Page 262 of 283
727
Maintenance
Remove the valve cap from the tire
valve stem. Press the tire gauge firm-
ly onto the valve to get a pressure
measurement. If the cold tire inflation
pressure matches the recommended
pressure on the tire and loading
information label, no further adjust-
ment is necessary. If the pressure is
low, add air until you reach the rec-
ommended amount.
If you overfill the tire, release air by
pushing on the metal stem in the cen-
ter of the tire valve. Recheck the tire
pressure with the tire gauge. Be sure
to put the valve caps back on the
valve stems. They help prevent leaks
by keeping out dirt and moisture.Tire rotation
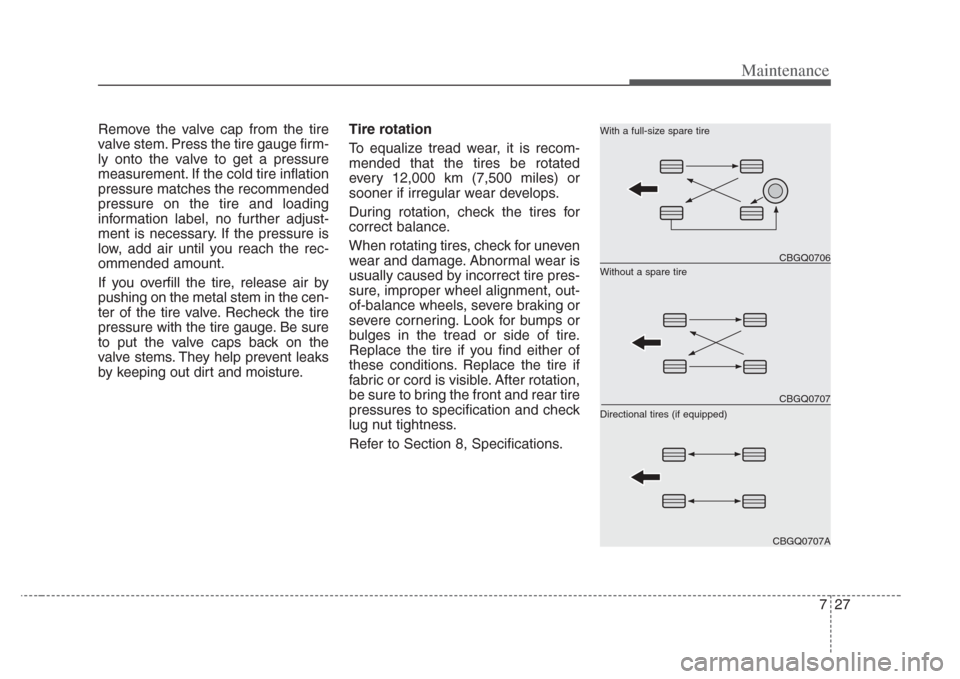
To equalize tread wear, it is recom-
mended that the tires be rotated
every 12,000 km (7,500 miles) or
sooner if irregular wear develops.
During rotation, check the tires for
correct balance.
When rotating tires, check for uneven
wear and damage. Abnormal wear is
usually caused by incorrect tire pres-
sure, improper wheel alignment, out-
of-balance wheels, severe braking or
severe cornering. Look for bumps or
bulges in the tread or side of tire.
Replace the tire if you find either of
these conditions. Replace the tire if
fabric or cord is visible. After rotation,
be sure to bring the front and rear tire
pressures to specification and check
lug nut tightness.
Refer to Section 8, Specifications.
CBGQ0706
CBGQ0707
CBGQ0707A
Without a spare tire With a full-size spare tire
Directional tires (if equipped)
Page 263 of 283
Maintenance
287
Disc brake pads should be inspectedfor wear whenever tires are rotated.
Rotate radial tires that have an
a symmetric tread pattern only
from front to rear and not from
right to left.
Tire replacement
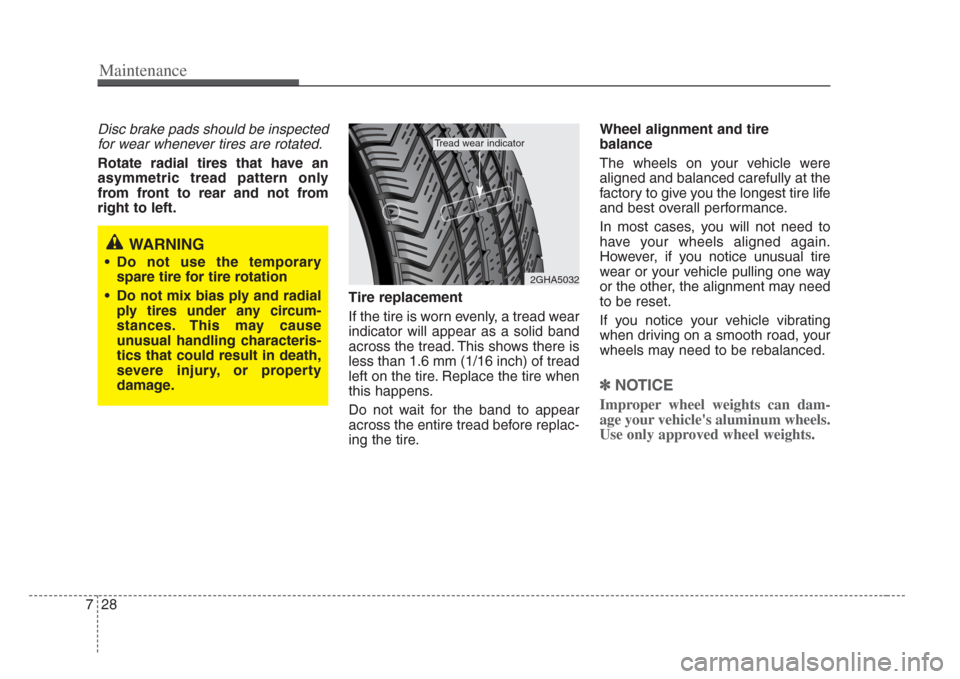
If the tire is worn evenly, a tread wear
indicator will appear as a solid band
across the tread. This shows there is
less than 1.6 mm (1/16 inch) of tread
left on the tire. Replace the tire when
this happens.
Do not wait for the band to appear
across the entire tread before replac-
ing the tire.Wheel alignment and tire
balance
The wheels on your vehicle were
aligned and balanced carefully at the
factory to give you the longest tire life
and best overall performance.
In most cases, you will not need to
have your wheels aligned again.
However, if you notice unusual tire
wear or your vehicle pulling one way
or the other, the alignment may need
to be reset.
If you notice your vehicle vibrating
when driving on a smooth road, your
wheels may need to be rebalanced.
✽
NOTICE
Improper wheel weights can dam-
age your vehicle's aluminum wheels.
Use only approved wheel weights.
2GHA5032
Tread wear indicator
WARNING
• Do not us e the temporary
spare tire for tire rotation
• Do not mix bias ply and radial ply tires under any circum-
stances . This may caus e
unusual handling characteri s-
tics that could re sult in death,
s evere injury, or property
damage.
Page 266 of 283

731
Maintenance
86 - Load Index, a numerical codeassociated with the maximum
load the tire can carry.
H - Speed Rating Symbol. See the speed rating chart in this section
for additional information.
Wheel size designation
Wheels are also marked with impor-
tant information that you need if you
ever have to replace one. The follow-
ing explains what the letters and
numbers in the wheel size designa-
tion mean.
Example wheel size designation:
5.5JX14
5.5 - Rim width in inches.
J - Rim contour designation.
14 - Rim diameter in inches. Tire speed ratings
The chart below lists many of the dif-
ferent speed ratings currently being
used for passenger cars. The speed
rating is part of the tire size designa-
tion on the sidewall of the tire. This
symbol corresponds to that tire's
designed maximum safe operating
speed.3. Checking tire life (TIN : Tire
Identification Number)
Any tires that are over 6 years, based
on the manufacturing date, tire
strength and performance, decline
with age naturally (even unused
spare tires). Therefore, the tires
(including the spare tire) should be
replaced by new ones. You can find
the manufacturing date on the tire
sidewall (possibly on the inside of the
wheel), displaying the DOT Code.
The DOT Code is a series of num-
bers on a tire consisting of numbers
and English letters. The manufactur-
ing date is designated by the last four
digits (characters) of the DOT code.
DOT : XXXX XXXX OOOO
The front part of the DOT means a
plant code number, tire size and
tread pattern and the last four num-
bers indicate week and year manu-
factured.
For example:
DOT XXXX XXXX 1606 represents
that the tire was produced in the 16th
week of 2006.
S 112 mph (180 km/h)
T 118 mph (190 km/h)
H 130 mph (210 km/h) V 149 mph (240 km/h)Z Above 149 mph (240 km/h)
Maximum Speed
Speed
Rating
Symbol
Page 279 of 283
83
Specifications
LubricantVolume Classification
Engine oil *1
5.2l(5.49 US qt.) API Service SL or above,
(with filter change) ILSAC GF-3 or above
Transaxle fluid 10.9 l(11.5 US qt.) DIAMOND ATF SP-III or SK ATF SP-III
Power steering 1.0 l (1.1 US qt.)PSF-IV
Coolant 8.7 l(9.2 US qt.) Ethylene glycol base for aluminum radiator
Brake fluid 0.7~0.8 l(0.7~0.8 US qt.) FMVSS116 DOT-3 or DOT-4
Fuel 70 l(18.5 US gal) Unleaded gasoline with AKI 87 or higher
*¹Refer to the recommended SAE viscosity numbers on the page 7-37.
Tires
Item Recommended Cold TireWheel lug nut torque
Tire Wheel Inflation Pressure
kPa (psi) kg·m (lb·ft, N·m)
Full size tire
P235/55 R 17 6.5J×17 210 (30) 9~11 (65~79, 88~107)
P225/60 R 16 6.5J×16 210 (30) 9~11 (65~79, 88~107)
Compact spare tire
T125/80D16 420 (60) 9~11 (65~79, 88~107)
Capacities