re
size” on page 459.
2. DOT and Tire Identification Number (TIN)— For details, see
“—DOT and Tire Identification
Number (TIN)” on page 458.
3. Uniform tire quality grading— For details, see “—Uniform tire
quality grading” on page 460.
4. The location of the treadwear indicators— For details, see
“Checking and replacing tires” on
page 556.
5. Tire ply composition and mate- rials— Plies mean a layer of rub-
ber −coated parallel cords. Cords
mean the strands forming the plies
in the tire.
6. Radial tires or bias�ply tires— A
radial tire has “RADIAL” on the
sidewall. A tire not marked with
“RADIAL” is a bias −ply tir e.
Tire information—
—Tire symbols
XS20011
Page 468 of 621
458
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
7. “TUBELESS” or “TUBE
TYPE”— A tubeless tire does not
have a tube inside the tire and air
is directly filled in the tire. A tube
type tire has a tube inside the tire
and the tube maintains the air
pressure.
8. Load limit at maximum cold tire inflation pressure— For details,
see “Checking and replacing tires”
on page 556.
9. Maximum cold tire inflation pressure— This means the pres-
sure to which a tire may be in-
flated. For details about recom-
mended cold tire inflation
pressure, see “Tires” on page 594.
10.Summer tire or all season tire— An all season tire has “M+S”
on the sidewall. The tire not
marked with “M+S” is a summer
tire. For details, see “Types of
tires” on page 472.
XS20014
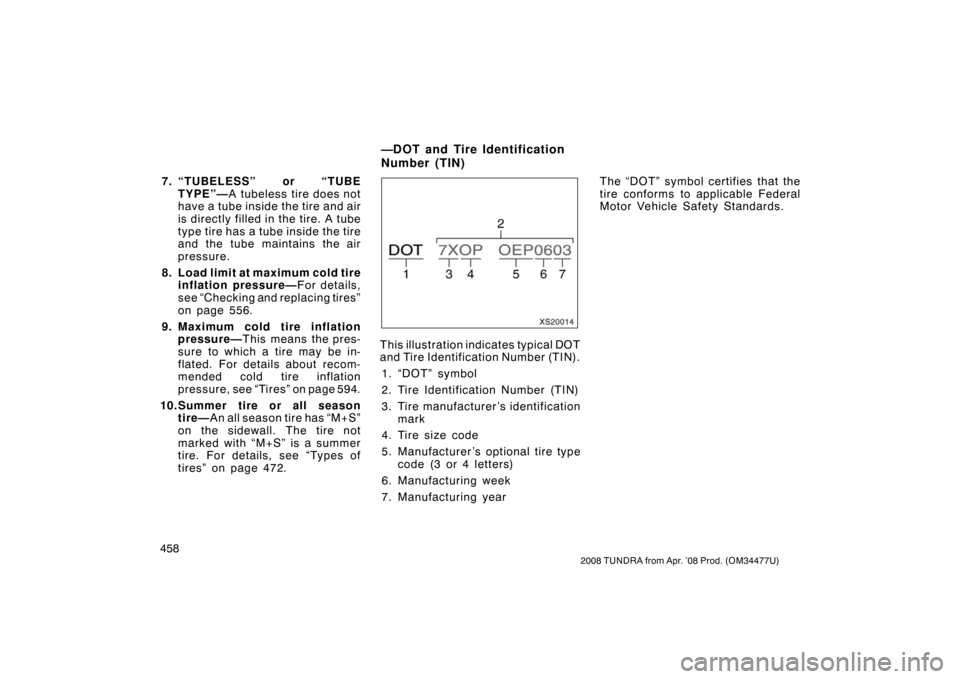
This illustration indicates typical DOT
and Tire Identification Number (TIN).
1. “DOT” symbol
2. Tire Identification Number (TIN)
3. Tire manufacturer ’s identification mark
4. Tire size code
5. Manufacturer ’s optional tire type code (3 or 4 letters)
6. Manufacturing week
7. Manufacturing year The “DOT” symbol certifies that the
tire conforms to applicable Federal
Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
—DOT and Tire Identification
Number (TIN)
Page 469 of 621
459
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
XS20012
This illustration indicates typical tire
size.
1. Tire use (P=Passenger car, T=Temporary use)
2. Section width (in millimeters)
3. Aspect ratio (tire height to section width)
4. Tire construction code (R=Radial, D=Diagonal)
5. Wheel diameter (in inches)
6. Load index (2 digits or 3 digits)
7. Speed symbol (alphabet with one letter)
SU21026a
1. Section width
2. Tire height
3. Wheel diameter
SU21027
1. Bead
2. Sidewall
3. Shoulder
4. Tread
5. Belt
6. Inner liner
7. Reinforcing rubber
8. Carcass
9. Rim lines
10.Bead wires
11. Chafer
—Tire size —Name of each section of tire
Page 473 of 621

463
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
Ti r e relat ed ter mMeaning
Occupant distributiondistribution of occupants in a vehicle as specified in the third column of Table
1 that follows
Production options weight
the combined weight of those installed regular production options weighing over
2.3 kg (5 lb.) in excess of those standard items which they replace, not pre-
viously considered in curb weight or accessory weight, including heavy duty
brakes, ride levelers, roof rack, heavy duty battery, and special trim
Rima metal support for a tire or a tire and tube assembly upon which the tire beads
are seated
Rim diameter (Wheel diameter)nominal diameter of the bead seat
Rim size designationrim diameter and width
Rim type designationthe industry of manufacturer ’s designation for a rim by style or code
Rim widt hnominal distance between rim flanges
Vehicle capacity weight
(Total load capacity)the rated cargo and luggage load plus 68 kg (150 lb.) times the vehicle’s desig-
nated seating capacity
Vehicle maximum load on the tirethe load on an individual tire that is determined by distributing to each axle
its share of the maximum loaded vehicle weight and dividing by two
Vehicle normal load on the tire
the load on an individual tire that is determined by distributing to each axle
its share of the curb weight, accesso ry weight, and normal occupant weight
(distributed in accordance with Table 1 that follows) and dividing by two
Page 479 of 621

469
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
Vehicle load limits include total load
capacity, seating capacity, towing
capacity and cargo capacity. Follow
the load limits shown below. Total
load capacity and seating capacity
are also described on the tire and
loading information label. For location
of the tire and loading information
label, see “Checking tire inflation
pressure” on page 553.
Total load capacity:
Total load capacity means combined
weight of occupants, cargo and
luggage. Tongue load is included
when trailer towing. For the total load
capacity about your vehicle, see
“Vehicle capacity weight” on page 580
in Section 8. Seating capacity:
Regular cab modelsWith separate seats
Tot al 2
With bench seats Tot al 3
Double cab and Crew Max models With separate seatsTotal 5 (Front 2, Rear 3)
With bench seats
Total 6 (Front 3, Rear 3)
Seating capacity means the maximum
number of occupants whose esti-
mated average weight is 68 kg (150
lb.) per person. Depending on the
weight of each person, the seating ca-
pacity given may exceed the total
load capacity.
NOTICE
Even if the number of occupants
are within the seating capacity,
do not exceed the total load ca-
pacity.
Towing capacity:
Towing capacity means the maximum
allowable gross trailer weight (trailer
weight plus its cargo weight) that your
vehicle is able to tow. For the towing
capacity about your vehicle, see
“Towing capacity” on page 586 in Sec-
tion 8.
Cargo capacity
Cargo capacity may increase or de-
crease depending on the size (weight)
and the number of occupants. For de-
tails, see “Capacity and distribution”
that follows.
CAUTION
Do not apply the load more than
each load limit. That may cause
not only damage to the tires, but
also deterioration to the steering
ability and braking ability, which
may cause an accident.
Veh icle lo ad limit s
Page 482 of 621

472
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
Determine what kind of tires your
vehicle is originally equipped with.
1. Summer tires
Summer tires are high −speed capabil-
ity tires best suited to highway driving
under dry conditions.
Since summer tires do not have the
same traction performance as snow
tires, summer tires are inadequate for
driving on snow −covered or icy roads.
For driving on snow −covered or icy
roads, we recommend using snow
tires. If installing snow tires, be sure
to replace all four tires.
2. All season tires
All season tires are designed to pro-
vide better traction in snow and to be
adequate for driving in most winter
conditions, as well as for use all year
round. All season tires, however, do not have
adequate traction performance
compared with snow tires in heavy or
loose snow. Also, all season tires fall
short in acceleration and handling
performance compared with summer
tires in highway driving.
The details about how to distinguish
summer tires from all season tires are
described on page 457.
CAUTION
�
Do not mix summer and all sea-
son tires on your vehicle as
this can cause dangerous han-
dling characteristics, resulting
in loss of control.
� Do not use tires other than the
manufacture’s designated
tires, and never mix tires or
wheels of the sizes different
from the originals.
Types of tires
Page 564 of 621
554
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
Keep your tire inflation pressures
at the proper level.
The recommended cold tire inflation
pressures, tire sizes and the com-
bined weight of occupants and cargo
(vehicle capacity weight) are de-
scribed on page 580 in Section 8.
They are also described on the tire
and loading information label as
shown.
You should check the tire inflation
pressure every two weeks, or at least
once a month. And do not forget the
spare! The following instructions for
checking tire inflation pressure
should be observed:
� The pressure s hould be
checked only when the tires are
cold. If your vehicle has been
parked for at least 3 hours and has
not been driven for more than 1.5
km or 1 mile since, you will get
an accurate cold tire inflation pres-
sure reading.
� Always use a tire pressure
gauge. The appearance of a tire
can be misleading. Besides, tire
inflation pressures that are even
just a few pounds off can degrade
ride and handling.
� Do not bleed or reduce tire
inflation pressure after driving.
It is normal for the tire inflation
pressure to be higher after driving.
� Never exceed the vehicle capac-
ity weight. Passenger and lug-
gage weight should be located so
that the vehicle is balanced.
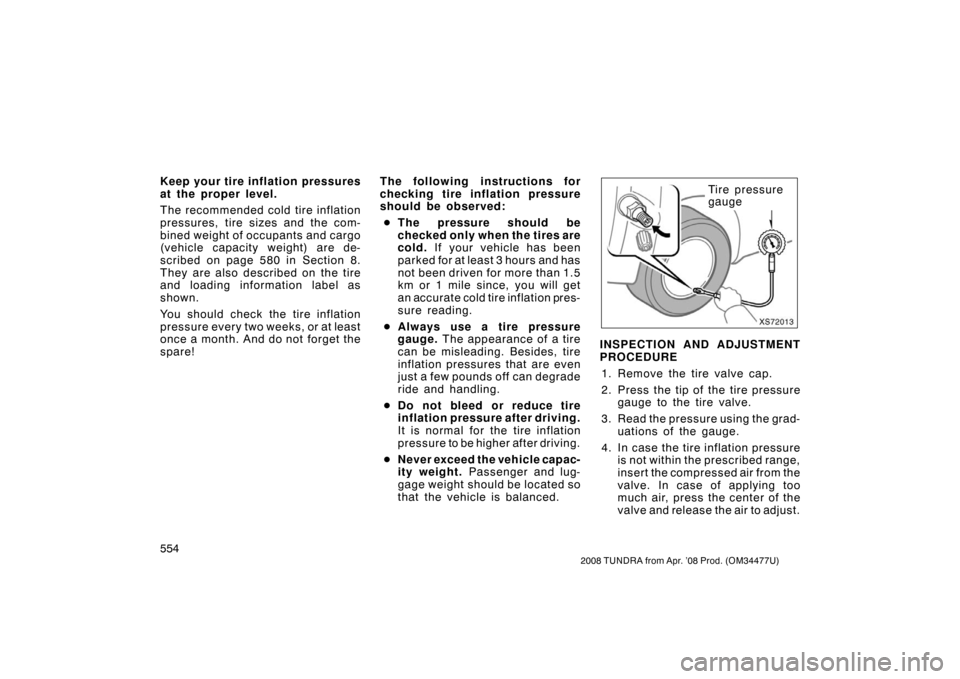
XS72013
Tire pressure
gauge
INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE
1. Remove the tire valve cap.
2. Press the tip of the tire pressure gauge to the tire valve.
3. Read the pressure using the grad- uations of the gauge.
4. In case the tire inflation pressure
is not within the prescribed range,
insert the compressed air from the
valve. In case of applying too
much air, press the center of the
valve and release the air to adjust.
Page 566 of 621

556
2008 TUNDRA from Apr. ’08 Prod. (OM 34477U)
Treadwear indicator
CHECKING YOUR TIRES
Check the tire’s tread for treadwear
indicators. If the indicators show,
replace the tires. The location of
treadwear indicators is shown by
the “TWI” or “
Δ” marks, etc.,
molded on the sidewall of each
tire. The tires on your Toyota have built
−in
treadwear indicators to help you know
when the tires need replacement.
When the tread depth wears to 1.6
mm (0.06 in.) or less, the indicators
will appear. If you can see the indica-
tors in two or more adjacent grooves,
the tire should be replaced. The lower
the tread, the higher the risk of skid-
ding.
The effectiveness of snow tires is
lost if the tread wears down below
4 mm (0.16 in.).
If you have tire damage such as
cuts, splits, cracks deep e nough to
expose the fabric, or bulges indi-
cating internal damage, the tire
should be repl aced.
If a tire often goes flat or cannot be
properly repaired due to the size or
location of a cut or other damage, it
should be replaced. If you are not
sure, consult with your Toyota dealer. If air loss occurs while driving, do not
continue driving. Driving even a short
distance can damage a tire beyond
repair.
An y ti res wh i ch are over 6 years
old must be checked by a qualified
technician even if damage is not
obvious.
Tires deteriorate with age even if they
have never or seldom been used.
This applies also to the temporary
spare tire and tires stored for future
use.
Checking and replacing tires