2008 AUDI A5 steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 125 of 313
Driving123
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data braking force of the parking brake is only released when there is
enough power at the wheels to make the vehicle move in the desired
direction.
Note
For safety reasons the parking brake will only release automatically
if the driver's seat belt is engaged in its buckle.Driving away when towing a trailer
Please note the following points to prevent the vehicle
from rolling back unintentionally on a gradient.– Pull and hold the parking brake switch and press the
accelerator. The parking brake will remain engaged and
prevent any tendency to roll back down the slope.
– You can release the parking brake switch as soon as the
engine is delivering enough power to the wheels.Depending on the weight of the vehicle and trailer and the steep-
ness of the slope, there may be a tendency to roll back downhill
when driving away from a standstill. You can prevent this by pulling
out the parking brake switch as you press the accelerator (in the
same way as with a conventional handbrake).Emergency braking function
This feature enables you to stop the vehicle if the main
brake system should fail or if the pedal is obstructed.– Pull out and hold the parking brake switch to stop the
vehicle with the parking brake in an emergency.
– The brakes will be released immediately if you release the
switch or press down the accelerator.
If you pull out and hold the parking brake switch at a road speed
above about 8 km/h, this will initiate an emergency brake applica-
tion. The brakes are then applied hydraulically at all four wheels.
The effect is the same as an emergency stop (full brake application)
⇒
To prevent the emergency braking function from being used acci-
dentally, a warning buzzer sounds when the switch is operated. The
brakes are released immediately when you release the switch or
press down the accelerator.
WARNING
You should only use the emergency braking function in a real
emergency, for example if the brake system should fail or if the
brake pedal is obstructed. If you use the emergency braking func-
tion by activating the parking brake switch, the effect is similar to
a full brake application (emergency stop). Please remember that
the ESP (with its combined ABS, EDL and traction control func-
tions) is still subject to certain physical limits. In a corner or in bad
road or weather conditions an emergency stop can cause the
vehicle to skid or lose steering control.Driver messages in the instrument cluster displayCaution: Vehicle parked too steep
This message can appear when you apply the parking brake if the
car is parked on a gradient steeper than about 30%.
In this case the parking brake may not be strong enough to prevent
the vehicle from rolling back accidentally.
Please release parking brake
However, please remember that, for safety reasons, the parking
brake will only release automatically if the driver's seat belt is
buckled.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 123 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 137 of 313
Automatic gearbox135
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data When the vehicle slows down (for instance when braking), the
gearbox automatically shifts down into the next gear when the
minimum engine speed is reached.
Changing down to a lower gear increases the engine braking effect
on downhill gradients.
When the accelerator pedal is pressed right down past the point of
resistance at full throttle, the gearbox will select a lower gear,
depending on road speed and engine speed.
Applies to vehicles: with multitronic®Back-up programme
A back-up system is in place should a fault occur in the
control system.The automatic gearbox switches to the back-up programme if a fault
should occur in the control system. This is indicated by all segments
of the display panel either lighting up together or going out
completely.
It is still possible to move the selector lever to all positions. The
manual shift programme (tiptronic) is not available when the back-
up programme is active.
It will still be possible to use reverse gear in the normal way.
However, the electronic lock for reverse gear will be switched off.
Caution
Should the gearbox ever switch into the back-up programme, you
should take the vehicle to an Audi dealer or qualified workshop as
soon as possible.
Applies to vehicles: Tiptronic controls on steering wheelSteering wheel with tiptronic controls
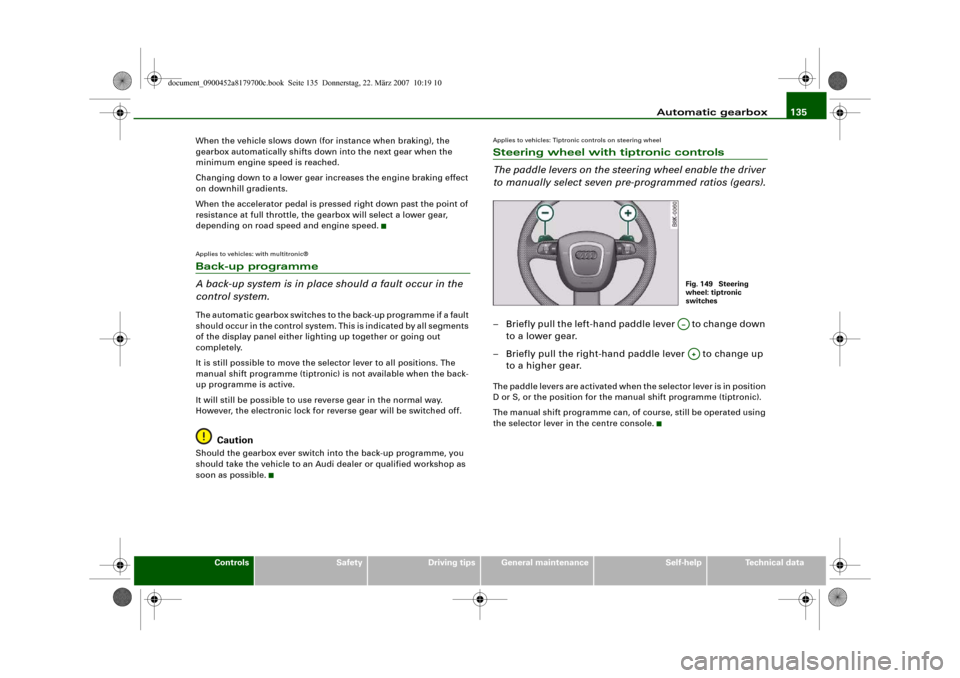
The paddle levers on the steering wheel enable the driver
to manually select seven pre-programmed ratios (gears).– Briefly pull the left-hand paddle lever to change down
to a lower gear.
– Briefly pull the right-hand paddle lever to change up
to a higher gear.The paddle levers are activated when the selector lever is in position
D or S, or the position for the manual shift programme (tiptronic).
The manual shift programme can, of course, still be operated using
the selector lever in the centre console.
Fig. 149 Steering
wheel: tiptronic
switchesA…A+
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 135 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 149 of 313
Audi parking system147
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
– Press the control button for Mode ⇒page 145,
fig. 161. “Parking mode 2” ⇒fig. 162 will appear in the
MMI display.
– Reverse and align the position of your vehicle in such a
way that the dark blue area marking ⇒fig. 162
borders onto the vehicle behind or onto the parking
space line marking. If you are not parking next to obsta-
cles ⇒page 150 the long side of the dark blue marking
should border onto the kerb. The complete dark blue
area marking must fit into the parking space ⇒page 143,
fig. 157.
– When the vehicle is stationary turn the steering wheel to
the right as far as it will go.
– Reverse into the parking space. If you are not parking
next to obstacles ⇒page 150 the dark blue marking
should touch the kerb ⇒page 146, fig. 163. Stop your
vehicle.
– Turn the steering wheel to the left as far as it will go
(vehicle is stationary).
– Continue to reverse into the parking space until the
vehicle is standing parallel to the kerb. When reversing
you must also keep a close watch on the front end of the
vehicle ⇒.You can use “Parking mode 2” to park on the left or the right side of
the road. For this reason, the blue markings are shown in various
shades of blue. The dark blue area marking and the dark blue
curve are used when parking on the right side of the road. The
light blue area marking and the light blue curve are used
when parking on the left side of the road.When the turn signals are on, the display will only show the mark-
ings for the relevant side. To change the display to the other side,
just switch on the opposite turn signals.
The light blue and dark blue cur v e s s h o w y o u w h e n t o t u r n t h e
steering wheel in the other direction, i.e. when the curve touches
the kerb. ⇒page 146, fig. 163.
The distance from your rear bumper to the red line is approx.
40 cm. From here at the latest, the driver should not reverse any
further ⇒page 151.
WARNING
Please note that objects which are not touching the ground may
appear to be further away than they actually are (e.g. the bumper
of a parked vehicle, a towing bracket or the rear end of a truck). In
this case you should not use the orientation lines for judging the
distance (accident risk).
Caution
The MMI display shows the path of the rear end of the vehicle if you
were to reverse using the current steering angle. NB: The front end
of the vehicle swings out further than the rear.
Note
To ensure that the reversing camera works properly, the lens of the
camera ⇒page 140, fig. 154 must be kept clean and free of snow
and ice. Please observe the additional notes on ⇒page 152.Applies to vehicles: with parking system and towing bracketTo w i n g b r a c k e tOnce the electrical connector for the trailer socket is plugged in on
vehicles with a factory-fitted towing bracket the rear sensors for the
AAA2
A4
A2
A4
A1
A3
A3
A4
A5
A6
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 147 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 166 of 313
Safe driving 164Correct sitting positionsCorrect sitting position for driver
The correct driving position is important for safe and
fatigue-free driving.For your own safety, and to reduce the risk of injury in the
event of an accident, we recommend the following driving
position.
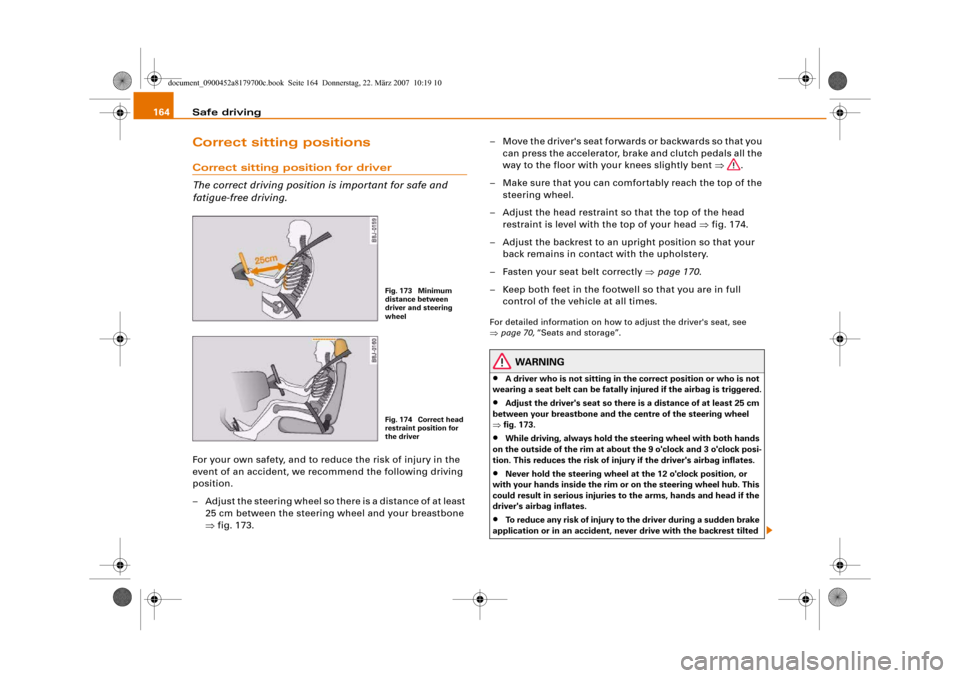
– Adjust the steering wheel so there is a distance of at least
25 cm between the steering wheel and your breastbone
⇒fig. 173.– Move the driver's seat forwards or backwards so that you
can press the accelerator, brake and clutch pedals all the
way to the floor with your knees slightly bent ⇒.
– Make sure that you can comfortably reach the top of the
steering wheel.
– Adjust the head restraint so that the top of the head
restraint is level with the top of your head ⇒fig. 174.
– Adjust the backrest to an upright position so that your
back remains in contact with the upholstery.
– Fasten your seat belt correctly ⇒page 170.
– Keep both feet in the footwell so that you are in full
control of the vehicle at all times.
For detailed information on how to adjust the driver's seat, see
⇒page 70, “Seats and storage”.
WARNING
•
A driver who is not sitting in the correct position or who is not
wearing a seat belt can be fatally injured if the airbag is triggered.
•
Adjust the driver's seat so there is a distance of at least 25 cm
between your breastbone and the centre of the steering wheel
⇒fig. 173.
•
While driving, always hold the steering wheel with both hands
on the outside of the rim at about the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock posi-
tion. This reduces the risk of injury if the driver's airbag inflates.
•
Never hold the steering wheel at the 12 o'clock position, or
with your hands inside the rim or on the steering wheel hub. This
could result in serious injuries to the arms, hands and head if the
driver's airbag inflates.
•
To reduce any risk of injury to the driver during a sudden brake
application or in an accident, never drive with the backrest tilted
Fig. 173 Minimum
distance between
driver and steering
wheelFig. 174 Correct head
restraint position for
the driver
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 164 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 174 of 313
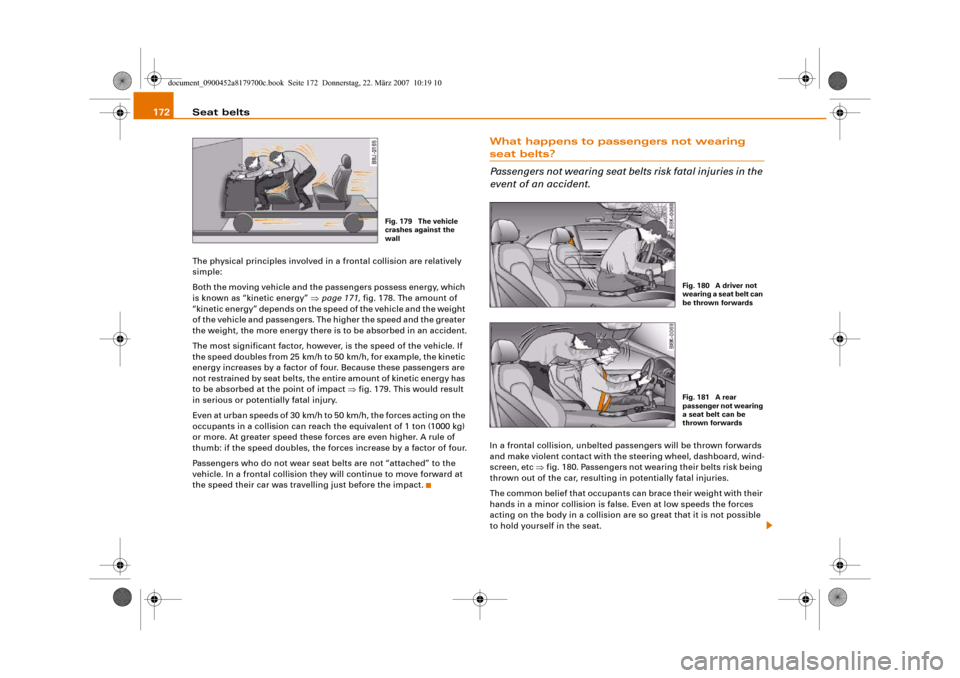
Seat belts 172The physical principles involved in a frontal collision are relatively
simple:
Both the moving vehicle and the passengers possess energy, which
is known as “kinetic energy” ⇒page 171, fig. 178. The amount of
“kinetic energy” depends on the speed of the vehicle and the weight
of the vehicle and passengers. The higher the speed and the greater
the weight, the more energy there is to be absorbed in an accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the speed of the vehicle. If
the speed doubles from 25 km/h to 50 km/h, for example, the kinetic
energy increases by a factor of four. Because these passengers are
not restrained by seat belts, the entire amount of kinetic energy has
to be absorbed at the point of impact ⇒fig. 179. This would result
in serious or potentially fatal injury.
Even at urban speeds of 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the forces acting on the
occupants in a collision can reach the equivalent of 1 ton (1000 kg)
or more. At greater speed these forces are even higher. A rule of
thumb: if the speed doubles, the forces increase by a factor of four.
Passengers who do not wear seat belts are not “attached” to the
vehicle. In a frontal collision they will continue to move forward at
the speed their car was travelling just before the impact.
What happens to passengers not wearing seat belts?
Passengers not wearing seat belts risk fatal injuries in the
event of an accident.In a frontal collision, unbelted passengers will be thrown forwards
and make violent contact with the steering wheel, dashboard, wind-
screen, etc ⇒fig. 180. Passengers not wearing their belts risk being
thrown out of the car, resulting in potentially fatal injuries.
The common belief that occupants can brace their weight with their
hands in a minor collision is false. Even at low speeds the forces
acting on the body in a collision are so great that it is not possible
to hold yourself in the seat.
Fig. 179 The vehicle
crashes against the
wall
Fig. 180 A driver not
wearing a seat belt can
be thrown forwardsFig. 181 A rear
passenger not wearing
a seat belt can be
thrown forwards
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 172 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 180 of 313
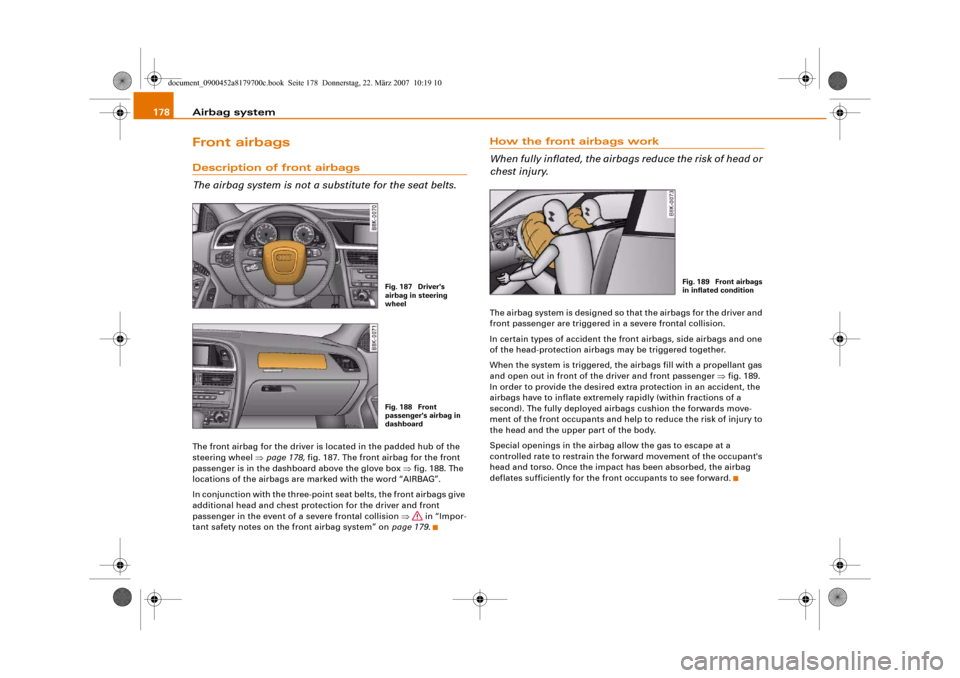
Airbag system 178Front airbagsDescription of front airbags
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belts.The front airbag for the driver is located in the padded hub of the
steering wheel ⇒page 178, fig. 187. The front airbag for the front
passenger is in the dashboard above the glove box ⇒fig. 188. The
locations of the airbags are marked with the word “AIRBAG”.
In conjunction with the three-point seat belts, the front airbags give
additional head and chest protection for the driver and front
passenger in the event of a severe frontal collision ⇒ in “Impor-
tant safety notes on the front airbag system” on page 179.
How the front airbags work
When fully inflated, the airbags reduce the risk of head or
chest injury.The airbag system is designed so that the airbags for the driver and
front passenger are triggered in a severe frontal collision.
In certain types of accident the front airbags, side airbags and one
of the head-protection airbags may be triggered together.
When the system is triggered, the airbags fill with a propellant gas
and open out in front of the driver and front passenger ⇒fig. 189.
In order to provide the desired extra protection in an accident, the
airbags have to inflate extremely rapidly (within fractions of a
second). The fully deployed airbags cushion the forwards move-
ment of the front occupants and help to reduce the risk of injury to
the head and the upper part of the body.
Special openings in the airbag allow the gas to escape at a
controlled rate to restrain the forward movement of the occupant's
head and torso. Once the impact has been absorbed, the airbag
deflates sufficiently for the front occupants to see forward.
Fig. 187 Driver's
airbag in steering
wheelFig. 188 Front
passenger's airbag in
dashboard
Fig. 189 Front airbags
in inflated condition
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 178 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 181 of 313
Airbag system179
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
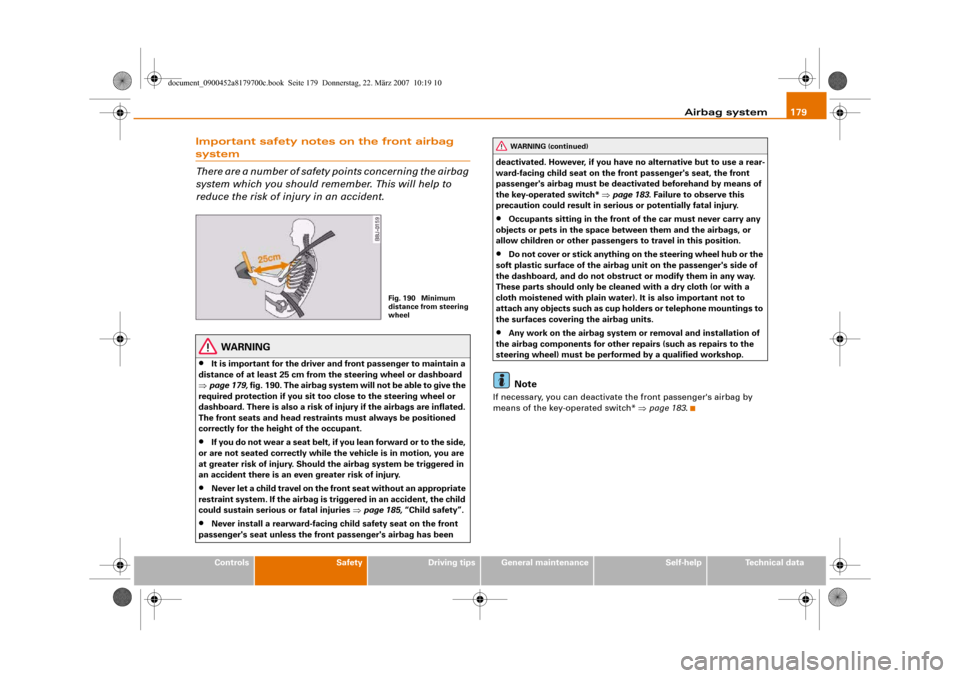
Important safety notes on the front airbag system
There are a number of safety points concerning the airbag
system which you should remember. This will help to
reduce the risk of injury in an accident.
WARNING
•
It is important for the driver and front passenger to maintain a
distance of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel or dashboard
⇒page 179, fig. 190. The airbag system will not be able to give the
required protection if you sit too close to the steering wheel or
dashboard. There is also a risk of injury if the airbags are inflated.
The front seats and head restraints must always be positioned
correctly for the height of the occupant.
•
If you do not wear a seat belt, if you lean forward or to the side,
or are not seated correctly while the vehicle is in motion, you are
at greater risk of injury. Should the airbag system be triggered in
an accident there is an even greater risk of injury.
•
Never let a child travel on the front seat without an appropriate
restraint system. If the airbag is triggered in an accident, the child
could sustain serious or fatal injuries ⇒page 185, “Child safety”.
•
Never install a rearward-facing child safety seat on the front
passenger's seat unless the front passenger's airbag has been deactivated. However, if you have no alternative but to use a rear-
ward-facing child seat on the front passenger's seat, the front
passenger's airbag must be deactivated beforehand by means of
the key-operated switch* ⇒page 183. Failure to observe this
precaution could result in serious or potentially fatal injury.
•
Occupants sitting in the front of the car must never carry any
objects or pets in the space between them and the airbags, or
allow children or other passengers to travel in this position.
•
Do not cover or stick anything on the steering wheel hub or the
soft plastic surface of the airbag unit on the passenger's side of
the dashboard, and do not obstruct or modify them in any way.
These parts should only be cleaned with a dry cloth (or with a
cloth moistened with plain water). It is also important not to
attach any objects such as cup holders or telephone mountings to
the surfaces covering the airbag units.
•
Any work on the airbag system or removal and installation of
the airbag components for other repairs (such as repairs to the
steering wheel) must be performed by a qualified workshop.Note
If necessary, you can deactivate the front passenger's airbag by
means of the key-operated switch* ⇒page 183.
Fig. 190 Minimum
distance from steering
wheel
WARNING (continued)
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 179 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
Page 198 of 313
Intelligent technology 196Intelligent technologyElectronic stabilisation program (ESP)General notes
The electronic stabilisation program increases the car's
stability on the road.The ESP is designed to enhance the control over the vehicle in crit-
ical handling situations, such as when accelerating and cornering.
It reduces the tendency to skid under all road conditions and
improves the stability and roadholding of the vehicle. The system
works at all speeds.The anti-lock brake system (ABS), the electronic differential lock
(EDL) and the traction control system (ASR) are all integrated into
the electronic stabilisation program.
How the system works
The ESP control unit processes data from the three integrated
systems. It also processes additional inputs provided by other high-
precision sensors. These register the vehicle's rotation about the
vertical axis (yaw rate), lateral acceleration, brake pressure and
steering wheel angle.
The system uses the steering wheel angle and road speed to calcu-
late the changes of direction intended by the driver, and constantly
compares them with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If the
desired course is not being maintained (for instance, if the car is
starting to skid), then the ESP compensates automatically by
braking the appropriate wheel.
The forces acting on the braked wheel effectively bring the car back
to a stable condition. If the car is oversteering (rear wheels losing
grip first) the brake application is concentrated on the outside front
wheel; if the car is understeering (front wheels losing grip first), ESP
brakes the inside rear wheel. This automatic brake application is
accompanied by characteristic noises.
The ESP works in conjunction with the ABS ⇒page 197. If a
malfunction should occur in the ABS, the ESP will also be out of
action.
Switching on
The ESP is switched on automatically when the engine is started
and performs a self-test routine. As soon as this routine is complete,
the system switches back to normal operating mode. You can press
the button ⇒fig. 203 or ⇒fig. 204 to switch on the ESP or traction
control system (ASR) if they have been switched off. The message
ESP/ASR on will appear briefly in the display.
Fig. 203 Without MMI:
Centre console with
ESP switchFig. 204 Centre
console with ESP
switch
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 196 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10