2008 SKODA OCTAVIA airbag off
[x] Cancel search: airbag offPage 86 of 304

Seats and Stowage85
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Note
•The seat heating should only be switched on when the engine is running. This
has a significant effect of sa ving on the battery capacity.
•If the on-board voltage drop s, the seat heating is switched off automatically, in
order to provide sufficient electrical energy for the engine control.
Pedals
Concerning a secure depressing of the pe dal, you should use only footmats from
the Škoda genuine accessories.
Operation of the pedals must not be hindered!
WARNING
•Greater pedal distances may be needed when there is a fault in the brake
system.
•Do not place any footmats or other additional floor coverings in the area
of the pedals in order to ensure that all the pedals can be fully depressed and
are able to return unobstructed to their initial position - risk of accident!
•There must be no objects on the floor which could roll under the pedals.
You would then no longer be able to apply the brakes, operate the clutch or
accelerator - risk of accident!
luggage compartment
Loading the luggage compartment
Please observe the following in the inte rest of having good handling char-
acteristics of your vehicle:
– Distribute the items of luggage as evenly as possible.
– Place heavy objects as far forward as possible. – Attach the items of luggage to the lashing eyes or the safety net*
⇒page 86.
In the event of an accident, there is such a high kinetic energy which is produced by
small and light objects that they can caus e severe injuries. The magnitude of the
kinetic energy depends on the speed at wh ich the vehicle is travelling and on the
weight of the object. The speed at which the vehicle is travelling is in this case the
more significant factor.
Example: In the event of a frontal collision at a speed of 50 km/h, an unsecured
object with a weight of 4.5 kg produces an energy, which corresponds to 20 times
its own weight. This means that it results in a weight of approx. 90 kg. You can
imagine the injuries that can occur, if this “bullet” is flying through the interior
compartment and hits an occupant.
WARNING
•Store the objects in the luggage compartment and attach them to the
lashing eyes.
•Loose objects in the passenger co mpartment can be thrown forward
during a sudden manoeuvre or in case of an accident and can injure the
occupants or other oncoming traffic. This risk is still increased, if the objects
which are flying around are hit by a deployed airbag. In this case, the objects
which are thrown back can injure the occupants - hazard.
•Please note that the handling properties of your vehicle may be affected
when transporting heavy objects as a result of the displacement of the
centre of gravity. The speed and style of driving must be adjusted accord-
ingly.
•The items carried in the luggage compartment should be stored in such
a way that no objects are able to slip forward if there are any sudden driving
or braking manoeuvres under taken - risk of injury!
•Never drive with the boot lid fully opened or slightly ajar otherwise
exhaust gases may get into the interior of the vehicle - risk of poisoning!
•On no account exceed the permissible axle loads and the permissible
gross weight of the vehicle - risk of accident!
•Never transport occupants in the luggage compartment!
20A5Facelift.book Page 85 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 108 of 304
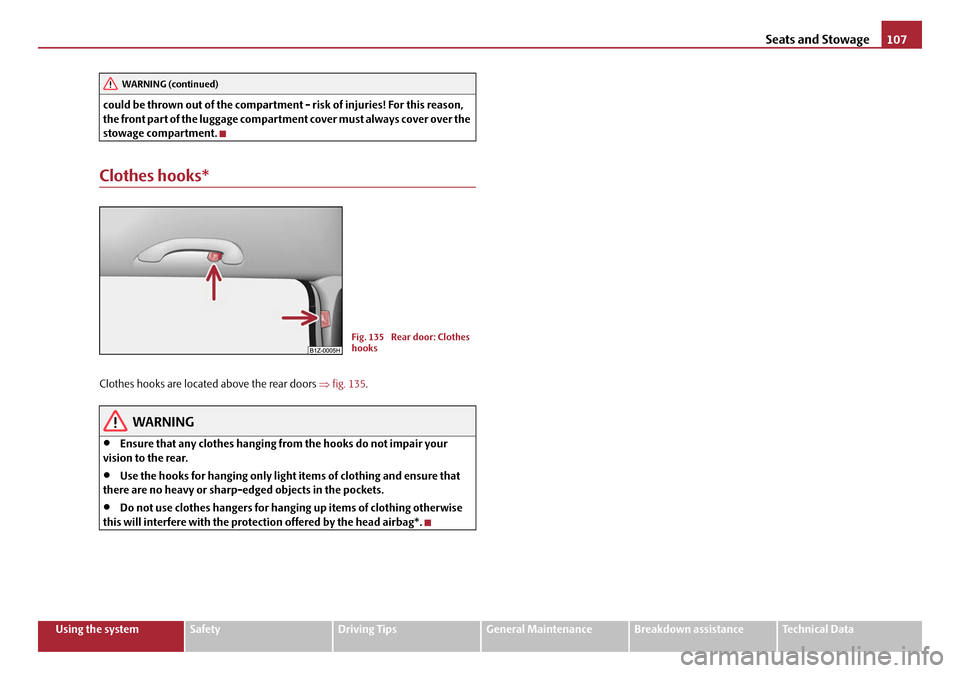
Seats and Stowage107
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
could be thrown out of the compartment - risk of injuries! For this reason,
the front part of the luggage compartmen
t cover must always cover over the
stowage compartment.
Clothes hooks*
Clothes hooks are located above the rear doors ⇒fig. 135 .
WARNING
•Ensure that any clothes hanging from the hooks do not impair your
vision to the rear.
•Use the hooks for hanging only light items of clothing and ensure that
there are no heavy or sharp- edged objects in the pockets.
•Do not use clothes hangers for hanging up items of clothing otherwise
this will interfere with the protection offered by the head airbag*.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 135 Rear door: Clothes
hooks
20A5Facelift.book Page 107 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 125 of 304

Starting-off and Driving
124
Starting-off and Driving
Setting steering wheel position
You can set the height and the forward/back position of the steering
wheel to the desired position.
– Adjust the driver seat ⇒page 12.
– Pull the lever below the steering column ⇒fig. 144 down ⇒.
– Set the steering wheel to the desired position (concerning height and forward/back position). – Push the lever upwards as far as the stop.
WARNING
•You must not adjust the steering wh
eel when the vehicle is moving!
•The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering
wheel ⇒fig. 145 . Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the
airbag system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
•For s afe ty re a so ns t he le ve r m ust al wa y s b e fi rm ly pus he d up to a voi d the
steering wheel alteri ng its position unintentionally when driving - risk of
accident!
•If you adjust the steering wheel furthe r towards the head, you will reduce
the protection offered by the driver airb ag in the event of an accident. Check
that the steering wheel is aligned to the chest.
•When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the
outer edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering
wheel firmly in the 12 o'clock position or in another way (e.g. in the middle
of the steering wheel or at the inner steering wheel edge). In such cases,
injuries to the arms, the hands and the head can occur when the driver
airbag is deployed.
Fig. 144 Adjustable steering
wheel: Lever below steering
column
Fig. 145 Safe distance to
steering wheel
20A5Facelift.book Page 124 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 166 of 304

Passive Safety165
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident, we
recommend the following setting:
•Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance between the steering wheel and
your chest is at least 25 cm ⇒page 164, fig. 168 .
•Position the driver seat in the forward/back direction so that you are able to
press the pedals with your legs at a slight angle .
•Adjust the backrest so that you are able to reach the highest point of the steering
wheel with your arms at a slight angle.
•Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the same
level as the upper part of your head ⇒fig. 169 .
•Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 170, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
Manual driver seat adjustment ⇒page 12, “Adjusting the front seats”.
Electrical driver seat adjustment ⇒page 77, “Adjusting front seats electrically*”.
WARNING
•The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your
occupants.
•The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering
wheel ⇒page 164, fig. 168 . Not maintaining this minimum distance will
mean that the airbag system will not be able to properly protect you -
hazard!
•When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the
outer edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering
wheel firmly in the 12 o'clock position or in another way (e.g. in the middle
of the steering wheel or at the inner steering wheel edge). In such cases,
injuries to the arms, the hands and the head can occur when the driver
airbag is deployed.
•The backrests must not be angled to o far back when driving otherwise
this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag system -
risk of injury!
•Ensure that there are no objects in the footwell as any objects may get
behind the pedals during a driving or braking manoeuvre. You would then
no longer be able to operate the clutch, to brake or accelerate.
Correct seated position for the front passenger
The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from
the dash panel so that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety
when an airbag is deployed.
For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of
an accident, we recommend the following setting:
•Adjust the front passenger seat as far as possible to the rear.
•Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the same
level as the upper part of your head ⇒fig. 169 .
•Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 170, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
In exceptional cases the front pass enger airbag can be deactivated ⇒page 181,
“Deactivating an airbag”.
Fig. 169 The correct head
restraint adjustment for the
driver
WARNING (continued)
20A5Facelift.book Page 165 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 167 of 304

Passive Safety
166
Manual front passenger adjustment ⇒page 12, “Adjusting the front seats”.
Electrical front passenger seat adjustment ⇒page 77, “Adjusting front seats electri-
cally*”.
WARNING
•The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your
occupants.
•The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the
dash panel. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the
airbag system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
•Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven - never
place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the
surfaces of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it
becomes necessary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an
airbag is deployed, you may suffer fata l injuries when adopting an incorrect
seated position!
•The backrests must not be angled too far back when driving otherwise
this will affect proper operation of th e seat belts and of the airbag system -
risk of injury!
Correct seated position for the occupants on the rear seats
Occupants on the rear seats must si t upright, keep the feet in the
footwell and must have their se at belts correctly fastened.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an acci-
dent, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following:
•Adjust the head restraints so that the top edge of the head restraints are at the
same level as the upper part of your head ⇒page 165, fig. 169 .
•Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 170, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
•If you are transporting ⇒page 184, “Transporting children safely” children in
the vehicle, please use a suitable child restraint system.
WARNING
•The head restraints must always be adjusted to match the body size, in
order to offer an optimal protection for you and your occupants.
•Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven - never
put your feet out of the window or on the surfaces of the seats. You will be
exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply the brake
or in the event of an accident. If an airbag is deployed, you may suffer fatal
injuries when adopting an incorrect seated position!
•If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury
is increased due to incorrec t routing of the seat belt.
Examples of an incorrect seated position
An incorrect seated position can lead to severe injuries or death for
the occupants.
Seat belts offer their optimum protection on ly if the webbing of the seat belts is
properly routed. Incorrect seated positio ns considerably reduce the protective
functions of the seat belts and therefore incr ease the risk of injury due to an incor-
rect routing of the seat belt. The driver is fully responsible for himself and the occu-
pants, in particular for the children. Do not permit an occupant to adopt an incor-
rect seated position when the car is moving.
The following list contains the examples of seated positions which are dangerous
for the occupants. This list is not comple te, however we would like you to get inter-
ested in this subject.
Therefore, while the car is moving never:
•stand up in the vehicle,
•stand up on the seats,
•kneel onto the seats,
•tilt the backrest fully to the back,
20A5Facelift.book Page 166 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 168 of 304

Passive Safety167
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
•lean against the dash panel,
•lie on the rear seats,
•only sit on the front area of the seat,
•sit to the side,
•lean out of the window,
•put the feet out of the window,
•put the feet on the dash panel,
•put the feet on the seat upholstery,
•occupy the footwell,
•have the seat belt not fastened,
•occupy the luggage compartment.
WARNING
•If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
•Before setting off, please adopt the correct seated position and do not
change this seated position while the car is moving. Also advise your occu-
pants to adopt the correct seated position and not to change this seated
position while the car is moving.
20A5Facelift.book Page 167 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 169 of 304

Seat belts
168
Seat belts
Why seat belts?
It is a proven fact that seat belt s offer good protection in accidents ⇒fig. 170 . Thus
wearing a seat belt is a legal requirement in most countries.
Seat belts which have been correctly fastened and adjusted hold the occupants of
the car in the correc t seated position ⇒fig. 170 . The belts reduce the kinetic energy
(energy of motion) to a considerable extent. They also prevent uncontrolled move-
ments which, in turn, may well result in severe injuries.
The occupants of a vehicle who have fastened and correctly adjusted their seat belt,
profit to a major extent from the fact that the kinetic energy is optimally absorbed
by the belts. The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other passive safety
measures, such as the airbag system, also contribute to reducing the kinetic energy.
The energy produced is thus absorbed and there is less risk of injury.
Accident statistics prove that seat belts which are fastened and properly adjusted
reduce the risk of an injury and enhance the chance of survival in a major accident
⇒ page 169. It is important that you pay attention to
safety measures, particularly when trans-
porting children in the vehicle ⇒page 184, “What you should know about trans-
porting children!”.
WARNING
•Fasten your seat belt each time before setting off, also when driving in
town! This also applies to the people seated at the rear - risk of injury!
•Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way
of ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child ⇒page 170.
•It is important for the belt webbing to be properly routed if the seat belts
are to offer the maximum protection. You can see a description of how safety
belts should be fitted pr operly on the next pages.
Note
Please comply with any differing legal requirements when using the seat belts.
Fig. 170 Driver wearing seat
belt
20A5Facelift.book Page 168 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM
Page 173 of 304

Seat belts
172
Taking seat belts off
– Press the red button in the belt lock ⇒fig. 176 . The spring force causes
the tongue of the lock to jump out.
– Guide the belt back with your hand to enable the inertia reel to wind
up the belt webbing more easily.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is easy
to get hold of.
Three-point safety belt for the middle rear seat
Your car is equipped as standa rd with the three-point seat belt in the middle rear
seat. It is used in the same way as the three-point seat belts on the left and right (at
front and rear).
WARNING
The three-point safety belt for the rear middle seat can only fulfil its function
reliably when the backrests are correctly locked into position ⇒page 81.
Belt tensioners
Safety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced by
the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat belts, in
addition to the protection af forded by the airbag system.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal colli-
sion of a certain severity. Th e belt tensioners can also be deployed if the seat belts
are not fastened.
The belt tensioner is deployed in the event of a frontal collision of major severity. A
powder charge is ignited in the inertia reels during deployment. The belt webbing
is pulled into the inertia reels by a mech anical system and the belt is tensioned.
The belt tensioners are not activated in case of minor frontal and rear-end colli-
sions, in the case of vehicle rollover or accidents, through which no long delays are
incurred to the vehicle. In the case of a side collision, only the belt tensioner of the
front seat on the side on which th e collision takes place is deployed.
WARNING
•Any work on the system including removal and installation of system
components because of other repair work, must only be carried out by a
specialist garage.
•The protective function of the system is only adequate for a single acci-
dent. If the belt tensioners have been deployed, it is then necessary to
replace the entire system.
•The Owner's Manual must also be ha nded over to the new owner if the
vehicle is sold.
Note
•Smoke is generated when the belt tensione rs are deployed. This is not an indi-
cation of a fire in the vehicle.
•It is essential to pay attention to relevant safety regulations if the vehicle or indi-
vidual parts of the system are scrapped. Specialist garages are familiar with these
regulations and will be able to provide you with detailed information in this respect.
Fig. 176 Releasing lock
tongue from belt lock
20A5Facelift.book Page 172 Saturday, September 6, 2008 2:13 PM