2008 AUDI A5 brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 143 of 313
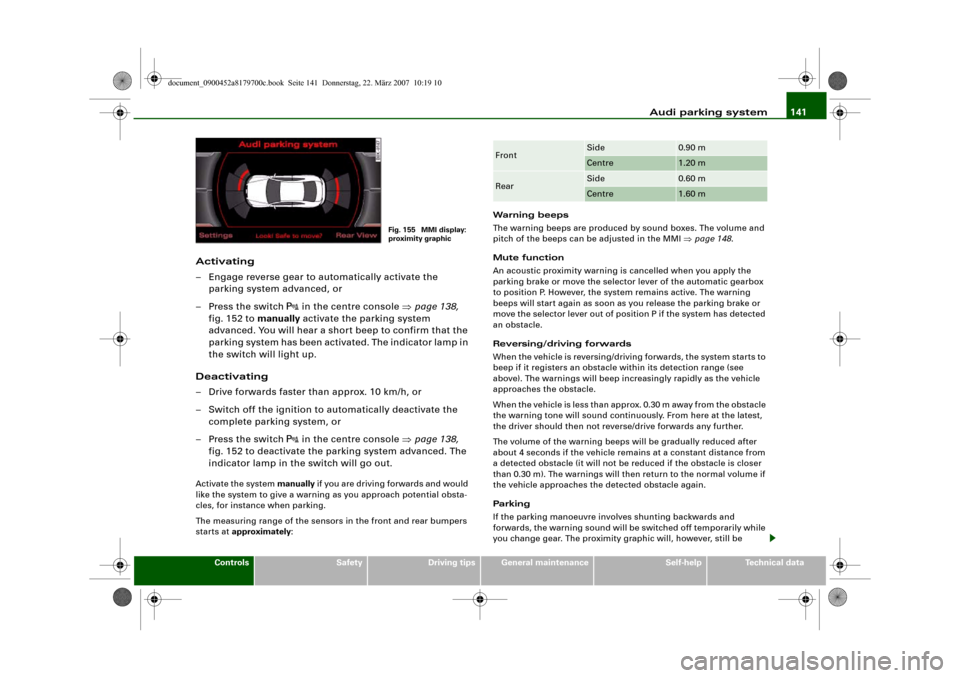
Audi parking system141
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Activating
– Engage reverse gear to automatically activate the
parking system advanced, or
– Press the switch
in the centre console ⇒page 138,
fig. 152 to manually activate the parking system
advanced. You will hear a short beep to confirm that the
parking system has been activated. The indicator lamp in
the switch will light up.
Deactivating
– Drive forwards faster than approx. 10 km/h, or
– Switch off the ignition to automatically deactivate the
complete parking system, or
– Press the switch
in the centre console ⇒page 138,
fig. 152 to deactivate the parking system advanced. The
indicator lamp in the switch will go out.
Activate the system manually if you are driving forwards and would
like the system to give a warning as you approach potential obsta-
cles, for instance when parking.
The measuring range of the sensors in the front and rear bumpers
starts at approximately:Warning beeps
The warning beeps are produced by sound boxes. The volume and
pitch of the beeps can be adjusted in the MMI ⇒page 148.
Mute function
An acoustic proximity warning is cancelled when you apply the
parking brake or move the selector lever of the automatic gearbox
to position P. However, the system remains active. The warning
beeps will start again as soon as you release the parking brake or
move the selector lever out of position P if the system has detected
an obstacle.
Reversing/driving forwards
When the vehicle is reversing/driving forwards, the system starts to
beep if it registers an obstacle within its detection range (see
above). The warnings will beep increasingly rapidly as the vehicle
approaches the obstacle.
When the vehicle is less than approx. 0.30 m away from the obstacle
the warning tone will sound continuously. From here at the latest,
the driver should then not reverse/drive forwards any further.
The volume of the warning beeps will be gradually reduced after
about 4 seconds if the vehicle remains at a constant distance from
a detected obstacle (it will not be reduced if the obstacle is closer
than 0.30 m). The warnings will then return to the normal volume if
the vehicle approaches the detected obstacle again.
Parking
If the parking manoeuvre involves shunting backwards and
forwards, the warning sound will be switched off temporarily while
you change gear. The proximity graphic will, however, still be
Fig. 155 MMI display:
proximity graphic
Front
Side
0.90 m
Centre
1.20 m
Rear
Side
0.60 m
Centre
1.60 m
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 141 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 166 of 313
Safe driving 164Correct sitting positionsCorrect sitting position for driver
The correct driving position is important for safe and
fatigue-free driving.For your own safety, and to reduce the risk of injury in the
event of an accident, we recommend the following driving
position.
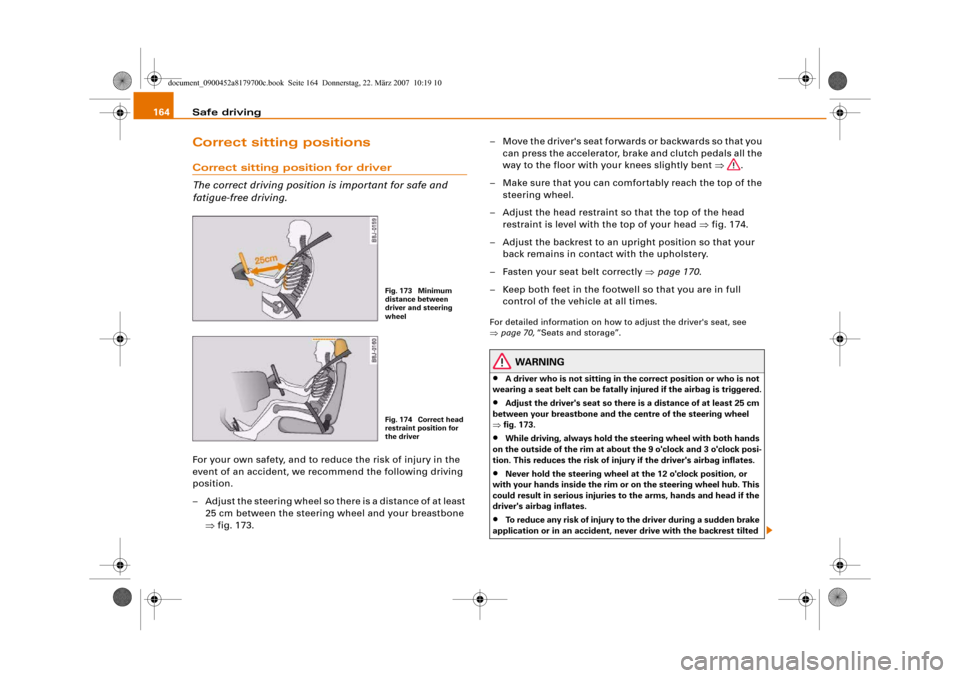
– Adjust the steering wheel so there is a distance of at least
25 cm between the steering wheel and your breastbone
⇒fig. 173.– Move the driver's seat forwards or backwards so that you
can press the accelerator, brake and clutch pedals all the
way to the floor with your knees slightly bent ⇒.
– Make sure that you can comfortably reach the top of the
steering wheel.
– Adjust the head restraint so that the top of the head
restraint is level with the top of your head ⇒fig. 174.
– Adjust the backrest to an upright position so that your
back remains in contact with the upholstery.
– Fasten your seat belt correctly ⇒page 170.
– Keep both feet in the footwell so that you are in full
control of the vehicle at all times.
For detailed information on how to adjust the driver's seat, see
⇒page 70, “Seats and storage”.
WARNING
•
A driver who is not sitting in the correct position or who is not
wearing a seat belt can be fatally injured if the airbag is triggered.
•
Adjust the driver's seat so there is a distance of at least 25 cm
between your breastbone and the centre of the steering wheel
⇒fig. 173.
•
While driving, always hold the steering wheel with both hands
on the outside of the rim at about the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock posi-
tion. This reduces the risk of injury if the driver's airbag inflates.
•
Never hold the steering wheel at the 12 o'clock position, or
with your hands inside the rim or on the steering wheel hub. This
could result in serious injuries to the arms, hands and head if the
driver's airbag inflates.
•
To reduce any risk of injury to the driver during a sudden brake
application or in an accident, never drive with the backrest tilted
Fig. 173 Minimum
distance between
driver and steering
wheelFig. 174 Correct head
restraint position for
the driver
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 164 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 169 of 313
Safe driving167
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Examples of incorrect sitting positions
Occupants can suffer severe or fatal injuries injuries if
they sit in an incorrect position while the vehicle is
moving.Seat belts can only provide maximum protection if the belt
webbing is positioned correctly. Sitting out of position
greatly reduces the effectiveness of the seat belts and
increases the risk of injury since the belt webbing is not
worn in the position for which it is designed. The driver is
responsible for the safety of all vehicle occupants, espe-
cially for children.
– Never allow anyone to sit out of position while the
vehicle is moving ⇒.The following list shows just some examples of incorrect sitting
positions which can be dangerous to all occupants. The list is not
complete, but will help to make you aware of possible dangers
which can be avoided.
Therefore, whenever the vehicle is moving:•
never stand up in the vehicle,
•
never stand on the seats,
•
never kneel on the seats,
•
never travel with the backrest reclined too far,
•
never lean against the dash panel,
•
never lie down on the rear seat,
•
never sit on the front edge of a seat,
•
never sit sideways,
•
never lean out of the window,
•
never put your feet out of the window,
•
never put your feet on the dash panel,
•
never put your feet on the seat cushion,
•
never ride in the footwell,
•
never travel on a seat without wearing the seat belt,
•
never climb into the luggage compartment.
WARNING
Sitting out of position increases the risk of severe injuries.•
Sitting out of position exposes the occupants to potentially
fatal injuries: if the airbags inflate they can strike any occupant
who is not in one of the designed seat positions.
•
Before starting a trip, sit in the correct position and stay in this
position as long as the vehicle is moving. Before every trip, make
sure all passengers are sitting in the correct positions and remain
correctly seated at all times ⇒page 70, “Seats and storage”.
Pedal are aPedal s
The pedals must always be free to move and must never
be obstructed by floor mats or any objects in the footwell.– Make sure that the accelerator, brake and clutch pedals
are not obstructed and can be pressed all the way down
to the floor.
– Make sure that all pedals are able to return freely to their
original positions.Only use floor mats which leave the pedal area free and can be
securely fastened in the footwell.
If one of the brake circuits should fail, increased brake pedal travel
will be required to bring the vehicle safely to a stop.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 167 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 172 of 313

Seat belts 170Seat beltsWhy is it so important to use seat
belts?Seat belts provide effective protection
The common belief that passengers can brace their
weight with their hands in a minor collision is false.It is an established fact that seat belts provide good protection in
accidents. Therefore wearing a seat belt is required by law in most
countries.
Properly worn seat belts hold the occupants in the best position for
maximum protection ⇒fig. 177. The seat belts are capable of
absorbing much of the kinetic energy arising in a collision. Also they
help to prevent uncontrolled movements which could lead to severe
injuries ⇒page 171, “Important safety instructions for using seat
belts”.
If they wear the seat belts correctly, the passengers benefit greatly
from the ability of the belts to reduce the kinetic energy gradually.
The front crumple zones and other passive safety features (such as
the airbag system) are also designed to absorb the kinetic energy
generated in a collision. Taken together, all these features reduce the forces acting on the occupants and consequently the risk of
injury.
Although these examples are based on a frontal collision, the phys-
ical principles involved are the same in other types of accidents and
for vehicles with an airbag system. This is why it is so important to
put on the seat belts before every trip – even when “just driving
around the corner”. Ensure that your passengers wear their seat
belts as well ⇒.
Properly worn seat belts have been shown to be an effective means
of reducing the potential for injury and improving the chances of
survival in a serious accident ⇒page 171, “Forces acting in a colli-
sion”.
For information on how children can travel safely in the car
⇒page 185, “Points to remember if children are travelling in the
car”.
WARNING
•
Seat belts must be put on before every trip – even when driving
in town. This also applies to the rear passengers (injury risk).
•
During pregnancy, women should always ensure they wear a
seat belt. The best way to protect the unborn child is to protect the
mother ⇒page 174, “Wearing and adjusting the seat belts during
pregnancy”.
Fig. 177 Driver
protected by the prop-
erly worn seat belt
during a sudden brake
manoeuvre
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 170 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 198 of 313
Intelligent technology 196Intelligent technologyElectronic stabilisation program (ESP)General notes
The electronic stabilisation program increases the car's
stability on the road.The ESP is designed to enhance the control over the vehicle in crit-
ical handling situations, such as when accelerating and cornering.
It reduces the tendency to skid under all road conditions and
improves the stability and roadholding of the vehicle. The system
works at all speeds.The anti-lock brake system (ABS), the electronic differential lock
(EDL) and the traction control system (ASR) are all integrated into
the electronic stabilisation program.
How the system works
The ESP control unit processes data from the three integrated
systems. It also processes additional inputs provided by other high-
precision sensors. These register the vehicle's rotation about the
vertical axis (yaw rate), lateral acceleration, brake pressure and
steering wheel angle.
The system uses the steering wheel angle and road speed to calcu-
late the changes of direction intended by the driver, and constantly
compares them with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If the
desired course is not being maintained (for instance, if the car is
starting to skid), then the ESP compensates automatically by
braking the appropriate wheel.
The forces acting on the braked wheel effectively bring the car back
to a stable condition. If the car is oversteering (rear wheels losing
grip first) the brake application is concentrated on the outside front
wheel; if the car is understeering (front wheels losing grip first), ESP
brakes the inside rear wheel. This automatic brake application is
accompanied by characteristic noises.
The ESP works in conjunction with the ABS ⇒page 197. If a
malfunction should occur in the ABS, the ESP will also be out of
action.
Switching on
The ESP is switched on automatically when the engine is started
and performs a self-test routine. As soon as this routine is complete,
the system switches back to normal operating mode. You can press
the button ⇒fig. 203 or ⇒fig. 204 to switch on the ESP or traction
control system (ASR) if they have been switched off. The message
ESP/ASR on will appear briefly in the display.
Fig. 203 Without MMI:
Centre console with
ESP switchFig. 204 Centre
console with ESP
switch
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 196 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 199 of 313
Intelligent technology197
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data Switching off
The ESP should normally be left switched on at all times. If required,
you can press the ESP OFF button to switch off the traction control
system (ASR) or the electronic stabilisation program (ESP).
•
Switching off the traction control system (ASR): Press the ESP
button briefly. The traction control system (ASR) can be switched off
in special driving conditions, e.g. if you are driving with snow chains
⇒page 198. The message ASR off will appear in the display.
•
Switching off the ESP/traction control system (ASR): Press the
ESP button for longer than 3 seconds. The ESP/ASR warning lamp
lights up when the system is switched off, see ⇒page 16. The
message ESP switched off will appear in the display.
WARNING
•
The ESP is not able to overcome the physical limits of adhesion.
Even with ESP, you should always adjust your speed to suit the
conditions. Please bear this in mind, especially on wet or slippery
road surfaces. Do not let the extra safety provided tempt you into
taking any risks when driving – this can cause accidents.
•
Please note that, when the ESP or ESP/traction control system
(ASR) is switched off, the driven wheels may start to spin, causing
the vehicle to lose grip, in particular on slippery or wet roads -
danger of skidding!
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up under braking.The anti-lock brake system (ABS) is an important part of the car's
active safety system. However, the ABS will not necessarily guar-
antee shorter stopping distances in all conditions. For instance, on
loose gravel or fresh snow on top of an icy surface (conditions which
anyway require extreme care and reduced speed), the stopping
distance with ABS may even be slightly longer.How the ABS works
The system runs an automatic self-check when the car reaches a
road speed of about 6 km/h. This may be accompanied by a noise
from the ABS pump.
If one of the wheels is turning too slowly in relation to the road
speed, and is close to locking up, the system will reduce the pres-
sure in the brake line to this wheel. The driver is made aware of this
control process by a pulsating of the brake pedal and accompa-
nying noise. This is a deliberate warning to the driver that one or
more of the wheels is tending to lock up and the ABS control func-
tion has intervened. In this situation it is important to keep the brake
pedal fully depressed so the ABS can regulate the brake application
- do not “pump” the brake pedal.
WARNING
The grip provided by ABS is still subject to the physical limits of
adhesion. Always bear this in mind, especially on wet or slippery
roads. If you notice that the ABS is working (to counteract locked
wheels under braking), you should reduce speed immediately to
suit the road and traffic conditions. Do not let the extra safety
provided tempt you into taking any risks when driving – this can
cause accidents.
Note
If a malfunction should occur in the ABS, this is indicated by a
warning lamp ⇒page 18.Brake assist system
The brake assist system helps the driver to achieve
optimum braking effect.The brake assist system helps to increase braking power and thus to
achieve a shorter stopping distance. If the driver presses the brake
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 197 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 200 of 313
Intelligent technology 198pedal very quickly, the brake assist system automatically boosts the
braking force to the maximum level, up to the point where the anti-
lock brake function (ABS) intervenes to stop the wheels from
locking. You should then keep the brake pedal pressed until the
vehicle has braked to the required speed. The brake assist system
switches itself off as soon as you release the brake pedal.
The brake assist system will not be operative if there is a malfunc-
tion in the ABS.
WARNING
Please remember that the accident risk always increases if you
drive too fast, especially in corners or on a slippery road, or if you
follow too close behind the vehicle in front of you. An increased
accident risk cannot be compensated even by the brake assist
system, so always be sure to maintain a safe speed.Traction control system (ASR)
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels
from spinning when the car is accelerating.General notes
The traction control system (ASR) is one of the functions incorpo-
rated in the electronic stabilisation program (ESP).
The traction control system (ASR) helps the car to start moving,
accelerate and climb a gradient in slippery conditions where this
may otherwise be difficult or even impossible.
How the system works
The ASR acts automatically i.e. without the driver's intervention.
With the aid of the ABS sensors ⇒page 197, the ASR monitors the
speed of the driven wheels. If the wheels start to spin, the engine
power is reduced automatically to match the amount of grip avail-
able. The system works at all speeds.The ASR works in conjunction with the ABS. If a malfunction should
occur in the ABS, the ASR will also be out of action.
Switching on
The ESP is switched on automatically when the engine is started
and performs a self-test routine. As soon as this routine is complete,
the system switches back to normal operating mode. If the traction
control system (ASR) has been deactivated (for one of the reasons
noted below) you can switch it back on manually by pressing the
switch ⇒page 196, fig. 203. The message ESP/ASR on will appear
briefly in the display. If the traction control system (ASR) has been
deactivated, it will switch back on automatically at a speed of about
70 km/h on vehicles with front-wheel drive.
You can switch the traction control system (ASR) on again if neces-
sary by pressing the switch ⇒page 196, fig. 203.
Switching off
If required, the ASR can also be switched off manually by pressing
the switch briefly ⇒page 196, fig. 203 (for less than 3 seconds). The
ESP warning lamp lights up when the traction control system (ASR)
is switched off, see ⇒page 16. The message ASR off will appear in
the display. For safety reasons, the system can only be switched off
at speeds below 50 km/h on vehicles with front-wheel drive. The
ASR can be deactivated at any speed on vehicles with four-wheel
drive.
The traction control system should normally remain switched on at
all times. It should only be switched off manually in particular
circumstances where a certain amount of wheel slip may be desir-
able. For example:
•
when driving with snow chains
•
when driving in deep snow or on loose surfaces
•
when rocking the car backwards and forwards to free it.
The ASR should be switched on again afterwards as soon as
possible.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 198 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 201 of 313
Intelligent technology199
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Note
To ensure that the ASR works properly, all four wheels must be fitted
with identical tyres. Any differences in the rolling radius of the tyres
can cause the system to reduce engine power when this is not
desired. Also refer to ⇒page 245, “Replacing wheels and tyres”.Electronic differential lock (EDL)
The electronic differential lock monitors the speed of the
driven wheels.General notes
The electronic differential lock (EDL) helps the car to start moving,
accelerate and climb a gradient in slippery conditions where this
may otherwise be difficult or even impossible.
How the system works
The EDL acts automatically. With the aid of the ABS sensors
⇒page 197, the system monitors the rotational speed of the driven
wheels on each axle. Whenever it detects a significant difference in
the speed of the driven wheels of one axle (for example, if the road is
slippery on one side) the system applies the brake to slow down the
spinning wheel so that more of the power is directed to the other
wheel of this axle (or to the three other wheels on vehicles with four-
wheel drive). This function is active up to about 100 km/h. The brake
system will make noises while it is working.
Driving away from a standstill
Sometimes one wheel has less grip and starts spinning, for
example, if one of the driven wheels is on ice. In this case, keep
pressing the accelerator gradually until the car starts moving, even
though the wheel with less grip will still spin.
Overheating of the brakes
To prevent the disc brake of the braked wheel from overheating, the
EDL cuts out automatically if subjected to excessive loads. The car remains operational and will behave in the same way as a car
without EDL.
The EDL will switch on again automatically when the brake has
cooled down.
WARNING
•
When accelerating on a uniformly slippery surface (for instance
all four wheels on ice or snow), press the accelerator gradually and
carefully. The driven wheels may otherwise start to spin (in spite
of the EDL), which would impair the car's stability and could lead
to an accident.
•
Even with EDL, you should always adjust your speed to suit the
conditions. Do not let the extra safety provided tempt you into
taking any risks when driving – this can cause accidents.Note
If the ABS warning lamp lights up, this can also mean there is a fault
in the EDL. Please contact a qualified workshop as soon as
possible.BrakesNew brake pads
New brake pads do not give full braking effect for the first 400 km,
they must first be “bedded in”. However, you can compensate for
the slightly reduced braking effect by applying more pressure on
the brake pedal. Avoid placing a heavy load on the brakes during the
running-in period.
We ar
The rate of wear on the brake pads depends a great deal on how you
drive and the conditions in which the vehicle is operated. Negative
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 199 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10