2006 SUZUKI SWIFT Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search: 7fPage 17 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-12
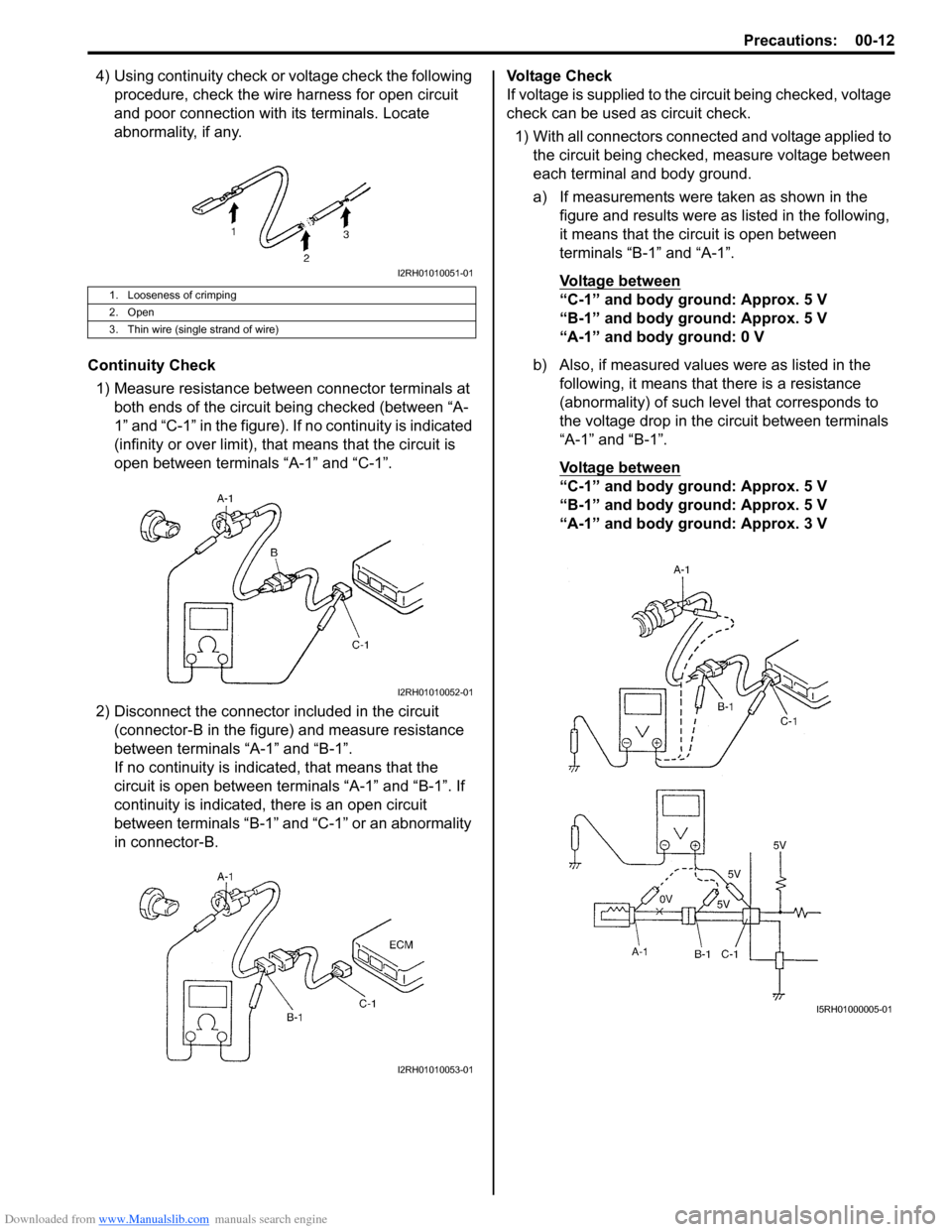
4) Using continuity check or voltage check the following procedure, check the wire harness for open circuit
and poor connection with its terminals. Locate
abnormality, if any.
Continuity Check 1) Measure resistance between connector terminals at both ends of the circuit being checked (between “A-
1” and “C-1” in the figure). If no continuity is indicated
(infinity or over limit), that means that the circuit is
open between terminals “A-1” and “C-1”.
2) Disconnect the connector included in the circuit (connector-B in the figure) and measure resistance
between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”.
If no continuity is indica ted, that means that the
circuit is open between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”. If
continuity is indicated, there is an open circuit
between terminals “B-1” and “C-1” or an abnormality
in connector-B. Voltage Check
If voltage is supplied to the circuit being checked, voltage
check can be used as circuit check.
1) With all connectors connected and voltage applied to the circuit being checked, measure voltage between
each terminal and body ground.
a) If measurements were taken as shown in the figure and results were as listed in the following,
it means that the circuit is open between
terminals “B-1” and “A-1”.
Voltage between
“C-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“B-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“A-1” and body ground: 0 V
b) Also, if measured values were as listed in the following, it means that there is a resistance
(abnormality) of such le vel that corresponds to
the voltage drop in the circuit between terminals
“A-1” and “B-1”.
Voltage between
“C-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“B-1” and body ground: Approx. 5 V
“A-1” and body ground: Approx. 3 V
1. Looseness of crimping
2. Open
3. Thin wire (single strand of wire)
I2RH01010051-01
I2RH01010052-01
I2RH01010053-01
I5RH01000005-01
Page 18 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-13 Precautions:
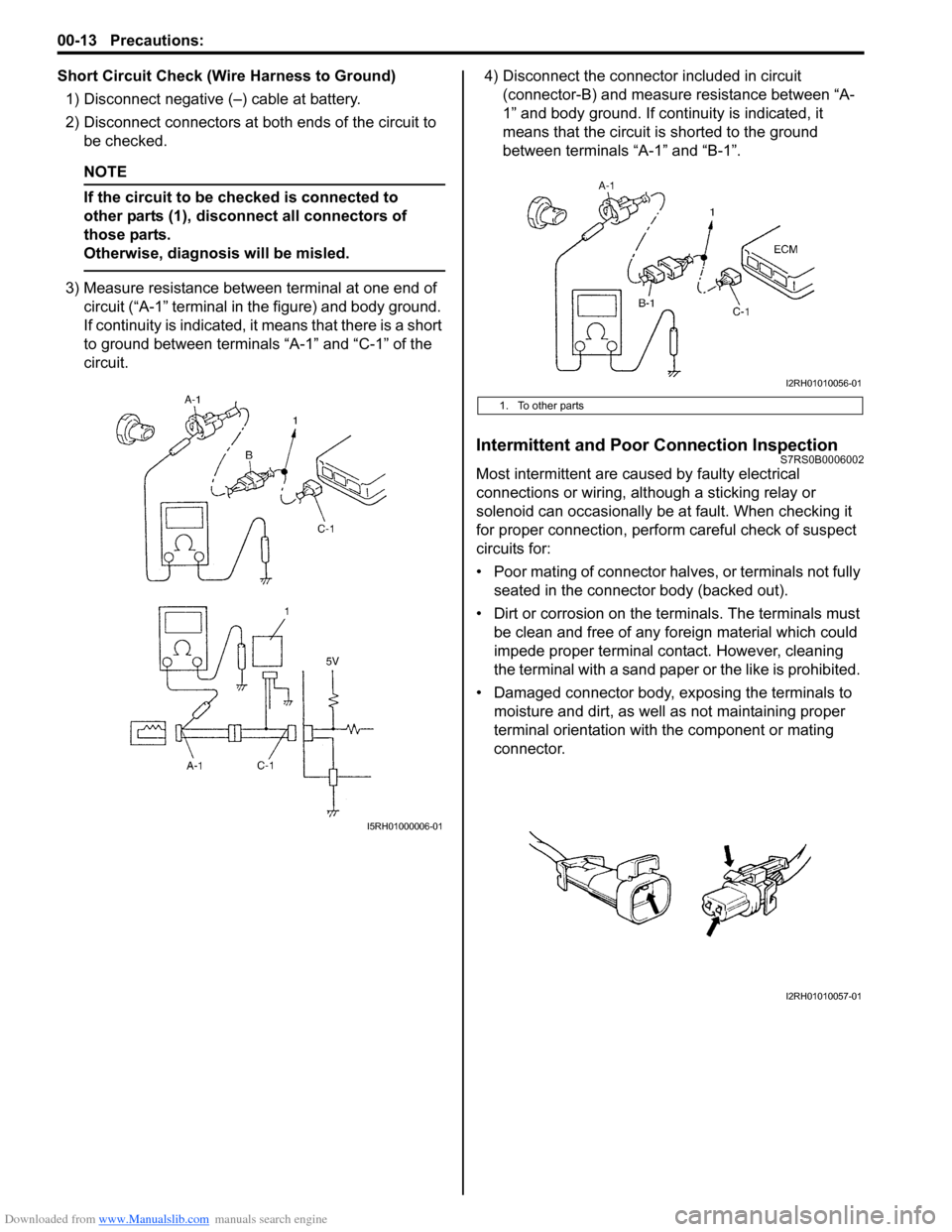
Short Circuit Check (Wire Harness to Ground)1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connectors at bot h ends of the circuit to
be checked.
NOTE
If the circuit to be checked is connected to
other parts (1), disconnect all connectors of
those parts.
Otherwise, diagnosis will be misled.
3) Measure resistance between terminal at one end of circuit (“A-1” terminal in the figure) and body ground.
If continuity is indicated, it means that there is a short
to ground between terminals “A-1” and “C-1” of the
circuit. 4) Disconnect the connector included in circuit
(connector-B) and measure resistance between “A-
1” and body ground. If continuity is indicated, it
means that the circuit is shorted to the ground
between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”.
Intermittent and Poor Connection InspectionS7RS0B0006002
Most intermittent are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring, although a sticking relay or
solenoid can occasionally be at fault. When checking it
for proper connection, perfor m careful check of suspect
circuits for:
• Poor mating of connector halves, or terminals not fully seated in the connector body (backed out).
• Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. The terminals must be clean and free of any foreign material which could
impede proper terminal contact. However, cleaning
the terminal with a sand paper or the like is prohibited.
• Damaged connector body, exposing the terminals to moisture and dirt, as well as not maintaining proper
terminal orientation with the component or mating
connector.
I5RH01000006-01
1. To other parts
I2RH01010056-01
I2RH01010057-01
Page 19 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-14
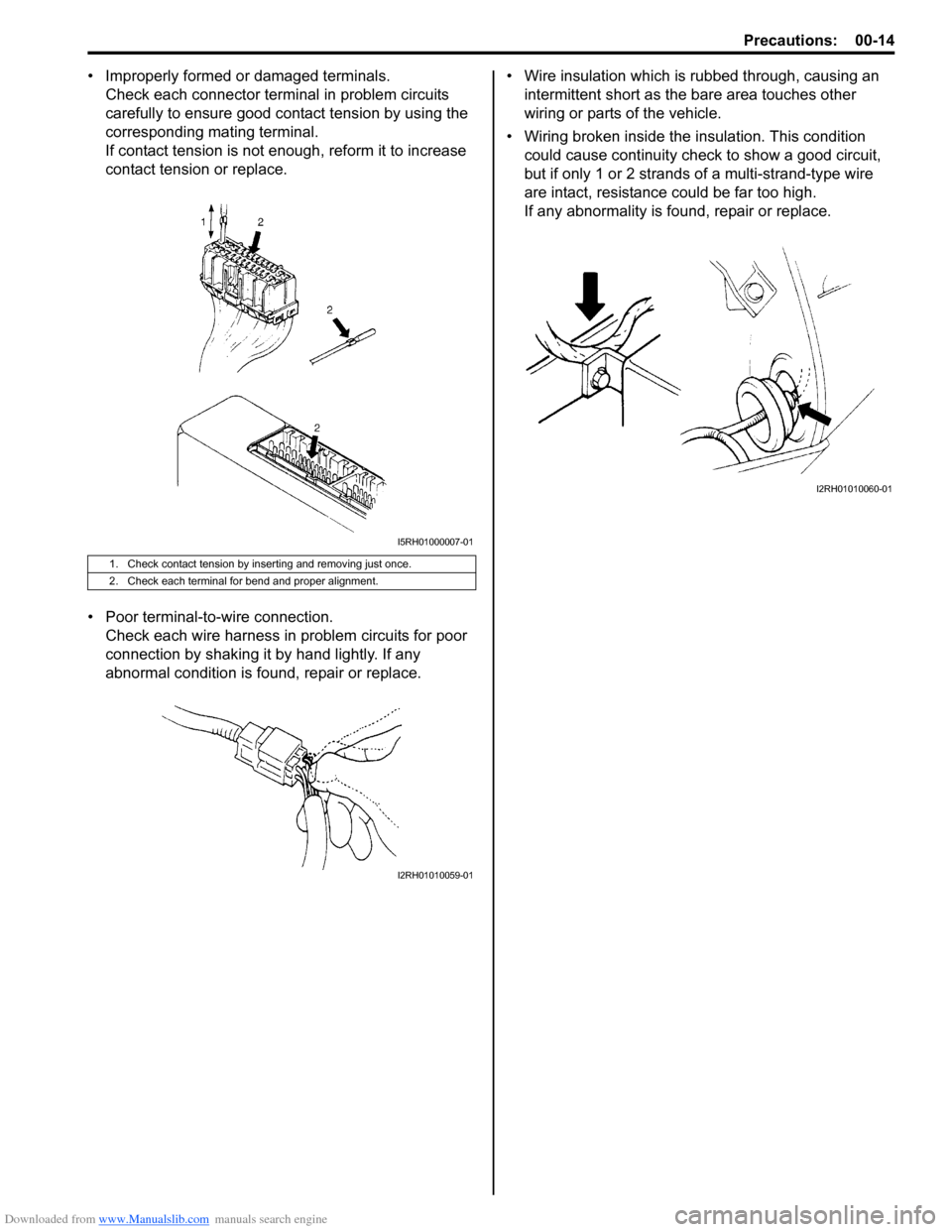
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals.Check each connector terminal in problem circuits
carefully to ensure good contact tension by using the
corresponding mating terminal.
If contact tension is not enough, reform it to increase
contact tension or replace.
• Poor terminal-to -wire connection.
Check each wire harness in problem circuits for poor
connection by shaking it by hand lightly. If any
abnormal condition is found, repair or replace. • Wire insulation which is rubbed through, causing an
intermittent short as the bare area touches other
wiring or parts of the vehicle.
• Wiring broken inside the insulation. This condition
could cause continuity check to show a good circuit,
but if only 1 or 2 strands of a multi-strand-type wire
are intact, resistance could be far too high.
If any abnormality is found, repair or replace.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just once.
2. Check each terminal for bend and proper alignment.
I5RH01000007-01
I2RH01010059-01
I2RH01010060-01
Page 20 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-15 Precautions:
Page 21 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 0- i
0
Section 0
CONTENTS
General Information
General Information ................................ 0A-1
General Description ............................................. 0A-1
Abbreviations ...................................................... 0A-1
Symbols .............................................................. 0A-2
Wire Color Symbols ............................................ 0A-2
Fasteners Information ......................................... 0A-3
Vehicle Lifting Points ........................................... 0A-5
Engine Supporting Points ................................... 0A-7
Vehicle Identification Number ............................. 0A-7
Engine Identification Number .............................. 0A-7
Transmission Identification Number .................... 0A-7
Component Locatio n ........................................... 0A-8
Warning, Caution and Information Labels Location ............................................................ 0A-8
Maintenance and Lubricat ion ................. 0B-1
Precautions........................................................... 0B-1
Precautions for Maintenance and Lubrication ..... 0B-1
Scheduled Maintenance ...................................... 0B-1 Maintenance Schedule under Normal Driving Conditions ......................................................... 0B-1
Maintenance Recommended under Severe Driving Conditions ............................................. 0B-2
Repair Instructions .............................................. 0B-3 Accessory Drive Belt Inspection.......................... 0B-3
Accessory Drive Belt Repl acement ..................... 0B-4
Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection ..................... 0B-4
Engine Oil and Filter Change .............................. 0B-4
Engine Coolant Change ...... ................................ 0B-5
Exhaust System Inspection ................................. 0B-6
Spark Plug Replacement .................................... 0B-6
Air Cleaner Filter Inspection ................................ 0B-6
Air Cleaner Filter Replac ement ........................... 0B-6 Fuel Lines and Connections Inspection .............. 0B-6
Fuel Filter Replacement ...................................... 0B-7
Fuel Tank Inspection ........................................... 0B-7
PCV Valve Inspection ......................................... 0B-7
Fuel Evaporative Emission Control System
Inspection .......................................................... 0B-7
Brake Discs and Pads Inspection ....................... 0B-7
Brake Hoses and Pipes Inspection ..................... 0B-7
Brake Fluid Inspection......................................... 0B-8
Brake Fluid Replacement .................................... 0B-8
Brake Lever and Cable Inspection ...................... 0B-8
Clutch Fluid Inspection ........................................ 0B-8
Tires Inspection ................................................... 0B-9
Wheel Discs Inspection ....................................... 0B-9
Wheel Bearing Inspection ................................... 0B-9
Suspension System Inspection ........................... 0B-9
Steering System Inspection .............................. 0B-10
Drive Shaft (Axle) Boots Inspection .................. 0B-10
Manual Transaxle Oil Inspection ....................... 0B-10
Manual Transaxle Oil Replacement .................. 0B-10
Automatic Transaxle Fluid Level Inspection...... 0B-11
Automatic Transaxle Fluid Replacement .......... 0B-11
Automatic Transaxle Fluid Cooler Hose Inspection ........................................................ 0B-11
All Latches, Hinges and Locks Inspection......... 0B-11
HVAC Air Filter (If Equipped) Inspection ........... 0B-12
HVAC Air Filter (If Equipped) Replacement ...... 0B-12
Final Inspection for Maint enance Service ......... 0B-12
Specifications .................... .................................0B-13
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 0B-13
Special Tools and Equipmen t ...........................0B-13
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants............... 0B-13
Special Tool ...................................................... 0B-14
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 23 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine General Information: 0A-2
SAS: Steering Angle Sensor
SDM: Sensing and Diagnostic Module (Air Bag Controller, Air bag Control Module)
SDT: Smart Diagnostic Tester
SFI: Sequential Multipor t Fuel Injection
SOHC: Single Over Head Camshaft
T:
TBI: Throttle Body Fuel Injection (Single-Point Fuel
Injection, SPI)
TCC: Torque Converter Clutch
TCM: Transmission Control Module (A/T Controller, A/T
Control Module)
TDC: Top Dead Center
TP Sensor: Throttle Position Sensor TVV:
Thermal Vacuum Valve (Thermal Vacuum
Switching Valve, TVSV, Bi metal Vacuum Switching
Valve, BVSV)
TWC: Three Way Catalytic Converter (Three Way
Catalyst)
2WD: 2 Wheel Drive
U:
USB: Universal Serial Bus
V:
VIN: Vehicle Identification Number
VSS: Vehicle Speed Sensor
VVT: Variable Valve Timing (Camshaft Position Control)
W:
WU-OC: Warm Up Oxidation Catalytic Converter
WU-TWC: Warm Up Three Way Catalytic Converter
SymbolsS7RS0B0101002
Wire Color SymbolsS7RS0B0101003
Symbol Definition SymbolDefinition
Tightening torque Apply SUZUKI BOND NO. 1216B
99000-31230
Apply oil (engine, transmission, transfer,
differential) Apply SILICONE SEALANT
99000-31120
Apply fluid (brake, power steering or
automatic transmission fluid) Apply SEALING COMPOUND 366E
99000-31090
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE A
99000-25011
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE C
99000-25030 Apply THREAD LOCK 1322
99000-32110
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE E
99000-25050 Apply THREAD LOCK 1333B
99000-32020
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE H
99000-25121 Apply THREAD LOCK 1342
99000-32050
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE I
99000-25210
Apply SUZUKI BOND NO. 1215
99000-31110 Do not reuse
Apply SUZUKI BO ND NO. 1207F
99000-31250 Note on reassembly
Apply SUZUKI BO ND NO. 1217G
99000-31260
Symbol Wire Color SymbolWire Color
B BLK Black O, Or ORN Orange
Bl BLU Blue RRED Red
Br BRN Brown WWHT White
G GRN Green YYEL Yellow
Gr GRY Gray PPNK Pink
Lbl LT BLU Light blueVPPL Violet
Lg LT GRN Light green
Page 24 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-3 General Information:
There are two kinds of colored wire used in this vehicle. One is single-colored wire and the other is dual-colored
(striped) wire.
The single-colored wire uses only one color symbol (i.e. “GRN”).
The dual-colored wire uses two color sy mbols (i.e. “GRN/YEL”). The first symbo l represents the base color of the wire
(“GRN” in the figure) and the second symbol represents the color of the stripe (“YEL” in the figure).
Fasteners InformationS7RS0B0101004
Metric Fasteners
Most of the fasteners used for this vehicle are JIS-
defined and ISO-defined metric fasteners. When
replacing any fasteners, it is most important that
replacement fasteners be the correct diameter, thread
pitch and strength.
CAUTION!
Even when the nominal diameter (1) of thread
is the same, the thread pitch (2) or the width
across flats (3) may vary between ISO and
JIS. Refer to JIS-TO-ISO Main Fasteners
Comparison Table below for the difference.
Installing a mismatched bolt or nut will cause
damage to the thread.
Before installing, check the thread pitch for
correct matching and then tighten it by hand
temporarily. If it is tight, recheck the thread
pitch.
JIS-TO-ISO Main Fasteners Comparison Table Fastener Strength Identification
Most commonly used metric fastener strength property
classes are 4T, 6.8, 7T, 8.8 and radial line with the class
identification embossed on the head of each bolt. Some
metric nuts will be marked with punch, 6 or 8 mark
strength identification on the nut face. Figure shows the
different strength markings.
When replacing metric fasteners, be careful to use bolts
and nuts of the same strength or greater than the original
fasteners (the same number marking or higher). It is
likewise important to select replacement fasteners of the
correct diameter and thread
pitch. Correct replacement
bolts and nuts are available through the parts division.
Metric bolts: Identification class numbers or marks
correspond to bolt strength (increasing numbers
represent increasing strength).
I2RH01010010-01
Nominal diameter
M6 M8 M10 M12 M14
JIS Thread pitch 1.0 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.5
Width across flats 10 12 14 17 19
ISO Thread pitch 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.5 1.5
Width across flats 10 13 16 18 21
I4RH0A010005-01
1. Nut strength identification
I5RH01010001-01