2008 NISSAN TIIDA ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 2141 of 2771
LT-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HEADLAMP (FOR USA)
HEADLAMP (FOR USA)
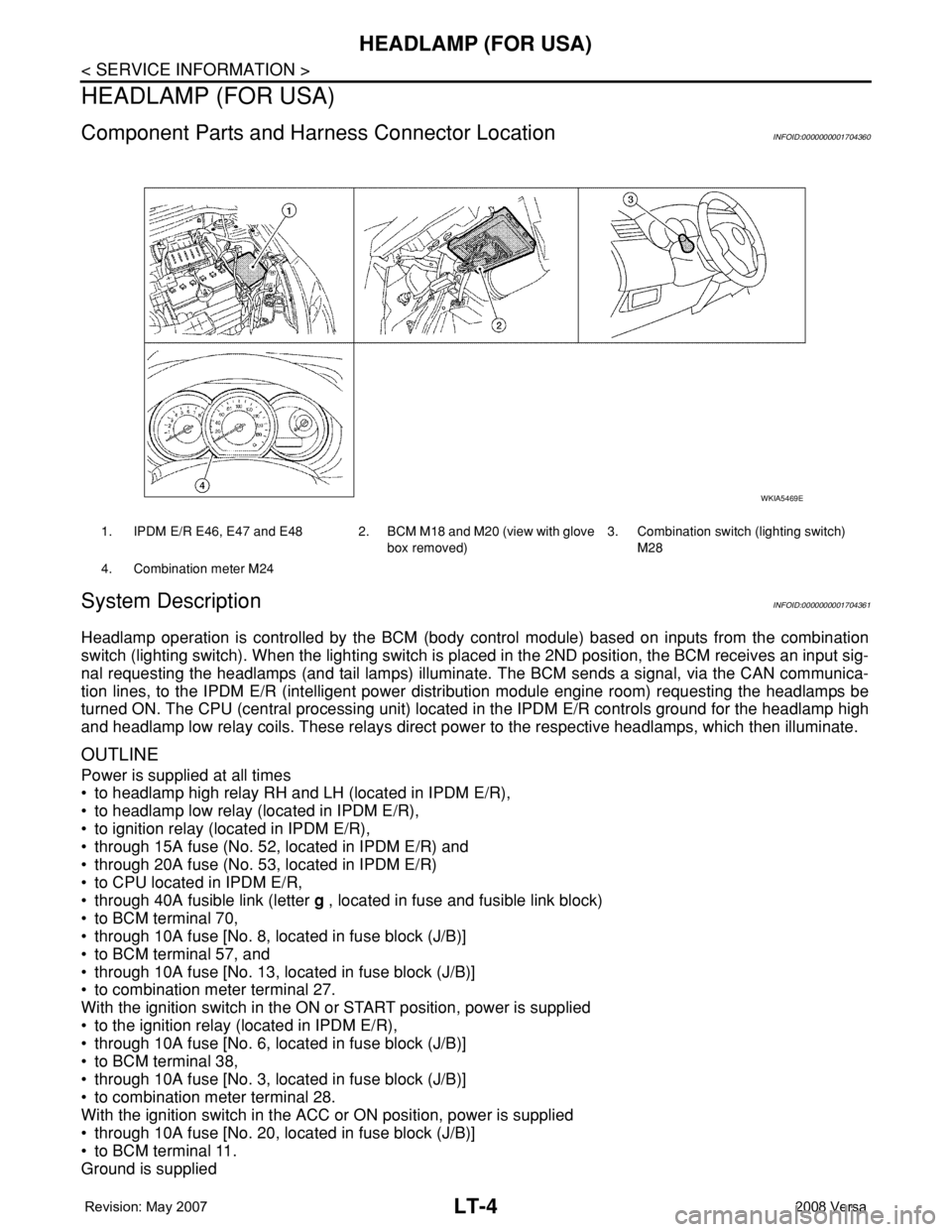
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationINFOID:0000000001704360
System DescriptionINFOID:0000000001704361
Headlamp operation is controlled by the BCM (body control module) based on inputs from the combination
switch (lighting switch). When the lighting switch is placed in the 2ND position, the BCM receives an input sig-
nal requesting the headlamps (and tail lamps) illuminate. The BCM sends a signal, via the CAN communica-
tion lines, to the IPDM E/R (intelligent power distribution module engine room) requesting the headlamps be
turned ON. The CPU (central processing unit) located in the IPDM E/R controls ground for the headlamp high
and headlamp low relay coils. These relays direct power to the respective headlamps, which then illuminate.
OUTLINE
Power is supplied at all times
• to headlamp high relay RH and LH (located in IPDM E/R),
• to headlamp low relay (located in IPDM E/R),
• to ignition relay (located in IPDM E/R),
• through 15A fuse (No. 52, located in IPDM E/R) and
• through 20A fuse (No. 53, located in IPDM E/R)
• to CPU located in IPDM E/R,
• through 40A fusible link (letter g , located in fuse and fusible link block)
• to BCM terminal 70,
• through 10A fuse [No. 8, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 57, and
• through 10A fuse [No. 13, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to combination meter terminal 27.
With the ignition switch in the ON or START position, power is supplied
• to the ignition relay (located in IPDM E/R),
• through 10A fuse [No. 6, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 38,
• through 10A fuse [No. 3, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to combination meter terminal 28.
With the ignition switch in the ACC or ON position, power is supplied
• through 10A fuse [No. 20, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 11.
Ground is supplied
1. IPDM E/R E46, E47 and E48 2. BCM M18 and M20 (view with glove
box removed)3. Combination switch (lighting switch)
M28
4. Combination meter M24
WKIA5469E
Page 2162 of 2771
HEADLAMP (FOR CANADA) - DAYTIME LIGHT SYSTEM -
LT-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
LT
N
O
P
HEADLAMP (FOR CANADA) - DAYTIME LIGHT SYSTEM -
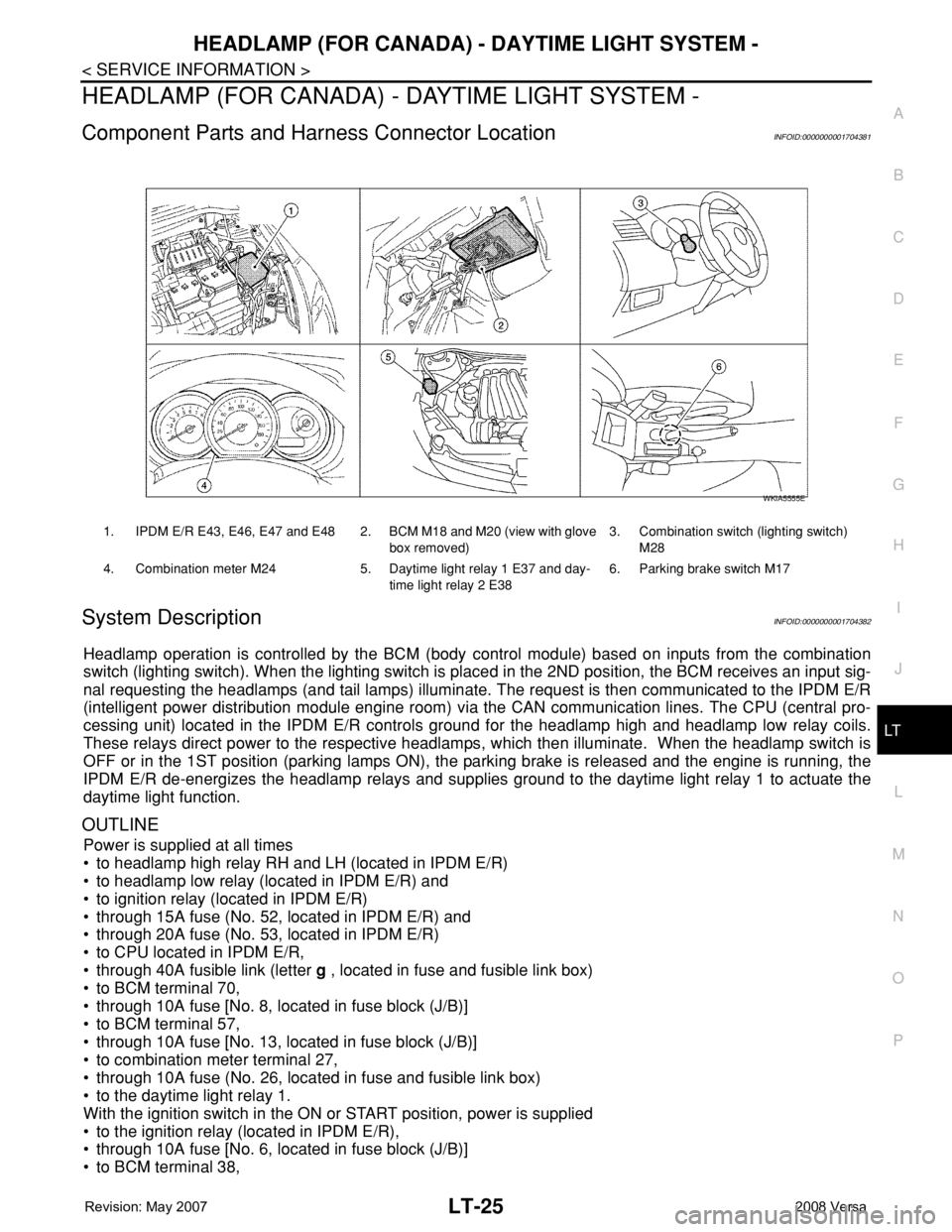
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationINFOID:0000000001704381
System DescriptionINFOID:0000000001704382
Headlamp operation is controlled by the BCM (body control module) based on inputs from the combination
switch (lighting switch). When the lighting switch is placed in the 2ND position, the BCM receives an input sig-
nal requesting the headlamps (and tail lamps) illuminate. The request is then communicated to the IPDM E/R
(intelligent power distribution module engine room) via the CAN communication lines. The CPU (central pro-
cessing unit) located in the IPDM E/R controls ground for the headlamp high and headlamp low relay coils.
These relays direct power to the respective headlamps, which then illuminate. When the headlamp switch is
OFF or in the 1ST position (parking lamps ON), the parking brake is released and the engine is running, the
IPDM E/R de-energizes the headlamp relays and supplies ground to the daytime light relay 1 to actuate the
daytime light function.
OUTLINE
Power is supplied at all times
• to headlamp high relay RH and LH (located in IPDM E/R)
• to headlamp low relay (located in IPDM E/R) and
• to ignition relay (located in IPDM E/R)
• through 15A fuse (No. 52, located in IPDM E/R) and
• through 20A fuse (No. 53, located in IPDM E/R)
• to CPU located in IPDM E/R,
• through 40A fusible link (letter g , located in fuse and fusible link box)
• to BCM terminal 70,
• through 10A fuse [No. 8, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 57,
• through 10A fuse [No. 13, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to combination meter terminal 27,
• through 10A fuse (No. 26, located in fuse and fusible link box)
• to the daytime light relay 1.
With the ignition switch in the ON or START position, power is supplied
• to the ignition relay (located in IPDM E/R),
• through 10A fuse [No. 6, located in fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 38,
1. IPDM E/R E43, E46, E47 and E48 2. BCM M18 and M20 (view with glove
box removed)3. Combination switch (lighting switch)
M28
4. Combination meter M24 5. Daytime light relay 1 E37 and day-
time light relay 2 E386. Parking brake switch M17
WKIA5555E
Page 2200 of 2771

COMBINATION SWITCH
LT-63
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
LT
N
O
P
Terminal and Reference Value for BCMINFOID:0000000001704434
Refer to BCS-11, "Terminal and Reference Value for BCM" .
CONSULT-III Function (BCM)INFOID:0000000001704435
Refer to LT- 11 , "CONSULT-III Function (BCM)" .
Combination Switch InspectionINFOID:0000000001704436
1.SYSTEM CHECK
Referring to table below, check which system malfunctioning switch belongs to.
>> Check the system to which the switch belongs, and GO TO 2.
2.SYSTEM CHECK
With CONSULT-III
CAUTION:
If CONSULT-III is used with no connection of CONSULT-III CONVERTER, malfunctions might be
detected in self-diagnosis depending on control unit which carry out CAN communication.
1. Connect CONSULT-III, and select “COMB SW” on “SELECT TEST ITEM” screen.
2. Select “DATA MONITOR”.
3. Select “START”, and confirm that other switches in the system operate normally.
Example: When turn signal LH is inoperative, confirm that PASSING, HEAD LAMP 2 or FRONT FOG (if
equipped) turn ON-OFF normally.
Without CONSULT-III
Operating combination switch, and confirm that other switches in the system operate normally.
Example: When a turn signal switch is inoperative, confirm that FRONT WIPER LO or FRONT WIPER INT
turn ON-OFF normally.
Check results
Other switches in the system operate normally.>>Replace lighting switch or wiper switch.
Other switches in the system do not operate normally.>>GO TO 3.
3.HARNESS INSPECTION
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector and combination switch connector.
3. Check for continuity between BCM harness connector of the suspect system and the corresponding com-
bination switch harness connector.
System 1 System 2 System 3 System 4 System 5
— FRONT WASHER FRONT WIPER LO TURN LH TURN RH
FRONT WIPER HI — FRONT WIPER INT PASSING HEAD LAMP 1
INT VOLUME 1 — — HEAD LAMP 2 HI BEAM
— INT VOLUME 3 — — LIGHT SW 1ST
INT VOLUME 2 — — FRONT FOG —
Page 2394 of 2771
MTC-56
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CONTROLLER
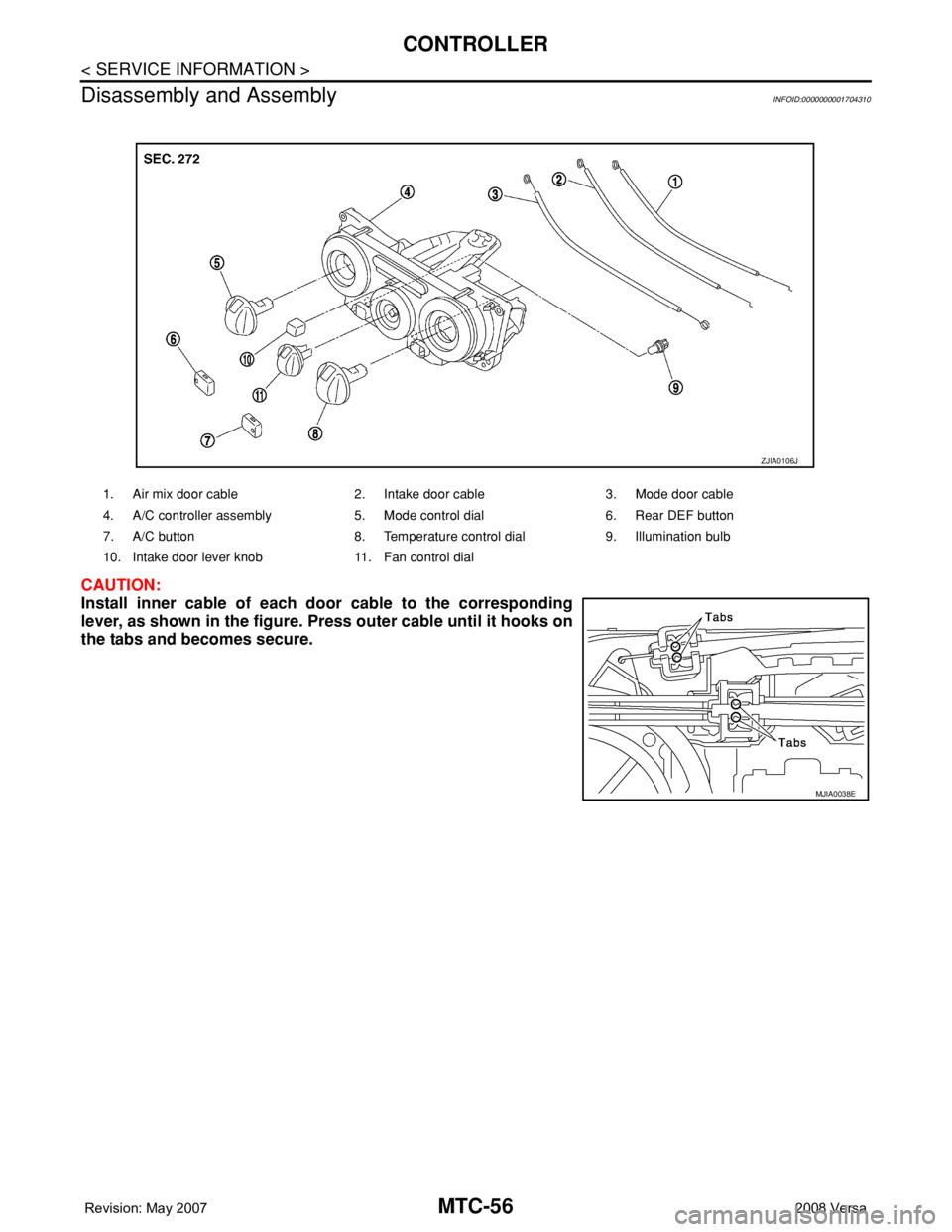
Disassembly and Assembly
INFOID:0000000001704310
CAUTION:
Install inner cable of each door cable to the corresponding
lever, as shown in the figure. Press outer cable until it hooks on
the tabs and becomes secure.
1. Air mix door cable 2. Intake door cable 3. Mode door cable
4. A/C controller assembly 5. Mode control dial 6. Rear DEF button
7. A/C button 8. Temperature control dial 9. Illumination bulb
10. Intake door lever knob 11. Fan control dial
ZJIA0106J
MJIA0038E
Page 2448 of 2771
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING CIRCUIT
PG-15
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
PG
N
O
P
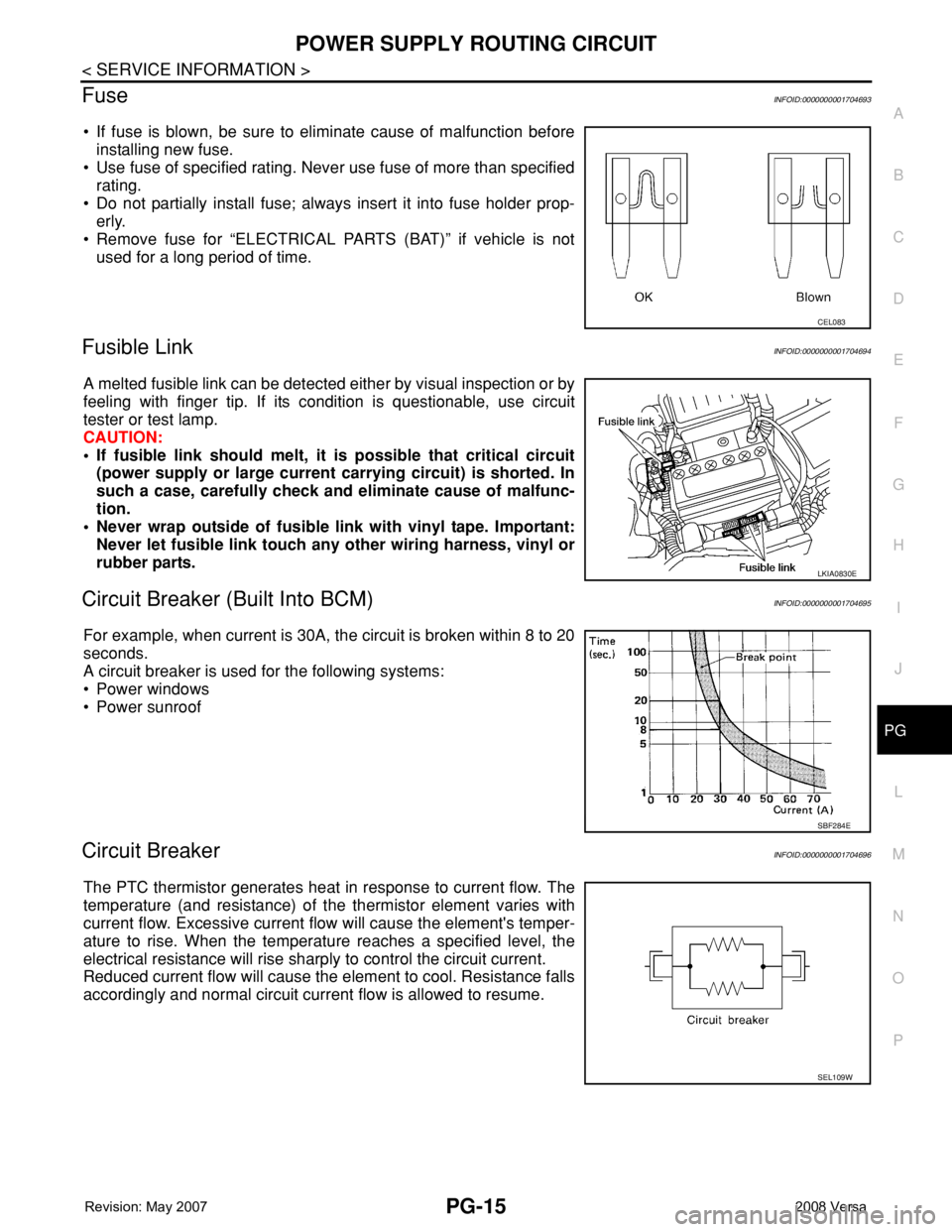
FuseINFOID:0000000001704693
• If fuse is blown, be sure to eliminate cause of malfunction before
installing new fuse.
• Use fuse of specified rating. Never use fuse of more than specified
rating.
• Do not partially install fuse; always insert it into fuse holder prop-
erly.
• Remove fuse for “ELECTRICAL PARTS (BAT)” if vehicle is not
used for a long period of time.
Fusible LinkINFOID:0000000001704694
A melted fusible link can be detected either by visual inspection or by
feeling with finger tip. If its condition is questionable, use circuit
tester or test lamp.
CAUTION:
• If fusible link should melt, it is possible that critical circuit
(power supply or large current carrying circuit) is shorted. In
such a case, carefully check and eliminate cause of malfunc-
tion.
• Never wrap outside of fusible link with vinyl tape. Important:
Never let fusible link touch any other wiring harness, vinyl or
rubber parts.
Circuit Breaker (Built Into BCM)INFOID:0000000001704695
For example, when current is 30A, the circuit is broken within 8 to 20
seconds.
A circuit breaker is used for the following systems:
• Power windows
• Power sunroof
Circuit BreakerINFOID:0000000001704696
The PTC thermistor generates heat in response to current flow. The
temperature (and resistance) of the thermistor element varies with
current flow. Excessive current flow will cause the element's temper-
ature to rise. When the temperature reaches a specified level, the
electrical resistance will rise sharply to control the circuit current.
Reduced current flow will cause the element to cool. Resistance falls
accordingly and normal circuit current flow is allowed to resume.
CEL083
LKIA0830E
SBF284E
SEL109W
Page 2498 of 2771
HARNESS CONNECTOR
PG-65
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
PG
N
O
P
HARNESS CONNECTOR
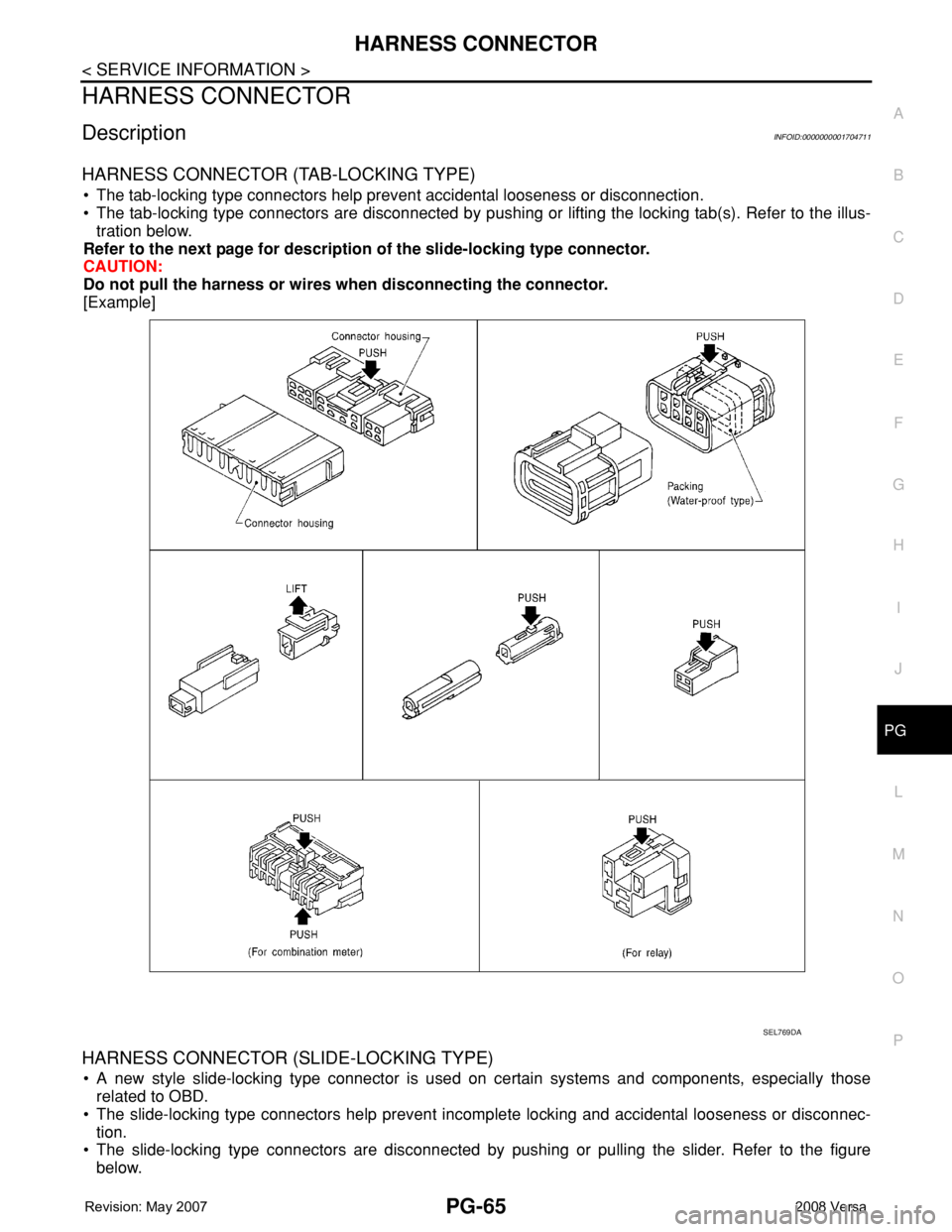
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001704711
HARNESS CONNECTOR (TAB-LOCKING TYPE)
• The tab-locking type connectors help prevent accidental looseness or disconnection.
• The tab-locking type connectors are disconnected by pushing or lifting the locking tab(s). Refer to the illus-
tration below.
Refer to the next page for description of the slide-locking type connector.
CAUTION:
Do not pull the harness or wires when disconnecting the connector.
[Example]
HARNESS CONNECTOR (SLIDE-LOCKING TYPE)
• A new style slide-locking type connector is used on certain systems and components, especially those
related to OBD.
• The slide-locking type connectors help prevent incomplete locking and accidental looseness or disconnec-
tion.
• The slide-locking type connectors are disconnected by pushing or pulling the slider. Refer to the figure
below.
SEL769DA
Page 2534 of 2771
RF-4
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Work FlowINFOID:0000000001704188
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
SBT842
Page 2612 of 2771
SE-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Work FlowINFOID:0000000001704259
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to SE-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
SBT842