Page 396 of 650
4 - 78
ENGCDI MAGNETO
EC4L0000
CDI MAGNETO
Extent of removal:1 CDI magneto removal
Extent of removal Order Part name Q’ty Remarks
CDI MAGNETO REMOVAL
Preparation for removal Seat and fuel tank Refer to “SEAT, FUEL TANK AND SIDE
COVERS” section.
Disconnect the CDI magneto lead.
1 Crankcase cover (left) 1
2 Gasket 1
3 Dowel pin 2
4 Nut (rotor) 1 Use special tool.
Refer to “REMOVAL POINTS”.
5 Rotor 1
6 Stator 1
7 Woodruff key 1
1
Page 398 of 650
4 - 79
ENGCDI MAGNETO
EC4L3000
REMOVAL POINTS
EC4L3101
Rotor
1. Remove:
Nut (rotor) 1
Plain washer
2. Remove:
Rotor 1
Use the rotor puller 2.
Rotor puller:
YM-04151/90890-04151
EC4L4000
INSPECTION
EC4L4101
CDI magneto
1. Inspect:
Rotor inner surface a
Stator outer surface b
Damage → Inspect the crankshaft runout
and crankshaft bearing.
If necessary, replace CDI magneto and/
or stator.
EC4L4200
Woodruff key
1. Inspect:
Woodruff key 1
Damage → Replace.
EC4L5000
ASSEMBLY AND INSTALLATION
CDI magneto
1. Install:
Stator 1
Screw (stator) 2
NOTE:
Apply the sealant to the grommet of the CDI
magneto lead.
Tighten the screws using the T30 bit.
YAMAHA Bond No. 1215
(ThreeBond® No. 1215):
90890-85505
T R..10 Nm (1.0 m · kg, 7.2 ft · lb)
Page 400 of 650
4 - 80
ENGCDI MAGNETO
2. Install:
Woodruff key 1
Rotor 2
NOTE:
Clean the tapered portions of the crankshaft
and rotor.
When installing the woodruff key, make sure
that its flat surface a is in parallel with the
crankshaft center line b.
When installing the rotor, align the keyway c
of the rotor with the woodruff key.
3. Install:
Plain washer
Nut (rotor) 1
T R..56 Nm (5.6 m · kg, 40 ft · lb)
4. Connect:
CDI magneto lead
Refer to “CABLE ROUTING DIAGRAM”
section in the CHAPTER 2.
5. Install:
Dowel pin
O-ring
Gasket [crankcase cover (left)]
Crankcase cover (left) 1
Hose holder (cylinder head breather
hose) 2
Bolt [crankcase cover (left)]
NOTE:
Apply the lithium soap base grease on the O-
ring.
Tighten the bolts in stage, using a crisscross
pattern.
New
New
T R..10 Nm (1.0 m · kg, 7.2 ft · lb)
Page 402 of 650
4 - 81
ENGENGINE REMOVAL
EC4M0000
ENGINE REMOVAL
Extent of removal Order Part name Q’ty Remarks
ENGINE REMOVAL
Preparation for removal Hold the machine by placing the
suitable stand under the frame.
WARNING
Support the machine securely so there is nodanger of it falling over.
Seat and fuel tank Refer to “SEAT, FUEL TANK AND SIDE
COVERS” section.
Rear shock absorber Refer to “REAR SHOCK ABSORBER”
section in the CHAPTER 5.
Carburetor Refer to “CARBURETOR” section.
Exhaust pipe and silencer Refer to “EXHAUST PIPE AND
SILENCER” section.
Clutch cable Disconnect at engine side.
Radiator Refer to “RADIATOR” section.
Shift pedal Refer to “KICK AXLE AND SHIFT
SHAFT” section.
Cylinder head breather hose Refer to “CAMSHAFTS” section.
Drain the engine oil Refer to “ENGINE OIL REPLACEMENT”
section in the CHAPTER 3.
Ignition coil
Disconnect the CDI magneto lead.
Engine guard
Page 412 of 650
4 - 86
ENGCRANKCASE AND CRANKSHAFT
CRANKCASE AND CRANKSHAFT
CRANKCASE AND CRANKSHAFT
Extent of removal:
1 Crankcase separation
2 Crankshaft removal
Extent of removal Order Part name Q’ty Remarks
CRANKCASE SEPARATION
Preparation for removal Engine Refer to “ENGINE REMOVAL” section.
Piston Refer to “CYLINDER AND PISTON” sec-
tion.
Balancer Refer to “BALANCER” section.
Kick axle assembly
Refer to “KICK AXLE AND SHIFT
SHAFT” section.
Segment
Stator Refer to “CDI MAGNETO” section.
1 Timing chain guide (rear) 1
2 Timing chain 1
3 Bolt (50 mm) 7
Refer to “REMOVAL POINTS”. 4 Bolt (60 mm) 2
5 Bolt (80 mm) 3
6 Hose guide 1
21
Page 576 of 650

6 - 1
–+ELECELECTRICAL COMPONENTS AND WIRING DIAGRAM
EC600000
ELECTRICAL
EC610000
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS AND WIRING DIAGRAM
EC611000
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
1“ENGINE STOP” button
2TPS (throttle position sensor)
3Neutral switch
4CDI magneto
5Ignition coil
6Spark plug
7CDI unitCOLOR CODE
B ...................... Black
Br .................... Brown
G ..................... Green
L ...................... Blue
O ..................... Orange
P ...................... Pink
R ..................... Red
Sb.................... Sky blue
EC612000
WIRING DIAGRAM
71
5
62
3
4
B/WB/W
B/L
B/Y
SbSb
G/B
LYLY
P
B
B
B
B
G
O
WR
P
GW
R PP
B Br W
W
B/YGBr
G RR
OB Sb Sb Y
Y
WY
W
GG
B
PP
Br BrR R
OL
B SbY LL
B/L B/WB/W G/B
B B
B/L L Sb
B/L
G/B B/Y
B/Y
G/B B/W
O B/W
BrBr
W ..................... White
Y ...................... Yellow
B/L ................... Black/Blue
B/W .................. Black/White
B/Y ................... Black/Yellow
G/B................... Green/Black
L/W .................. Blue/White
R/W .................. Red/White
Page 578 of 650

–+ELEC
6 - 2
MAP-CONTROLLED CDI UNIT
MAP-CONTROLLED CDI UNIT
A map-controlled, CDI ignition system is used in the YZ450F.
The microcomputer in the CDI unit detects the engine speed and throttle position, thus determining
the optimum ignition timing through the entire operating range. In this way, quick throttle response
can be achieved according to various riding conditions.
Throttle position sensorCDI unitIgnition coil
Pickup coilCDI magneto rotor
�Function of Component
Component Function
TPS
(throttle position sensor)Detects throttle valve opening and inputs it into the computer in the
CDI unit as a throttle opening signal.
Pickup coil Detects signal rotor revolutions and inputs them into the computer in
the CDI unit as engine revolution signals.
CDI unit The signals of the TPS and pickup coil sensor are analyzed by the
computer in the CDI unit, which then adjusts ignition timing for the
operation requirements.
�Principal of 3-Dimensional Control
Conventionally, ignition timing was controlled only
by engine revolutions (2-dimensional control).
However, ignition timing needs advancement also
by engine load. Thus, accurate ignition timing can
be determined by adding throttle opening to deter-
mine ignition timing (3-dimensional control).
3-D Image Map of Ignition Timing
(different from actual characteristics)
Ignition timing
Thr
ot
tl
e
ope
ni
ngR
evo
l
ut
io
ns
Page 579 of 650
–+ELEC
BOITIER CDI COMMANDE PAR PRESSION ABSOLUE DE
LA TUBULURE D’ADMISSION
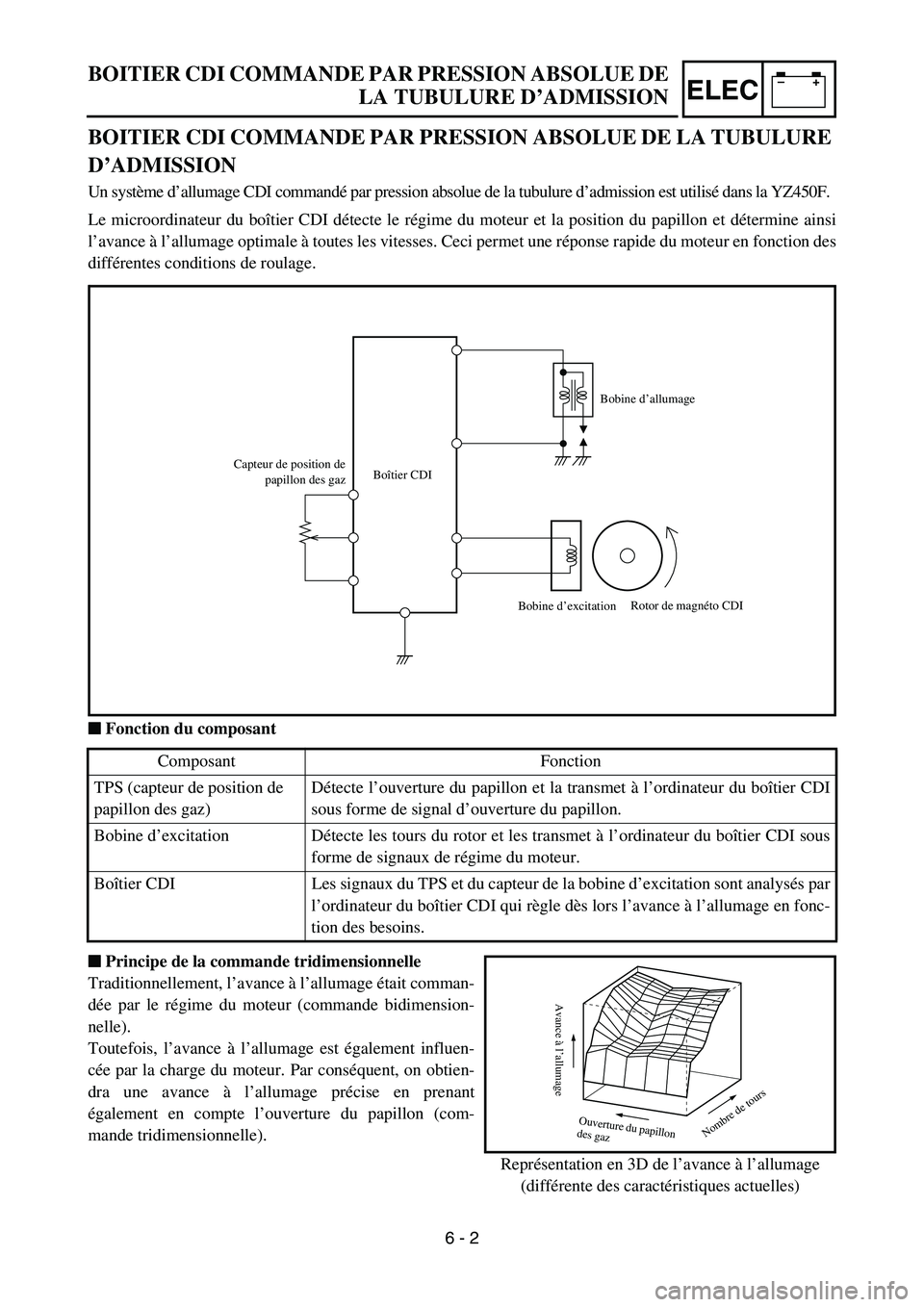
BOITIER CDI COMMANDE PAR PRESSION ABSOLUE DE LA TUBULURE
D’ADMISSION
Un système d’allumage CDI commandé par pression absolue de la tubulure d’admission est utilisé dans la YZ450F.
Le microordinateur du boîtier CDI détecte le régime du moteur et la position du papillon et détermine ainsi
l’avance à l’allumage optimale à toutes les vitesses. Ceci permet une réponse rapide du moteur en fonction des
différentes conditions de roulage.
�
�� �
Fonction du composant
�
�� �
Principe de la commande tridimensionnelle
Traditionnellement, l’avance à l’allumage était comman-
dée par le régime du moteur (commande bidimension-
nelle).
Toutefois, l’avance à l’allumage est également influen-
cée par la charge du moteur. Par conséquent, on obtien-
dra une avance à l’allumage précise en prenant
également en compte l’ouverture du papillon (com-
mande tridimensionnelle).
Représentation en 3D de l’avance à l’allumage
(différente des caractéristiques actuelles) Composant Fonction
TPS (capteur de position de
papillon des gaz)Détecte l’ouverture du papillon et la transmet à l’ordinateur du boîtier CDI
sous forme de signal d’ouverture du papillon.
Bobine d’excitation Détecte les tours du rotor et les transmet à l’ordinateur du boîtier CDI sous
forme de signaux de régime du moteur.
Boîtier CDI Les signaux du TPS et du capteur de la bobine d’excitation sont analysés par
l’ordinateur du boîtier CDI qui règle dès lors l’avance à l’allumage en fonc-
tion des besoins.
Capteur de position de
papillon des gazBoîtier CDIBobine d’allumage
Bobine d’excitationRotor de magnéto CDI
Avance à l’allumage
Ouv
er
tu
re
du
pa
pi
ll
on
d
es
ga
zNo
m
br
e
de
tou
r
s
6 - 2