2008 AUDI S4 warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 216 of 342
Child safety
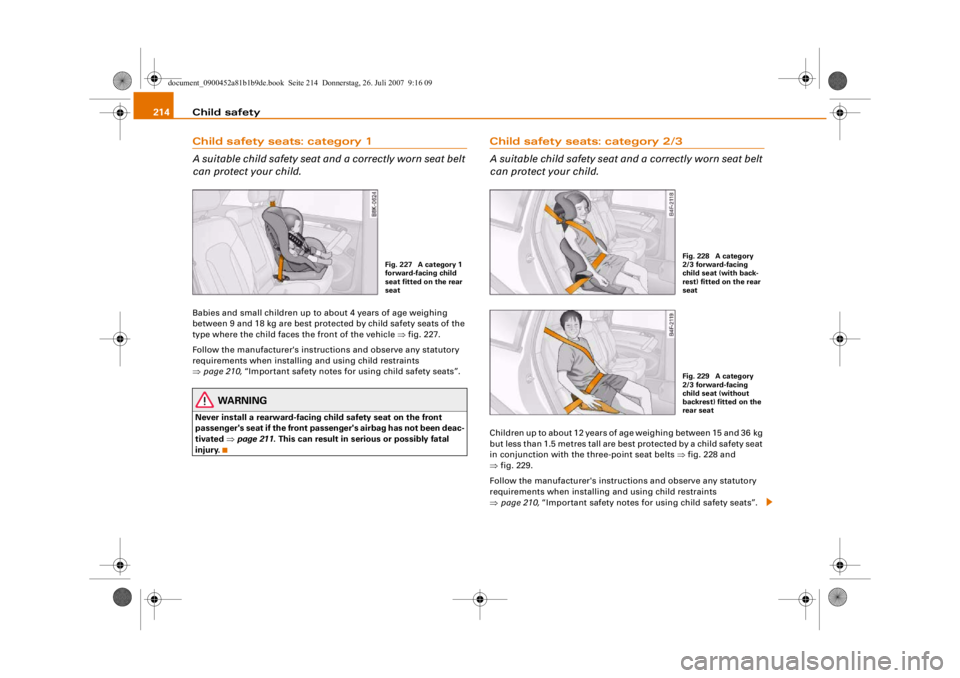
214Child safety seats: category 1
A suitable child safety seat and a correctly worn seat belt
can protect your child.Babies and small children up to about 4 years of age weighing
between 9 and 18 kg are best protected by child safety seats of the
type where the child faces the front of the vehicle ⇒fig. 227.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions and observe any statutory
requirements when installing and using child restraints
⇒ page 210, “Important safety notes for using child safety seats”.
WARNING
Never install a rearward-facing child safety seat on the front
passenger's seat if the front pass enger's airbag has not been deac-
tivated ⇒page 211 . This can result in serious or possibly fatal
injury.
Child safety seats: category 2/3
A suitable child safety seat and a correctly worn seat belt
can protect your child.Children up to about 12 years of age weighing between 15 and 36 kg
but less than 1.5 metres tall are best protected by a child safety seat
in conjunction with the three-point seat belts ⇒fig. 228 and
⇒ fig. 229.
Follow the manufacturer's instru ctions and observe any statutory
requirements when installing and using child restraints
⇒ page 210, “Important safety notes for using child safety seats”.
Fig. 227 A category 1
forward-facing child
seat fitted on the rear
seat
Fig. 228 A category
2/3 forward-facing
child seat (with back-
rest) fitted on the rear
seatFig. 229 A category
2/3 forward-facing
child seat (without
backrest) fitted on the
rear seat
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 214 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
-+ +-
Page 217 of 342

Child safety215
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
WARNING
The diagonal part of the belt s hould be positioned roughly over the
centre of the shoulder and fit clos ely against the upper part of the
body. It must never be allowed to run across the neck. The lap part
of the belt should fit closely over the hips. It must not be posi-
tioned over the stomach. Pull the bel t tight if necessary to take up
any slack.
Note
We recommend that you fit child safety seats with backrests.
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 215 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
[I]
•
-+ +-
Page 220 of 342
Child safety
218Possible alternatives for securing a child safety seat
A child safety seat can be secured on the rear seats and
on the front passenger's seat.The following alternatives are available for safely securing a child
safety seat on the rear seats and on the front passenger's seat.•
Child safety seats of the categories 0 to 3 can be secured with the
standard three-point seat belts.
•
Child safety seats of the categories 0, 0+ and 1 with the “ISOFIX”
system can be secured without seat belts using the “ ISOFIX”
retainers* ⇒page 218 .
Compatibility of vehicle seat positions for child safety seats
(according to EC directive 77/541):
“universally compatible”
The front passenger's backrest must be set as far forward as
possible or adapted to the child safety seat as required, and the
seat height must be adjusted to its highest position.
The front passenger's airbag must be deactivated if a rearward-
facing child seat is used.
The front passenger's seat ca n be equipped with optional
“ ISOFIX ” retainers.
The rear seats can be equipped with optional “ ISOFIX” retainers.
WARNING
While the vehicle is moving, chil dren must always be protected
with a restraint system which is suited to their age, height and
weight. Please refer to the chapter “Child seat categories”.•
Never install a rearward-facing ch ild safety seat on the front
passenger's seat unless the fr ont passenger's airbag has been
deactivated. This could result in potentially fatal injuries. If you
have no alternative but to let a ch ild travel on the front passenger's
seat, the front passenger's airbag must be deactivated before-
hand. Please refer to the chapter “Deactivating airbags”.
•
Note the important information and warnings concerning the
use of child safety seats found in the chapter “Important safety
notes when using child safety seats” and in the installation
instructions provided by the manufacturer of the child safety
seat.
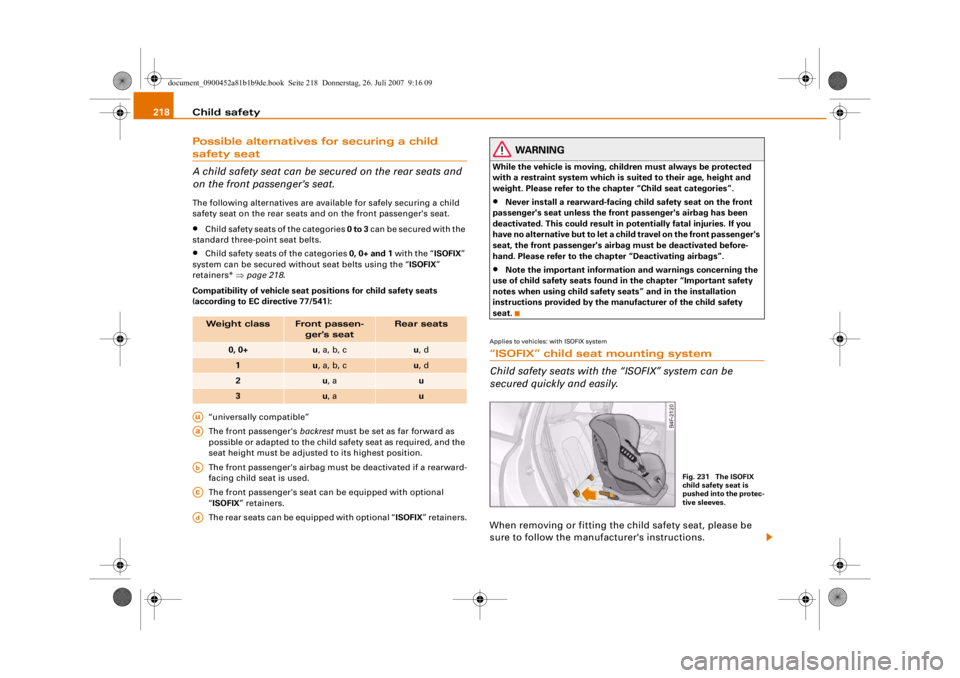
Applies to vehicles: with ISOFIX system“ISOFIX” child seat mounting system
Child safety seats with the “ISOFIX” system can be
secured quickly and easily.When removing or fitting the child safety seat, please be
sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions.
Weight class
Front passen-
ger's seat
Rear seats
0, 0+
u, a, b, c
u, d
1
u , a, b, c
u, d
2
u, a
u
3
u, a
u
AuAaAbAcAd
Fig. 231 The ISOFIX
child safety seat is
pushed into the protec-
tive sleeves.
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 218 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
-+
•
+-
Page 221 of 342

Child safety219
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
– Fit the protective sleeves onto the retainers
between the backrest and the seat cushion ⇒page 218,
fig. 231.
– Push the mountings on the child safety seat into the protective sleeves until they engage audibly (2x)
⇒page 218, fig. 231.
– Pull on the child safety seat to check whether both
catches have engaged properly.Child safety seats with the “ISOFI X” system can be secured quickly
and safely on the rear seat* or on the front passenger's seat*.
Detailed fitting instructions are supplied with the child safety seat.
Child seats with “ISOFIX” mountings are available from Audi dealers
and specialist retailers.
If required, the “ISOFIX” mounting system can be retrofitted.
WARNING
The retainers used here are specially designed for child safety
seats with “ISOFIX” mountings. Do not attempt to secure other
types of child safety seat, seat belts or other objects with these
retainers – this could result in serious or possibly fatal injury.
AA
AB
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 219 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
. I
+-
Page 224 of 342

Intelligent technology
222Intelligent technologyElectronic stabilisation program (ESP)DescriptionESP increases the car's stability. It reduces the tendency to skid and
improves the stability and roadhold ing of the vehicle. ESP detects
critical handling situations, such as understeer, oversteer and
wheelspin on the driven wheels. It stabilises the vehicle by braking
individual wheels or by reducing the engine torque. The warning
lamp
in the instrument cluster starts flashing as soon as the ESP
intervenes.
The ESP incorporates the functions of the anti-lock brake system
(ABS), the traction control system (ASR), the electronic differential
lock (EDL) and the dynamic steering*.
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up under braking until the
vehicle has reached a virtual standstill. You can continue to steer the
vehicle even when the brakes are on full. Keep your foot on the brake
pedal and do not pump the brakes. You will feel the brake pedal
pulsate while the anti-lock brake system is working.
Brake assist system
The brake assist system can speed up the braking process and
shorten the braking distance. It au tomatically boosts the braking
force if you press the brake pedal quickly in an emergency. On vehi-
cles with adaptive cruise control*, the brake assist system will build
up a small amount of pressure in the hydraulic brake system if it
senses that you are too close to the vehicle in front.
Traction control system (ASR)
In the event of wheelspin, the traction control system reduces the
engine torque to match the amount of grip available. This helps the
car to start moving, accelerate or climb a gradient. Electronic differential lock (EDL)
When the EDL detects wheelspin, it brakes the spinning wheel and
directs the power to the other driven wheel (or wheels on quattro*
versions). This function is active up to about 100 km/h.
To prevent the disc brake of the braked wheel from overheating, the
EDL cuts out automatically if subjected to excessive loads. The
vehicle can still be driven. The EDL will switch on again automati-
cally when the brake has cooled down.
Dynamic steering*
On vehicles with dynamic steering*, the ESP can also intervene in
the steering to stabilise the vehicle in critical situations.
WARNING
•
The grip provided by the ESP,
ABS, ASR, EDL and dynamic
steering* systems is still subject to the physical limits of adhesion.
Always bear this in mind, especia lly on wet or slippery roads. If
you notice the systems cutting in , you should reduce your speed
immediately to suit the road and traffic conditions. Do not let the
extra safety provided tempt you into taking any risks when driving
– this can cause accidents.
•
Please remember that the acciden t risk always increases if you
drive fast, especially in corners or on a slippery road, or if you
follow too close behind th e vehicle in front of you. Please bear in
mind that even ESP, ABS, brak e assist, EDL, ASR and dynamic
steering* cannot compensate for the increased accident risk.
•
When accelerating on a uniformly slippery surface (for instance
all four wheels on ice or snow), pr ess the accelerator gradually and
carefully. The driven wheels may ot herwise start to spin (in spite
of the integrated control systems), which would impair the car's
stability and could lead to an accident.
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 222 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
-+ +-
Page 225 of 342

Intelligent technology223
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Note
•
To ensure that the ASR works properly, all four wheels must be
fitted with identical tyres. Any differences in the rolling radius of the
tyres can cause the system to reduce engine power when this is not
desired.
•
Should a malfunction occur in the ABS or EDL, both the ABS
warning lamp
and the ESP warning lamp
⇒ page 19 will light
up.
•
In the event of a malfunction in the ESP system, the warning
lamp ⇒ page 17 will light up.
•
If a malfunction should occur in the ABS, the ESP, EDL and ASR
will also be out of action.
•
The systems can make noises when they intervene.
Switching on and off
The ESP is switched on automatically when the engine is
started.
Switching off the traction control system (ASR)
In particular circumstances, it may be advisable to switch off the
traction control system (ASR) to allow a certain amount of wheel
slip. For example:•
Rocking the car backwards and forwards to free it
•
Driving in deep snow or on loose surfaces
•
Driving with snow chains
Press the button briefly ⇒fig. 232 or ⇒fig. 233. The
warning lamp
will light up and the message ASR off will appear
in the driver information system display.
The traction control system (ASR) can only be switched off at speeds
below 50 km/h on vehicles with front-wheel drive. At 70 km/h it will
switch on again automatically. The ASR can be deactivated at any
speed on vehicles with four-wheel drive.
Switching off the ESP
Press the button for longer than 3 seconds. The ESP
warning lamp will light up and the message ESP switched off will
appear in the display. The ASR is also deactivated when the ESP is
switched off.
Switching on
Press the button again. The message ESP/ASR on will
appear briefly on the display.
Fig. 232 Version A:
Centre console
(bottom), ESP OFF
button
Fig. 233 Version B:
Centre console (top),
ESP OFF button
ESP OFFESP OFFESP OFF
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 223 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-
(I]
T
•
-+
I I
+-
I I
I I
Page 226 of 342

Intelligent technology
224
WARNING
You should switch off the ESP only if your driving ability and traffic
conditions allow you to do so safely. Please note that, when the
ASR and ESP are switched off, the driven wheels may start to spin,
causing the vehicle to lose grip, in particular on slippery or wet
roads - danger of skidding!
Note
The ASR and ESP cannot be switched off when the adaptive cruise
control (ACC)* is on.BrakesNew brake pads
New brake pads do not give full braking effect for the first 400 km,
they must first be “bedded in”. However, you can compensate for
the slightly reduced braking effect by applying more pressure on
the brake pedal. Avoid placing a heavy load on the brakes during the
running-in period.
We ar
The rate of wear on the brake pads depends a great deal on how you
drive and the conditions in which the vehicle is operated. Negative
factors are, for instance, city tra ffic, frequent short trips or hard
driving with abrupt starts and stops.
Wet roads; road salt
When you are driving at a speed higher than 80 km/h and have the
windscreen wipers switched on the brake pads are very briefly
brought into contact with the brak e discs. This automatic process
which goes unnoticed by the driver is carried out at regular intervals
and is intended to improve braking response in wet conditions. In certain conditions, such as in heavy rain, or after washing the car
or driving through water, the full braking effect can be delayed by
moisture (or in winter by ice) on the discs and brake pads. The
brakes should be “dried” by pressing the pedal to restore full
braking effect.
The effectiveness of the brakes can also be temporarily reduced if
the car is driven for some distance without using the brakes when
there is a lot of salt on the road in
winter. The layer of salt that accu-
mulates on the discs and pads can be removed with a few cautious
brake applications.
Corrosion
There may be a tendency for dirt to build up on the brake pads and
corrosion to form on the discs if the car is used infrequently, or if
you only drive low mileages without using the brakes very much.
If the brakes are not used frequently, or if corrosion has formed on
the discs, it is advisable to clean off the pads and discs by braking
firmly a few times from a moderately high speed ⇒.
Faults in the brake system
If the brake pedal travel should ever increase suddenly, this may
mean that one of the two brake circuits has failed. Drive immedi-
ately to the nearest qualified workshop and have the fault rectified.
On the way to the dealer, be prepared to use more pressure on the
brake pedal and allow for longer stopping distances.
Low brake fluid level
Malfunctions can occur in the brake system if the brake fluid level is
too low. The brake fluid level is monitored electronically.
Brake servo
The brake servo amplifies the pressure you apply to the brake pedal.
It only works when the engine is running.
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 224 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
[I]
•
-+ +-
Page 227 of 342

Intelligent technology225
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
WARNING
•
When applying the brakes to clean off deposits on the pads and
discs, select a clear, dry road. Be sure not to inconvenience or
endanger other road users; do not risk an accident.
•
Never let the car coast with the engine switched off (this can
cause accidents).Caution
•
Never let the brakes “drag” by leaving your foot on the pedal
when you do not really intend to brake. This overheats the brakes,
resulting in longer stopping distances and greater wear.
•
Before driving down a long, steep gradient, it is advisable to
reduce speed and move the selector lever to a lower gear. In this
way you will make use of the engine braking effect and relieve the
load on the brakes. If you still have to use the brakes, it is better to
brake firmly at intervals than to apply the brakes continuously.Note
•
If the brake servo is out of action due to a malfunction, or if the
car has to be towed, you will have to press the brake pedal consid-
erably harder to make up for the lack of servo assistance.
•
If you wish to equip the car with accessories such as a front
spoiler or wheel covers, it is impo rtant that the flow of air to the
front wheels is not obstructed, otherwise the brakes can overheat.
Power steering (servotronic)The power steering assists th e driver when turning the
steering wheel (with the engine running).The power steering assists the driver by reducing the force needed
to turn the steering wheel. The degree of power assistance is
adapted electronically , depending on the speed. If a fault should occur in the
servotronic system the power steering
will still operate. The degree of power assistance will, however, no
longer adapt to different speeds. If the electronic regulating system
is not working properly, this is most noticeable when turning the
steering wheel at low speeds (for instance when parking) – more
effort will be required than usual. The fault should be corrected by
a qualified workshop as soon as possible.
The power steering does not function when the engine is switched
off. In this case the steering wheel is very hard to turn.
If the steering is held at its turning limit when the car is stationary,
this will place an excessive load on the power steering system. In
this case, the power steering system will make noises. It will also
reduce the idling speed of the engine.
Caution
Do not keep the steering in the full-lock position for longer than
15 seconds when the engine is running – this could cause damage
to the power steering system.
Note
•
If the power steering should fail at any time or the engine is
switched off (for instance when being towed), the car can still be
steered. However, more effort will be required to turn the steering
wheel.
•
If the system is leaking or malfunctioning, please take the car to
a qualified workshop as soon as possible.
•
The power steering requires a special hydraulic fluid. The fluid
reservoir is located at the front of the engine compartment on the
left ⇒page 256 . The correct fluid level in the reservoir is important
for the power steering to function properly. The hydraulic fluid level
is checked at the Inspection Service.
document_0900452a81b1b9de.book Seite 225 Donnerstag, 26. Juli 2007 9:16 09
--4 -
-T
CD
-+
CD
[I]
[I]
+-
•
•