2008 CHEVROLET AVEO change wheel
[x] Cancel search: change wheelPage 75 of 384

Adding Equipment to Your
Airbag-Equipped Vehicle
Q:Is there anything I might add to or change
about the vehicle that could keep the airbags
from working properly?
A:Yes. If you add things that change your vehicle’s
frame, bumper system, height, front end or side
sheet metal, they may keep the airbag system from
working properly. Changing or moving any parts
of the front seats, safety belts, the airbag sensing
and diagnostic module, steering wheel, instrument
panel, front sensors, or airbag wiring can affect
the operation of the airbag system.
In addition, your vehicle has a passenger sensing
system for the right front passenger’s position,
which includes sensors that are part of the
passenger’s seat. The passenger sensing system
may not operate properly if the original seat
trim is replaced with non-GM covers, upholstery
or trim, or with GM covers, upholstery or trim
designed for a different vehicle. Any object, such
as an aftermarket seat heater or a comfort
enhancing pad or device, installed under or on
top of the seat fabric, could also interfere with
the operation of the passenger sensing system.This could either prevent proper deployment of
the passenger airbag(s) or prevent the passenger
sensing system from properly turning off the
passenger airbag(s). SeePassenger Sensing
System on page 1-65.
If you have any questions about this, you should
contact Customer Assistance before you modify
your vehicle. The phone numbers and addresses
for Customer Assistance are in Step Two of
the Customer Satisfaction Procedure in this manual.
SeeCustomer Satisfaction Procedure on page 7-2.
Q:Because I have a disability, I have to get
my vehicle modi�ed. How can I �nd out whether
this will affect my airbag system?
A:If you have questions, call Customer Assistance.
The phone numbers and addresses for Customer
Assistance are in Step Two of the Customer
Satisfaction Procedure in this manual. See
Customer Satisfaction Procedure on page 7-2.
In addition, your dealer/retailer and the service manual
have information about the location of the airbag
sensors, sensing and diagnostic module and airbag
wiring.
1-71
Page 115 of 384

Instrument Panel Overview...............................3-4
Hazard Warning Flashers................................3-8
Other Warning Devices...................................3-8
Horn.............................................................3-8
Tilt Wheel.....................................................3-9
Turn Signal/Multifunction Lever.........................3-9
Turn and Lane-Change Signals.......................3-10
Headlamp High/Low-Beam Changer.................3-10
Flash-to-Pass...............................................3-10
Windshield Wipers........................................3-11
Windshield Washer.......................................3-12
Rear Window Wiper/Washer (Hatchback).........3-12
Cruise Control..............................................3-13
Exterior Lamps.............................................3-15
Headlamps on Reminder................................3-16
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL).......................3-16
Fog Lamps..................................................3-17
Instrument Panel Brightness...........................3-17
Dome Lamp.................................................3-18
Inadvertent Power Battery Saver.....................3-18
Accessory Power Outlet(s).............................3-18
Ashtray(s) and Cigarette Lighter......................3-19
Clock..........................................................3-20Climate Controls............................................3-20
Climate Control System.................................3-20
Outlet Adjustment.........................................3-24
Passenger Compartment Air Filter...................3-24
Warning Lights, Gages, and Indicators............3-26
Instrument Panel Cluster................................3-27
Speedometer and Odometer...........................3-29
Trip Odometer..............................................3-29
Tachometer.................................................3-29
Safety Belt Reminders...................................3-30
Airbag Readiness Light.................................
.3-30
Passenger Airbag Status Indicator (Sedan).......3-31
Charging System Light..................................3-33
Brake System Warning Light..........................3-33
Antilock Brake System Warning Light...............3-34
Hold Mode Light...........................................3-35
Engine Coolant Temperature Gage..................3-35
Tire Pressure Light.......................................3-36
Malfunction Indicator Lamp.............................3-36
Oil Pressure Light.........................................3-39
Fog Lamp Light............................................3-40
Cruise Control Light......................................3-40
Section 3 Instrument Panel
3-1
Page 123 of 384
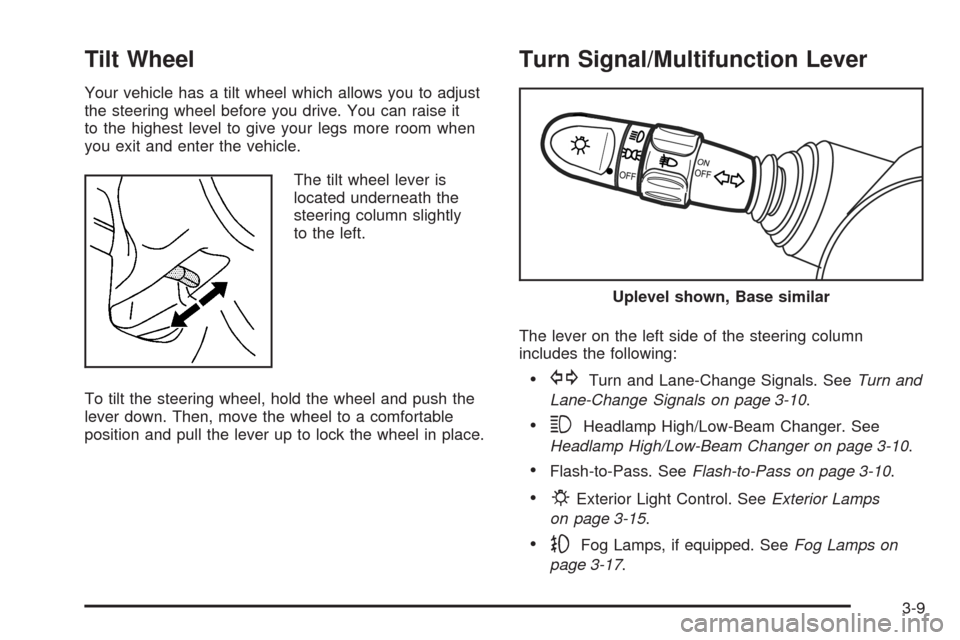
Tilt Wheel
Your vehicle has a tilt wheel which allows you to adjust
the steering wheel before you drive. You can raise it
to the highest level to give your legs more room when
you exit and enter the vehicle.
The tilt wheel lever is
located underneath the
steering column slightly
to the left.
To tilt the steering wheel, hold the wheel and push the
lever down. Then, move the wheel to a comfortable
position and pull the lever up to lock the wheel in place.
Turn Signal/Multifunction Lever
The lever on the left side of the steering column
includes the following:
•GTurn and Lane-Change Signals. SeeTurn and
Lane-Change Signals on page 3-10.
•3Headlamp High/Low-Beam Changer. See
Headlamp High/Low-Beam Changer on page 3-10.
•Flash-to-Pass. SeeFlash-to-Pass on page 3-10.
•PExterior Light Control. SeeExterior Lamps
on page 3-15.
•-Fog Lamps, if equipped. SeeFog Lamps on
page 3-17.
Uplevel shown, Base similar
3-9
Page 127 of 384
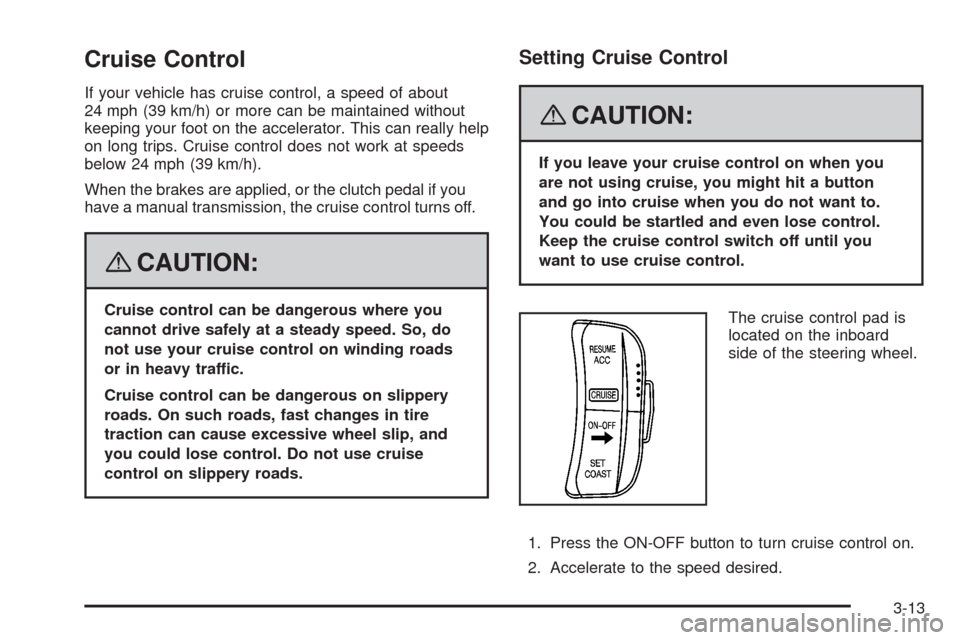
Cruise Control
If your vehicle has cruise control, a speed of about
24 mph (39 km/h) or more can be maintained without
keeping your foot on the accelerator. This can really help
on long trips. Cruise control does not work at speeds
below 24 mph (39 km/h).
When the brakes are applied, or the clutch pedal if you
have a manual transmission, the cruise control turns off.
{CAUTION:
Cruise control can be dangerous where you
cannot drive safely at a steady speed. So, do
not use your cruise control on winding roads
or in heavy traffic.
Cruise control can be dangerous on slippery
roads. On such roads, fast changes in tire
traction can cause excessive wheel slip, and
you could lose control. Do not use cruise
control on slippery roads.
Setting Cruise Control
{CAUTION:
If you leave your cruise control on when you
are not using cruise, you might hit a button
and go into cruise when you do not want to.
You could be startled and even lose control.
Keep the cruise control switch off until you
want to use cruise control.
The cruise control pad is
located on the inboard
side of the steering wheel.
1. Press the ON-OFF button to turn cruise control on.
2. Accelerate to the speed desired.
3-13
Page 192 of 384

When information is not available, No Info (information)
displays.
Press this button for longer than two seconds to change
display mode.
Audio Steering Wheel Controls
If your vehicle has this feature, some audio controls can
be adjusted at the steering wheel. They include the
following:
PWR (Power):Press and release this knob to turn the
system on. Press and hold this knob for more than
two seconds to turn the system off.When the system is on, press and release this knob to
mute the system. Press and release this knob again
to turn the sound back on.
SEEK:Press and release this button within 0.5 seconds
to go to the next preset station.
Press and hold this button for longer than 0.5 seconds to
go to the next radio station. The radio seeks stations only
with a strong signal that are in the selected band.
When playing a CD, press and release this button within
0.5 seconds to go to the next track. Press and hold this
button for longer than 0.5 seconds to fast forward through
the tracks.
MODE:Press and release this button to select FM1,
FM2, FM-A, AM1, AM2, AM-A, or CD (MP3). Press and
release this button multiple times to cycle through the
audio playback options that are available on your
vehicle.
+ VOLUME−:Press the toggle bar located below
the + VOLUME−to adjust the volume. Press the left
side of the toggle bar, below the + (plus) sign to increase
the volume. Press the right side of the toggle bar,
below the−(minus) sign to decrease the volume. Front View of the
Steering Wheel Controls
Side View of the Volume
Control
3-78
Page 199 of 384

ABS can change the brake pressure faster than any
driver could. The computer is programmed to make the
most of available tire and road conditions. This can
help you steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As you brake, the computer keeps receiving updates
on wheel speed and controls braking pressure
accordingly.
Remember: ABS does not change the time you need to
get your foot up to the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too close to the vehicle
in front of you, you will not have time to apply the brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops. Always leave
enough room up ahead to stop, even though you
have ABS.
Using ABS
Do not pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal
down firmly and let antilock work for you. You might
feel a slight brake pedal pulsation or notice some
noise, but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
At some time, nearly every driver gets into a situation
that requires hard braking.
If you have ABS, you can steer and brake at the same
time. However, if you do not have ABS, your first
reaction — to hit the brake pedal hard and hold it
down — might be the wrong thing to do. Your wheels
can stop rolling. Once they do, the vehicle cannot
respond to your steering. Momentum will carry it in
whatever direction it was headed when the wheels
stopped rolling. That could be off the road, into the
very thing you were trying to avoid, or into traffic.
If you do not have ABS, use a “squeeze” braking
technique. This will give you maximum braking while
maintaining steering control. You can do this by pushing
on the brake pedal with steadily increasing pressure.
In an emergency, you will probably want to squeeze
the brakes hard without locking the wheels. If you hear
or feel the wheels sliding, ease off the brake pedal.
This will help you retain steering control. If you do have
ABS, it is different. SeeAntilock Brake System (ABS)
on page 4-4.
In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the very best braking.
4-5
Page 200 of 384

Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer
but it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
It is important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned
on the news happen on curves. Here is why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject
to the same laws of physics when driving on curves.
The traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it possible for the vehicle to change its path when
you turn the front wheels. If there is no traction, inertia
will keep the vehicle going in the same direction.
If you have ever tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice,
you will understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of the tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you
are in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Suppose you are steering through a sharp curve.
Then you suddenly apply the brakes. Both control
systems — steering and braking — have to do theirwork where the tires meet the road. Unless you have
antilock brakes, adding the hard braking can demand
too much of those places. You can lose control.
The same thing can happen if you are steering through
a sharp curve and you suddenly accelerate. Those
two control systems — steering and acceleration — can
overwhelm those places where the tires meet the road
and make you lose control.
What should you do if this ever happens? Ease up on
the brake or accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the
way you want it to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should adjust
your speed. Of course, the posted speeds are based on
good weather and road conditions. Under less favorable
conditions you will want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while the front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed so you can drive through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait
to accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
Adding non-dealer/non-retailer accessories can affect
your vehicle’s performance. SeeAccessories and
Modifications on page 5-3.
4-6
Page 203 of 384

Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not overdriving
those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, the wheels
are not rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to
slip and lose cornering force. And in the acceleration
skid, too much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best
handled by easing your foot off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough,
your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs.Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel, or other material is on the road. For safety,
you will want to slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with reduced traction,
try your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration,
or braking, including reducing vehicle speed by shifting
to a lower gear. Any sudden changes could cause
the tires to slide. You may not realize the surface
is slippery until your vehicle is skidding. Learn to
recognize warning clues — such as enough water,
ice, or packed snow on the road to make a mirrored
surface — and slow down when you have any doubt.
If you have the Antilock Brake System (ABS), remember:
It helps avoid only the braking skid. If you do not have
ABS, then in a braking skid, where the wheels are no
longer rolling, release enough pressure on the brakes to
get the wheels rolling again. This restores steering
control. Push the brake pedal down steadily when you
have to stop suddenly. As long as the wheels are rolling,
you will have steering control.
4-9