2006 SUZUKI SWIFT Gear Oil
[x] Cancel search: Gear OilPage 40 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-10 Maintenance and Lubrication:
Steering System InspectionS7RS0B0206024
1) Check steering wheel for play and rattle, holding vehicle straight on ground.
Steering wheel play
“a”: 0 – 30 mm (0 – 1.1 in.)
2) Check bolts and nuts for tightness and retighten them as necessary. Repair or replace defective
parts, if any.
3) Check steering linkage for looseness and damage. Repair or replace defective parts, if any.
4) Check boots (1) and (2) of steering linkage and steering gear case for damage (leak, detachment,
tear, etc.). If damage is fo und, replace defective boot
with new one.
If any dent is found on steering gear case boots,
correct it to original shape by turning steering wheel
to the right or left as far as it stops and holding it for a
few seconds.
5) Check universal joints (3) of steering shaft for rattle and damage. If rattle or damage is found, replace
defective part with a new one.
6) Check that steering wheel can be turned fully to the
right and left. Repair or replace defective parts, if
any.
7) If equipped with power steering system, check also, in addition to check items, that steering wheel can be
turned fully to the right and left more lightly when
engine is running at idle speed than when it is
stopped. Repair, if found faulty.
8) Check wheel alignment referring to “Front Wheel Alignment Inspection and Adjustment in Section 2B”.
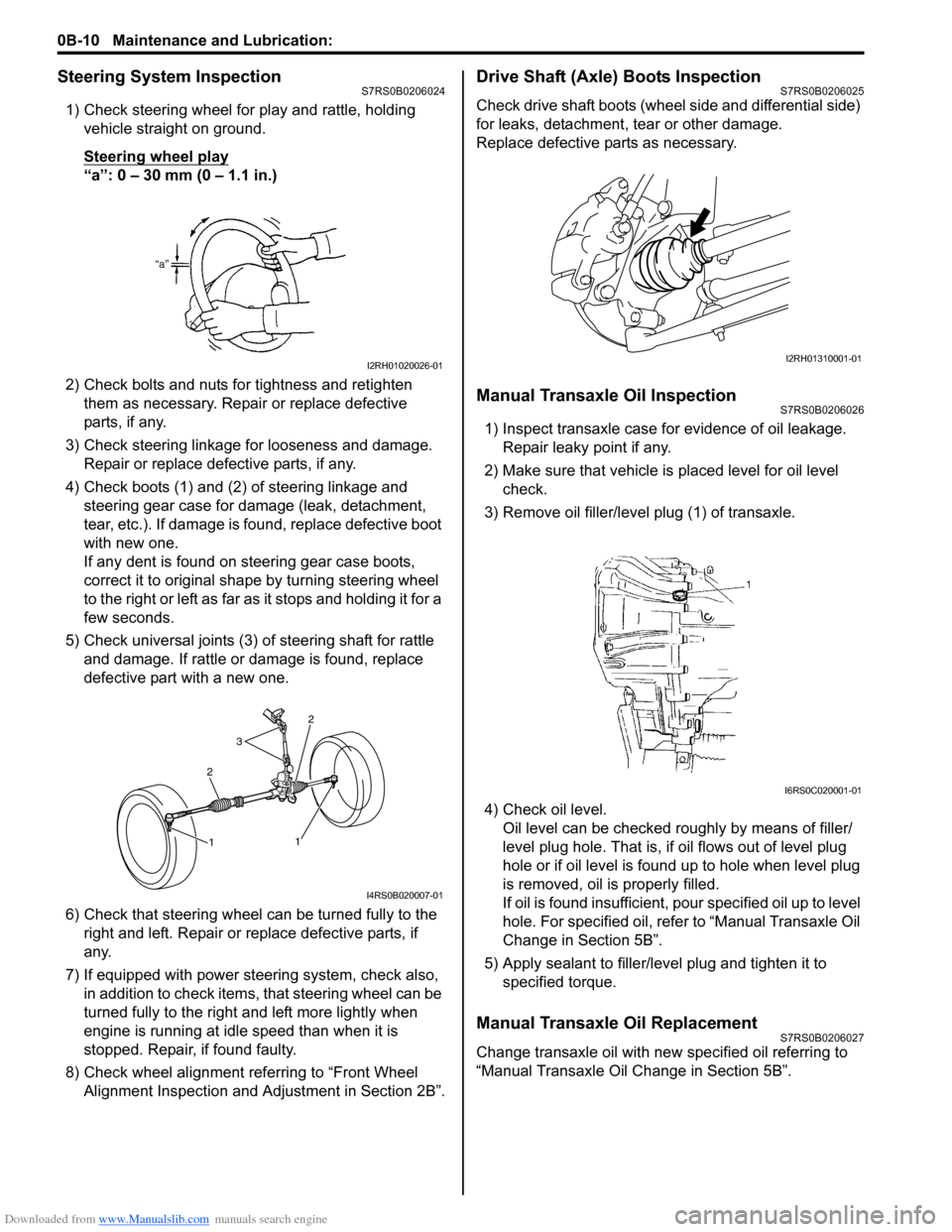
Drive Shaft (Axle) Boots InspectionS7RS0B0206025
Check drive shaft boots (wheel side and differential side)
for leaks, detachment, tear or other damage.
Replace defective parts as necessary.
Manual Transaxle Oil InspectionS7RS0B0206026
1) Inspect transaxle case for evidence of oil leakage. Repair leaky point if any.
2) Make sure that vehicle is placed level for oil level
check.
3) Remove oil filler/leve l plug (1) of transaxle.
4) Check oil level. Oil level can be checked roughly by means of filler/
level plug hole. That is, if oil flows out of level plug
hole or if oil level is found up to hole when level plug
is removed, oil is properly filled.
If oil is found insufficient, po ur specified oil up to level
hole. For specified oil, refe r to “Manual Transaxle Oil
Change in Section 5B”.
5) Apply sealant to filler/leve l plug and tighten it to
specified torque.
Manual Transaxle Oil ReplacementS7RS0B0206027
Change transaxle oil with new specified oil referring to
“Manual Transaxle Oil Change in Section 5B”.
I2RH01020026-01
2
3
2
1
1
I4RS0B020007-01
I2RH01310001-01
I6RS0C020001-01
Page 58 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
CAN communication system uses the serial communication in which data is transmitted at a high speed. It uses a
twisted pair of two communication lines for the high-speed da ta transmission. As one of its characteristics, multiple
control modules can communicate simultaneously. In addition, it has a function to detect a communication error
automatically. Each module reads necessary data from the received data and transmits data. ECM communicates
control data with each control module as follows.
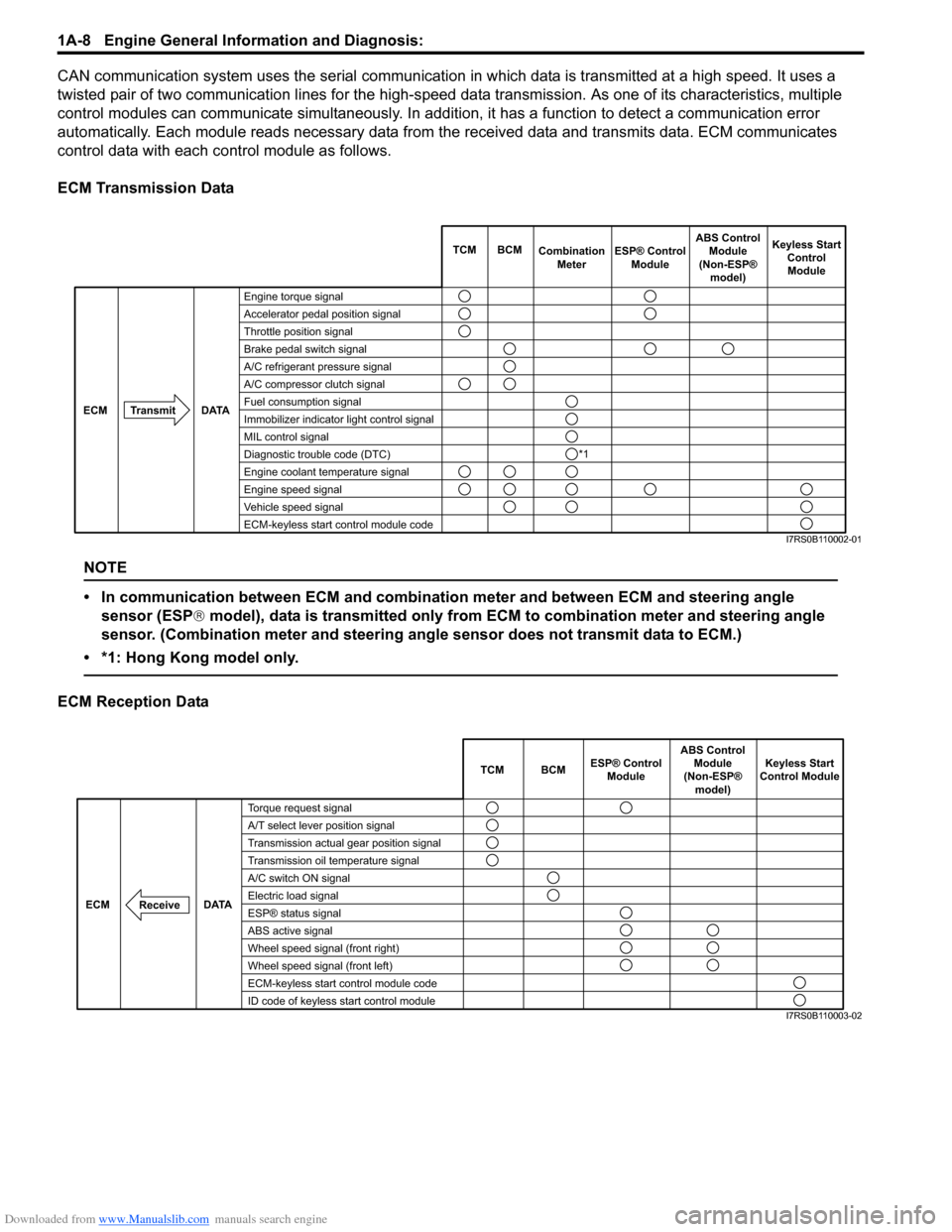
ECM Transmission Data
NOTE
• In communication between ECM and combination meter and between ECM and steering angle sensor (ESP ® model), data is transmitted only from ECM to combination meter and steering angle
sensor. (Combination meter and steering angle sensor does not transmit data to ECM.)
• *1: Hong Kong model only.
ECM Reception Data
Engine torque signal
Accelerator pedal position signal
Throttle position signal
Brake pedal switch signal
A/C refrigerant pressure signal
A/C compressor clutch signal
Fuel consumption signal
Immobilizer indicator light control signal
MIL control signal
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Engine coolant temperature signal
Engine speed signal
Vehicle speed signal
ECM-keyless start control module code TCM BCM
Combination
Meter Keyless Start
ControlModule
Transmit DATA
ECM
ESP® Control
Module ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
*1
I7RS0B110002-01
TCM BCM Keyless Start
Control Module
DATA
ECM
Torque request signal
A/T select lever position signal
Transmission actual gear position signal
Transmission oil temperature signal
A/C switch ON signal
Electric load signal
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ECM-keyless start control module code
ID code of keyless start control module
Receive
ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
ESP® Control
Module
I7RS0B110003-02
Page 102 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-52 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC P0011 / P0012: “A” Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance / -
Retarded
S7RS0B1104014
System Description
Actual value of advanced valve timing does not reach target value.
Valve timing is advanced although ECM command is most retarding.
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that the following conditions are satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) Clear DTC. Refer to “DTC Clearance”.
2) Start engine and drive vehicle under usual driving condition for 5 minutes or longer until engine is warmed up to normal operating temperature.
3) Stop vehicle.
4) Run engine at idle speed for 1 minute.
5) Start vehicle and increase vehicle speed up to 80 km/h (50 mile/h).
6) Keep vehicle speed at 80 km/h (50 mile/h) for 1 minute or longer at 5th gear position or D range.
7) Decrease vehicle speed gradually.
8) Stop vehicle and turn OFF ignition switch.
9) Repeat Step 4) to 7) one time.
10) Stop vehicle. 11) Check DTC and pending DTC. DTC detecting condition
Trouble area
Actual value of advanced valve timing does not reach
target value, or valve timi ng is advanced although ECM
command is most retarding.
(2 driving cycle detection logic) • Oil control valve
• Oil galleries of timing sprocket
• Intake camshaft timing sprocket (Camshaft position
control (VVT) actuator)
• Oil control valve circuit
•ECM
Page 103 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-53
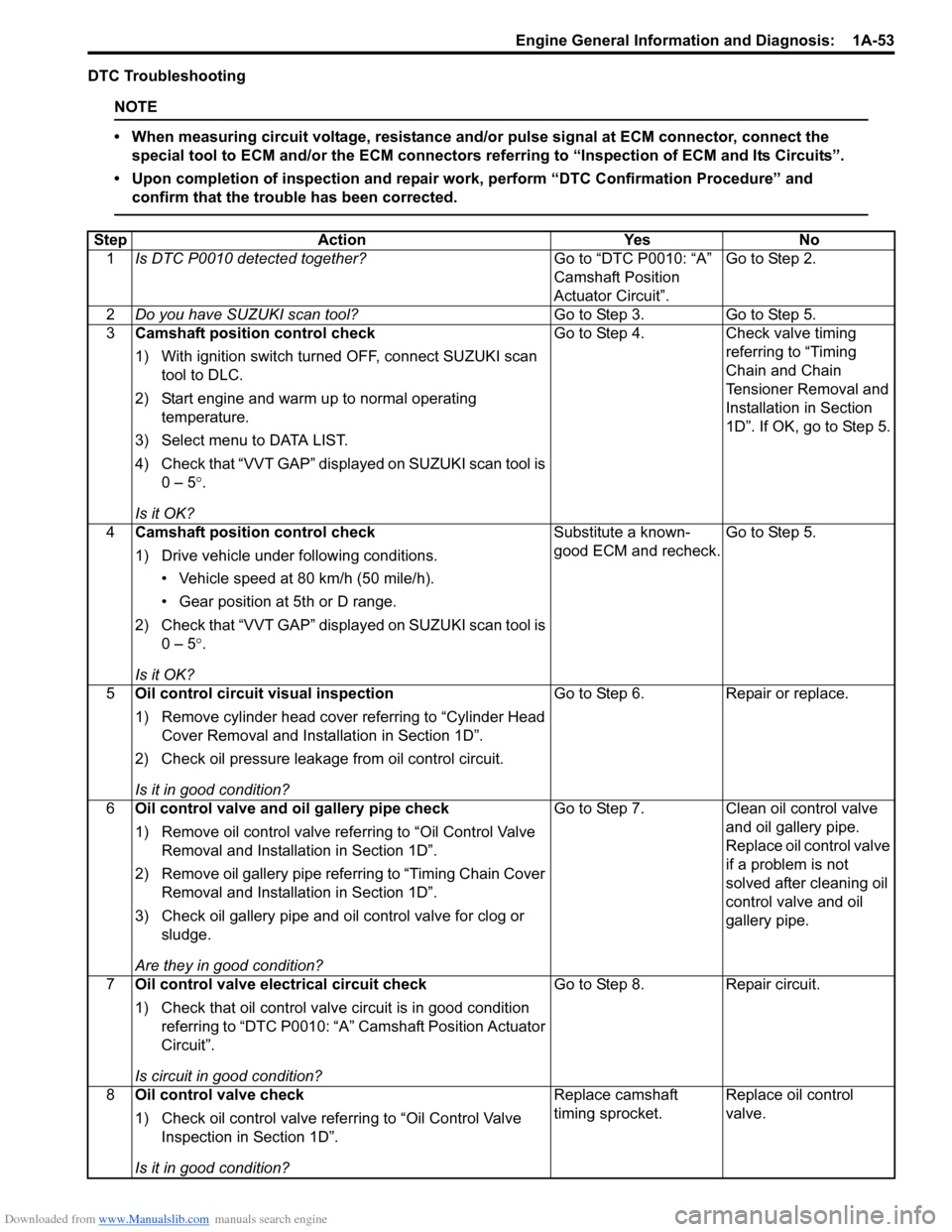
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Is DTC P0010 detected together? Go to “DTC P0010: “A”
Camshaft Position
Actuator Circuit”.Go to Step 2.
2 Do you have SUZUKI scan tool? Go to Step 3.Go to Step 5.
3 Camshaft position control check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect SUZUKI scan
tool to DLC.
2) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature.
3) Select menu to DATA LIST.
4) Check that “VVT GAP” displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is 0 – 5 °.
Is it OK? Go to Step 4.
Check valve timing
referring to “Timing
Chain and Chain
Tensioner Removal and
Installation in Section
1D”. If OK, go to Step 5.
4 Camshaft position control check
1) Drive vehicle under following conditions.
• Vehicle speed at 80 km/h (50 mile/h).
• Gear position at 5th or D range.
2) Check that “VVT GAP” displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is 0 – 5 °.
Is it OK? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Go to Step 5.
5 Oil control circuit visual inspection
1) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head
Cover Removal and Insta llation in Section 1D”.
2) Check oil pressure leakage from oil control circuit.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 6.
Repair or replace.
6 Oil control valve and oil gallery pipe check
1) Remove oil control valve re ferring to “Oil Control Valve
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
2) Remove oil gallery pipe refe rring to “Timing Chain Cover
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
3) Check oil gallery pipe and o il control valve for clog or
sludge.
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 7.
Clean oil control valve
and oil gallery pipe.
Replace oil control valve
if a problem is not
solved after cleaning oil
control valve and oil
gallery pipe.
7 Oil control valve electrical circuit check
1) Check that oil control valve circuit is in good condition
referring to “DTC P0010: “A” Camshaft Position Actuator
Circuit”.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 8.
Repair circuit.
8 Oil control valve check
1) Check oil control valve refe rring to “Oil Control Valve
Inspection in Section 1D”.
Is it in good condition? Replace camshaft
timing sprocket.
Replace oil control
valve.
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
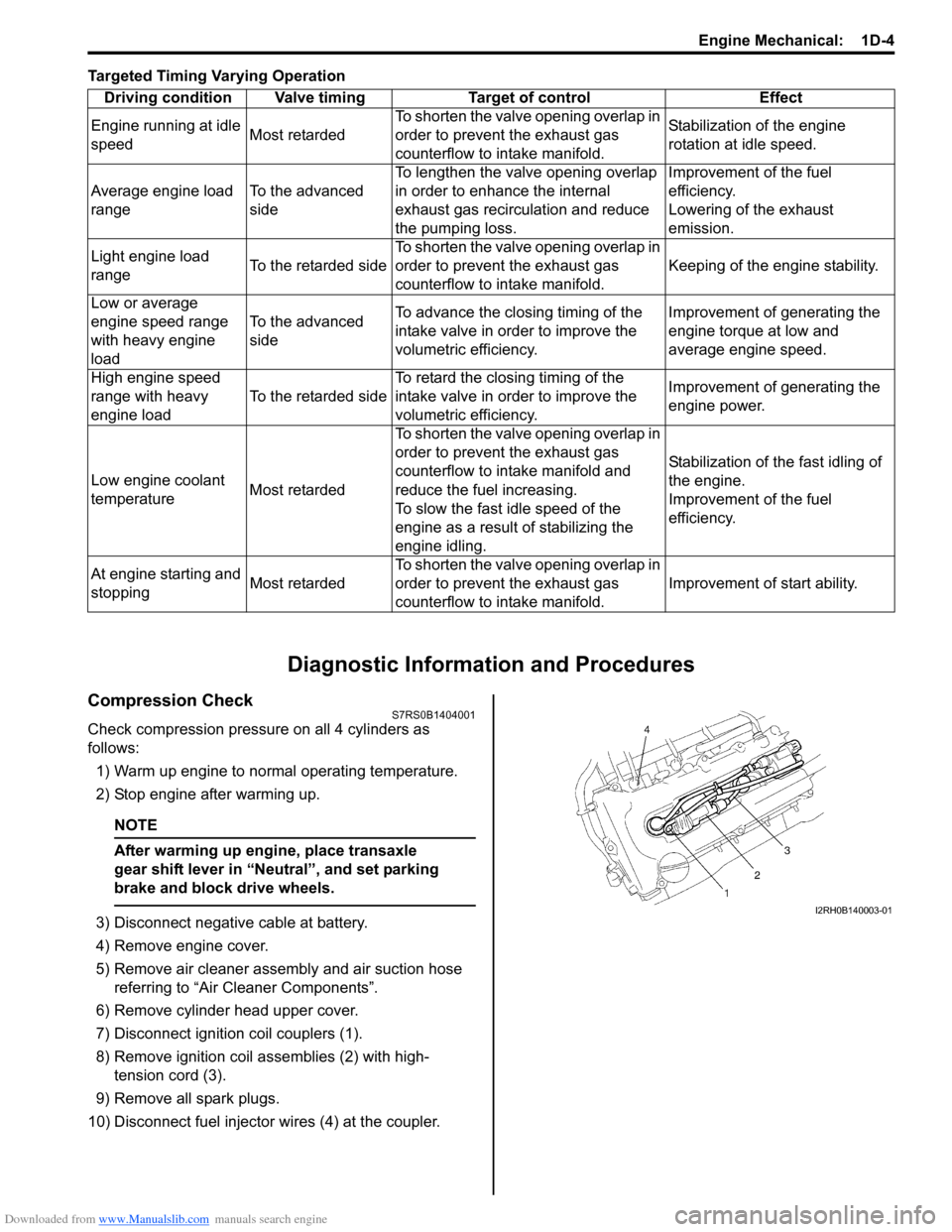
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 290 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 302 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-17 Engine Mechanical:
Engine Assembly Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1406011
NOTE
After replacing electric throttle body
assembly, perform calibration of throttle
valve referring to “Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1C”.
Removal1) Relieve fuel pressure according to “Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure in Section 1G”.
2) Disconnect negative and pos itive cable at battery.
3) Remove battery and tray.
4) Remove engine hood after disconnecting windshield washer hose.
5) Remove right and left side engine under covers.
6) Remove A/C compressor belt by referring to “Compressor Drive Belt Remo val and Installation in
Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive Belt Removal and
Installation in Section 7B”.
7) Drain engine oil, transaxle oil and coolant.
8) Remove cowl top plate referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
9) Remove air cleaner assembly referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
10) With hose connected, detach A/C compressor from its bracket (A/C model) referring to “Compressor
Assembly Removal and Installation in Section 7B” or
“Compressor Assembly Removal and Installation in
Section 7B”.
CAUTION!
Suspend removed A/C compressor at a place
where no damage will be caused during
removal and installation of engine assembly.
11) Remove intake manifold rear stiffener (1) from intake manifold and cylinder block. 12) Disconnect the following electric wires:
• MAP sensor (1)
• ECT sensor (2)
•EGR valve (3)
• CMP sensor (4)
• Electric throttle body assembly (5)
• Ignition coil assembly (6)
• Injectors (7)
• Heated oxygen sensor No. 2 (8) and No. 1 (9)
• Oil control valve (10)
• Engine oil pressure switch (11)
• CKP sensor (12)
• Knock sensor (13)
• Back up light switch (14)
• Generator (15)
• Starting motor (16)
• Ground terminal (17) from intake manifold
• Battery ground terminal (18) from exhaust manifold
• Battery ground cable (19) from transaxle
• Magnet clutch switch of A/C compressor (A/C model)
• Each wire harness clamps
• Output shaft speed sensor (VSS) (34) (A/T model)
• Solenoid valve (33) (A/T model)
• Transmission range sensor (32) (A/T model)
• Input shaft speed sensor (31) (A/T model)
13) Remove fuse box from its bracket.
14) Disconnect the following cables: • Gear select control cable (23) (M/T model)
• Gear shift control cable (24) (M/T model)
• A/T select cable (A/T model)
15) Disconnect the following hoses: • Brake booster hose (26) from intake manifold
• Radiator inlet and outlet hoses (20) from each pipe
• Heater inlet and outlet hoses (21) from each pipe
• Fuel feed hoses (22) from fuel feed pipe
• EVAP canister purge valve hose (30) from purge pipe
• A/T fluid cooler hoses (A/T model)
16) With hose connected, detach clutch operating cylinder (25). (M/T model)
CAUTION!
Suspend removed clutch operating cylinder
at a place where no damage will be caused
during removal and installation of engine
assembly.
1
I6RS0B141014-01
Page 348 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-63 Engine Mechanical:
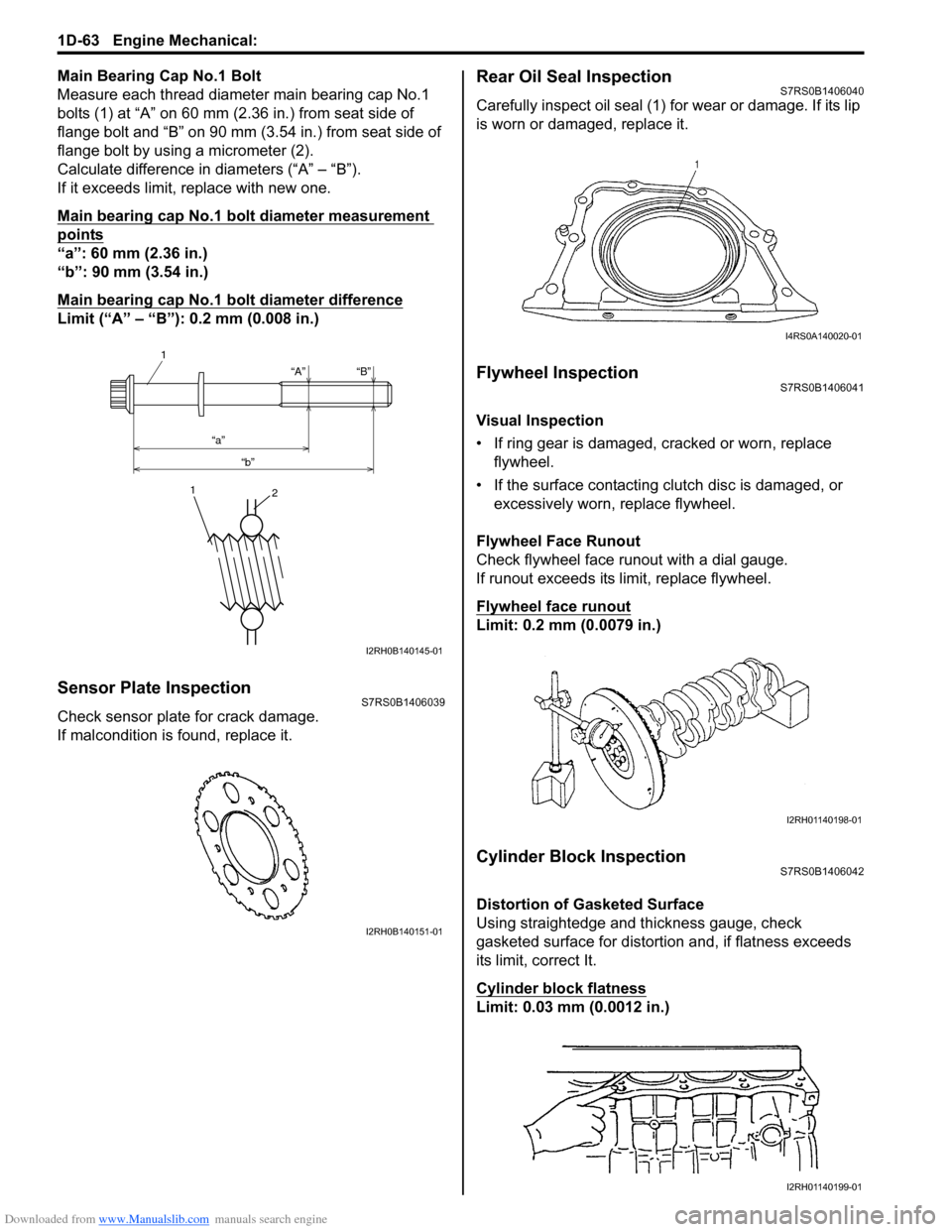
Main Bearing Cap No.1 Bolt
Measure each thread diameter main bearing cap No.1
bolts (1) at “A” on 60 mm (2.36 in.) from seat side of
flange bolt and “B” on 90 mm (3.54 in.) from seat side of
flange bolt by using a micrometer (2).
Calculate difference in diameters (“A” – “B”).
If it exceeds limit, replace with new one.
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt diameter measurement
points
“a”: 60 mm (2.36 in.)
“b”: 90 mm (3.54 in.)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt diameter difference
Limit (“A” – “B”): 0.2 mm (0.008 in.)
Sensor Plate InspectionS7RS0B1406039
Check sensor plate for crack damage.
If malcondition is found, replace it.
Rear Oil Seal InspectionS7RS0B1406040
Carefully inspect oil seal (1) for wear or damage. If its lip
is worn or damaged, replace it.
Flywheel InspectionS7RS0B1406041
Visual Inspection
• If ring gear is damaged, cracked or worn, replace flywheel.
• If the surface contacting cl utch disc is damaged, or
excessively worn, replace flywheel.
Flywheel Face Runout
Check flywheel face runout with a dial gauge.
If runout exceeds its limit, replace flywheel.
Flywheel face runout
Limit: 0.2 mm (0.0079 in.)
Cylinder Block InspectionS7RS0B1406042
Distortion of Gasketed Surface
Using straightedge and thickness gauge, check
gasketed surface for distortion and, if flatness exceeds
its limit, correct It.
Cylinder block flatness
Limit: 0.03 mm (0.0012 in.)
“A”
“a” “b” “B”
1
1
2
I2RH0B140145-01
I2RH0B140151-01
I4RS0A140020-01
I2RH01140198-01
I2RH01140199-01