2006 SUZUKI SWIFT crank pulley
[x] Cancel search: crank pulleyPage 330 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-45 Engine Mechanical:
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1406030
Removal1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
3) Mark cylinder number on all pistons, connecting rods
and connecting rod caps using silver pencil or quick
drying paint.
4) Remove rod bearing caps.
5) Decarbonize top of cylinder bore before removing piston from cylinder.
6) Push piston and connecting rod assembly out through the top of cylinder bore.
Installation 1) Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls, connecting rod bearings and crank pins.
NOTE
Do not apply oil between connecting rod and
bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
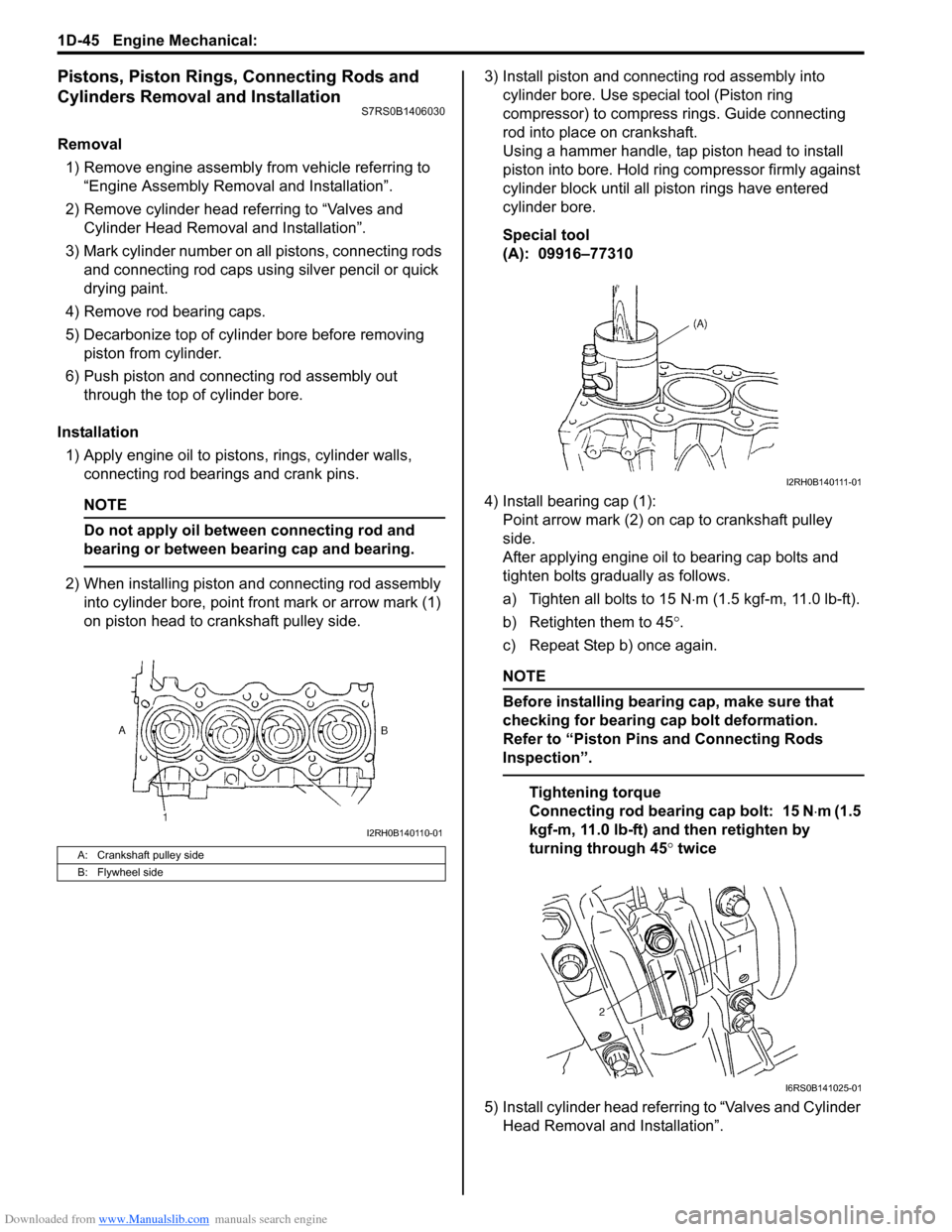
2) When installing piston and connecting rod assembly into cylinder bore, point front mark or arrow mark (1)
on piston head to crankshaft pulley side. 3) Install piston and connecting rod assembly into
cylinder bore. Use special tool (Piston ring
compressor) to compress rings. Guide connecting
rod into place on crankshaft.
Using a hammer handle, tap piston head to install
piston into bore. Hold ring compressor firmly against
cylinder block until all piston rings have entered
cylinder bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–77310
4) Install bearing cap (1): Point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley
side.
After applying engine oil to bearing cap bolts and
tighten bolts gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all bolts to 15 N ⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft).
b) Retighten them to 45 °.
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
NOTE
Before installing bearing cap, make sure that
checking for bearing cap bolt deformation.
Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecting Rods
Inspection”.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt: 15 N ⋅m (1.5
kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 45 ° twice
5) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
A: Crankshaft pulley side
B: Flywheel side
I2RH0B140110-01
I2RH0B140111-01
I6RS0B141025-01
Page 336 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-51 Engine Mechanical:
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance1) Before checking bearing clearance, clean bearing and crank pin.
2) Install bearing in connecting rod and bearing cap.
3) Place a piece of gauging plastic (1) to full width of crank pin as contacted by bearing (parallel to
crankshaft), avoiding oil hole.
4) Install rod bearing cap (1) to connecting rod. When installing cap, be sure to point arrow mark (2)
on cap to crankshaft pulley side, as shown in figure.
After applying engine oil to bearing cap bolts (3),
tighten bearing cap bolts (3) gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all bearing cap bolts to 15 N ⋅m (1.5 kgf-
m, 11.0 lb-ft)
b) Retighten them to 45°
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt: 15 N ⋅m (1.5
kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 45 ° twice 5) Remove cap and using a scale (1) on gauging
plastic envelope (2), measure gauging plastic (2)
width at the widest point (clearance).
If clearance exceed its limit, use a new standard size
bearing referring to “Selection of Connecting Rod
Bearings: ”.
After selecting new bearing, recheck clearance.
Connecting rod bearing clearance
Standard: 0.029 – 0.047 mm (0.0011 – 0.0018 in.)
Limit: 0.065 mm (0.0026 in.)
6) If clearance can not be brought to its limit even by using a new standard size bearing, use next thicker
bearing and recheck clearance or regrind crank pin
to undersize and use 0.25 mm undersize bearing.
Selection of Connecting Rod Bearings
NOTE
• If bearing is in malcondition, or bearing clearance is out of specification, select a
new standard bearing according to the
following procedure and install it.
• When replacing crankshaft or connecting rod and its bearing due to any reason,
select new standard bearings to be
installed by referring to numbers stamped
on connecting rod and its cap and/or
alphabets stamped on crank web of No.3
cylinder.
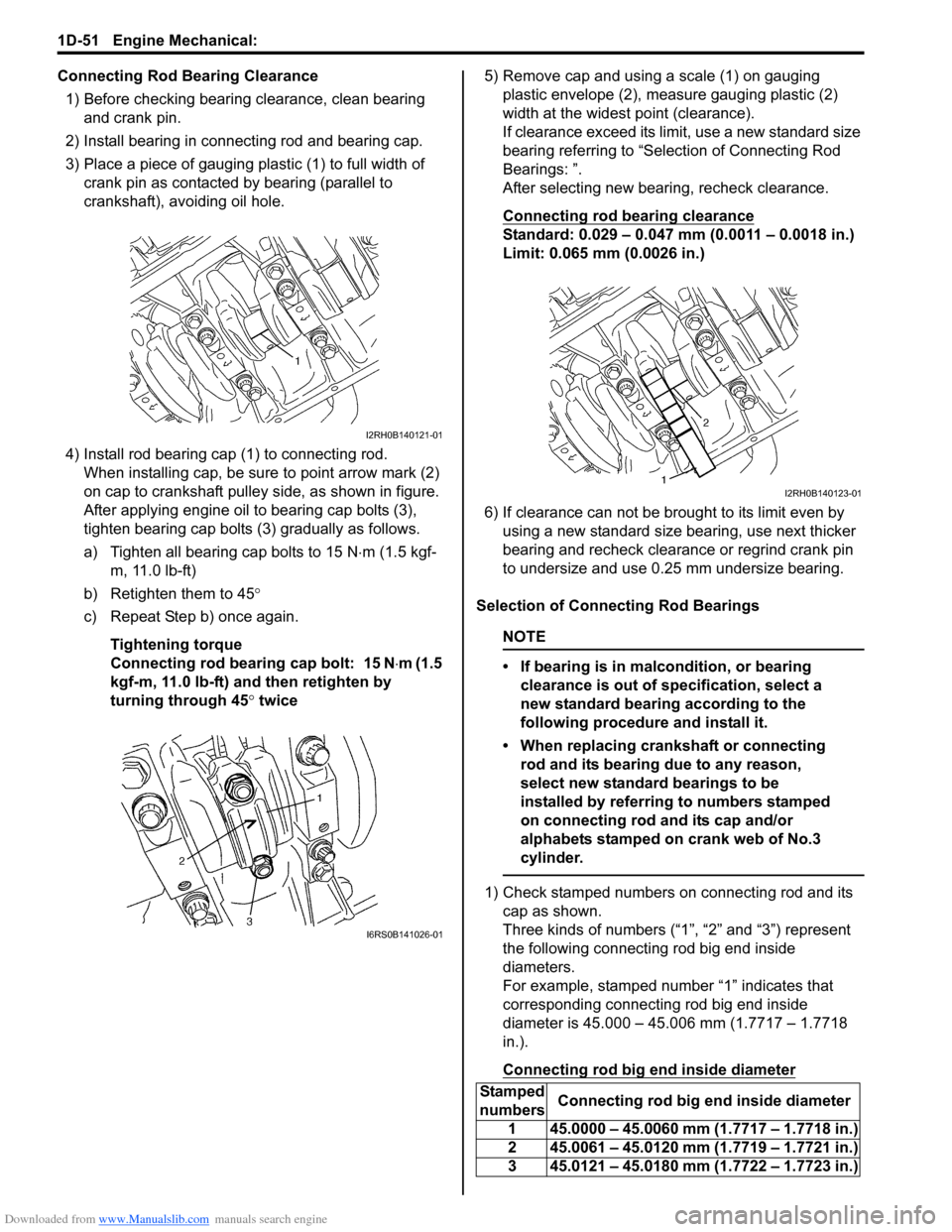
1) Check stamped numbers on connecting rod and its cap as shown.
Three kinds of numbers (“1”, “2” and “3”) represent
the following connecting rod big end inside
diameters.
For example, stamped number “1” indicates that
corresponding connecting rod big end inside
diameter is 45.000 – 45.006 mm (1.7717 – 1.7718
in.).
Connecting rod big end inside diameter
I2RH0B140121-01
I6RS0B141026-01
Stamped
numbers Connecting rod big end inside diameter
1 45.0000 – 45.0060 mm (1.7717 – 1.7718 in.)
2 45.0061 – 45.0120 mm (1.7719 – 1.7721 in.)
3 45.0121 – 45.0180 mm (1.7722 – 1.7723 in.)
I2RH0B140123-01
Page 341 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-56
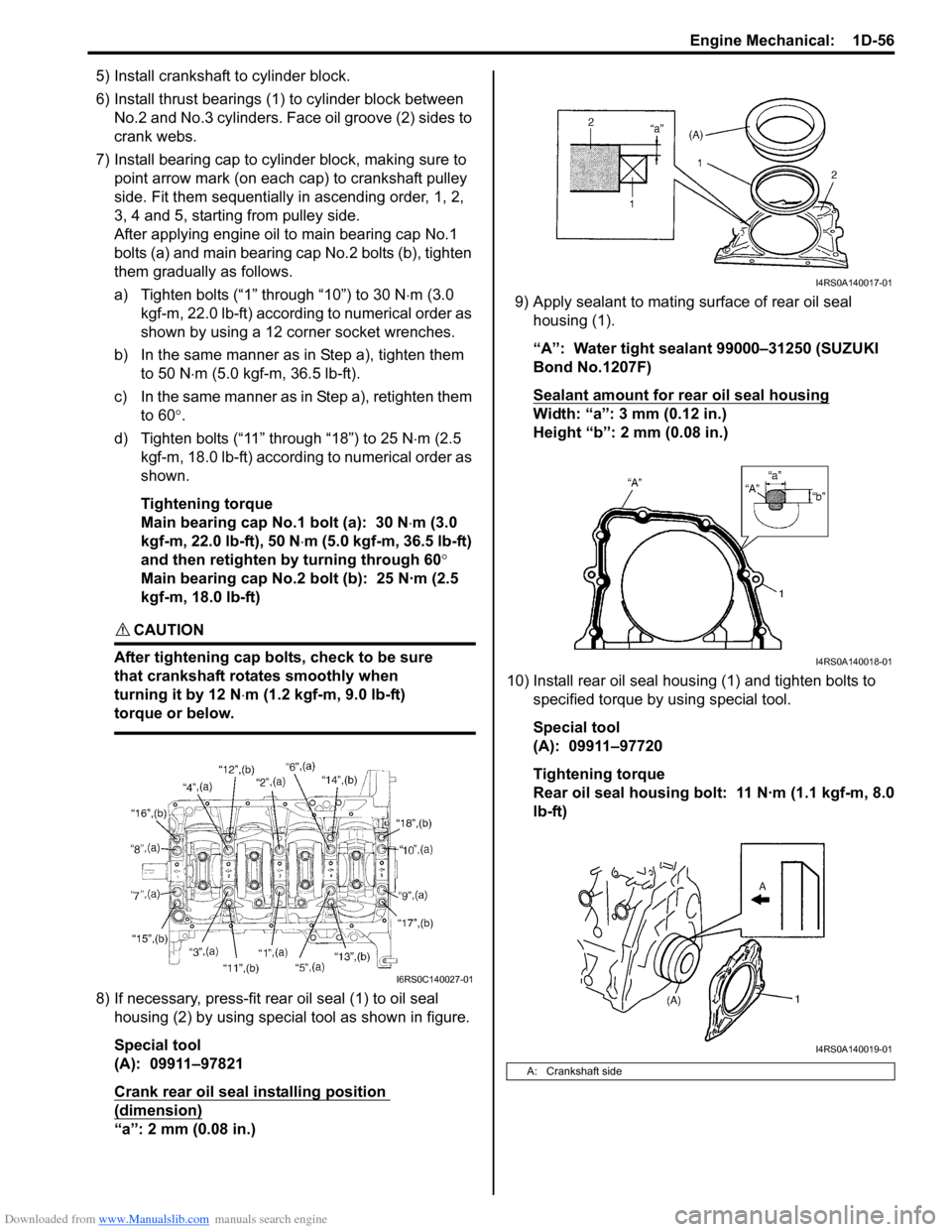
5) Install crankshaft to cylinder block.
6) Install thrust bearings (1) to cylinder block between No.2 and No.3 cylinders. Face oil groove (2) sides to
crank webs.
7) Install bearing cap to cylinder block, making sure to point arrow mark (on each cap) to crankshaft pulley
side. Fit them sequentially in ascending order, 1, 2,
3, 4 and 5, starting from pulley side.
After applying engine oil to main bearing cap No.1
bolts (a) and main bearing cap No.2 bolts (b), tighten
them gradually as follows.
a) Tighten bolts (“1” through “10”) to 30 N ⋅m (3.0
kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order as
shown by using a 12 corner socket wrenches.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them to 50 N ⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft).
c) In the same manner as in Step a), retighten them to 60 °.
d) Tighten bolts (“11” through “18”) to 25 N ⋅m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order as
shown.
Tightening torque
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt (a): 30 N ⋅m (3.0
kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
and then retighten by turning through 60 °
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt (b): 25 N·m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
CAUTION!
After tightening cap bolts, check to be sure
that crankshaft rotates smoothly when
turning it by 12 N ⋅m (1.2 kgf-m, 9.0 lb-ft)
torque or below.
8) If necessary, press-fit rear oil seal (1) to oil seal housing (2) by using special tool as shown in figure.
Special tool
(A): 09911–97821
Crank rear oil seal installing position
(dimension)
“a”: 2 mm (0.08 in.) 9) Apply sealant to mating surface of rear oil seal
housing (1).
“A”: Water tight sealant 99000–31250 (SUZUKI
Bond No.1207F)
Sealant amount for rear oil seal housing
Width: “a”: 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Height “b”: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
10) Install rear oil seal housing (1) and tighten bolts to specified torque by using special tool.
Special tool
(A): 09911–97720
Tightening torque
Rear oil seal housing bolt: 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0
lb-ft)
I6RS0C140027-01
A: Crankshaft side
I4RS0A140017-01
I4RS0A140018-01
I4RS0A140019-01
Page 349 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-64
Honing or Reboring Cylinders1) When any cylinder needs reboring, all other cylinders must also be rebored at the same time.
2) Select oversized piston according to amount of cylinder wear.
Oversize piston specification
Oversize 0.50: 78.453 – 78.468 mm (3.0887 –
3.0893 in.)
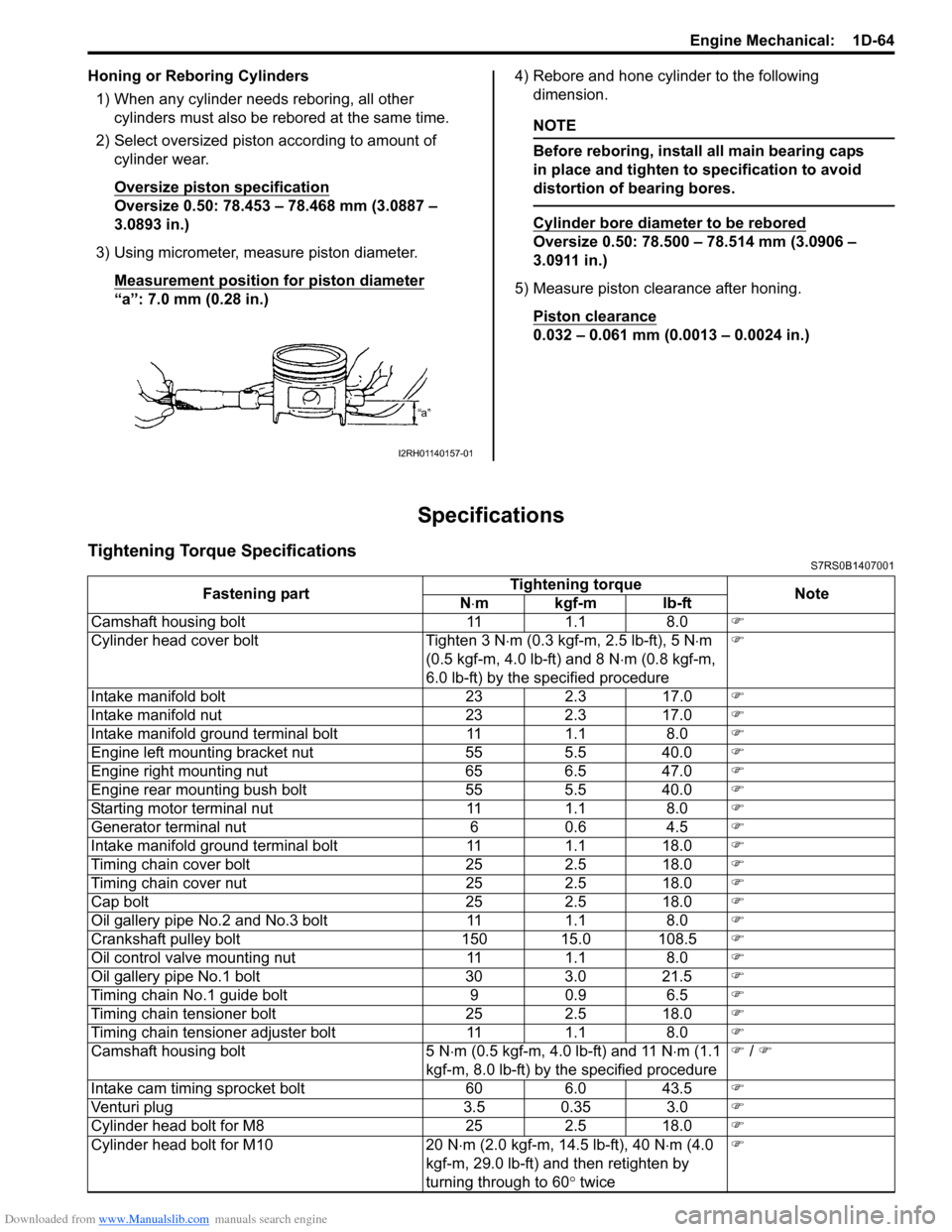
3) Using micrometer, measure piston diameter. Measurement position for piston diameter
“a”: 7.0 mm (0.28 in.) 4) Rebore and hone cylinder to the following
dimension.
NOTE
Before reboring, install all main bearing caps
in place and tighten to specification to avoid
distortion of bearing bores.
Cylinder bore diameter to be rebored
Oversize 0.50: 78.500 – 78.514 mm (3.0906 –
3.0911 in.)
5) Measure piston clearance after honing. Piston clearance
0.032 – 0.061 mm (0.0013 – 0.0024 in.)
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1407001
I2RH01140157-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Camshaft housing bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Cylinder head cover bolt Tighten 3 N ⋅m (0.3 kgf-m, 2.5 lb-ft), 5 N ⋅m
(0.5 kgf-m, 4.0 lb-ft) and 8 N ⋅m (0.8 kgf-m,
6.0 lb-ft) by the specified procedure �)
Intake manifold bolt 23 2.3 17.0 �)
Intake manifold nut 23 2.3 17.0 �)
Intake manifold ground terminal bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Engine left mounting bracket nut 55 5.5 40.0 �)
Engine right mounting nut 65 6.5 47.0 �)
Engine rear mounting bush bolt 55 5.5 40.0 �)
Starting motor terminal nut 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Generator terminal nut 6 0.6 4.5 �)
Intake manifold ground terminal bolt 11 1.1 18.0 �)
Timing chain cover bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Timing chain cover nut 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Cap bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Oil gallery pipe No.2 and No.3 bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Crankshaft pulley bolt 150 15.0 108.5 �)
Oil control valve mounting nut 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Oil gallery pipe No.1 bolt 30 3.0 21.5 �)
Timing chain No.1 guide bolt 9 0.9 6.5 �)
Timing chain tensioner bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Timing chain tensioner adjuster bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Camshaft housing bolt 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-m, 4.0 lb-ft) and 11 N ⋅m (1.1
kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) by the specified procedure �)
/ �)
Intake cam timing sprocket bolt 60 6.0 43.5 �)
Venturi plug 3.5 0.35 3.0 �)
Cylinder head bolt for M8 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Cylinder head bolt for M10 20 N ⋅m (2.0 kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft), 40 N ⋅m (4.0
kgf-m, 29.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through to 60 ° twice �)
Page 414 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 423 of 1496
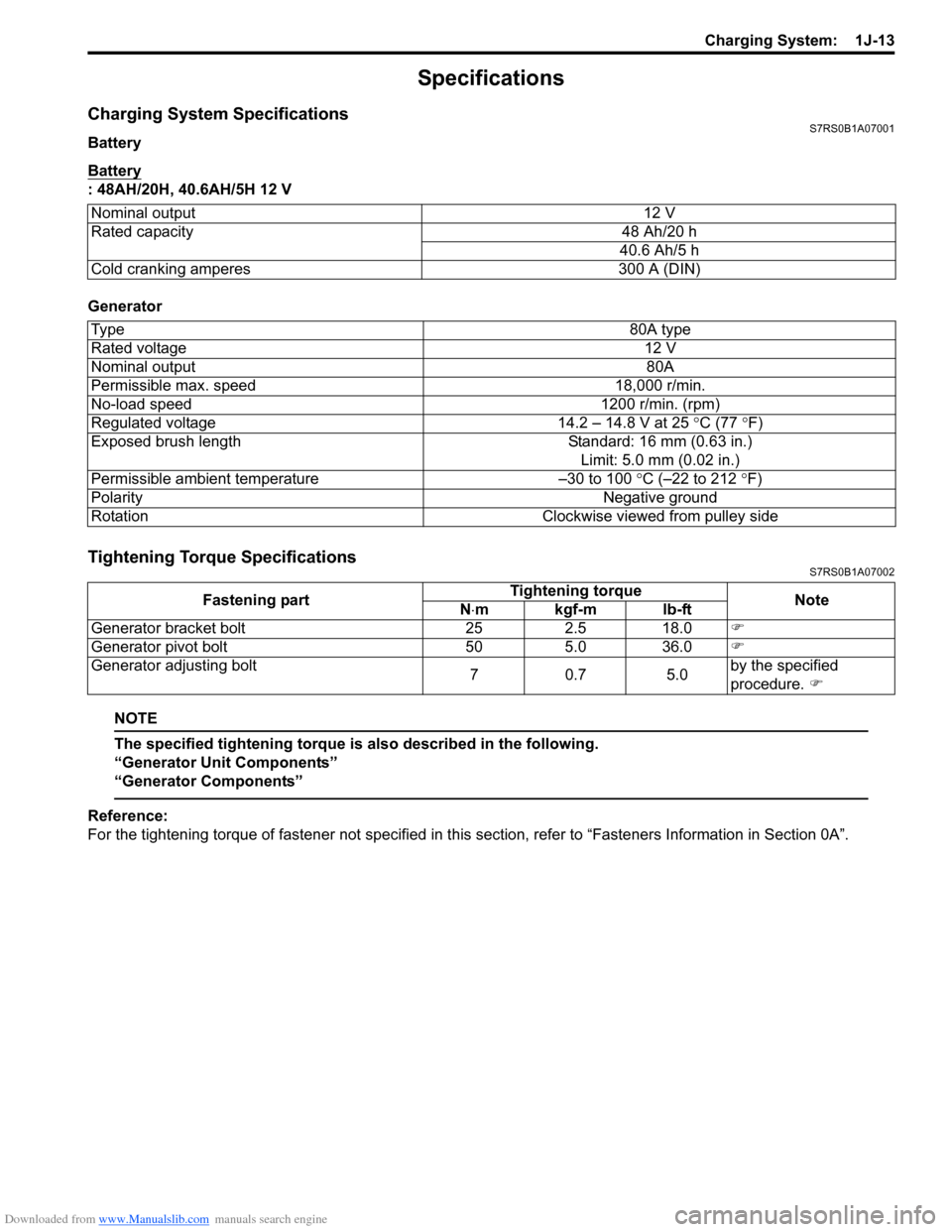
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-13
Specifications
Charging System SpecificationsS7RS0B1A07001
Battery
Battery
: 48AH/20H, 40.6AH/5H 12 V
Generator
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1A07002
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Generator Unit Components”
“Generator Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Nominal output
12 V
Rated capacity 48 Ah/20 h
40.6 Ah/5 h
Cold cranking amperes 300 A (DIN)
Ty p e 80A type
Rated voltage 12 V
Nominal output 80A
Permissible max. speed 18,000 r/min.
No-load speed 1200 r/min. (rpm)
Regulated voltage 14.2 – 14.8 V at 25 ° C (77 °F)
Exposed brush length Standard: 16 mm (0.63 in.)
Limit: 5.0 mm (0.02 in.)
Permissible ambient temperature –30 to 100 °C (–22 to 212 °F)
Polarity Negative ground
Rotation Clockwise viewed from pulley side
Fastening partTightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Generator bracket bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Generator pivot bolt 50 5.0 36.0 �)
Generator adjusting bolt 70.7 5.0by the specified
procedure.
�)
Page 957 of 1496
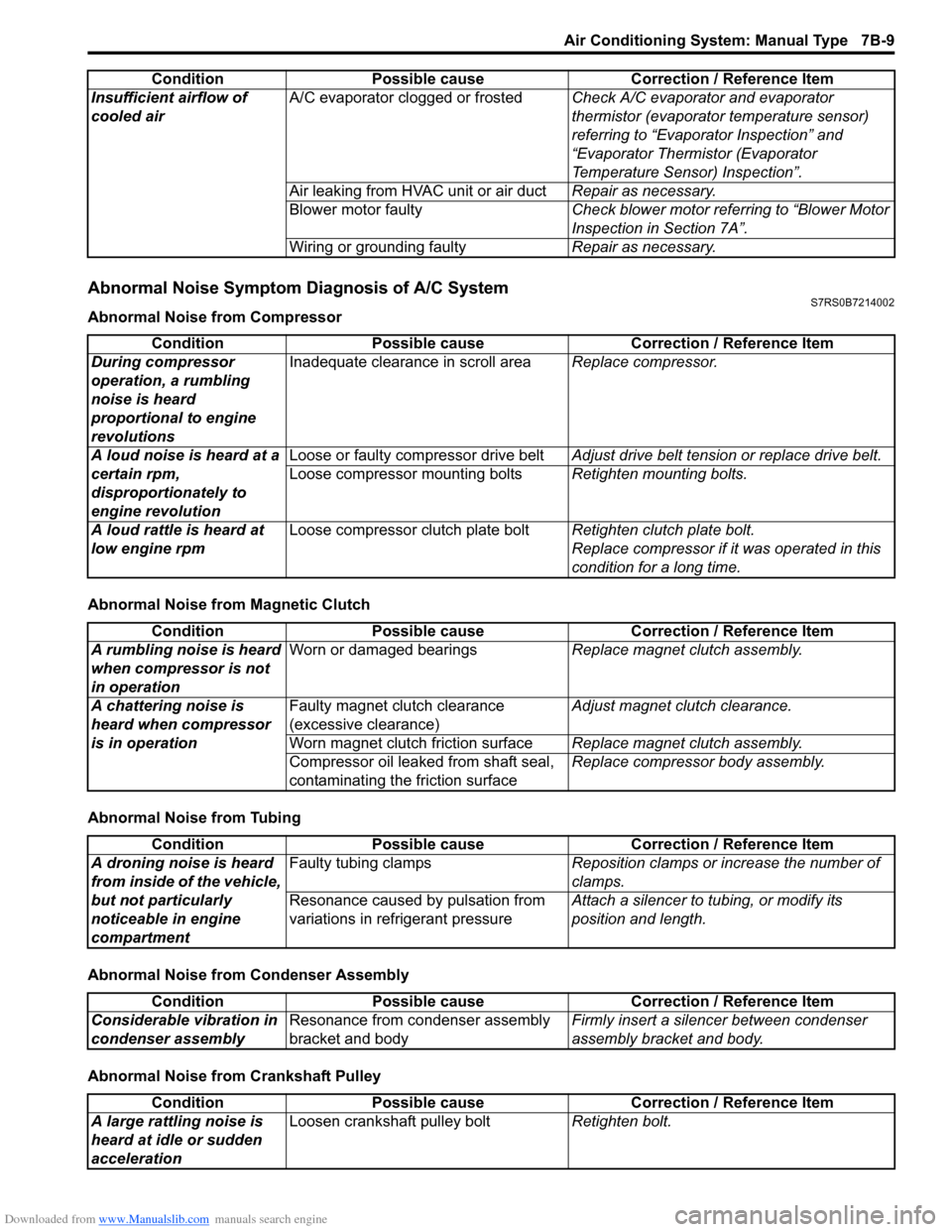
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Conditioning System: Manual Type 7B-9
Abnormal Noise Symptom Diagnosis of A/C SystemS7RS0B7214002
Abnormal Noise from Compressor
Abnormal Noise from Magnetic Clutch
Abnormal Noise from Tubing
Abnormal Noise from Condenser Assembly
Abnormal Noise from Crankshaft PulleyInsufficient airflow of
cooled air
A/C evaporator clogged or frosted
Check A/C evaporator and evaporator
thermistor (evaporator temperature sensor)
referring to “Evaporator Inspection” and
“Evaporator Thermistor (Evaporator
Temperature Sensor) Inspection”.
Air leaking from HVAC unit or air duct Repair as necessary.
Blower motor faulty Check blower motor referring to “Blower Motor
Inspection in Section 7A”.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Condition
Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
During compressor
operation, a rumbling
noise is heard
proportional to engine
revolutions Inadequate clearance in scroll area
Replace compressor.
A loud noise is heard at a
certain rpm,
disproportionately to
engine revolution Loose or faulty compressor drive belt
Adjust drive belt tension or replace drive belt.
Loose compressor mounting bolts Retighten mounting bolts.
A loud rattle is heard at
low engine rpm Loose compressor clutch plate bolt
Retighten clutch plate bolt.
Replace compressor if it was operated in this
condition for a long time.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
A rumbling noise is heard
when compressor is not
in operation Worn or damaged bearings
Replace magnet clutch assembly.
A chattering noise is
heard when compressor
is in operation Faulty magnet clutch clearance
(excessive clearance)
Adjust magnet clutch clearance.
Worn magnet clutch friction surface Replace magnet clutch assembly.
Compressor oil leaked from shaft seal,
contaminating the friction surface Replace compressor body assembly.
Condition
Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
A droning noise is heard
from inside of the vehicle,
but not particularly
noticeable in engine
compartment Faulty tubing clamps
Reposition clamps or increase the number of
clamps.
Resonance caused by pulsation from
variations in re frigerant pressure Attach a silencer to tubing, or modify its
position and length.
Condition
Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Considerable vibration in
condenser assembly Resonance from condenser assembly
bracket and body Firmly insert a silenc
er between condenser
assembly bracket and body.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
A large rattling noise is
heard at idle or sudden
acceleration Loosen crankshaft pulley bolt
Retighten bolt.
Page 958 of 1496
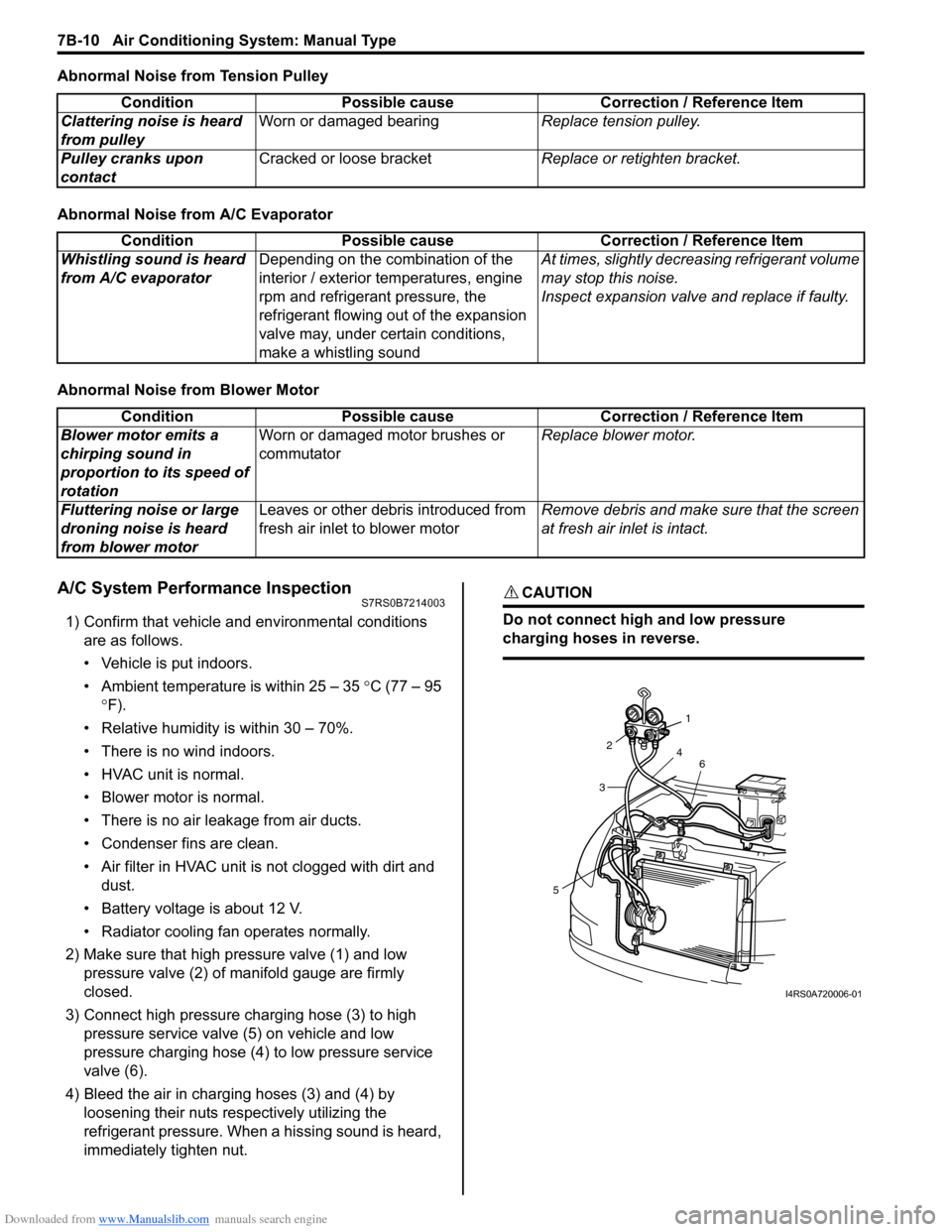
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-10 Air Conditioning System: Manual Type
Abnormal Noise from Tension Pulley
Abnormal Noise from A/C Evaporator
Abnormal Noise from Blower Motor
A/C System Performance InspectionS7RS0B7214003
1) Confirm that vehicle and environmental conditions are as follows.
• Vehicle is put indoors.
• Ambient temperature is within 25 – 35 °C (77 – 95
° F).
• Relative humidity is within 30 – 70%.
• There is no wind indoors.
• HVAC unit is normal.
• Blower motor is normal.
• There is no air leakage from air ducts.
• Condenser fins are clean.
• Air filter in HVAC unit is not clogged with dirt and
dust.
• Battery voltage is about 12 V.
• Radiator cooling fan operates normally.
2) Make sure that high pressure valve (1) and low pressure valve (2) of manifold gauge are firmly
closed.
3) Connect high pressure charging hose (3) to high pressure service valve (5) on vehicle and low
pressure charging hose (4) to low pressure service
valve (6).
4) Bleed the air in charging hoses (3) and (4) by loosening their nuts respectively utilizing the
refrigerant pressure. When a hissing sound is heard,
immediately tighten nut.
CAUTION!
Do not connect high and low pressure
charging hoses in reverse.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Clattering noise is heard
from pulley Worn or damaged bearing
Replace tension pulley.
Pulley cranks upon
contact Cracked or loose bracket
Replace or retighten bracket.
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Whistling sound is heard
from A/C evaporator Depending on the combination of the
interior / exterior temperatures, engine
rpm and refrigerant pressure, the
refrigerant flowing out of the expansion
valve may, under certain conditions,
make a whistling sound At times, slightly decrea
sing refrigerant volume
may stop this noise.
Inspect expansion valve and replace if faulty.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Blower motor emits a
chirping sound in
proportion to its speed of
rotation Worn or damaged motor brushes or
commutator
Replace blower motor.
Fluttering noise or large
droning noise is heard
from blower motor Leaves or other debris introduced from
fresh air inlet to blower motor
Remove debris and make sure that the screen
at fresh air inlet is intact.
53
2
1
4 6
I4RS0A720006-01