2008 SUZUKI SWIFT oil control valve inspection in section 1d
[x] Cancel search: oil control valve inspection in section 1dPage 99 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-49
Troubleshooting
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
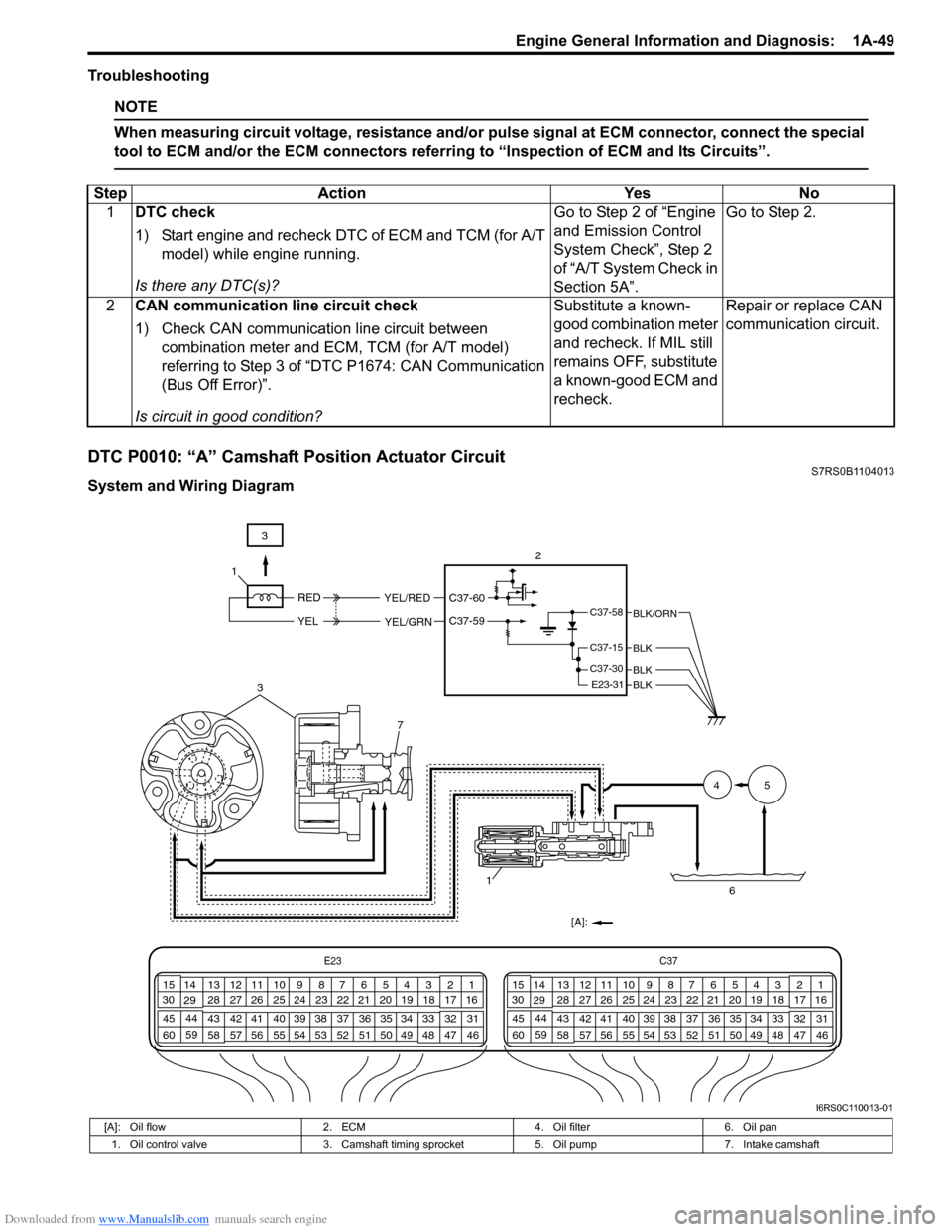
DTC P0010: “A” Camshaft Position Actuator CircuitS7RS0B1104013
System and Wiring DiagramStep Action Yes No
1 DTC check
1) Start engine and recheck DTC of ECM and TCM (for A/T
model) while engine running.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 2 of “Engine
and Emission Control
System Check”, Step 2
of “A/T System Check in
Section 5A”.Go to Step 2.
2 CAN communication line circuit check
1) Check CAN communication line circuit between
combination meter and ECM, TCM (for A/T model)
referring to Step 3 of “DTC P1674: CAN Communication
(Bus Off Error)”.
Is circuit in good condition? Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains OFF, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
Repair or replace CAN
communication circuit.
3
7
1[A]: 45
6
C37-58
C37-15
C37-30
E23-31BLK
BLK
BLK/ORN
RED
YEL
YEL/RED
YEL/GRN
C37-60
C37-59
3 2
1
E23 C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
BLK
I6RS0C110013-01
[A]: Oil flow
2. ECM4. Oil filter6. Oil pan
1. Oil control valve 3. Camshaft timing sprocket5. Oil pump7. Intake camshaft
Page 101 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-51
6Oil control valve electrical circuit for ground short
check
1) Measure resistance between “C37-59” terminal of ECM
connector and engine ground.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 9.
“YEL/GRN” wire is
shorted to ground
circuit.
7 Oil control valve electrical circuit for short check
1) Disconnect connector from oil control valve with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “C37-60” and “C37-59” terminals of ECM connector.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 9.
“YEL/RED” wire is
shorted to “YEL/GRN”
wire.
8 Oil control valve electrical circuit check
1) Disconnect connector from oil control valve with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “C37-60” terminal of ECM connector and “YEL/RED” wire terminal of oil control
valve connector and between “C37-59” terminal of ECM
connector and “YEL/GRN” wir e terminal of oil control
valve connector.
Is resistance below 1
Ω? Go to Step 9. “YEL/RED” or “YEL/
GRN” wire circuit is
open or high resistance.
9 Oil control valve check
Check oil control valve refe rring to “Oil Control Valve
Inspection in Section 1D”.
Is resistance within specified value? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Faulty oil control valve.
Step Action Yes No
Page 103 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-53
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Is DTC P0010 detected together? Go to “DTC P0010: “A”
Camshaft Position
Actuator Circuit”.Go to Step 2.
2 Do you have SUZUKI scan tool? Go to Step 3.Go to Step 5.
3 Camshaft position control check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect SUZUKI scan
tool to DLC.
2) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature.
3) Select menu to DATA LIST.
4) Check that “VVT GAP” displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is 0 – 5 °.
Is it OK? Go to Step 4.
Check valve timing
referring to “Timing
Chain and Chain
Tensioner Removal and
Installation in Section
1D”. If OK, go to Step 5.
4 Camshaft position control check
1) Drive vehicle under following conditions.
• Vehicle speed at 80 km/h (50 mile/h).
• Gear position at 5th or D range.
2) Check that “VVT GAP” displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is 0 – 5 °.
Is it OK? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Go to Step 5.
5 Oil control circuit visual inspection
1) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head
Cover Removal and Insta llation in Section 1D”.
2) Check oil pressure leakage from oil control circuit.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 6.
Repair or replace.
6 Oil control valve and oil gallery pipe check
1) Remove oil control valve re ferring to “Oil Control Valve
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
2) Remove oil gallery pipe refe rring to “Timing Chain Cover
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
3) Check oil gallery pipe and o il control valve for clog or
sludge.
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 7.
Clean oil control valve
and oil gallery pipe.
Replace oil control valve
if a problem is not
solved after cleaning oil
control valve and oil
gallery pipe.
7 Oil control valve electrical circuit check
1) Check that oil control valve circuit is in good condition
referring to “DTC P0010: “A” Camshaft Position Actuator
Circuit”.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 8.
Repair circuit.
8 Oil control valve check
1) Check oil control valve refe rring to “Oil Control Valve
Inspection in Section 1D”.
Is it in good condition? Replace camshaft
timing sprocket.
Replace oil control
valve.
Page 169 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-119
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Description”.
2 EGR valve power supply circuit check
1) Remove air intake pipe.
2) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect EGR valve
connector.
3) With ignition switch turned ON, measure voltage between “BLK/RED” wire terminal of EGR valve
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is check voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 3.
“BLK/RED” wire is open
circuit.
3 Wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch.
3) Measure voltage between engine ground and each “GRN/RED”, “GRN/ORN”, “W HT/RED”, “BRN/YEL” wire
terminals of EGR valve connector.
Is each voltage 0 V? Go to Step 4.
Faulty wire(s) are
shorted to other circuit.
If wires are OK,
substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
4 Wire circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, measure resistance
between engine ground and each “GRN/RED”, “GRN/
ORN”, “WHT/RED”, “BRN/YEL” wire terminals of EGR
valve connector.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 5.
Faulty wire(s) are
shorted to ground
circuit.
If wires are OK,
substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
5 Short circuit check for EGR valve control circuit
1) With ignition turned OFF, measure resistance between
each EGR valve control circ uit wire (“GRN/RED”, “GRN/
ORN”, “WHT/RED” and “BRN/ YEL” wire) and each EGR
valve control circuit wire.
Is each resistance infinity? Go to Step 6.
Faulty wire(s) are short
circuit.
6 EGR valve stepper motor coil circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect EGR valve
connector.
2) Measure resistance between “E23-1/16” and each “C37- 4”, “C37-3”, “C37-19”, “C37-18” terminals of ECM
connector.
Is each resistance 20 – 31
Ω at 20 °C, 68 °F? Faulty ECM. Substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
Go to Step 7.
7 EGR valve check
1) Check EGR valve resistance referring to “EGR Valve
Inspection in Section 1B”.
Is resistance within specified value? Faulty wire(s) are open
or high resistance
circuit. If wires are OK,
substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Faulty EGR valve.
Page 305 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-20
15) Install A/C compressor to its bracket (if equipped) referring to “Compressor Assembly Removal and
Installation in Section 7B” or “Compressor Assembly
Removal and Installa tion in Section 7B”.
16) Adjust A/C compressor belt tension (if equipped) referring to “Compressor Drive Belt Inspection and
Adjustment in Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive Belt
Inspection and Adjustment in Section 7B”.
17) Check to ensure that a ll removed parts are back in
place.
Reinstall any necessary parts which have not been
reinstalled.
18) Refill cooling system with coolant referring to “Cooling System Flush and Refill in Section 1F”. 19) Refill engine with engine oil
referring to “Engine Oil
and Filter Change in Section 0B”.
20) Refill transaxle with transa xle oil referring to“Manual
Transaxle Oil Change in Section 5B” or “A/T Fluid
Change in Section 5A”.
21) Install battery and tray.
22) Connect positive and negative cable at battery.
23) Install engine hood and connect windshield washer hose.
24) Verify that there is no fu el leakage, coolant leakage,
oil leakage and exhaust gas leakage at each
connection.
Timing Chain Cover ComponentsS7RS0B1406012
I6RS0C140015-02
1. Crankshaft pulley bolt 13. Oil gallery pipe No.2 bolt
2. Crankshaft pulley 14. Oil gallery pipe No.3
3. Oil seal : Apply engine oil to oil seal lip. 15. Oil gallery pipe No.3 bolt
4. Timing chain cover : Apply sealant 99000-31140 to the mating surface of cylinder and cylinder head.
: Apply sealant 99000-31260 to the mating surface of timing chain cover referring to the
figure of Step 4) of “Installation” under “Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation”. 16. O-ring
: Apply engine oil.
5. Pin 17. Oil control valve
6. Cap bolt 18. Oil control valve mounting nut
7. Timing chain cover mounting bolts 19. Cap
8. Timing chain cover mounting nut : 11 N ⋅m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
9. Oil gallery pipe No.1 :25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
Page 308 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-23 Engine Mechanical:
8) Install new O-ring (1) to oil gallery pipes No.2 (2) and
No.3 (3).
9) Install oil gallery pipes No.2 and No.3 to cylinder
head (4) and timing chain cover (5).
Tighten bolts to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Oil gallery pipe No.2 and No.3 bolt (a): 11 N·m (
1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
10) Install water pump pulley. 11) Install cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
12) Install oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Strainer Removal and Installation in Section 1E”.
13) Install crankshaft pulley (1). Tighten bolt (2) to specified torque. To lock crankshaft pulley, use
special tool with it as shown in figure.
Special tool
(A): 09917–68221
Tightening torque
Crankshaft pulley bolt (a): 150 N·m (15.0 kgf-m,
108.5 lb-ft)
14) Install engine assembly to vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
Timing Chain Cover InspectionS7RS0B1406014
Oil Seal
Check oil seal lip for fault or other damage. Replace as
necessary. Timing Chain Cover
Inspect strainer (1) of oil passage for driving intake cam
timing sprocket assembly (VVT actuator).
If clog or foreign matter exists, clean strainer.
Oil Control Valve Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1406015
Removal
Remove oil gallery pipe No.1
(1) and oil control valve (2)
from timing chain cover (3).
Installation
1) Install new O-ring (4) to oil control valve.
2) Install oil control valve to timing chain cover. Tighten nuts to specification.
Tightening torque
Oil control valve mounting nut (a): 11 N·m (1.1
kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
3) Install oil gallery pipe No .1 with new copper washers
(5) to timing chain cover.
Tighten bolts to specification.
Tightening torque
Oil gallery pipe No.1 bolt (b): 30 N·m (3.0 kgf-m,
21.5 lb-ft)
(a)
(a) 1
2
3
4
5
I3RH0B140027-01
I2RH0B140056-01
1
I3RH0B140028-01
1
5
(b) 3
(a)
2 4
5
I3RM0A140027-01
Page 645 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-1
Transmission / Transaxle
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B5100001
• Do not disconnect couplers from TCM, battery cable from battery, TCM ground wire harness from engine or
main fuse before checking the diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in TCM memory.
Such disconnection will clea r memorized information
in TCM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in TCM memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool or generic scan tool. Before using scan tool, read
its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have
good understanding as to what functions are available
and how to use it.
It is indistinguishable wh ich module turns on MIL
because not only ECM but also TCM turns on MIL.
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM for DTC when
MIL lights on.
When checking TCM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by TCM.
– Generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM simultaneously.
• Using SUZUKI scan tool the diagnostic information stored in TCM memory can be checked and cleared
as well. Before its use, be sure to read Operator’s
Manual supplied with it carefully to have good
understanding of its functions and usage.
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• TCM replacement
– When substituting a known-good TCM, check that all relays and actuators have resistance of
specified value.
Neglecting this check may result in damage to good
TCM.
• Communication of ECUs , ECM, TCM, ABS control
module, keyless start control module and BCM is
established by CAN (Controller Area Network).
Therefore, handle CAN communication line with care
referring to “Precaution for CAN Communication
System in Section 00”.
Precautions for Disassembly and ReassemblyS7RS0B5100002
When repairing automatic transaxle, it is necessary to
conduct the on-vehicle test to investigate where the
cause of the trouble lies first.
Then whether overhaul should be done or not is
determined. If the transaxle is disassembled without
such preliminary procedure, not only the cause of the
trouble would be unknown, but also a secondary trouble
may occur and often time would be wasted.
As the automatic transaxle consists of high precision
component, the following cautions should be strictly
observed when handling its parts in disassembly and
reassembly.
• Disassembling valve body assembly is prohibited
essentially. However, a few parts can be
disassembled. When disassembling valve body
component parts, confirm whether their parts are
allowed to disassemble or not referring to “Valve Body
Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly”.
• When component part of forward clutch, direct clutch, 2nd brake and/or O/D and 2nd coast brake, namely
clutch disc, brake disc, retaining plate and/or
separator plate, have been replaced, all learned
contents, which have been stored in TCM memory by
executing learning control, should be initialized
referring to “Learning Control Initialization”.
• Make sure to wash dirt off from the transaxle so that no such dirt will enter the transaxle during
dismounting and remounting.
• Select a clean place free from dust and dirt for overhauling.
• Place a rubber mat on the work bench to protect parts from damage.
• Work gloves or shop cloth should not be used. (Use a nylon cloth or a paper towel.)
• When separating the case joint, do not pry with a screwdriver or such but tap with a plastic hammer
lightly.
• Make sure to wash dirt off from the transaxle so that no such dirt will enter the transaxle during
disassembly and reassembly.
• Wash the disassembled parts in ATF (Automatic Transaxle Fluid) or kerosene (using care not to allow
ATF or kerosene to get on your face, etc.) and confirm
that each fluid passage is not clogged by blowing air
into it. But use kerosene to wash the discs, resin
washers and rubber parts.
• Replace each gasket, oil seal and O-ring with a new one.
• Apply ATF to sliding or rotating parts before
reassembly.
Page 684 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-40 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
Trouble Diagnosis 3
Off-vehicle repairNon operate TCC (lock-
up) system
Malfunction of TCC solenoid valve
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of shift solenoid valve-A
and/or -B Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of output shaft speed
sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of input shaft speed sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of transmission range
sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of transmission fluid
temperature sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of pressure control solenoid
valve Inspect. If NG, replace valve body assembly.
Malfunction of throttle position sensor Inspect referring to “Electric Throttle Body
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection in Section
1C”. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of engine coolant
temperature sensor Inspect referring to “ECT Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of brake light switch Inspect referring to “Brake Light Switch
Inspection in Section 9B”. If NG, replace.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Excessive “N”
→ “D” or
“N”
→ “R” time lag Malfunction of transmission fluid
temperature sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Pressure control solenoid valve circuit
faulty Inspect. If NG, replace valve body assembly.
Clogged oil strainer Replace.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Condition
Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Unable to run in all range Faulty oil pump Inspect. If NG, replace.
Seized or broken planetary gear Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.2 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Damaged drive plate Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty forward clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty reverse clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty 1st and reverse brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty torque converter Replace.
Excessive “N”
→ “D” shift
shock Faulty forward clutch
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Excessive “N”
→ “R” shift
shock Faulty reverse clutch
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty 1st and reverse brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Poor 1
→ 2 shift,
excessive shock or
slippage Faulty 2nd brake
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.1 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Poor 2
→ 3 shift,
excessive shock or
slippage Faulty direct clutch
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Poor 3
↔ O/D shift,
excessive shock or
slippage Faulty forward clutch
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty O/D and 2nd coast brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Poor 3
→ 2 shift,
excessive shock or
slippage Faulty direct clutch
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.1 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Poor 2
→ 1 shift,
excessive shock or
slippage Faulty 2nd brake
Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.2 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.