2007 SUZUKI SWIFT circuit
[x] Cancel search: circuitPage 5 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 00- i
00
Section 00
CONTENTS
Precautions
Precautions ............................................... 00-1
Precautions........................................................... 00-1
Precautions for Vehicles Equipped with a Supplemental Restraint (A ir Bag) System ........ 00-1
General Precautions ........... ................................ 00-4
Warning for Wheel (with tire) Removal ............... 00-7
Warning for Handling Emergency Flat Tire Repair Kit .......................................................... 00-7
Precautions for Catalytic Converter .................... 00-7
Precautions for Installing Mobile Communication Equipment ............................... 00-7
Precaution for CAN Communication System ...... 00-7 Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service ............ 00-8
Air Bag Warning ................................................ 00-10
Air Bag System Service Warning ...................... 00-10
Fastener Caution............................................... 00-10
Suspension Caution .......................................... 00-10
Wheels and Tires Caution ................................. 00-10
Precaution for Vehicle Equipped with ESP
®
System ............................................................ 00-11
Brake Caution ................................................... 00-11
Repair Instructions ........ .................................... 00-11
Electrical Circuit Inspection Procedure ............. 00-11
Intermittent and Poor Co nnection Inspection .... 00-13
Page 7 of 1496
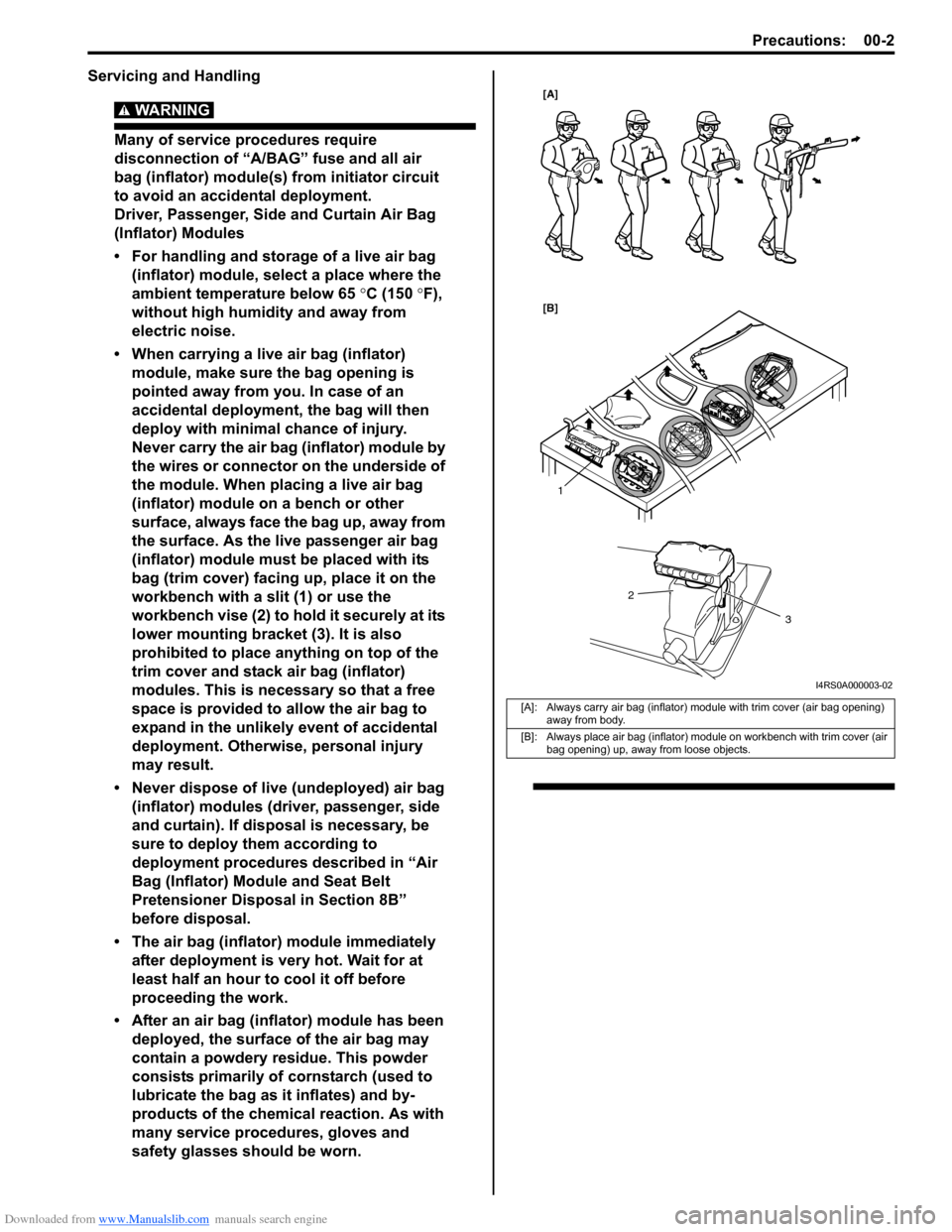
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-2
Servicing and Handling
WARNING!
Many of service procedures require
disconnection of “A/BAG” fuse and all air
bag (inflator) module(s) from initiator circuit
to avoid an accidental deployment.
Driver, Passenger, Side and Curtain Air Bag
(Inflator) Modules
• For handling and storage of a live air bag (inflator) module, select a place where the
ambient temperature below 65 °C (150 ° F),
without high humidity and away from
electric noise.
• When carrying a live air bag (inflator) module, make sure the bag opening is
pointed away from you. In case of an
accidental deployment, the bag will then
deploy with minimal chance of injury.
Never carry the air bag (inflator) module by
the wires or connector on the underside of
the module. When placing a live air bag
(inflator) module on a bench or other
surface, always face the bag up, away from
the surface. As the live passenger air bag
(inflator) module must be placed with its
bag (trim cover) facing up, place it on the
workbench with a slit (1) or use the
workbench vise (2) to hold it securely at its
lower mounting bracket (3). It is also
prohibited to place anything on top of the
trim cover and stack air bag (inflator)
modules. This is necessary so that a free
space is provided to allow the air bag to
expand in the unlikely event of accidental
deployment. Otherwise, personal injury
may result.
• Never dispose of live (undeployed) air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side
and curtain). If disposal is necessary, be
sure to deploy them according to
deployment procedures described in “Air
Bag (Inflator) Module and Seat Belt
Pretensioner Disposal in Section 8B”
before disposal.
• The air bag (inflator) module immediately
after deployment is very hot. Wait for at
least half an hour to cool it off before
proceeding the work.
• After an air bag (inflator) module has been deployed, the surface of the air bag may
contain a powdery residue. This powder
consists primarily of cornstarch (used to
lubricate the bag as it inflates) and by-
products of the chemical reaction. As with
many service procedures, gloves and
safety glasses should be worn.
[A]: Always carry air bag (inflator) module with trim cover (air bag opening) away from body.
[B]: Always place air bag (inflator) module on workbench with trim cover (air bag opening) up, away from loose objects.
1
2
3
[A]
[B]
I4RS0A000003-02
Page 13 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-8
Precautions for Electrical Circuit ServiceS7RS0B0000008
• When replacing a fuse, make sure to use a fuse of the specified capacity. Use of a fuse with a larger capacity
will cause a damage to the electrical parts and a fire.
• When disconnecting and connecting coupler, make sure to turn ignition switch OFF, or electronic parts
may get damaged.
• When disconnecting connectors, never pull the wiring harness. Unlock the connecto r lock first and then pull
them apart by holding connectors themselves. • When connecting connectors, also hold connectors
and put them together until th ey lock securely (a click
is heard).
• When installing the wiring harness, fix it with clamps so that no slack is left.
• When installing vehicle parts, be careful so that the wiring harness is not interfered with or caught by any
other part.
• To avoid damage to the harnes s, protect its part which
may contact against a part forming a sharp angle by
winding tape or the like around it.
I2RH01010038-01
I2RH01010039-01
I2RH01010040-01
I2RH01010041-01
I2RH01010042-01
I2RH01010043-01
I2RH01010044-01
Page 16 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-11 Precautions:
Precaution for Vehicle Equipped with ESP®
System
S7RS0B0000015
• When testing with any of the following equipments
(when vehicle is tested by rotating wheels (tires)
under vehicle stop), be sure to deactivate ESP ®
system referring to “Precautions in Speedometer Test
or Other Tests in Section 4F” to obtain correct data.
– 2 or 4-wheel chassis dynamometer
– Speedometer tester
– Brake tester
–Etc.
ESP ® control module
• When ESP ® control module is removed / installed, do
not use impact wrenches which generate shock or
impact to avoid damaging sensors in ESP ® control
module.
• When any of the following operation is done, calibrate steering angle sensor referring to “Sensor Calibration
in Section 4F”.
– When battery or dome fuse is removed.
– When steering angle sensor is replaced.
Brake CautionS7RS0B0000014
CAUTION!
All brake fasteners are important attaching
parts in that they could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems, and/
or could result in major repair expense. They
must be replaced with one of same part
number or with an eq uivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use
a replacement part of lesser quality or
substitute design. Torque values must be
used as specified during reassembly to
assure proper retention of all parts. There is
to be no welding as it may result in extensive
damage and weakening of the metal.
Repair Instructions
Electrical Circuit Inspection ProcedureS7RS0B0006001
While there are various electrical circuit inspection
methods, described here is a general method to check
its open and short circuit by using an ohmmeter and a
voltmeter.
Open Circuit Check
Possible causes for the open circuit are as follows. As
the cause is in the connector or terminal in many cases,
they need to be checked particularly carefully.
• Loose connection of connector
• Poor contact of terminal (due to dirt, corrosion or rust
on it, poor contact tension, entry of foreign object etc.)
• Wire harness being open
When checking system circuits including an electronic
control unit such as ECM, TCM, ABS control module,
etc., it is important to perfor m careful check, starting with
items which are easier to check.
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable from battery
2) Check each connector at both ends of the circuit being checked for loose connection. Also check lock
condition of connector if equipped with connector
lock. 3) Using a test male terminal
, check both terminals of
the circuit being checked for contact tension of its
female terminal. Check each terminal visually for
poor contact (possibly caused by dirt, corrosion, rust
entry of foreign object, etc.). At the same time, check
to make sure that each te rminal is locked in the
connector fully.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just for once.
I2RH01010049-01
I2RH01010050-01
Page 17 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-12
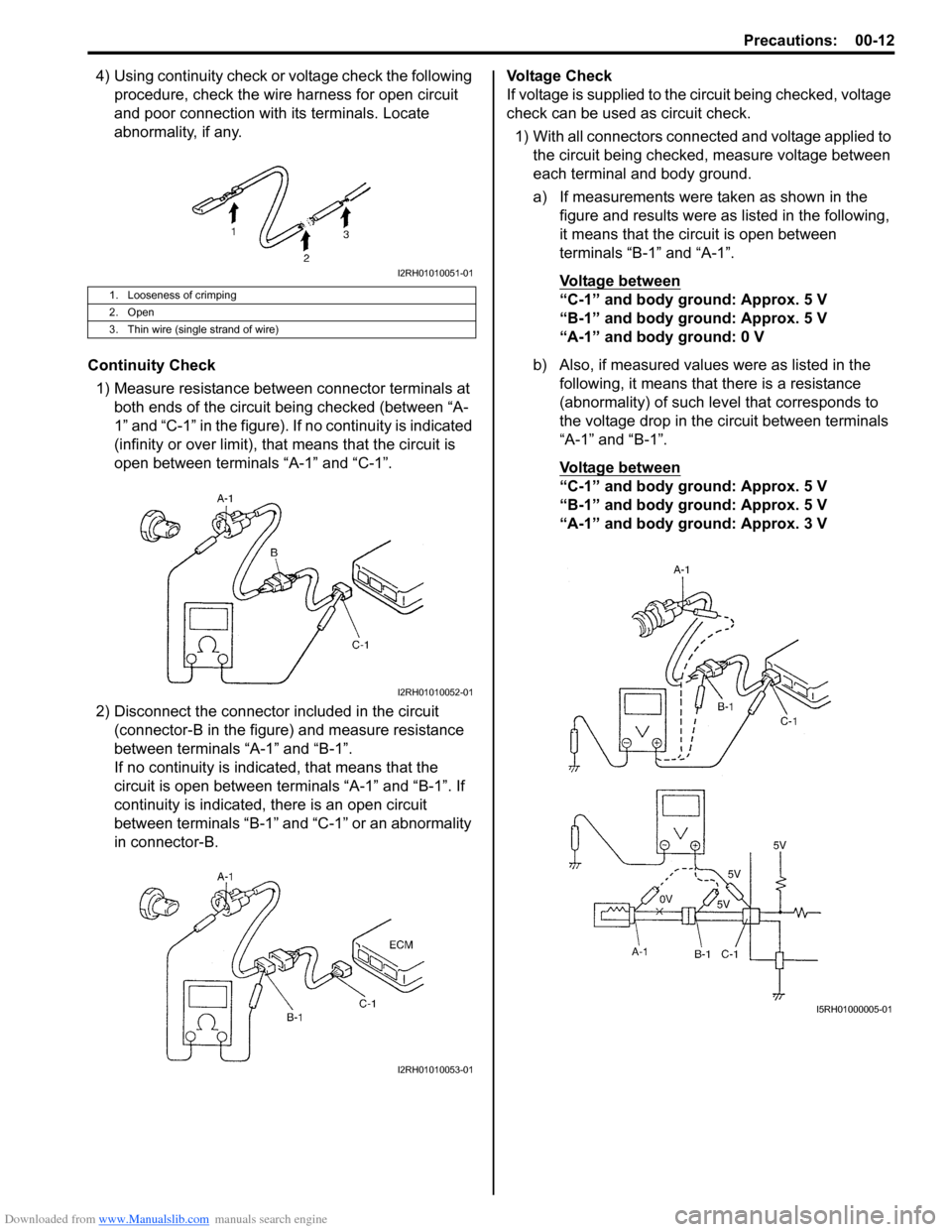
4) Using continuity check or voltage check the following procedure, check the wire harness for open circuit
and poor connection with its terminals. Locate
abnormality, if any.
Continuity Check 1) Measure resistance between connector terminals at both ends of the circuit being checked (between “A-
1” and “C-1” in the figure). If no continuity is indicated
(infinity or over limit), that means that the circuit is
open between terminals “A-1” and “C-1”.
2) Disconnect the connector included in the circuit (connector-B in the figure) and measure resistance
between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”.
If no continuity is indica ted, that means that the
circuit is open between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”. If
continuity is indicated, there is an open circuit
between terminals “B-1” and “C-1” or an abnormality
in connector-B. Voltage Check
If voltage is supplied to the circuit being checked, voltage
check can be used as circuit check.
1) With all connectors connected and voltage applied to the circuit being checked, measure voltage between
each terminal and body ground.
a) If measurements were taken as shown in the figure and results were as listed in the following,
it means that the circuit is open between
terminals “B-1” and “A-1”.
Voltage between
“C-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“B-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“A-1” and body ground: 0 V
b) Also, if measured values were as listed in the following, it means that there is a resistance
(abnormality) of such le vel that corresponds to
the voltage drop in the circuit between terminals
“A-1” and “B-1”.
Voltage between
“C-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“B-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“A-1” and body ground: Approx. 3 V
1. Looseness of crimping
2. Open
3. Thin wire (single strand of wire)
I2RH01010051-01
I2RH01010052-01
I2RH01010053-01
I5RH01000005-01
Page 18 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-13 Precautions:
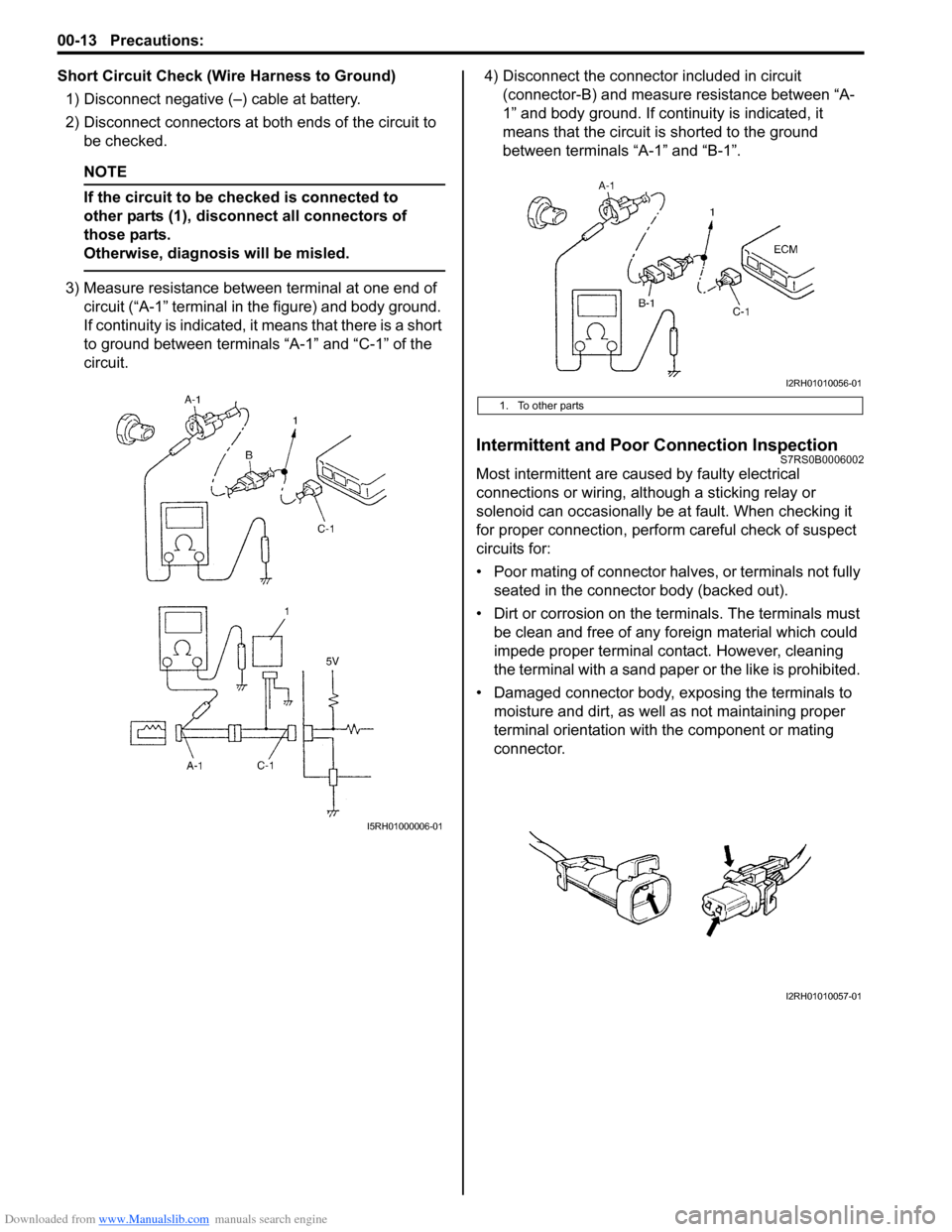
Short Circuit Check (Wire Harness to Ground)1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connectors at bot h ends of the circuit to
be checked.
NOTE
If the circuit to be checked is connected to
other parts (1), disconnect all connectors of
those parts.
Otherwise, diagnosis will be misled.
3) Measure resistance between terminal at one end of circuit (“A-1” terminal in the figure) and body ground.
If continuity is indicated, it means that there is a short
to ground between terminals “A-1” and “C-1” of the
circuit. 4) Disconnect the connector included in circuit
(connector-B) and measure resistance between “A-
1” and body ground. If continuity is indicated, it
means that the circuit is shorted to the ground
between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”.
Intermittent and Poor Connection InspectionS7RS0B0006002
Most intermittent are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring, although a sticking relay or
solenoid can occasionally be at fault. When checking it
for proper connection, perfor m careful check of suspect
circuits for:
• Poor mating of connector halves, or terminals not fully seated in the connector body (backed out).
• Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. The terminals must be clean and free of any foreign material which could
impede proper terminal contact. However, cleaning
the terminal with a sand paper or the like is prohibited.
• Damaged connector body, exposing the terminals to moisture and dirt, as well as not maintaining proper
terminal orientation with the component or mating
connector.
I5RH01000006-01
1. To other parts
I2RH01010056-01
I2RH01010057-01
Page 19 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-14
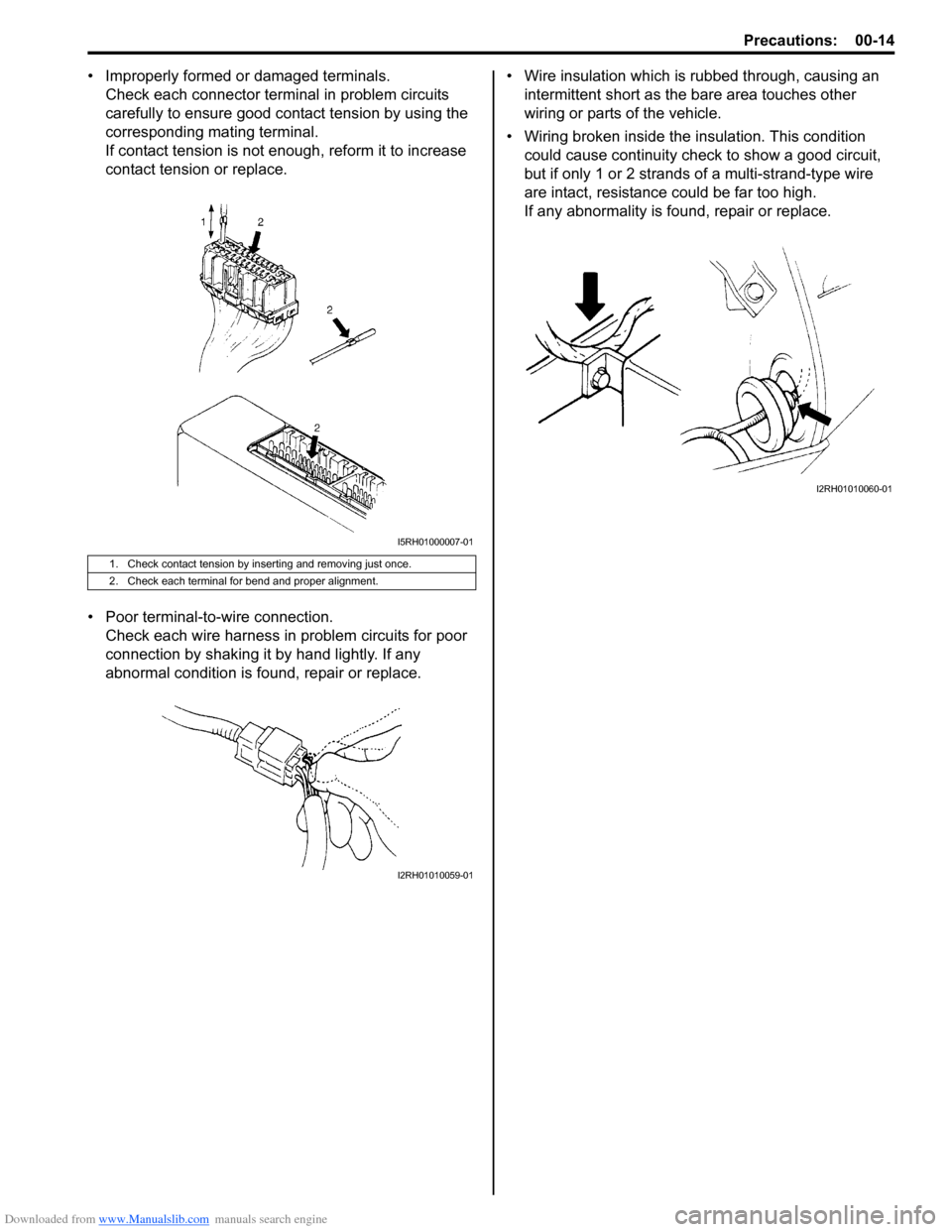
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals.Check each connector terminal in problem circuits
carefully to ensure good contact tension by using the
corresponding mating terminal.
If contact tension is not enough, reform it to increase
contact tension or replace.
• Poor terminal-to -wire connection.
Check each wire harness in problem circuits for poor
connection by shaking it by hand lightly. If any
abnormal condition is found, repair or replace. • Wire insulation which is rubbed through, causing an
intermittent short as the bare area touches other
wiring or parts of the vehicle.
• Wiring broken inside the insulation. This condition
could cause continuity check to show a good circuit,
but if only 1 or 2 strands of a multi-strand-type wire
are intact, resistance could be far too high.
If any abnormality is found, repair or replace.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just once.
2. Check each terminal for bend and proper alignment.
I5RH01000007-01
I2RH01010059-01
I2RH01010060-01
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers