2008 AUDI A5 weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 171 of 313
Safe driving169
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data inside. In this case the child would be unable to get out of the
vehicle without help. This could have fatal consequences.
•
Never allow children to play in or around the vehicle. Always
close and lock the boot lid and all the doors when you leave the
vehicle.
•
Never let passengers ride in the luggage compartment. All
occupants must be properly restrained by the seat belts at all
times ⇒page 170.Note
•
Air circulation in the vehicle helps reduce fogging of the
windows. Used air escapes through ventilation slots in the rear of
the vehicle. Make sure that these ventilation slots are not
obstructed.
•
Suitable belts for securing loads to the fastening rings* are
commercially available.
Applies to vehicles: with fastening ringsFastening rings
Unsecured loads are a hazard to all vehicle occupants.There are fastening rings in the luggage compartment
which can be used to secure luggage and other objects
⇒page 78.
– Use the fastening rings to secure items safely in the
luggage compartment ⇒ in “Loading the luggage
compartment” on page 77.During a collision or an accident, even small and light objects can
possess so much energy that they can cause very severe injuries.
The amount of this “kinetic energy” depends on the speed of the vehicle and the weight of the object. The most significant factor,
however, is the speed of the vehicle.
An example: An object weighing 4.5 kg is lying unsecured in the
vehicle. During a frontal collision at a speed of 50 km/h, this object
generates a force corresponding to 20 times its weight. That means
that the effective weight of the object increases to about 90 kg. You
can imagine the severity of the injuries which might be sustained if
this “projectile” strikes an occupant as it flies through the
passenger compartment.
WARNING
If items of luggage or other objects are secured to the fastening
rings with inappropriate or damaged retaining cords, injuries
could result in the event of sudden braking or a collision.•
To prevent pieces of luggage or other objects from flying
forward, always use appropriate retaining cords which are prop-
erly secured to the fastening rings.
•
Never secure a child seat on the fastening rings.
WARNING (continued)
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 169 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 172 of 313

Seat belts 170Seat beltsWhy is it so important to use seat
belts?Seat belts provide effective protection
The common belief that passengers can brace their
weight with their hands in a minor collision is false.It is an established fact that seat belts provide good protection in
accidents. Therefore wearing a seat belt is required by law in most
countries.
Properly worn seat belts hold the occupants in the best position for
maximum protection ⇒fig. 177. The seat belts are capable of
absorbing much of the kinetic energy arising in a collision. Also they
help to prevent uncontrolled movements which could lead to severe
injuries ⇒page 171, “Important safety instructions for using seat
belts”.
If they wear the seat belts correctly, the passengers benefit greatly
from the ability of the belts to reduce the kinetic energy gradually.
The front crumple zones and other passive safety features (such as
the airbag system) are also designed to absorb the kinetic energy
generated in a collision. Taken together, all these features reduce the forces acting on the occupants and consequently the risk of
injury.
Although these examples are based on a frontal collision, the phys-
ical principles involved are the same in other types of accidents and
for vehicles with an airbag system. This is why it is so important to
put on the seat belts before every trip – even when “just driving
around the corner”. Ensure that your passengers wear their seat
belts as well ⇒.
Properly worn seat belts have been shown to be an effective means
of reducing the potential for injury and improving the chances of
survival in a serious accident ⇒page 171, “Forces acting in a colli-
sion”.
For information on how children can travel safely in the car
⇒page 185, “Points to remember if children are travelling in the
car”.
WARNING
•
Seat belts must be put on before every trip – even when driving
in town. This also applies to the rear passengers (injury risk).
•
During pregnancy, women should always ensure they wear a
seat belt. The best way to protect the unborn child is to protect the
mother ⇒page 174, “Wearing and adjusting the seat belts during
pregnancy”.
Fig. 177 Driver
protected by the prop-
erly worn seat belt
during a sudden brake
manoeuvre
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 170 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 174 of 313
Seat belts 172The physical principles involved in a frontal collision are relatively
simple:
Both the moving vehicle and the passengers possess energy, which
is known as “kinetic energy” ⇒page 171, fig. 178. The amount of
“kinetic energy” depends on the speed of the vehicle and the weight
of the vehicle and passengers. The higher the speed and the greater
the weight, the more energy there is to be absorbed in an accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the speed of the vehicle. If
the speed doubles from 25 km/h to 50 km/h, for example, the kinetic
energy increases by a factor of four. Because these passengers are
not restrained by seat belts, the entire amount of kinetic energy has
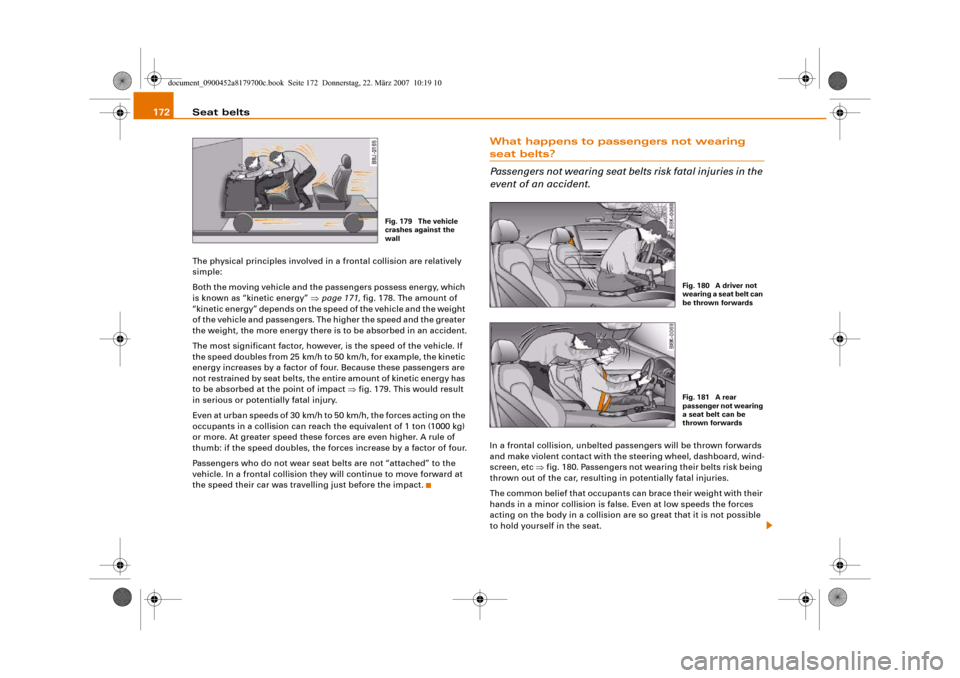
to be absorbed at the point of impact ⇒fig. 179. This would result
in serious or potentially fatal injury.
Even at urban speeds of 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the forces acting on the
occupants in a collision can reach the equivalent of 1 ton (1000 kg)
or more. At greater speed these forces are even higher. A rule of
thumb: if the speed doubles, the forces increase by a factor of four.
Passengers who do not wear seat belts are not “attached” to the
vehicle. In a frontal collision they will continue to move forward at
the speed their car was travelling just before the impact.
What happens to passengers not wearing seat belts?
Passengers not wearing seat belts risk fatal injuries in the
event of an accident.In a frontal collision, unbelted passengers will be thrown forwards
and make violent contact with the steering wheel, dashboard, wind-
screen, etc ⇒fig. 180. Passengers not wearing their belts risk being
thrown out of the car, resulting in potentially fatal injuries.
The common belief that occupants can brace their weight with their
hands in a minor collision is false. Even at low speeds the forces
acting on the body in a collision are so great that it is not possible
to hold yourself in the seat.
Fig. 179 The vehicle
crashes against the
wall
Fig. 180 A driver not
wearing a seat belt can
be thrown forwardsFig. 181 A rear
passenger not wearing
a seat belt can be
thrown forwards
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 172 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 183 of 313
Airbag system181
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Important safety notes on the side airbag system
There are a number of safety points concerning the airbag
system which you should remember. This will help to
reduce the risk of injury in an accident.
WARNING
•
If you do not wear a seat belt, if you lean forward, or are not
seated correctly while the vehicle is in motion, you are at greater
risk of injury should the side airbags be triggered in an accident.
•
If children are not seated correctly, they are at greater risk of
injury in an accident. This is particularly the case if the child is
travelling on the front passenger's seat and the airbag system is
triggered. This could result in serious or potentially fatal injury
⇒page 185, “Child safety”.
•
It is important not to attach any accessories (such as cup
holders) to the doors. This would impair the protection offered by
the side airbags.
•
The sensors for the airbags are located in the front doors. You
must therefore not make any modifications to the doors or door
trim (e.g. retrofitting loudspeakers), as this could impair the func-
tion of the side airbags. Any damage to the front doors could lead
to faults in the system. Repairs or any other work on the front
doors must therefore always be carried out by a qualified work-
shop.
•
The built-in coat hooks should only be used for lightweight
clothing. Do not leave any heavy or sharp-edged objects in the
pockets.
•
Do not apply excessive force to the sides of the backrests (such
as hard knocks or kicks), as this could damage parts of the system.
The side airbags could then fail to operate when required.
•
If you intend to fit protective covers over the seats, these must
be of the specific type approved for use on Audi seats with side
airbags. Conventional seat covers would obstruct the side airbag when it inflates out of the backrest, and seriously reduce the
airbag's effectiveness.
•
Any damage to the original seat upholstery or around the
seams of the side airbag units must be repaired immediately by a
qualified workshop.
•
Any work involving the side airbag system or removal and
installation of the airbag components for other repairs (such as
repairs to the seats) must always be performed by a qualified
workshop. Otherwise the airbag system may fail to work
properly.
Head-protection airbags (sideguard)Description of head-protection airbags
The head-protection airbags work together with the side
airbag system to give extra protection in a side impact.The head-protection airbags are located above the doors on the left
and right sides of the vehicle ⇒fig. 193. The locations of the airbags
are marked with the word “AIRBAG”.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 193 Location of
head-protection
airbags above the
doors
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 181 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 184 of 313
Airbag system 182In conjunction with the three-point seat belts and side airbags, the
head-protection airbags give the occupants additional protection
against head and neck injuries in a severe side collision ⇒ in
“Important safety notes on the head-protection airbags” on
page 182.
Together with other design features (including cross-braces in the
seats and the overall strength of the body structure), the sideguard
system offers an effective further improvement to occupant protec-
tion in side impacts.How the head-protection airbags work
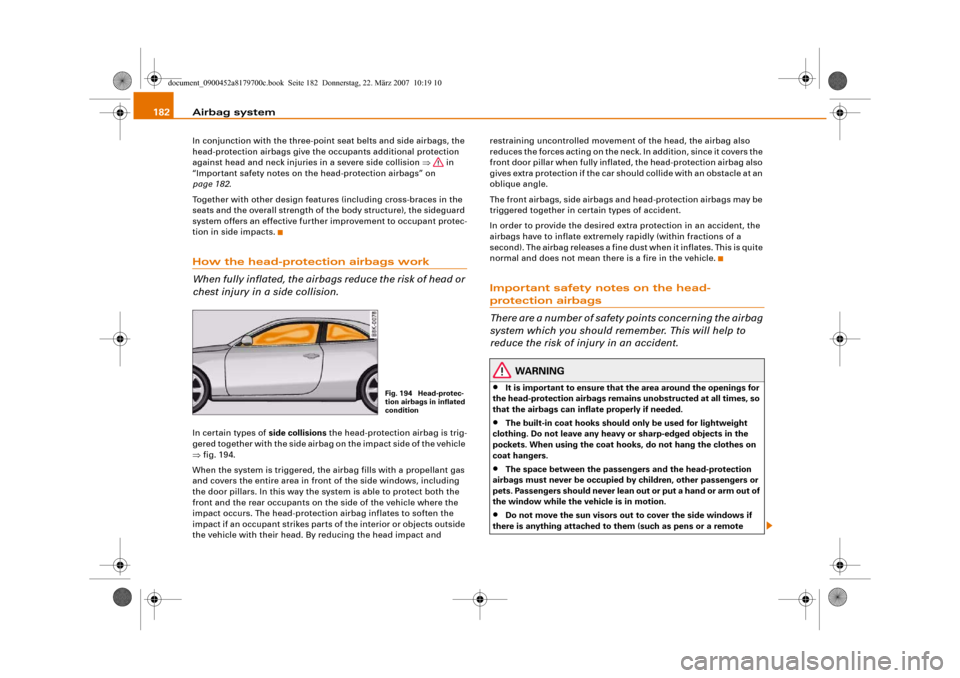
When fully inflated, the airbags reduce the risk of head or
chest injury in a side collision.In certain types of side collisions the head-protection airbag is trig-
gered together with the side airbag on the impact side of the vehicle
⇒fig. 194.
When the system is triggered, the airbag fills with a propellant gas
and covers the entire area in front of the side windows, including
the door pillars. In this way the system is able to protect both the
front and the rear occupants on the side of the vehicle where the
impact occurs. The head-protection airbag inflates to soften the
impact if an occupant strikes parts of the interior or objects outside
the vehicle with their head. By reducing the head impact and restraining uncontrolled movement of the head, the airbag also
reduces the forces acting on the neck. In addition, since it covers the
front door pillar when fully inflated, the head-protection airbag also
gives extra protection if the car should collide with an obstacle at an
oblique angle.
The front airbags, side airbags and head-protection airbags may be
triggered together in certain types of accident.
In order to provide the desired extra protection in an accident, the
airbags have to inflate extremely rapidly (within fractions of a
second). The airbag releases a fine dust when it inflates. This is quite
normal and does not mean there is a fire in the vehicle.
Important safety notes on the head-protection airbags
There are a number of safety points concerning the airbag
system which you should remember. This will help to
reduce the risk of injury in an accident.
WARNING
•
It is important to ensure that the area around the openings for
the head-protection airbags remains unobstructed at all times, so
that the airbags can inflate properly if needed.
•
The built-in coat hooks should only be used for lightweight
clothing. Do not leave any heavy or sharp-edged objects in the
pockets. When using the coat hooks, do not hang the clothes on
coat hangers.
•
The space between the passengers and the head-protection
airbags must never be occupied by children, other passengers or
pets. Passengers should never lean out or put a hand or arm out of
the window while the vehicle is in motion.
•
Do not move the sun visors out to cover the side windows if
there is anything attached to them (such as pens or a remote
Fig. 194 Head-protec-
tion airbags in inflated
condition
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 182 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 187 of 313
Child safety185
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Child safetyPoints to remember if children are
travelling in the carIntroduction
Statistics show that children are generally safer on the
rear seat than on the front passenger's seat.Children under 12 years of age should normally travel on the rear
seat
4). Children travelling on the rear seat must use a child restraint
system or the seat belts provided, depending on their age, height
and weight. For safety reasons, the child restraint system should be
installed behind the front passenger's seat.
The physical principles involved and the forces acting in a collision
apply to children just as much as adults ⇒page 171, “Forces acting
in a collision”. But, unlike adults, children do not have fully devel-
oped muscle and bone structures. This means that children are
subject to a greater risk of injury.
To reduce this risk, children must always use special child restraint
systems when travelling in the car.
Use only child restraint systems which are officially approved under
the European standard ECE R 44 and are suitable for the child. ECE R
refers to the Economic Commission of Europe Recommendation,
which categorises child restraint systems in 5 groups ⇒page 186,
“Child seat categories”. Child restraints that have been tested and
approved under the ECE R 44 standard bear the ECE-R 44 test mark
on the seat (the letter E in a circle with the test number below it).
We recommend using child restraint systems from the range of
Audi Genuine Accessories available from Audi dealers. The
“Huckepack” range includes suitable restraint systems for all ages. These systems have been specially developed and tested for use in
Audi vehicles and comply with the ECE-R 44 standard.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions and observe any statutory
requirements when installing and using child restraints ⇒ in
“Important safety notes for using child safety seats”.
Important safety notes for using child safety seats
Correct use of child safety seats can help to reduce the
risk of injury in an accident.
WARNING
•
All vehicle occupants, especially children, must wear a seat
belt while the vehicle is in motion.
•
Children who are less than 1.5 metres tall must not wear a
normal seat belt without a child restraint, as this could cause inju-
ries to the abdominal and neck areas.
•
Babies and children must never travel on another occupant's
lap.
•
A suitable child safety seat can protect your child ⇒page 186,
“Child safety seats”.
•
Never allow two children to occupy one child safety seat.
•
Never leave a child without supervision in a child safety seat.
•
Never allow a child to travel in the car without a suitable child
restraint.
•
Never allow a child to stand up or kneel on a seat while the car
is moving. In an accident, the child could be catapulted through
the car, causing possibly fatal injuries to itself and other occu-
pants.
4)Observe any restrictions or regulations to the contrary.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 185 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 189 of 313
Child safety187
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data Children who are taller than 1.5 metres can use the existing seat
belts without a booster cushion.
Child restraints that have been tested and approved under the ECE
R 44 standard bear the ECE-R 44 test mark on the seat (the letter E
in a circle with the test number below it).
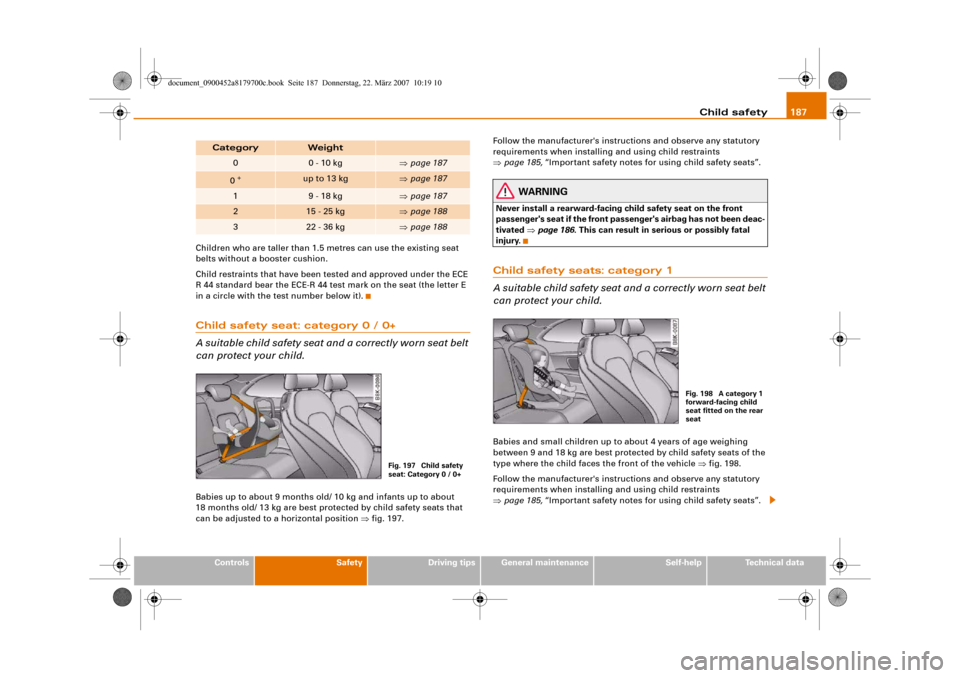
Child safety seat: category 0 / 0+
A suitable child safety seat and a correctly worn seat belt
can protect your child.Babies up to about 9 months old/ 10 kg and infants up to about
18 months old/ 13 kg are best protected by child safety seats that
can be adjusted to a horizontal position ⇒fig. 197.Follow the manufacturer's instructions and observe any statutory
requirements when installing and using child restraints
⇒page 185, “Important safety notes for using child safety seats”.
WARNING
Never install a rearward-facing child safety seat on the front
passenger's seat if the front passenger's airbag has not been deac-
tivated ⇒page 186. This can result in serious or possibly fatal
injury.Child safety seats: category 1
A suitable child safety seat and a correctly worn seat belt
can protect your child.Babies and small children up to about 4 years of age weighing
between 9 and 18 kg are best protected by child safety seats of the
type where the child faces the front of the vehicle ⇒fig. 198.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions and observe any statutory
requirements when installing and using child restraints
⇒page 185, “Important safety notes for using child safety seats”.
Category
Weight
0
0 - 10 kg
⇒page 187
0 +
up to 13 kg
⇒page 187
1
9 - 18 kg
⇒page 187
2
15 - 25 kg
⇒page 188
3
22 - 36 kg
⇒page 188Fig. 197 Child safety
seat: Category 0 / 0+
Fig. 198 A category 1
forward-facing child
seat fitted on the rear
seat
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 187 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 191 of 313
Child safety189
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Fitting child safety seatsGeneral information
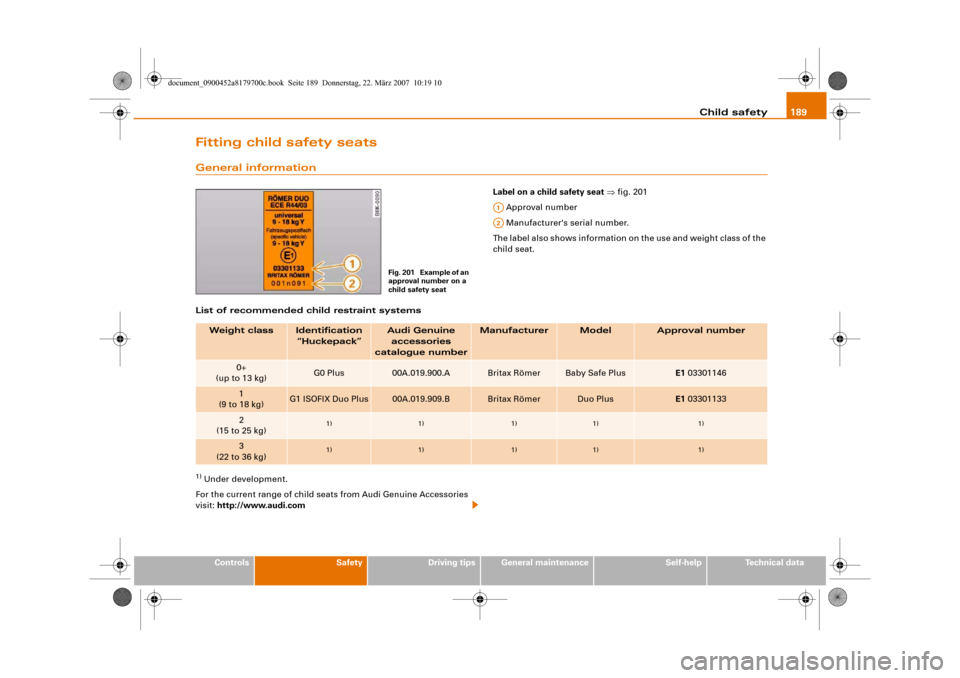
Label on a child safety seat ⇒fig. 201
Approval number
Manufacturer's serial number.
The label also shows information on the use and weight class of the
child seat.
List of recommended child restraint systems
1) Under development.
For the current range of child seats from Audi Genuine Accessories
visit: http://www.audi.com
Fig. 201 Example of an
approval number on a
child safety seat
A1A2
Weight class
Identification
“Huckepack”
Audi Genuine
accessories
catalogue number
Manufacturer
Model
Approval number
0+
(up to 13 kg)
G0 Plus
00A.019.900.A
Britax Römer
Baby Safe Plus
E1 03301146
1
(9 to 18 kg)
G1 ISOFIX Duo Plus
00A.019.909.B
Britax Römer
Duo Plus
E1 03301133
2
(15 to 25 kg)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
3
(22 to 36 kg)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 189 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10